https://github.com/tanema/gween
Tween animation library for go with a simple interface.
https://github.com/tanema/gween
easing-functions golang golang-library tween tweening
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
Tween animation library for go with a simple interface.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/tanema/gween
- Owner: tanema
- License: other
- Created: 2017-10-17T03:14:10.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-02-06T02:31:10.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-26T15:54:31.826Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: easing-functions, golang, golang-library, tween, tweening
- Language: Go
- Homepage:
- Size: 50.8 KB
- Stars: 90
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 8
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Gween [](http://godoc.org/github.com/tanema/gween)
Gween (go-between) is a small library to perform [tweening](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tweening) in Go. It has a minimal
interface, and it comes with several easing functions.
# Examples
```golang
package gween
import (
"github.com/tanema/gween/ease"
"github.com/tanema/gween/gween"
)
// increase the value from 0 to 5 in 10 seconds
var tweenLinear = gween.New(0, 5, 10, ease.Linear)
current, isFinished := tweenLinear.Update(dt)
// make some text fall from the top of the screen, bouncing on y=300, in 4 seconds
var tweenLabel = gween.new(0, 300, 4, ease.OutBounce)
label.Y, _ = tweenLabel.Update(dt)
// fade background from white to black and foregrond from black to red in 2 seconds
currentBGColor = [4]float32{255, 255, 255, 255}
currentColor = [4]float32{0, 0, 0, 0}
var tweenBackground = gween.new(255, 0, 2, ease.Linear)
var tweenRed = gween.new(255, 0, 2, ease.Linear)
currentBG, _ := tweenBackground.Update(dt)
currentBGColor = [4]float32{currentBG, currentBG, currentBG, currentBG}
currentColor[0], _ = tweenRed.Update(dt)
// sequence increasing linearly from 0 to 4 over 10 seconds,
// then decreasing outElastic 4 to 0 over 2 seconds
var sequence = gween.NewSequence(
gween.New(0, 4, 10, ease.Linear),
gween.New(4, 0, 2, ease.OutElastic),
)
// set to infinitely loop
sequence.SetLoop(-1)
val, tweenCompleted, seqenceCompleted = sequence.Update(dt)
```
# Interface
## Tween
### Creation
```golang
t := gween.New(begin, end, duration, easingFunction)
```
Creates a new tween.
* `begin` is the start value
* `end` is the ending value
* `duration` means how much the change will take until it's finished. It must be a positive number.
* `easingFunction` can be either a function or a function name (see the easing section below).
This function only creates and returns the tween. It must be captured in a variable
and updated via `t.Update(dt)` in order for the changes to take place.
### Methods
```golang
currentValue, isFinished := t.Update(dt)
```
Gradually changes the `currentValue` toward the `end` value as time passes.
* `t` is a tween returned by `gween.New`
* `dt` is the difference in time. It will be added to the internal time counter of
the tween. The current value at the current value will be returned using selected
easing function.
* `currentValue` is the current eased value for the current time.
* `isFinised` is `true` if the tween has reached its limit (its *internal clock* is `>= duration`). It is false otherwise.
When the tween is complete, the `currentValue` will be equal to the `end` value.
The way they change over time will depend on the chosen easing function.
If `dt` is positive, the easing will be applied until the internal clock equals
`duration`, at which point the easing will stop. If it is negative,
the easing will play "backwards", until it reaches the initial value.
```golang
currentValue, isFinished := t.Set(clock)
```
Moves a tween's internal clock to a particular moment.
* `t` is a tween returned by `gween.New`
* `clock` is a positive number or 0. It's the new value of the tween's internal clock.
* `currentValue` is the value of the tween at the time set.
* `isFinished` works like in `t.Update`; it's `true` if the tween has reached its
end, and `false` otherwise.
## Sequence
### Creation
```golang
s := gween.NewSeqence(tweens ...*Tween)
```
Sequences can be used to execute tweens in sequence. They also provide looping
and "yoyo" functionality.
* `tweens` the tweens to be executed in sequential order
This function only creates and returns the sequence. It must be captured in a variable
and updated via `s.Update(dt)` in order for the changes to take place.
### Methods
```golang
currentValue, tweenCompleted, seqeuenceCompleted := s.Update(dt)
```
Gradually changes the `currentValue` from the `begin` value to the `end` value
of each tween in the sequence as time passes. If a `dt` is too large for the current
tween, the "overflow" amount will automatically be carried into the next tween until the
entire `dt` is exhausted by the tweens in the sequence, or the sequence completes.
* `s` is a sequence returned by `gween.NewSequence`
* `dt` is the difference in time. It will be added to the internal time counter of
the current tween and "overflow" to the next until completed exhausted.
* `currentValue` is the current eased value for the current time.
* `tweenCompleted` is `true` if any tween within the sequence has completed during this update.
* `sequenceCompleted` is `true` if the entire sequence and all loops have completed.
* When configured to loop indefinitely, this will always be `false`
```golang
s.SetLoop(l)
```
Defaults to `1`
Configures the sequence to "loop" `l` times. When `l` is `-1`, sequence will
loop infinitely.
When used with `s.SetYoyo(true)`, a single "loop" starts and ends at the
`begin`ning of the first tween; making its way out to the `end` of the final
tween and back again.
```golang
s.SetYoyo(bool)
```
Defaults to `false`
Configures the sequence on whether to "yoyo" between the `begin`ning of the
first tween and the `end` of the last tween.
* When `yoyo` is `false`:
* A single loop of the sequence is when all tweens are completed in forward order.
* When the final loop of the sequence is complete, the `currentValue` will be
equal to the `end` value of the final tween.
* When `yoyo` is `true`:
* A single loop is when all tweens have completed in forward order, and then completed again in reverse order.
* When the final loop of the sequence is complete, the `currentValue` will be
equal to the `begin` value of the first tween.
```golang
s.Reset()
```
Resets all tweens in the sequence and sets the "current" tween back to the first. Also,
sets the remaining loop count back to the initial value last set using the
`.SetLoop()` function (or `1` if using the default).
```golang
s.SetReverse(bool)
```
Defaults to `false`
Configures the sequence to run in "reverse" or not.
* When `yoyo` is `false`:
* If `reverse` is `false`, the sequence will run forward and will loop back to
the beginning if available
* If `reverse` is `true`, the sequence will run backward and will loop back to
the end if available
* When `yoyo` is `true`:
* The sequence will run according to normal yoyo logic. If a sequence has gone
from the start to the end, and is coming back to the start (reverse is true)
and you set reverse to false, then the sequence will start heading towards the
end again. When it reaches the end it will simply yoyo as expected. The inverse
is also true, if the sequence is heading to the end and you reverse it before
the end, it'll simply head toward the start and if it reaches the start it will
consume a loop and, if possible, start again.
```golang
s.Add(tweens ...*Tween)
```
Adds the `tweens` provided, in order, at the end of the existing tween list
```golang
s.Remove(index)
```
Removes the tween at the desired `index`. If you call `.Remove()` on an index
out of bounds, nothing happens.
# Easing functions
Easing functions are functions that express how slow/fast the interpolation happens in tween.
Gween comes with 45 default easing functions already built-in (adapted from [Enrique García Cota's easing library](https://github.com/kikito/tween.lua)).
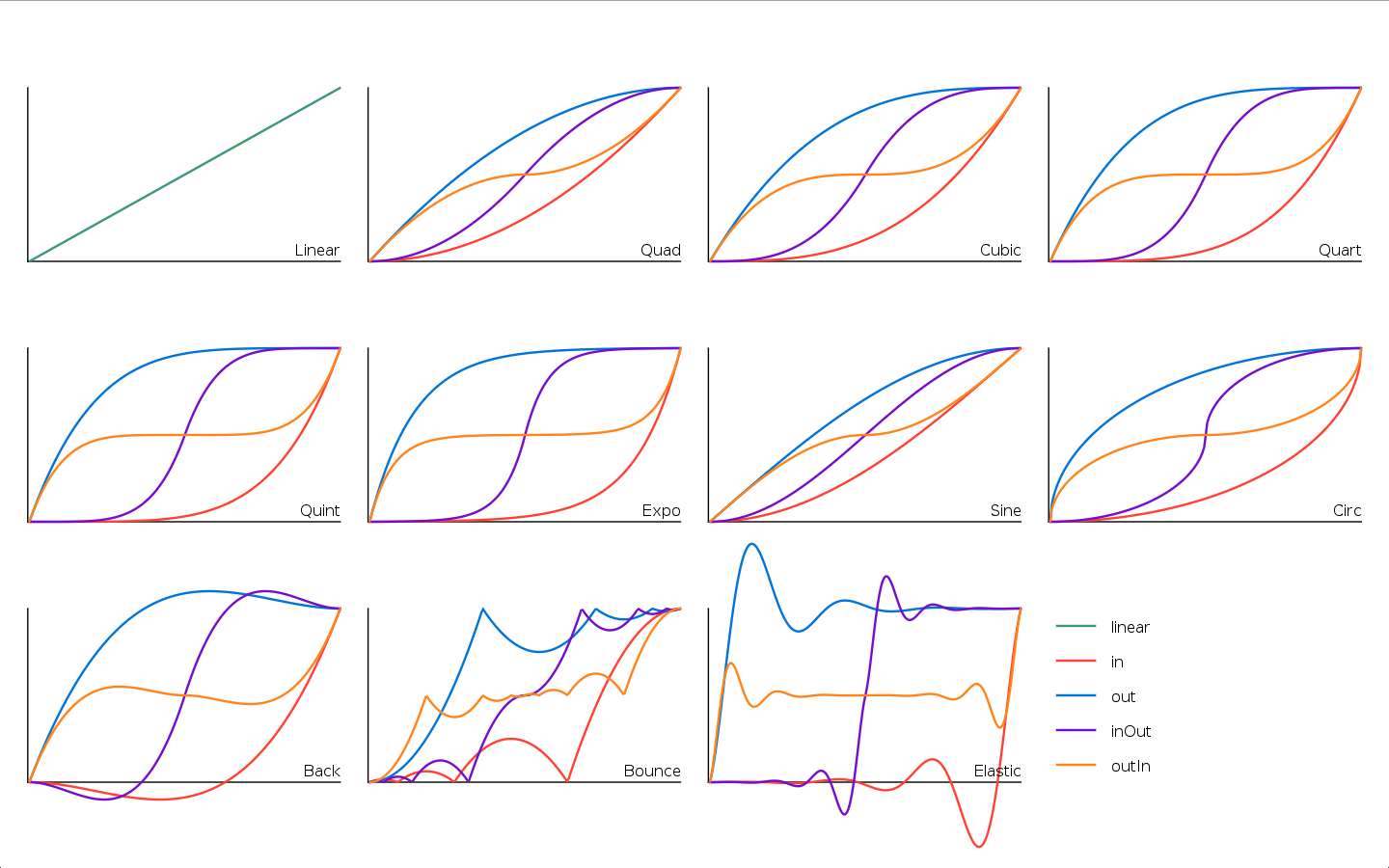
The easing functions can be found in the `ease` package.
They can be divided into several families:
* `linear` is the simplest easing function, straight from one value to the other.
* `quad`, `cubic`, `quart`, `quint`, `expo`, `sine` and `circle` are all "smooth" curves that will make transitions look natural.
* The `back` family starts by moving the interpolation slightly "backwards" before moving it forward.
* The `bounce` family simulates the motion of an object bouncing.
* The `elastic` family simulates inertia in the easing, like an elastic gum.
Each family (except `linear`) has 4 variants:
* `In` starts slow, and accelerates at the end
* `Out` starts fast, and decelerates at the end
* `InOut` starts and ends slow, but it's fast in the middle
* `OutIn` starts and ends fast, but it's slow in the middle
| family | in | out | inOut | outIn |
|-------------|-----------|------------|--------------|--------------|
| **Linear** | Linear | Linear | Linear | Linear |
| **Quad** | InQuad | OutQuad | InOutQuad | OutInQuad |
| **Cubic** | InCubic | OutCubic | InOutCubic | OutInCubic |
| **Quart** | InQuart | OutQuart | InOutQuart | OutInQuart |
| **Quint** | InQuint | OutQuint | InOutQuint | OutInQuint |
| **Expo** | InExpo | OutExpo | InOutExpo | OutInExpo |
| **Sine** | InSine | OutSine | InOutSine | OutInSine |
| **Circ** | InCirc | OutCirc | InOutCirc | OutInCirc |
| **Back** | InBack | OutBack | InOutBack | OutInBack |
| **Bounce** | InBounce | OutBounce | InOutBounce | OutInBounce |
| **Elastic** | InElastic | OutElastic | InOutElastic | OutInElastic |
## Custom easing functions
You are not limited to gween's easing functions; if you pass a function parameter
in the easing, it will be used.
The passed function will need to suite the TweenFunc interface: `func(t, b, c, d float32) float32`
* `t` (time): starts in 0 and usually moves towards duration
* `b` (begin): initial value of the of the property being eased.
* `c` (change): ending value of the property - starting value of the property
* `d` (duration): total duration of the tween
And must return the new value after the interpolation occurs.
Here's an example using a custom easing.
```golang
labelTween := tween.new(0, 300, 4, func(t, b, c, d) float32 {
return c*t/d + b // linear ease
})
```
# Credits
The easing functions have been translated from Enrique García Cota's project in
https://github.com/kikito/tween.lua
See the LICENSE file for details.