https://github.com/terkelg/deakins
🎥 Small Canvas 2D Camera
https://github.com/terkelg/deakins
camera canvas canvas2d game viewport
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
🎥 Small Canvas 2D Camera
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/terkelg/deakins
- Owner: terkelg
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-06-17T01:19:57.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-06-11T12:54:38.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-02T01:04:03.784Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: camera, canvas, canvas2d, game, viewport
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 6.29 MB
- Stars: 139
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 3
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: readme.md
- License: license
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-list - deakins
README
# Deakins
> Small Canvas 2D Camera
Small and simple 2D viewport/camera management for Canvas.
Named after the legendary English cinematographer [Roger Deakins](https://www.imdb.com/name/nm0005683/) known for Blade Runner, Fargo, No Country for Old Men, and The Shawshank Redemption.
## Install
```
$ npm install deakins
```
This module is delivered as:
* **ES Module**: [`dist/index.mjs`](https://unpkg.com/deakins/dist/index.mjs)
* **UMD**: [`dist/deakins.umd.js`](https://unpkg.com/deakins/dist/deakins.umd.js)
## Usage
```js
import { Deakins } from 'deakins';
const canvas = document.createElement(`canvas`);
const context = canvas.getContext(`2d`);
const camera = new Deakins(context);
const player = new Player();
function loop() {
camera.begin();
// Look at point in space,
camera.lookAt(player.position);
// Zoom
camera.zoomTo(500);
camera.end();
requestAnimationFrame(loop);
}
loop();
```
Moving the camera
```js
camera.lookAt([x, y]);
camera.zoomTo(z);
```
## API
### Deakins(context, [options])
Initializes a new `Deakins` camera instance.
#### context
Type: `CanvasRenderingContext2D`
#### options.fieldOfView
Type: `number`
Default: `1000`
This value is used to imitate a FOV camera effect as you zoom.
#### options.flipAspectRatio
Type: `boolean`
Default: `false`
By default, everything scales based on the width of the canvas. When `true`, the aspect ratio is defined by the height instead.
#### options.margin
Type: `LookAtMargins`
Default: `{top: 0, right: 0, bottom: 0, left: 0}`
Margins for all sides defined in screen space.
This is used if the `lazy` option in `lookAt` is `true`. If `true`, the camera only follows the look-at point when the point is inside the screen space margin.
### camera.lookAt(point, [lazy])
Move the centre of the viewport to the location specified by the point.
Call this in the RAF loop to follow a player character, for example.
```js
camera.moveTo([11, 8]);
```
#### point
Type: `[number, number]`
Default: `[0, 0]`
#### lazy
Type: `boolean`
Default: `false`
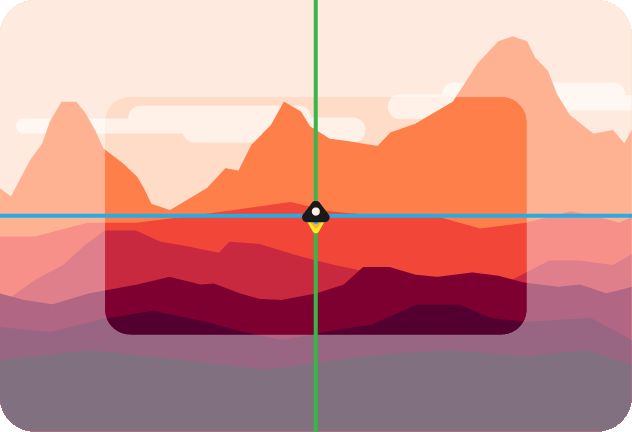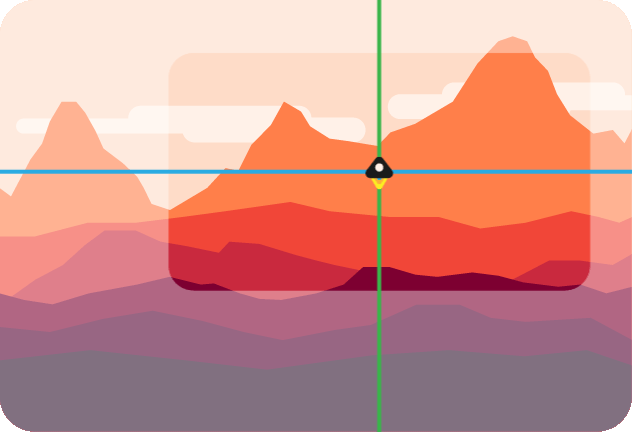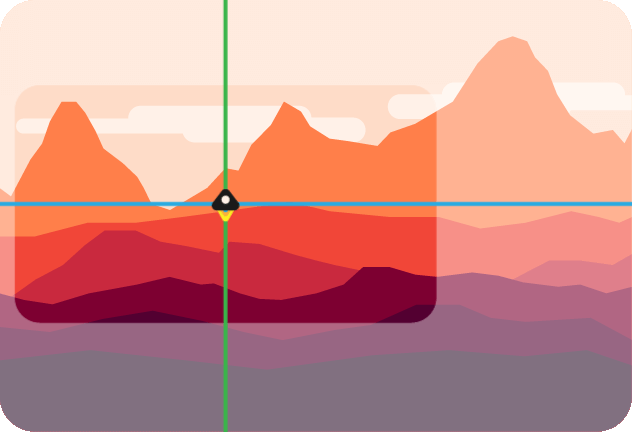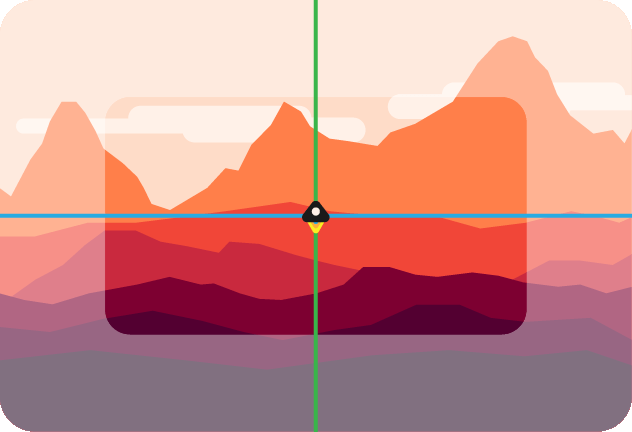
Enable lazy look-at. If true, the camera won't move before the look-at point is inside the margin defined in [`options.margin`](#optionsmargin). If false, the look-at point stays centered. Below is an illustration of a lazy camera.

### camera.zoomTo(zoom)
Zoom to the specified distance from the 2D plane.
```js
camera.zoomTo(500);
```
#### zoom
Type: `number`
Default: `1000`
### camera.begin()
On each render pass, call `.begin()` before drawing to set the right transforms.
Appropriate transformations will be applied to the context, and world coordinates can be used directly with all canvas context calls.
```js
camera.begin();
// Draw stuff here
camera.end();
```
### camera.end()
Call `.end()` when you're done drawing to reset the context.
### camera.worldToScreen(point)
#### point
Type: `[number, number]`
Transform a `point` from world coordinates into screen coordinates - useful for placing DOM elements over the scene.
### camera.screenToWorld()
Returns: `[number, number]`
Transform and return the world space coordinate of the current look-at point.
Useful if you want to project clicks and other screen space coordinates into 2D world coordinates.
### camera.resize()
Call this in your resize handler to make sure the viewport is updated.
## Credit
TypeScript conversion based on [camera](https://github.com/robashton/camera) by Rob Ashton with minor tweaks. Added support for more options, lazy camera movements, and slightly modified API.
## License
MIT © [Terkel Gjervig](https://terkel.com)