Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/terminalkitten/django-insights
Simple insights for Django projects
https://github.com/terminalkitten/django-insights
dashboard django insights metrics python visualization
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Simple insights for Django projects
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/terminalkitten/django-insights
- Owner: terminalkitten
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-02-24T20:08:46.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2023-12-21T07:49:33.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-04-23T06:00:57.748Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: dashboard, django, insights, metrics, python, visualization
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://terminalkitten.github.io/django-insights/
- Size: 4.92 MB
- Stars: 36
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
[](https://github.com/terminalkitten/django-insights/actions/workflows/main.yml)

## Features
Create insights for your app, store them in a SQLite database for further processing, these insights are written right next to your application logic.
### Note:
Still working on some small things, extending tests and improving the documentation.
For now focus is on:
- Django 3.2 (LTS), 4.0,4.1 and 4.2;
- Python ≥ 3.8
## Installation
Installing with:
```bash
pip install 'django-insights'
```
## Usage
First create a `insights.py` file in your app directory, for example:
```bash
project
└── testapp
└── insights.py
```
Each app can have it's own `insights.py` file, these files are auto-discovered by Django Insights, so at any given location it would pick up your metrics.
In these insights files you write out any metric you would like to track. Each metric starts with a question and some values to store. Below is a example of the `@metrics.counter` function:
```python
# project/testapp/insights.py
from django_insights.metrics import metrics
from project.testapp.models import Author
label = "Bookstore"
@metrics.counter(question="How many authors are there?")
def count_authors() -> int:
return Author.objects.count()
```
Insight apps can have a `label`, this is used in the dashboard or can be read from `insights_app` table later on.
### Settings
Add django_insights package, insights database and router to your settings
```python
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
"django_insights",
]
DATABASES = {
...
"insights": {
"ENGINE": "django.db.backends.sqlite3",
"NAME": os.path.join(BASE_DIR,"db/insights.db")
},
...
}
DATABASE_ROUTERS = ['django_insights.database.Router']
```
Note: please make sure you exclude the database in your `.gitignore` file
Migrate insights database:
```bash
workon myapp
python manage.py migrate insights --database=insights
```
Now collect your insights
```bash
python manage.py collect_insights
```
You now have a database containing all insights from your application.
Note: You need to run the `python manage.py collect_insights` command each time you want to update data on your dashboard. In production, you can setup a cron job to call this command at regular intervals depending on your use case.
You can inspect this database yourself with `sqlite3 db/insights.db` - or - you can use the Django Insights dashboard.
### Dashboard
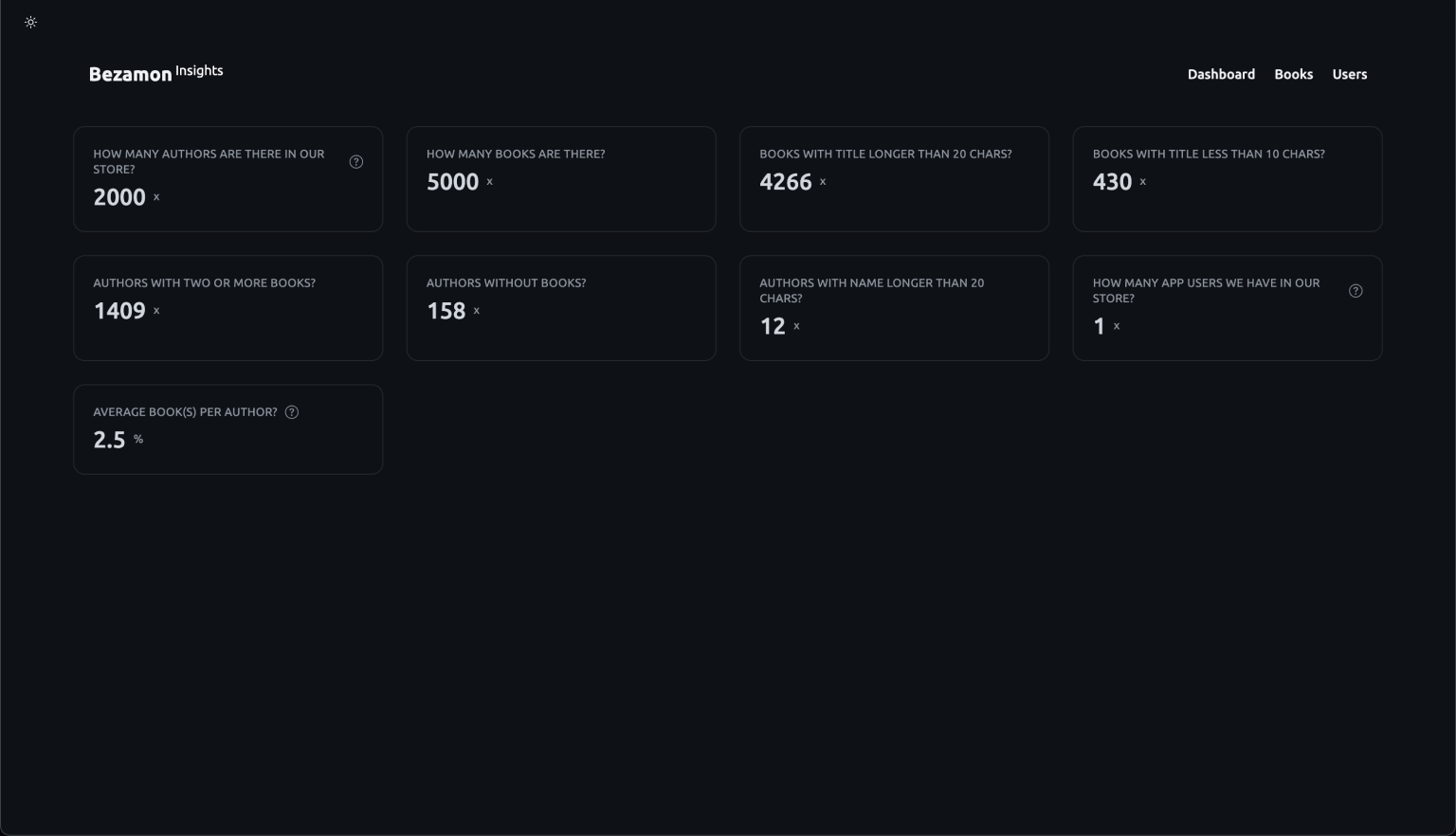
To enable this dashboard, add the following settings:
```python
from django.urls import include, path
urlpatterns = [
path(
'insights/',
include('django_insights.urls', namespace='insights'),
),
]
```
Now you can visit https://localhost:8000/insights to inspect your Django Insights database.
## Metrics
Django insights contains 5 types of metrics it can collect:
- `@metrics.counter`
- `@metrics.gauge`
- `@metrics.timeseries`
- `@metrics.scatterplot`
- `@metrics.barchart`
### Counter:
```python
from django_insights.metrics import metrics
from project.testapp.models import Author
@metrics.counter(question="How many authors are there?")
def count_authors() -> int:
return Author.objects.count()
```
### Gauge:
```python
from django.db.models import Avg, Count
from django_insights.metrics import metrics
from project.testapp.models import Author
@metrics.gauge(question="Average book(s) per author?")
def avg_books_per_author() -> int:
avg_total_books = (
Author.objects.prefetch_related('books')
.annotate(total_books=Count('books'))
.aggregate(Avg('total_books'))
.get('total_books__avg')
)
return avg_total_books
```
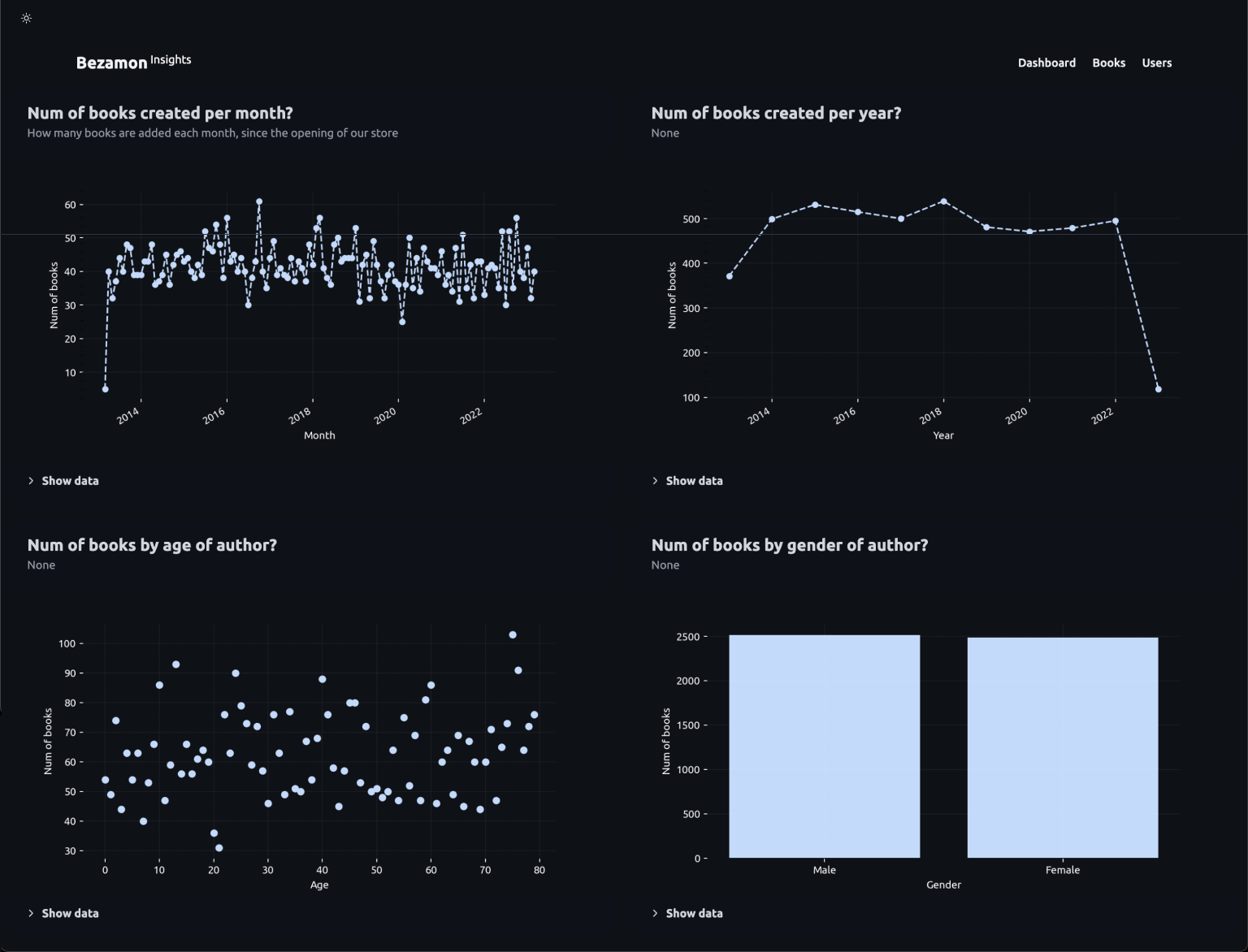
### Timeseries:
```python
from datetime import datetime
from django.db.models import Count
from django.db.models.functions import TruncMonth
from django_insights.metrics import metrics
from project.testapp.models import Book
@metrics.timeseries(
question="Num of books created per month?",
desc="How many books are added each month, since the opening of our store",
xlabel="Month",
xformat='%m',
ylabel="Num of books",
)
def num_of_books_per_month() -> list[tuple[datetime, int]]:
return (
Book.objects.all()
.annotate(month=TruncMonth('created'))
.values('month')
.filter(month__isnull=False)
.annotate(total=Count('pk'))
.values_list('month', 'total')
.order_by('month')
)
```
### Scatterplot:
```python
from datetime import datetime
from django.db.models import Count, Value
from django_insights.metrics import metrics
from project.testapp.models import Author
@metrics.scatterplot(
question="Num of books by age of author?",
xlabel="Age",
ylabel="Num of books",
)
def author_age_vs_num_of_books() -> list[tuple[float, float, Any]]:
return (
Author.objects.values('age')
.annotate(num_of_books=Count('books'), category=Value("author"))
.values_list('num_of_books', 'age', 'category')
)
```
### Barchart:
```python
from datetime import datetime
from django.db.models import Case, Count, Value, When
from django_insights.metrics import metrics
from project.testapp.models import Author
@metrics.barchart(
question="Num of books by gender of author?",
xlabel="Gender",
ylabel="Num of books",
)
def author_gender_vs_num_of_books() -> list[tuple[float, float, str]]:
return (
Author.objects.values('gender')
.annotate(
num_of_books=Count('books'),
gender_category=Case(
When(gender=1, then=Value('Male')),
When(gender=2, then=Value('Female')),
),
)
.values_list('num_of_books', 'gender', 'gender_category')
)
```
## Settings
```python
# Custom app name
INSIGHTS_APP_NAME = "Bezamon"
# Quality of chart images
INSIGHTS_CHART_DPI = 180
# Default theme for dashboard
INSIGHTS_THEME = "dark"
# Change primary color of dashboard
INSIGHTS_CHART_LIGHT_PRIMARY_COLOR = "#2563EB"
INSIGHTS_CHART_DARK_PRIMARY_COLOR = "#BFDBFE"
```
## Use-cases
Insights are gathered from your current application state, Django Insights is not intentend to be used as a realtime, incremementing data-source. You should be able to re-gather these insights from your actual data at any moment in time.
Yes:
- How many users, how many users invited a year
- How many reports a day, how many messages send on Wednesday's
No:
- How many GET request for url XXX a second
- Realtime profit target percentage
## Background
I'm currently working at a small company that is in the process of renewing some parts of our product. To gain insight into the usage over different periods, we have tried a few solutions. We initially attempted to periodically generate CSV files from queries, as well as send data to a dashboard at regular intervals.
We ended up with many exports that where spread out over multiple people. Additionally, exporting data directly from the database also posed a security risk, as it required constant movement of possible sensitive information. After several months of working with CSV files, which were often outdated and required conversion by other (paid) tools, we where looking for a better solution.
I wanted an easy-to-configure file within our various apps that would allow me to create "insights" easily, so Django Insights was born. I decided to switch to a local SQLite database which could be share on request, as a plus these files can be tracked by a security officer.
## Documentation
Write more about where to find documentation
## Ideas
- Connect to other datasources and export to different file-formats ( ArrowFile?, NDJSON )
## Is it any good?
[Yes.](http://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=3067434)
## License
The MIT License