https://github.com/sony/model_optimization
Model Compression Toolkit (MCT) is an open source project for neural network model optimization under efficient, constrained hardware. This project provides researchers, developers, and engineers advanced quantization and compression tools for deploying state-of-the-art neural networks.
https://github.com/sony/model_optimization
deep-learning deep-neural-networks edge-ai machine-learning network-compression network-quantization neural-network optimizer ptq pytorch qat quantization tensorflow
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Model Compression Toolkit (MCT) is an open source project for neural network model optimization under efficient, constrained hardware. This project provides researchers, developers, and engineers advanced quantization and compression tools for deploying state-of-the-art neural networks.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/sony/model_optimization
- Owner: sony
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2021-06-21T03:28:09.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-04-10T07:31:35.000Z (9 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-10T08:33:06.650Z (9 months ago)
- Topics: deep-learning, deep-neural-networks, edge-ai, machine-learning, network-compression, network-quantization, neural-network, optimizer, ptq, pytorch, qat, quantization, tensorflow
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/
- Size: 22 MB
- Stars: 382
- Watchers: 22
- Forks: 64
- Open Issues: 8
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-edge-computing - Model Compression Toolkit (MCT)
README
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
##
Getting Started
### Quick Installation
Pip install the model compression toolkit package in a Python>=3.9 environment with PyTorch>=2.3 or Tensorflow>=2.14.
```
pip install model-compression-toolkit
```
For installing the nightly version or installing from source, refer to the [installation guide](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/INSTALLATION.md).
**Important note**: In order to use MCT, you’ll need to provide a pre-trained floating point model (PyTorch/Keras) as an input.
### Tutorials and Examples
Our [tutorials](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/tutorials/README.md) section will walk you through the basics of the MCT tool, covering various compression techniques for both Keras and PyTorch models.
Access interactive notebooks for hands-on learning with popular models/tasks or move on to [Resources](#resources) section.
### Supported Quantization Methods
MCT supports various quantization methods as appears below.
Quantization Method | Complexity | Computational Cost | API | Tutorial
-------------------- | -----------|--------------------|---------|--------
PTQ (Post Training Quantization) | Low | Low (~1-10 CPU minutes) | [PyTorch API](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/api/api_docs/methods/pytorch_post_training_quantization.html) / [Keras API](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/api/api_docs/methods/keras_post_training_quantization.html) | 

GPTQ (parameters fine-tuning using gradients) | Moderate | Moderate (~1-3 GPU hours) | [PyTorch API](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/api/api_docs/methods/pytorch_gradient_post_training_quantization.html) / [Keras API](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/api/api_docs/methods/keras_gradient_post_training_quantization.html) | 

QAT (Quantization Aware Training) | High | High (~12-36 GPU hours) | [QAT API](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/api/api_docs/index.html#qat) | 
For each flow, **Quantization core** utilizes various algorithms and hyper-parameters for optimal [hardware-aware](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/model_compression_toolkit/target_platform_capabilities/README.md) quantization results.
For further details, please see [Supported features and algorithms](#high-level-features-and-techniques).
**Required input**: Pre-trained floating point model (PyTorch/Keras)
**Optional input**: Representative dataset - can be either provided by the user, or generated utilizing the [Data Generation](#data-generation-) capability

##
High level features and techniques
MCT offers a range of powerful features to optimize models for efficient edge deployment. These supported features include:
### Quantization Core Features
🏆 **Mixed-precision search** [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/tutorials/notebooks/mct_features_notebooks/pytorch/example_pytorch_mixed_precision_ptq.ipynb). Assigning optimal quantization bit-width per layer (for weights/activations)
📈 **Graph optimizations**.
Transforming the model to be best fitted for quantization process.
🔎 **Quantization parameter search** [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/tutorials/notebooks/mct_features_notebooks/keras/example_keras_activation_threshold_search.ipynb). Minimizing expected quantization-noise during thresholds search using methods such as MSE, No-Clipping and MAE.
🧮 **Advanced quantization algorithms** [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/tutorials/notebooks/mct_features_notebooks/keras/example_keras_activation_z_score_threshold.ipynb). Enhancing quantization performance for advanced cases is available with some algorithms that can be applied, such as Shift negative correction, Outliers filtering and clustering.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
### Hardware-aware optimization
🎯 **TPC (Target Platform Capabilities)**. Describes the target hardware’s constrains, for which the model optimization is targeted. See [TPC Readme](./model_compression_toolkit/target_platform_capabilities/README.md) for more information.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
### Data-free quantization (Data Generation) [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/tutorials/notebooks/mct_features_notebooks/pytorch/example_pytorch_data_generation.ipynb)
Generates synthetic images based on the statistics stored in the model's batch normalization layers, according to your specific needs, for when image data isn’t available. See [Data Generation Library](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/model_compression_toolkit/data_generation/README.md) for more.
The specifications of the method are detailed in the paper: _"**Data Generation for Hardware-Friendly Post-Training Quantization**"_ [5].
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
### Structured Pruning [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/tutorials/notebooks/mct_features_notebooks/pytorch/example_pytorch_pruning_mnist.ipynb)
Reduces model size/complexity and ensures better channels utilization by removing redundant input channels from layers and reconstruction of layer weights. Read more ([Pytorch API](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/api/api_docs/methods/pytorch_pruning_experimental.html) / [Keras API](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/api/api_docs/methods/keras_pruning_experimental.html)).
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
### **Debugging and Visualization**
**🎛️ Network Editor (Modify Quantization Configurations)** [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/tutorials/notebooks/mct_features_notebooks/keras/example_keras_network_editor.ipynb).
Modify your model's quantization configuration for specific layers or apply a custom edit rule (e.g adjust layer's bit-width) using MCT’s network editor.
**🖥️ Visualization**. Observe useful information for troubleshooting the quantized model's performance using TensorBoard. [Read more](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/guidelines/visualization.html).
**🔑 XQuant (Explainable Quantization)** [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/tutorials/notebooks/mct_features_notebooks/pytorch/example_pytorch_xquant.ipynb). Get valuable insights regarding the quality and success of the quantization process of your model. The report includes histograms and similarity metrics between the original float model and the quantized model in key points of the model. The report can be visualized using TensorBoard.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
### Enhanced Post-Training Quantization (EPTQ)
As part of the GPTQ capability, we provide an advanced optimization algorithm called EPTQ.
The specifications of the algorithm are detailed in the paper: _"**EPTQ: Enhanced Post-Training Quantization via Hessian-guided Network-wise Optimization**"_ [4].
More details on how to use EPTQ via MCT can be found in the [GPTQ guidelines](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/model_compression_toolkit/gptq/README.md).
##
Resources
* [User Guide](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/index.html) contains detailed information about MCT and guides you from installation through optimizing models for your edge AI applications.
* MCT's [API Docs](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/api/api_docs/) is separated per quantization methods:
* [Post-training quantization](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/api/api_docs/index.html#ptq) | PTQ API docs
* [Gradient-based post-training quantization](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/api/api_docs/index.html#gptq) | GPTQ API docs
* [Quantization-aware training](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/api/api_docs/index.html#qat) | QAT API docs
* [Debug](https://sony.github.io/model_optimization/guidelines/visualization.html) – modify optimization process or generate an explainable report
* [Release notes](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/releases)
##
Supported Versions
Currently, MCT is being tested on various Python, Pytorch and TensorFlow versions:
Supported Versions Table
| | PyTorch 2.3 | PyTorch 2.4 | PyTorch 2.5 | PyTorch 2.6 |
|-------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Python 3.9 | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python39_pytorch23.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python39_pytorch24.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python39_pytorch25.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python39_pytorch26.yml) |
| Python 3.10 | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python310_pytorch23.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python310_pytorch24.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python310_pytorch25.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python310_pytorch26.yml) |
| Python 3.11 | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python311_pytorch23.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python311_pytorch24.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python311_pytorch25.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python311_pytorch26.yml) |
| Python 3.12 | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python312_pytorch23.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python312_pytorch24.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python312_pytorch25.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python312_pytorch26.yml) |
| | TensorFlow 2.14 | TensorFlow 2.15 |
|-------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Python 3.9 | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python39_keras214.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python39_keras215.yml) |
| Python 3.10 | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python310_keras214.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python310_keras215.yml) |
| Python 3.11 | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python311_keras214.yml) | [](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/actions/workflows/run_tests_python311_keras215.yml) |
##
Results

MCT can quantize an existing 32-bit floating-point model to an 8-bit fixed-point (or less) model without compromising accuracy.
Below is a graph of [MobileNetV2](https://pytorch.org/vision/main/models/generated/torchvision.models.mobilenet_v2.html) accuracy on ImageNet vs average bit-width of weights (X-axis), using **single-precision** quantization, **mixed-precision** quantization, and mixed-precision quantization with GPTQ.
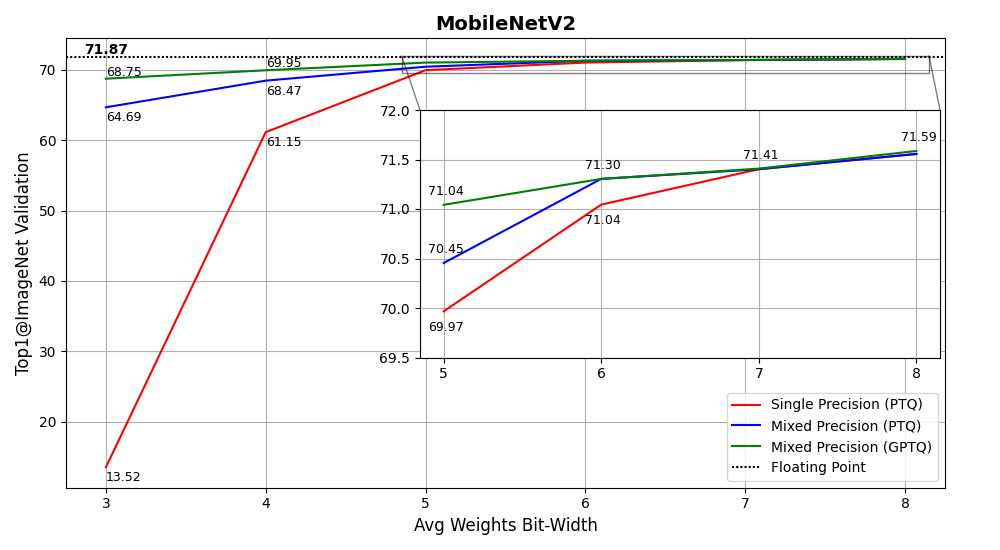
For more results, please see [1]
### Pruning Results
Results for applying pruning to reduce the parameters of the following models by 50%:
| Model | Dense Model Accuracy | Pruned Model Accuracy |
|-----------------|----------------------|-----------------------|
| ResNet50 [2] | 75.1 | 72.4 |
| DenseNet121 [3] | 74.44 | 71.71 |
##
Troubleshooting and Community
If you encountered a large accuracy degradation with MCT, check out the [Quantization Troubleshooting](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/tree/main/quantization_troubleshooting.md)
for common pitfalls and some tools to improve the quantized model's accuracy.
Check out the [FAQ](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/tree/main/FAQ.md) for common issues.
You are welcome to ask questions and get support on our [issues section](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/issues) and manage community discussions under the [discussions section](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/discussions).
##
Contributions
We'd love your input! MCT would not be possible without help from our community, and welcomes contributions from anyone!
*Checkout our [Contribution guide](https://github.com/sony/model_optimization/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md) for more details.
Thank you 🙏 to all our contributors!
##
License
MCT is licensed under Apache License Version 2.0. By contributing to the project, you agree to the license and copyright terms therein and release your contribution under these terms.
##
References
[1] Habi, H.V., Peretz, R., Cohen, E., Dikstein, L., Dror, O., Diamant, I., Jennings, R.H. and Netzer, A., 2021. [HPTQ: Hardware-Friendly Post Training Quantization. arXiv preprint](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.09113).
[2] [Keras Applications](https://keras.io/api/applications/)
[3] [TORCHVISION.MODELS](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/models.html)
[4] Gordon, O., Cohen, E., Habi, H. V., & Netzer, A., 2024. [EPTQ: Enhanced Post-Training Quantization via Hessian-guided Network-wise Optimization, European Conference on Computer Vision Workshop 2024, Computational Aspects of Deep Learning (CADL)](https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.11531)
[5] Dikstein, L., Lapid, A., Netzer, A., & Habi, H. V., 2024. [Data Generation for Hardware-Friendly Post-Training Quantization, Accepted to IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) 2025](https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/WACV2025/papers/Dikstein_Data_Generation_for_Hardware-Friendly_Post-Training_Quantization_WACV_2025_paper.pdf)





