https://github.com/taki0112/Tensorflow-Cookbook
Simple Tensorflow Cookbook for easy-to-use
https://github.com/taki0112/Tensorflow-Cookbook
tensorflow tensorflow-cookbook tensorflow-examples
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Simple Tensorflow Cookbook for easy-to-use
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/taki0112/Tensorflow-Cookbook
- Owner: taki0112
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-02-16T15:43:31.000Z (almost 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2020-02-09T06:12:49.000Z (about 6 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-11T21:10:21.251Z (over 1 year ago)
- Topics: tensorflow, tensorflow-cookbook, tensorflow-examples
- Language: Python
- Size: 3.02 MB
- Stars: 2,777
- Watchers: 118
- Forks: 472
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-list - Tensorflow Cookbook - Simple Tensorflow Cookbook for easy-to-use. (Machine Learning Tutorials / Data Management)
README

# [Web page](http://bit.ly/jhkim_tf_cookbook)
# [Tensorflow 2 Cookbook](https://github.com/taki0112/Tensorflow2-Cookbook)
## Contributions
In now, this repo contains general architectures and functions that are useful for the GAN and classificstion.
I will continue to add useful things to other areas.
Also, your pull requests and issues are always welcome.
And write what you want to implement on the issue. I'll implement it.
# How to use
## Import
* `ops.py`
* **operations**
* from ops import *
* `utils.py`
* **image processing**
* from utils import *
## Network template
```python
def network(x, is_training=True, reuse=False, scope="network"):
with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse=reuse):
x = conv(...)
...
return logit
```
## Insert data to network using DatasetAPI
```python
Image_Data_Class = ImageData(img_size, img_ch, augment_flag)
trainA_dataset = ['./dataset/cat/trainA/a.jpg',
'./dataset/cat/trainA/b.png',
'./dataset/cat/trainA/c.jpeg',
...]
trainA = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(trainA_dataset)
trainA = trainA.map(Image_Data_Class.image_processing, num_parallel_calls=16)
trainA = trainA.shuffle(buffer_size=10000).prefetch(buffer_size=batch_size).batch(batch_size).repeat()
trainA_iterator = trainA.make_one_shot_iterator()
data_A = trainA_iterator.get_next()
logit = network(data_A)
```
* See [this](https://github.com/taki0112/Tensorflow-DatasetAPI) for more information.
## Option
* `padding='SAME'`
* pad = ceil[ (kernel - stride) / 2 ]
* `pad_type`
* 'zero' or 'reflect'
* `sn`
* use [spectral_normalization](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1802.05957.pdf) or not
## Caution
* If you don't want to share variable, **set all scope names differently.**
---
## Weight
```python
weight_init = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.02)
weight_regularizer = tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.0001)
weight_regularizer_fully = tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.0001)
```
### Initialization
* `Xavier` : tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer()
```python
USE """tf.contrib.layers.variance_scaling_initializer()"""
if uniform :
factor = gain * gain
mode = 'FAN_AVG'
else :
factor = (gain * gain) / 1.3
mode = 'FAN_AVG'
```
* `He` : tf.contrib.layers.variance_scaling_initializer()
```python
if uniform :
factor = gain * gain
mode = 'FAN_IN'
else :
factor = (gain * gain) / 1.3
mode = 'FAN_OUT'
```
* `Normal` : tf.random_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.02)
* `Truncated_normal` : tf.truncated_normal_initializer(mean=0.0, stddev=0.02)
* `Orthogonal` : tf.orthogonal_initializer(1.0) / # if relu = sqrt(2), the others = 1.0
### Regularization
* `l2_decay` : tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.0001)
* `orthogonal_regularizer` : orthogonal_regularizer(0.0001) & orthogonal_regularizer_fully(0.0001)
## Convolution
### basic conv
```python
x = conv(x, channels=64, kernel=3, stride=2, pad=1, pad_type='reflect', use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='conv')
```

### partial conv (NVIDIA [Partial Convolution](https://github.com/NVIDIA/partialconv))
```python
x = partial_conv(x, channels=64, kernel=3, stride=2, use_bias=True, padding='SAME', sn=True, scope='partial_conv')
```


### dilated conv
```python
x = dilate_conv(x, channels=64, kernel=3, rate=2, use_bias=True, padding='VALID', sn=True, scope='dilate_conv')
```

---
## Deconvolution
### basic deconv
```python
x = deconv(x, channels=64, kernel=3, stride=1, padding='SAME', use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='deconv')
```

---
## Fully-connected
```python
x = fully_connected(x, units=64, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='fully_connected')
```

---
## Pixel shuffle
```python
x = conv_pixel_shuffle_down(x, scale_factor=2, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='pixel_shuffle_down')
x = conv_pixel_shuffle_up(x, scale_factor=2, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='pixel_shuffle_up')
```
* `down` ===> [height, width] -> [**height // scale_factor, width // scale_factor**]
* `up` ===> [height, width] -> [**height \* scale_factor, width \* scale_factor**]

---
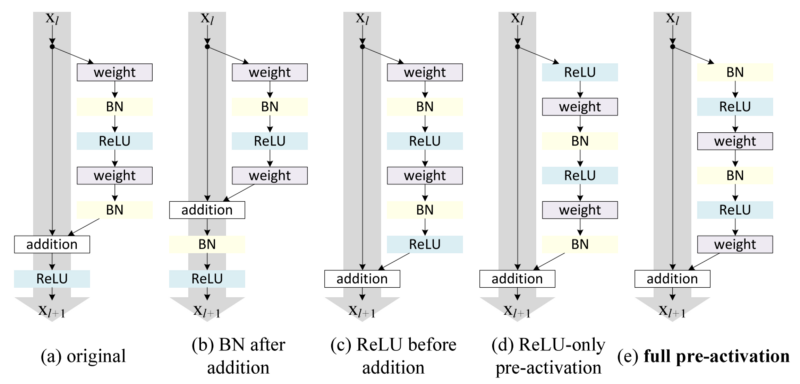
## Block
### residual block
```python
x = resblock(x, channels=64, is_training=is_training, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='residual_block')
x = resblock_down(x, channels=64, is_training=is_training, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='residual_block_down')
x = resblock_up(x, channels=64, is_training=is_training, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='residual_block_up')
```
* `down` ===> [height, width] -> [**height // 2, width // 2**]
* `up` ===> [height, width] -> [**height \* 2, width \* 2**]
### dense block
```python
x = denseblock(x, channels=64, n_db=6, is_training=is_training, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='denseblock')
```
* `n_db` ===> The number of dense-block

### residual-dense block
```python
x = res_denseblock(x, channels=64, n_rdb=20, n_rdb_conv=6, is_training=is_training, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='res_denseblock')
```
* `n_rdb` ===> The number of RDB
* `n_rdb_conv` ===> per RDB conv layer



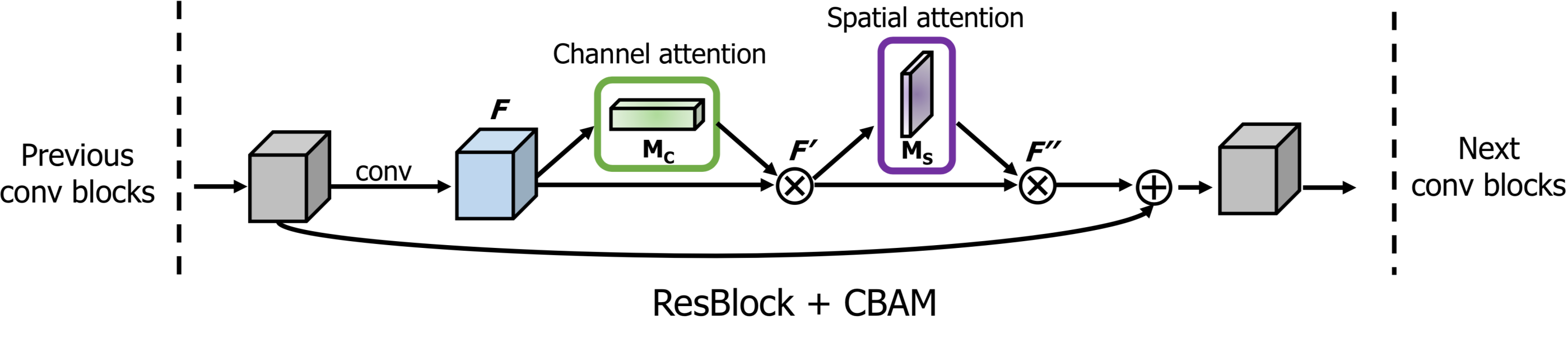
### attention block
```python
x = self_attention(x, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='self_attention')
x = self_attention_with_pooling(x, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='self_attention_version_2')
x = squeeze_excitation(x, ratio=16, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='squeeze_excitation')
x = convolution_block_attention(x, ratio=16, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='convolution_block_attention')
x = global_context_block(x, use_bias=True, sn=True, scope='gc_block')
x = srm_block(x, use_bias=False, is_training=is_training, scope='srm_block')
```

---


---

---

---

---
## Normalization
```python
x = batch_norm(x, is_training=is_training, scope='batch_norm')
x = layer_norm(x, scope='layer_norm')
x = instance_norm(x, scope='instance_norm')
x = group_norm(x, groups=32, scope='group_norm')
x = pixel_norm(x)
x = batch_instance_norm(x, scope='batch_instance_norm')
x = layer_instance_norm(x, scope='layer_instance_norm')
x = switch_norm(x, scope='switch_norm')
x = condition_batch_norm(x, z, is_training=is_training, scope='condition_batch_norm'):
x = adaptive_instance_norm(x, gamma, beta)
x = adaptive_layer_instance_norm(x, gamma, beta, smoothing=True, scope='adaLIN')
```
* See [this](https://github.com/taki0112/BigGAN-Tensorflow) for how to use `condition_batch_norm`
* See [this](https://github.com/taki0112/MUNIT-Tensorflow) for how to use `adaptive_instance_norm`
* See [this](https://github.com/taki0112/UGATIT) for how to use `adaptive_layer_instance_norm` & `layer_instance_norm`


---
## Activation
```python
x = relu(x)
x = lrelu(x, alpha=0.2)
x = tanh(x)
x = sigmoid(x)
x = swish(x)
x = elu(x)
```
---
## Pooling & Resize
```python
x = nearest_up_sample(x, scale_factor=2)
x = bilinear_up_sample(x, scale_factor=2)
x = nearest_down_sample(x, scale_factor=2)
x = bilinear_down_sample(x, scale_factor=2)
x = max_pooling(x, pool_size=2)
x = avg_pooling(x, pool_size=2)
x = global_max_pooling(x)
x = global_avg_pooling(x)
x = flatten(x)
x = hw_flatten(x)
```
---
## Loss
### classification loss
```python
loss, accuracy = classification_loss(logit, label)
loss = dice_loss(n_classes=10, logit, label)
```
### regularization loss
```python
g_reg_loss = regularization_loss('generator')
d_reg_loss = regularization_loss('discriminator')
```
* If you want to use `regularizer`, then you should write it
### pixel loss
```python
loss = L1_loss(x, y)
loss = L2_loss(x, y)
loss = huber_loss(x, y)
loss = histogram_loss(x, y)
loss = gram_style_loss(x, y)
loss = color_consistency_loss(x, y)
```
* `histogram_loss` means the difference in the color distribution of the image pixel values.
* `gram_style_loss` means the difference between the styles using gram matrix.
* `color_consistency_loss` means the color difference between the generated image and the input image.
### gan loss
```python
d_loss = discriminator_loss(Ra=True, loss_func='wgan-gp', real=real_logit, fake=fake_logit)
g_loss = generator_loss(Ra=True, loss_func='wgan-gp', real=real_logit, fake=fake_logit)
```
* `Ra`
* use [relativistic gan](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1807.00734.pdf) or not
* `loss_func`
* gan
* lsgan
* hinge
* wgan-gp
* dragan
* See [this](https://github.com/taki0112/BigGAN-Tensorflow/blob/master/BigGAN_512.py#L180) for how to use `gradient_penalty`

### [vdb loss](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.00821)
```python
d_bottleneck_loss = vdb_loss(real_mu, real_logvar, i_c) + vdb_loss(fake_mu, fake_logvar, i_c)
```
### kl-divergence (z ~ N(0, 1))
```python
loss = kl_loss(mean, logvar)
```
---
## Author
[Junho Kim](http://bit.ly/jhkim_ai)