https://github.com/skydoves/sealedx
🎲 Kotlin Symbol Processor that auto-generates extensive sealed classes and interfaces for Android and Kotlin.
https://github.com/skydoves/sealedx
android extensive kotlin-symbol-processing ksp sealed-class selaed-interface skydoves
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
🎲 Kotlin Symbol Processor that auto-generates extensive sealed classes and interfaces for Android and Kotlin.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/skydoves/sealedx
- Owner: skydoves
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2022-08-12T07:00:03.000Z (about 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-05-15T16:02:52.000Z (5 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-19T20:10:06.162Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: android, extensive, kotlin-symbol-processing, ksp, sealed-class, selaed-interface, skydoves
- Language: Kotlin
- Homepage:
- Size: 273 KB
- Stars: 343
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 12
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
- Codeowners: .github/CODEOWNERS
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-list - skydoves/sealedx - 🎲 Kotlin Symbol Processor that auto-generates extensive sealed classes and interfaces for Android and Kotlin. (Kotlin)
README
SealedX
🎲 Kotlin Symbol Processor to auto-generate extensive sealed classes and interfaces for Android and Kotlin.
## Why SealedX?
SealedX generates extensive sealed classes & interfaces based on common sealed classes for each different model. You can reduce writing repeated sealed classes for every different model by auto-generating based on KSP ([Kotlin Symbol Processor](https://kotlinlang.org/docs/ksp-overview.html)).
You can massively reduce writing repeated files such as `_UiState` sealed interfaces if your project is based on MVI architecture.
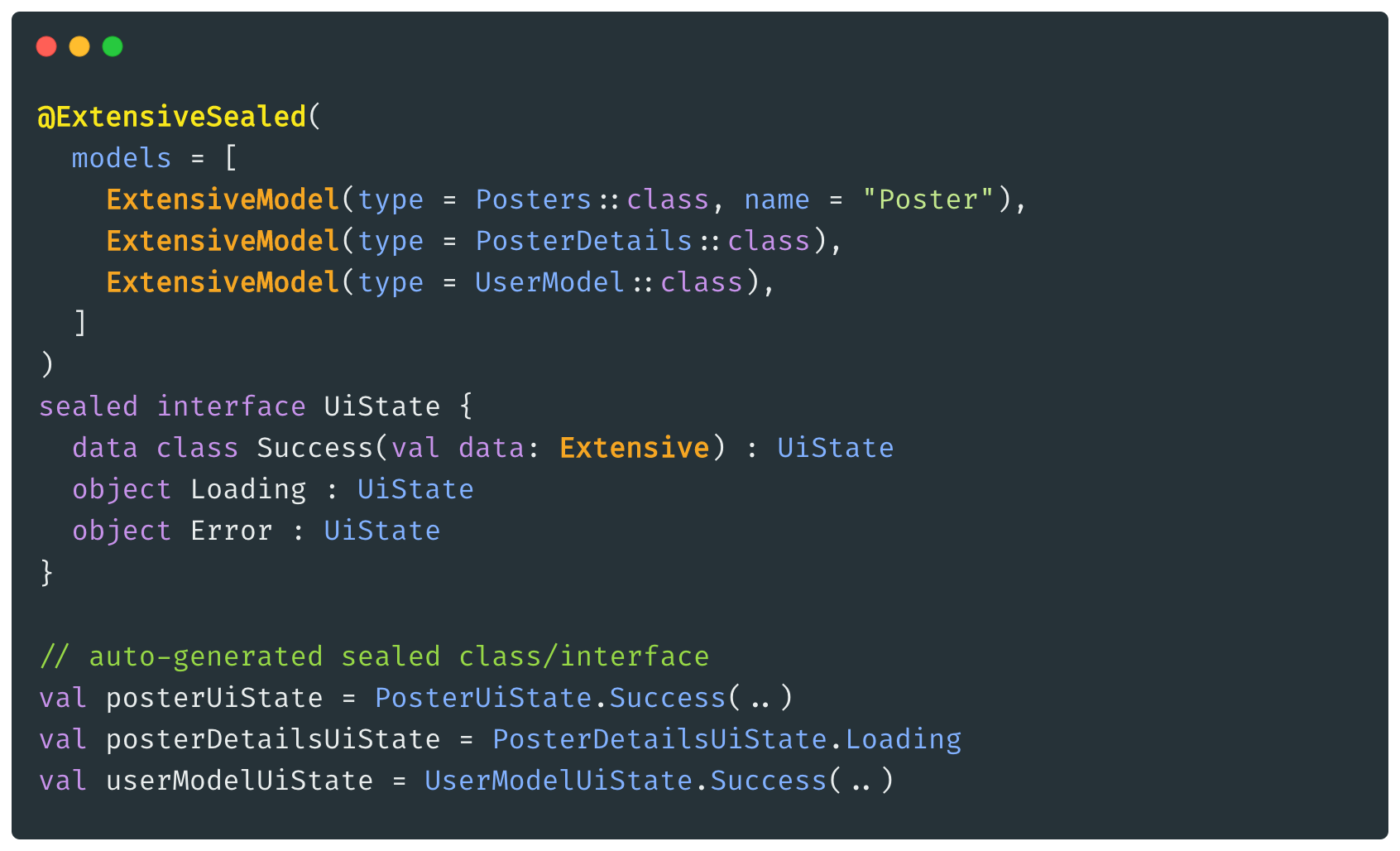
## Use Cases
If you want to learn more about how to migrate and use cases, check out the repositories below:
- **[WhatsApp Clone Compose](https://github.com/GetStream/whatsApp-clone-compose/pull/1)**
- **[Now in Android](https://github.com/advocacies/nowinandroid/pull/1)**
## Gradle Setup
To use [KSP (Kotlin Symbol Processing)](https://kotlinlang.org/docs/ksp-quickstart.html) and SealedX library in your project, you need to follow steps below.
### 1. Enable KSP in your module
Add the KSP plugin below into your **module**'s `build.gradle` file:
Kotlin (KTS)
```kotlin
plugins {
id("com.google.devtools.ksp") version "2.1.20-2.0.1"
}
```
Groovy
```kotlin
plugins {
id("com.google.devtools.ksp") version "2.1.20-2.0.1"
}
```
> **Note**: Make sure your current Kotlin version and [KSP version](https://github.com/google/ksp/releases) is the same.
### 2. Add SealedX dependencies
[](https://search.maven.org/search?q=g:%22com.github.skydoves%22%20AND%20a:%22sealedx-core%22)
Add the dependency below into your **module**'s `build.gradle` file:
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation("com.github.skydoves:sealedx-core:1.0.4")
ksp("com.github.skydoves:sealedx-processor:1.0.4")
}
```
### 3. Add KSP source path
To access generated codes from KSP, you need to set up the source path like the below into your **module**'s `build.gradle` file:
Android Kotlin (KTS)
```kotlin
kotlin {
sourceSets.configureEach {
kotlin.srcDir("$buildDir/generated/ksp/$name/kotlin/")
}
}
```
Android Groovy
```gradle
android {
applicationVariants.all { variant ->
kotlin.sourceSets {
def name = variant.name
getByName(name) {
kotlin.srcDir("build/generated/ksp/$name/kotlin")
}
}
}
}
```
Pure Kotlin (KTS)
```gradle
kotlin {
sourceSets.main {
kotlin.srcDir("build/generated/ksp/main/kotlin")
}
sourceSets.test {
kotlin.srcDir("build/generated/ksp/test/kotlin")
}
}
```
Pure Kotlin Groovy
```gradle
kotlin {
sourceSets {
main.kotlin.srcDirs += 'build/generated/ksp/main/kotlin'
test.kotlin.srcDirs += 'build/generated/ksp/test/kotlin'
}
}
```
## Usage
### ExtensiveSealed
`@ExtensiveSealed` annotation is the main trigger of the Kotlin Symbol Processor to run a sealed-extensive processor on compile time.
- `@ExtensiveSealed` must be annotated to sealed classes or interfaces, which should be a common model to generate extensive sealed classes and interfaces.
- `@ExtensiveSealed` receives an array of `@ExtensiveModel` annotations, which include the extensive model types.
- If you build your project, extensive sealed classes or interfaces will be generated based on those extensive models.
Let's see a common `UiState` sealed interface below that is annotated with `@ExtensiveSealed` annotation:
```kotlin
@ExtensiveSealed(
models = [
ExtensiveModel(Poster::class),
ExtensiveModel(PosterDetails::class)
]
)
sealed interface UiState {
data class Success(val data: Extensive) : UiState
object Loading : UiState
object Error : UiState
}
```
The example codes above will generate `PosterUiState` and `PosterDetailsUiState` sealed interfaces below:
**PosterUiState (generated)**:
```kotlin
public sealed interface PosterUiState {
public object Error : PosterUiState
public object Loading : PosterUiState
public data class Success(
public val `data`: Poster,
) : PosterUiState
}
```
**PosterDetailsUiState (generated)**:
```kotlin
public sealed interface PosterDetailsUiState {
public object Error : PosterDetailsUiState
public object Loading : PosterDetailsUiState
public data class Success(
public val `data`: PosterDetails,
) : PosterDetailsUiState
}
```
See further sealed class examples
In the case of the sealed classes, it's not different fundamentally from sealed interface examples.
```kotlin
@ExtensiveSealed(
models = [ ExtensiveModel(type = Poster::class) ]
)
sealed class UiState {
data class Success(val data: Extensive) : UiState()
object Loading : UiState()
object Error : UiState()
}
```
The example codes above will generate the `PosterUiState` sealed class below:
**PosterUiState (generated)**:
```kotlin
public sealed class PosterUiState {
public object Error : PosterUiState()
public object Loading : PosterUiState()
public data class Success(
public val `data`: Poster,
) : PosterUiState()
}
```
### ExtensiveModel
`@ExtensiveModel` annotation class contains information on extensive models like model type and a custom name, which decides the name of generated classes.
Basically, (the simple name of the `type`) + (the name of common sealed classes) will be used to name of generated classes, but you can modify the prefix with the `name` parameter like the example below:
```kotlin
@ExtensiveSealed(
models = [ ExtensiveModel(type = PosterExtensive::class, name = "Movie") ]
)
sealed interface UiState {
data class Success(val data: Extensive) : UiState
object Loading : UiState
object Error : UiState
}
```
The example codes above will generate `MovieUiState` file instead of `PosterExtensiveUiState` like the below:
**MovieUiState (generated)**:
```kotlin
public sealed interface MovieUiState {
public object Error : MovieUiState
public object Loading : MovieUiState
public data class Success(
public val `data`: PosterExtensive,
) : MovieUiState
}
```
#### Collection type in @ExtensiveModel
Basically, you can't set a collection type like a `List` to the `type` parameter of the `@ExtensiveModel` annotation.
So if you need to set a collection type as an extensive model, you need to write a wrapper class like the below:
```kotlin
data class PosterExtensive(
val posters: List
)
@ExtensiveSealed(
models = [ ExtensiveModel(type = PosterExtensive::class) ]
)
sealed interface UiState {
..
}
```
### Extensive
`Extensive` is an interface that is used to represent extensive model types of sealed classes and interfaces.
When you need to use an extensive model type in your primary constructor of data class, you can use the `Extensive` extensive type on your common sealed classes and interfaces.
It will be replaced by the extensive model type on compile time.
```kotlin
@ExtensiveSealed(
models = [ ExtensiveModel(type = PosterExtensive::class) ]
)
sealed interface UiState {
// You need to use the Extensive type if you want to use an extensive model type in the generated code.
data class Success(val data: Extensive) : UiState
..
}
```
The example codes above will generate `PosterExtensiveUiState` sealed interface like the below:
**PosterExtensiveUiState (generated)**:
```kotlin
public sealed interface PosterExtensiveUiState {
public object Error : PosterExtensiveUiState
public object Loading : PosterExtensiveUiState
public data class Success(
public val `data`: PosterExtensive,
) : PosterExtensiveUiState
}
```
As you can see from the example above, the `Extensive` interface type will be replaced with the extensive model by the SealedX processor on compile time.
## Find this repository useful? :heart:
Support it by joining __[stargazers](https://github.com/skydoves/sealedx/stargazers)__ for this repository. :star:
Also, __[follow me](https://github.com/skydoves)__ on GitHub for my next creations! 🤩
# License
```xml
Designed and developed by 2022 skydoves (Jaewoong Eum)
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
```

