https://github.com/stcarrez/etherscope
Ethernet traffic monitor on a STM32F746 board
https://github.com/stcarrez/etherscope
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
Ethernet traffic monitor on a STM32F746 board
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/stcarrez/etherscope
- Owner: stcarrez
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2016-09-22T21:36:06.000Z (over 9 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2017-12-03T09:24:51.000Z (about 8 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-07-31T20:45:29.849Z (over 1 year ago)
- Language: Ada
- Size: 90.8 KB
- Stars: 17
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 4
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.txt
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-ada - etherscope - Ethernet traffic monitor on a STM32F746 board. (Hardware and Embedded / Applications)
README
# Ethernet Traffic Monitor on a STM32F746
[](http://jenkins.vacs.fr/job/etherscope/)
[](LICENSE)

EtherScope is a monitoring tool that analyzes the Ethernet traffic.
It runs on a STM32F746 board, reads the Ethernet packets, do some
realtime analysis and displays the results on the 480x272 touch panel.
The EtherScope interface allows to filter the results at different
levels:
* Get and display statistics at the Ethernet level,
* Display information at some protocol levels: IPv4, TCP, UDP, ICMP
The EtherScope uses the following two GitHub projects:
* Ada_Drivers_Library https://github.com/AdaCore/Ada_Drivers_Library.git
* Ada Embedded Network https://github.com/stcarrez/ada-enet.git
You need the source of these two projects to buid EtherScope.
To help, these GitHub projects are registered as Git submodules and
the Makefile provides a target to perform the checkout. Just run:
make checkout
You will also need the GNAT Ada compiler for ARM available at http://libre.adacore.com/
# Build
Run the command:
make
to build the application and get the EtherScope image 'etherscope.bin'.
Then, flash the image with:
st-flash write etherscope.bin 0x8000000
or just
make flash
# Using EtherScope
To look at the network traffic, it is recommended to have a switch that supports
port monitoring. The switch is configured to monitor all the traffic to a given
port. The EtherScope is then connected to that port and it will receive all the
traffic, including the packets not destined to the board.
You can still use EtherScope without a switch and port mirroring but the EtherScope
will not be able to see all the network packets. Without port mirroring, we can
only see multicast and broadcast traffic, which means: ARP, ICMP, IGMP and UDP
packets on multicast groups.
Once powered up, the EtherScope starts the analysis and offers 4 buttons to
switch to different display modes:
* Ether displays the list of devices found on the network.
* Proto displays the different IPv4 protocols found on the network.
* IGMP displays the UDP multicast groups which are subscribed on the network.
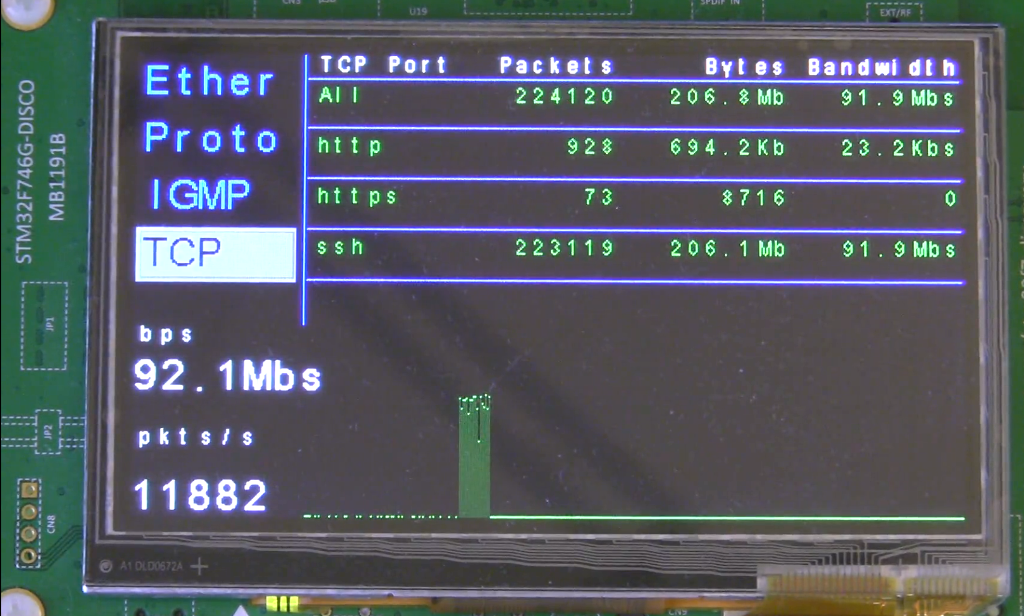
* TCP displays the list of high level application protocols (http, https, ssh, ...).
The following screenshot shows the TCP panel with 3 recognized TCP protocols and a running
SCP that uses almost all the bandwidth.
# Publication
* The EtherScope project was submitted to the [Make with Ada](http://www.makewithada.org/) competition.
* Article: [Ethernet Traffic Monitor on a STM32F746](http://blog.vacs.fr/vacs/blogs/post.html?post=2016/09/30/Ethernet-Traffic-Monitor-on-a-STM32F746)
* Article: [Using the Ada Embedded Network STM32 Ethernet Driver](http://blog.vacs.fr/vacs/blogs/post.html?post=2016/09/29/Using-the-Ada-Embedded-Network-STM32-Ethernet-Driver)
* Video: [EtherScope an Ethernet Traffic Monitor](https://youtu.be/zEtA-S5jvfY)