https://github.com/tamimehsan/go-dfs
A distributed file storage system with golang
https://github.com/tamimehsan/go-dfs
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
A distributed file storage system with golang
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/tamimehsan/go-dfs
- Owner: TamimEhsan
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-09-05T15:36:47.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-09-23T14:32:37.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-07T20:37:02.952Z (5 months ago)
- Language: Go
- Homepage:
- Size: 57.6 KB
- Stars: 3
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Go-Distributed-FS
Go-DFS is a distributed file system written in golang. The system has the capability to store, retrieve and delete files from local store and also from network. The synchronizations are done in the background with gossip protocol and is eventually consistent. So this is a AP system (from CAP theorem).
## Project Details
### Network layer
The system builds on top of TCP transport layer. The session, connections are managed by the system.
### Gossip protocol
To decrease the load on a single node, the synchronization between network is done through gossip protocol or epidemic protocol. This everntually makes the system consistent. Accroding to CAP theorem, the system is not immediately consistent but available and parition tolerant.
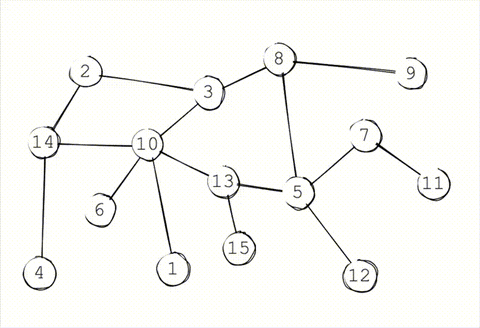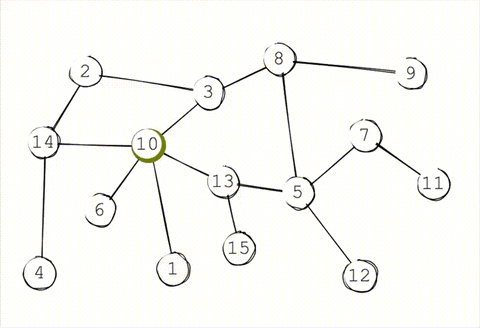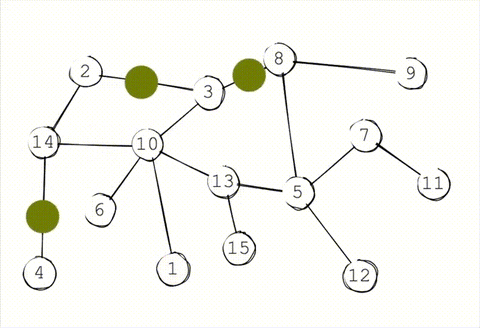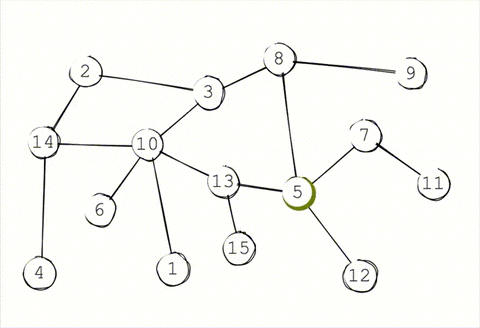
### Storage
The files are stored in the local file system with the help of a store encapsulation. The storage supports 5 main functionalities
- Check existence of a file
- Store a file
- Retrieve metadata of a file
- Retrieve a file
- Delete a file
#### Storing file
A file is stored with an associated key. Once the file is successfully saved, the client is notified of the upload status.
Synchronization between the peers in the network is then performed asynchronously using a gossip protocol. A random set of nodes is multicasted with the file data, and those nodes, in turn, propagate it to some of their peers, eventually leading to a consistent system.
See the [sequence diagram](#saving-a-file) for more clarity.
#### Retriving a file
Upon a retrieval request, if the file is present in the peer's storage, it responds with the file data. If the file is not present, a file request is broadcast to the network. If another node has the file, it sends it back, and the client is then provided with the file. If no node has the file, the client is notified of an error.
See the [sequence diagram](#get-a-file-through-network) for more clarity.
### Peer discovery
Peer discovery in system is also done by gossip. When a new node joins the cluster it needs to join through a known peer already in the cluster. That known peer sends the peer joining information to the rest of the cluster.
See the [sequence diagram](#peer-discovery-1) for more clarity.
## How to run
### Prequisites
Make sure you have golang installed in your device. Download and install golang from [here](https://go.dev/doc/install)
### Installation
At first clone this repository and then download the dependencies for the project
```bash
git clone https://github.com/TamimEhsan/go-dfs.git
cd go-dfs
go install .
```
### Running the nodes
The servers take 1 mandatory argument and optional arguments of the peers. The first node in the system doesn't need any peer address cause there aren't any. The subsequent nodes need at least one remote address to join the network
```bash
go run . 127.0.0.1:4001 # run the first node
go run . 127.0.0.1:4002 127.0.0.1:4001 # run the second node
```
You can add as much number of nodes you want
## Sequence Diagrams
### Saving a file
```mermaid
sequenceDiagram
participant Client
participant Server
participant Store1 as Server Storage
participant TL1 as Server Transport Layer
participant TL2 as Peer Transport Layer
participant Peer as Peers
participant Store2 as Peer Storage
Client->>Server: Upload file
activate Server
Server->>Store1: Save file
Server->>TL1: Send metadata (filename, size)
TL1->>TL2: Send metadata by TCP
activate TL2
TL2->>Peer: Send metadata (filename, size)
deactivate TL2
activate Peer
Peer->>TL2: Lock transport layer
Server->>Peer: Stream file data
deactivate Server
Peer->>Store2: Save file
Peer->>TL2: Unlock transport layer
deactivate Peer
```
### Get a file through network
```mermaid
sequenceDiagram
participant Client
participant Server
participant Store1 as Server Storage
participant TL1 as Server Transport Layer
participant TL2 as Peer Transport Layer
participant Peer as Peers
participant Store2 as Peer Storage
activate Client
Client->>Server: Request file
activate Server
Server->>Store1: Check local storage
alt File found
Store1->>Server: Send file
Server->>Client: Send file
else File not found
Store1->>Server: File not found
Server->>TL1: Broadcast file request
TL1->>TL2: File Request
TL2->>Peer: Peer receives file request
activate Peer
Peer->>Store2: Get file
activate Store2
Store2->>Peer: Retrieve File Stream
deactivate Store2
Peer->>TL2: Send metadata (filename, size)
TL2->>TL1: Send metadata (filename, size)
TL1->>Server: Send metadata (filename, size)
Server->>TL1: Lock transport layer
Peer->>Server: Stream file data
deactivate Peer
Server->>TL1: Unlock transport layer
Server->>Client: Serve file
end
deactivate Server
deactivate Client
```
### Peer discovery
```mermaid
sequenceDiagram
participant NodeA as New Node
participant NodeB as Known Peer NodeB
participant NodeC as Peer of NodeB
participant NodeD as Another Peer
NodeA->>NodeB: Establish TCP connection
NodeA->>NodeB: Send NodeA address
NodeB->>NodeC: Gossip NodeA address
NodeC->>NodeA: Connect to NodeA
NodeC->>NodeD: Gossip NodeA address
NodeD->>NodeA: Connect to NodeA
```
## Acknowledgement
The project is built on top of the tutorial by [Anthony](https://github.com/anthdm) and further modification and new features were added.