https://github.com/tf-encrypted/tf-seal
Bridge between TensorFlow and the Microsoft SEAL homomorphic encryption library
https://github.com/tf-encrypted/tf-seal
cryptography homomorphic-encryption machine-learning tensorflow
Last synced: 11 months ago
JSON representation
Bridge between TensorFlow and the Microsoft SEAL homomorphic encryption library
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/tf-encrypted/tf-seal
- Owner: tf-encrypted
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2019-07-08T12:28:53.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2020-01-22T11:44:54.000Z (about 6 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-09-18T15:24:40.922Z (over 1 year ago)
- Topics: cryptography, homomorphic-encryption, machine-learning, tensorflow
- Language: C++
- Homepage:
- Size: 83 KB
- Stars: 95
- Watchers: 17
- Forks: 16
- Open Issues: 18
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# TF SEAL
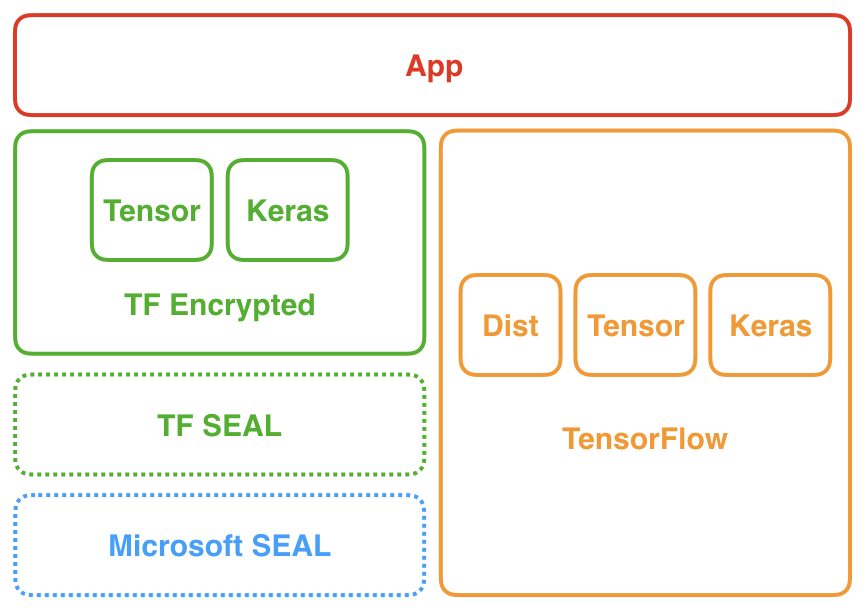
TF SEAL provides a bridge between [TensorFlow](https://tensorflow.org) and the [Microsoft SEAL](https://github.com/microsoft/SEAL) homomorphic encryption library, making it easier than ever to use this library to compute on encrypted data. It currently offers low-level operations for interacting with Microsoft SEAL via TensorFlow with [work in progress](#road-map) on a high-level integration into [TF Encrypted](https://tf-encrypted.io).
[](https://pypi.org/project/tf-seal/) [](https://circleci.com/gh/tf-encrypted/tf-seal/tree/master)
## Usage
The following demonstrates how the low-level interface can be used to perform a matrix multiplication using homomorphic encryption inside of TensorFlow.
```python
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import tf_seal as tfs
public_keys, secret_key = tfs.seal_key_gen(gen_relin=True, gen_galois=True)
# sample inputs in the form of tf.Tensors
a = tf.random.normal(shape=(2, 3), dtype=tf.float32)
b = tf.random.normal(shape=(2, 3), dtype=tf.float32)
# the plaintext equivalent of our computation
c = tf.matmul(a, tf.transpose(b))
# encrypt inputs, yielding tf_seal.Tensors
a_encrypted = tfs.convert_to_tensor(a, secret_key, public_keys)
b_encrypted = tfs.convert_to_tensor(b, secret_key, public_keys)
# perform computation on encrypted data
# - note that because of how the data is laid out in memory,
# tf_seal.matmul expects the right-hand matrix to be ordered
# column-major wise, i.e. already transposed
c_encrypted = tfs.matmul(a_encrypted, b_encrypted)
with tf.Session() as sess:
expected, actual = sess.run([c, c_encrypted])
np.testing.assert_almost_equal(actual, expected, decimal=3)
```
## Documentation
Blog posts:
- [Bridging Microsoft SEAL into TensorFlow](https://medium.com/dropoutlabs/bridging-microsoft-seal-into-tensorflow-b04cc2761ad4)
## Road map
We are currently working on integrating TF SEAL into [TF Encrypted](https://tf-encrypted.io) such that privacy-preserving machine learning applications can instead access the library through a high-level interface and take advantage of e.g. the Keras API. This includes adding logic that helps optimize homomorphic encryption for a perticular computation, making use even easier.
## Installation
We recommend using [Miniconda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html) or [Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/) to set up and use a Python 3.7 environment for all instructions below:
```
conda create -n tfseal python=3.7 -y
source activate tfseal
```
After installing the [custom build of TensorFlow](#custom-tensorflow) you can install [TF SEAL from PyPI](https://pypi.org/project/tf-seal/) using pip:
```
pip install tf-seal
```
## Examples
There is currently one example displaying how we can run a simple logistic regression prediction with TF SEAL.
Once TF SEAL is installed we can run the example by simplying running:
```
python logistic_regression.py
```
## Development
We recommend using [Miniconda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html) or [Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/) to set up and use a Python 3.7 environment for all instructions below:
```
conda create -n tfseal-dev python=3.7 -y
source activate tfseal-dev
```
The basic requirements are:
- Python (== 3.7)
- [Bazel](https://docs.bazel.build/versions/master/install.html) (>= 0.26.1)
- CMake
- [TensorFlow built with C++17](#custom-tensorflow)
The remaining PyPI packages can then be installed using:
```
pip install -r requirements-dev.txt
```
### Testing
All tests can be run via Bazel with:
```
make test
```
### Building
The pip package can be built using:
```
make build
```
with the resulting wheel file placed in `./artifacts`.
## Custom TensorFlow
A custom build of TensorFlow is currently needed to run TF SEAL due to a mismatch between the C++ version used by the official TensorFlow build (C++11) and the one needed by Microsoft SEAL (C++17). A [patched version of TensorFlow](https://github.com/dropoutlabs/tensorflow) built with C++17 can be installed as shown below.
#### Ubuntu binary
```
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/tf-pips/tf-c++17-support/tf_nightly-1.14.0-cp37-cp37m-linux_x86_64.whl
pip install tf_nightly-1.14.0-cp37-cp37m-linux_x86_64.whl
```
#### macOS binary
```
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/tf-pips/tf-c++17-support/tf_nightly-1.14.0-cp37-cp37m-macosx_10_7_x86_64.whl
pip install tf_nightly-1.14.0-cp37-cp37m-macosx_10_7_x86_64.whl
```
#### From source
We recommend using [Miniconda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html) or [Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/) to first set up and use a Python 3.7 environment:
```
conda create -n customtf python=3.7 -y
source activate customtf
```
This requires that [Bazel](https://docs.bazel.build/versions/master/install.html) (== 0.26.1) has been installed. The patched version of TensorFlow may then be built using:
```
git clone https://github.com/tf-encrypted/tf-seal.git
cd tf-seal
pip install -r requirements-customtf.txt
make tensorflow
pip install -U tf_nightly-1.14.0-cp37-cp37m-*
```