https://github.com/sitegui/feattle-rs
Feature toggles for Rust, extensible and with background synchronization and administration UI
https://github.com/sitegui/feattle-rs
crate feature-toggle rust
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Feature toggles for Rust, extensible and with background synchronization and administration UI
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/sitegui/feattle-rs
- Owner: sitegui
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2020-08-16T12:06:53.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-04-17T07:23:32.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-17T20:40:59.401Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: crate, feature-toggle, rust
- Language: Rust
- Homepage:
- Size: 766 KB
- Stars: 24
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 8
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE-APACHE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# feattle
[](https://crates.io/crates/feattle)
[](https://docs.rs/feattle)
[](https://github.com/sitegui/feattle-rs/actions)
[](https://coveralls.io/github/sitegui/feattle-rs?branch=master)
Featture toggles for Rust (called "feattles", for short), extensible and with background
synchronization and administration UI.
### Features
- Feature toggles that synchronize automatically with a backing storage
- Feature toggles can be as simple `bool`, but can also be lists, maps and arbitrary tpes (
(through the [`FeattleValue`] trait).
- Web UI with documentation, change history, validation
- JSON API to read and set the toggles
- Modular and extensible: use as much or as little of the bundled features as you want. Want to
use a different Web UI? A different storage layer? No problem.
### Example
```rust
use feattle::*;
use std::sync::Arc;
/// A struct with your feature toggles: you can use primitive types (like `bool`, `i32`, etc),
/// standard collections (like `Vec`, `BTreeSet`, etc) or any arbitrary type that implements
/// the required trait.
feattles! {
struct MyFeattles {
/// Is this usage considered cool?
is_cool: bool = true,
/// Limit the number of "blings" available.
/// This will not change the number of "blengs", though!
max_blings: i32,
/// List the actions that should not be available
blocked_actions: Vec,
}
}
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() {
// Store their values and history in AWS' S3
use std::future::IntoFuture;
use std::time::Duration;
use tokio::net::TcpListener;
let config = aws_config::load_from_env().await;
let persistence = Arc::new(S3::new(
&config,
"my-bucket".to_owned(),
"some/s3/prefix/".to_owned(),
));
// Create a new instance
let my_feattles = Arc::new(MyFeattles::new(persistence));
// Poll the storage in the background
BackgroundSync::new(&my_feattles).start().await;
// Start the admin UI with `warp`
let admin_panel = Arc::new(AdminPanel::new(my_feattles.clone(), "Project Panda - DEV".to_owned()));
tokio::spawn(run_warp_server(admin_panel.clone(), ([127, 0, 0, 1], 3030)));
// Or serve the admin panel with `axum`
let router = axum_router(admin_panel);
let listener = TcpListener::bind(("127.0.0.1", 3031)).await.unwrap();
tokio::spawn(axum::serve(listener, router.into_make_service()).into_future());
// Read values (note the use of `*`)
assert_eq!(*my_feattles.is_cool(), true);
assert_eq!(*my_feattles.max_blings(), 0);
assert_eq!(*my_feattles.blocked_actions(), Vec::::new());
}
```
You can run a full example locally with: `cargo run --example full --features='s3 uuid warp axum'`.
With this code, you'll get an Web Admin UI like:
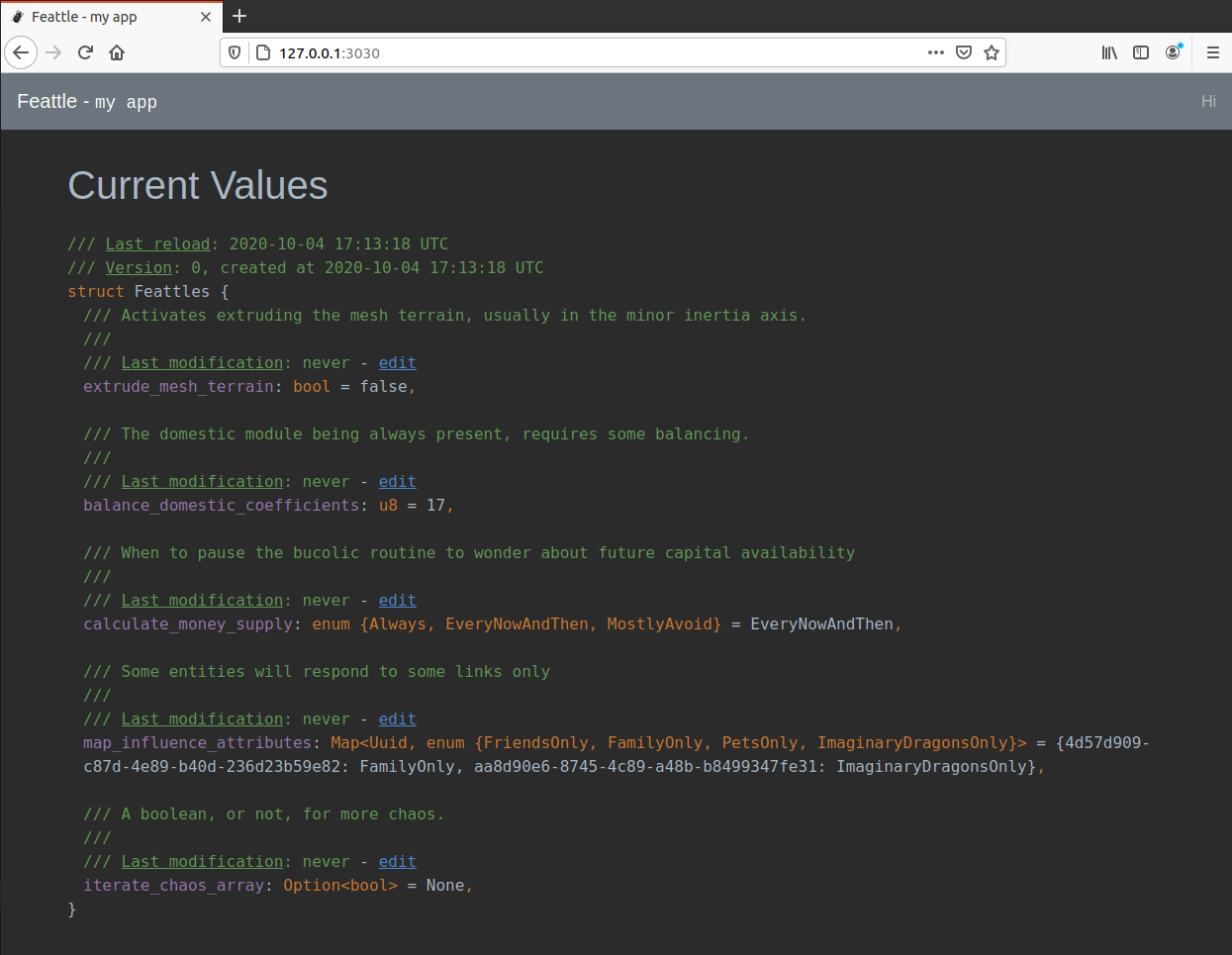
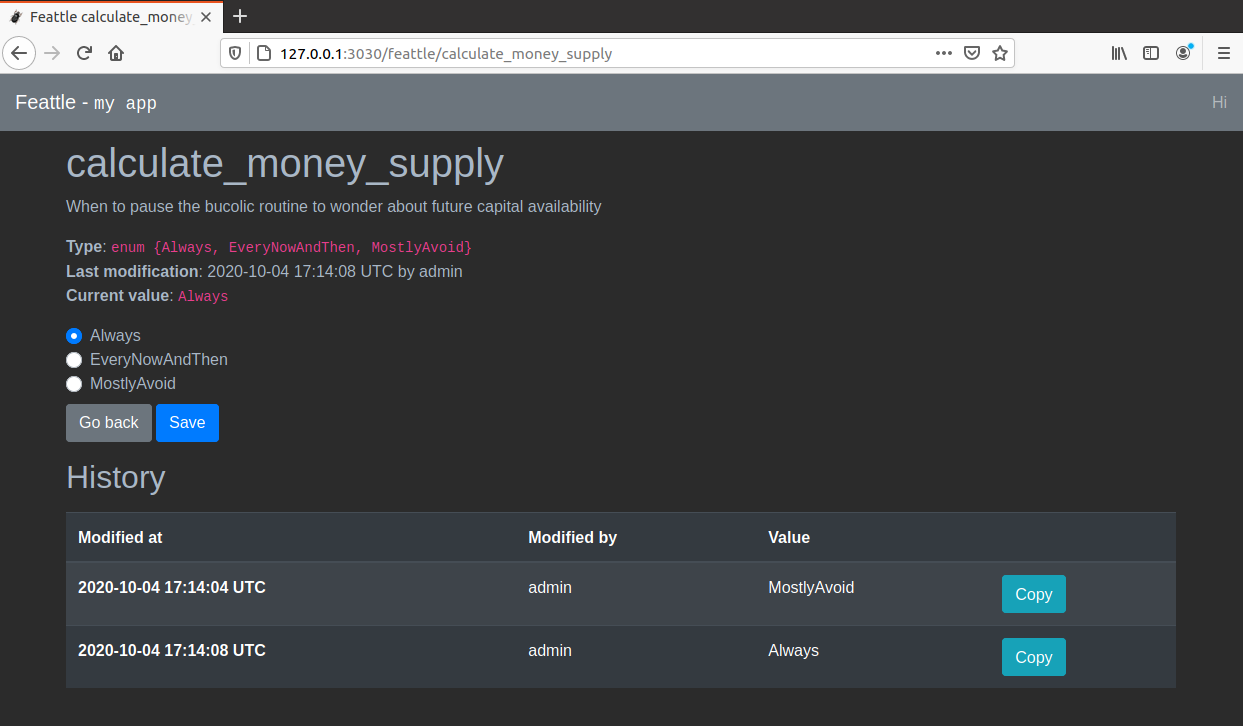
You can use the UI to edit the current values and see their change history. For example, this
is what you can expect when editing an `enum`:
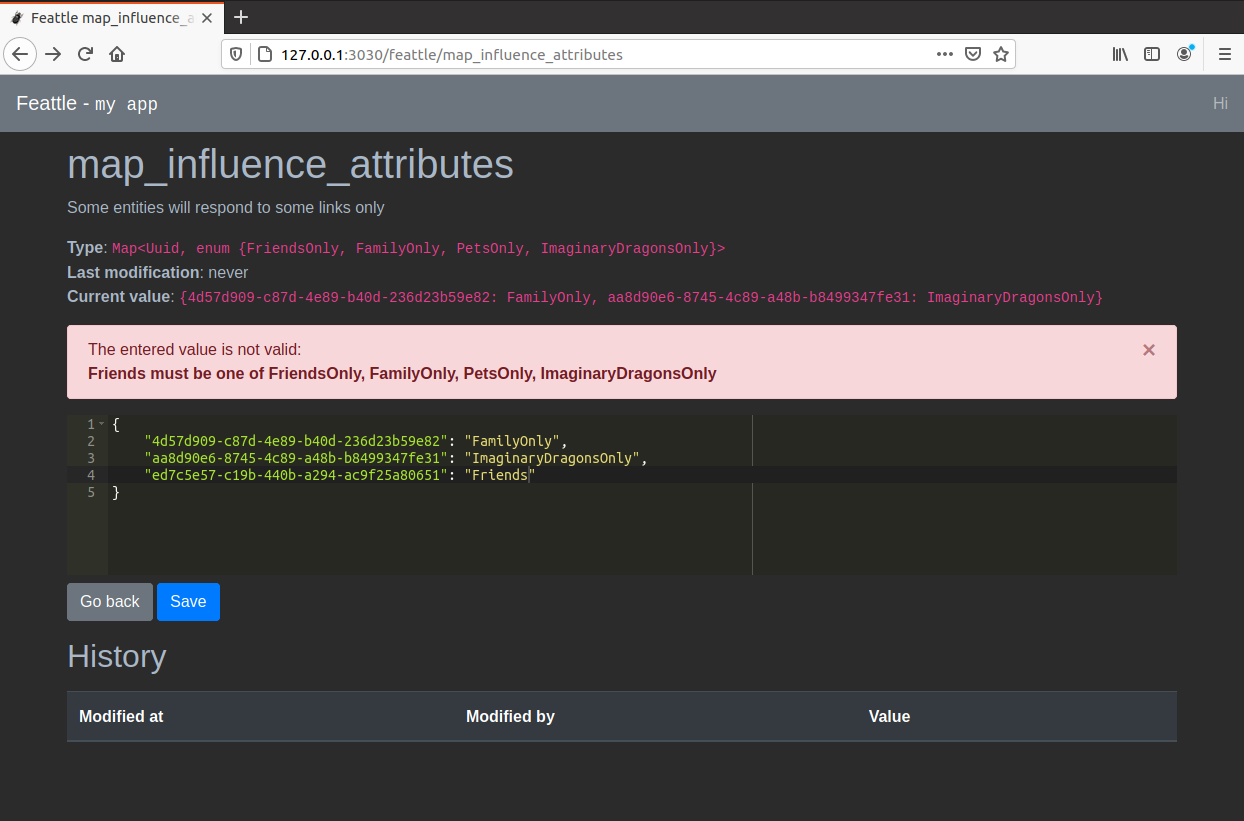
It also supports complex types with a JSON editor and helpful error diagnostics:
## How it works
The macro will generate a struct with the given name and visibility modifier (assuming private
by default). The generated struct implements [`Feattles`] and also exposes one method for each
feattle.
The methods created for each feattle allow reading their current value. For example, for a
feattle `is_cool: bool`, there will be a method like
`pub fn is_cool(&self) -> MappedRwLockReadGuard`. Note the use of
[`parking_lot::MappedRwLockReadGuard`] because the interior of the struct is stored behind a `RwLock` to
control concurrent access.
A feattle is created with the syntax `$key: $type [= $default]`. You can use doc coments (
starting with `///`) to describe nicely what they do in your system. You can use any type that
implements [`FeattleValue`] and optionally provide a default. If not provided, the default
will be created with `Default::default()`.
## Minimum supported Rust version
As of this release, the MSRV is 1.82.0, as tested in the CI. A patch release will never require
a newer MSRV.
## Optional features
You can easily declare feattles with your custom types, use another persistance storage logic
or Web Framework (or any at all). For some out-of-the-box functionality, you can activate these
cargo features:
- **uuid**: will add support for [`uuid::Uuid`].
- **rusoto_s3**: provides [`RusotoS3`] to integrate with AWS' S3
- **aws_sdk_s3**: provides [`S3`] to integrate with AWS' S3
- **warp**: provides [`run_warp_server`] for a read-to-use integration with [`warp`]
- **axum**: provides [`axum_router`] for a read-to-use integration with [`axum`]
### Crate's organization
This crate is a simple re-export of these three components:
* `feattle-core`: [](https://crates.io/crates/feattle-core)
* `feattle-sync`: [](https://crates.io/crates/feattle-sync)
* `feattle-ui`: [](https://crates.io/crates/feattle-ui)
Having them separate allows for leaner lower-level integration. If you're creating a crate to
provide a different storage or admin, you just need `feattle-core`.
## License
Licensed under either of
* Apache License, Version 2.0
([LICENSE-APACHE](LICENSE-APACHE) or http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
* MIT license
([LICENSE-MIT](LICENSE-MIT) or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
at your option.
## Contribution
Unless you explicitly state otherwise, any contribution intentionally submitted
for inclusion in the work by you, as defined in the Apache-2.0 license, shall be
dual licensed as above, without any additional terms or conditions.
See [CONTRIBUTING.md](CONTRIBUTING.md).