https://github.com/thep0y/python-logger
Colorful logger for python3
https://github.com/thep0y/python-logger
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Colorful logger for python3
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/thep0y/python-logger
- Owner: thep0y
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-05-21T05:48:31.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-06-18T12:29:48.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-19T20:33:09.817Z (8 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Size: 72.3 KB
- Stars: 2
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
Python Colorful Logger
A colorful logger for python3.
## How to use
### Install
```shell
pip install colorful-logger
```
### Usage
#### 1 Default Logger
You can directly use the default logger. Colored logs will be printed on the terminal. The default logger level is **warning**.
```python
from colorful_logger import logger
with logger:
logger.debug("default logger")
logger.info("default logger")
logger.warning("default logger")
logger.error("default logger")
```
`logger` needs to be executed inside a `with` statement, because this package uses `QueueListener` for log output. You need to call the `start` method before using `logger` to output logs, and call `stop` after you are done. I encapsulated these two methods inside `the` with statement. In most cases, there is no need to call `start` and `stop` separately.

#### 2 Custom Logger
You can also change the log level, save logs to a file, change the logger name, etc. Logs may not be printed to the terminal.
```python
from colorful_logger import get_logger, DEBUG
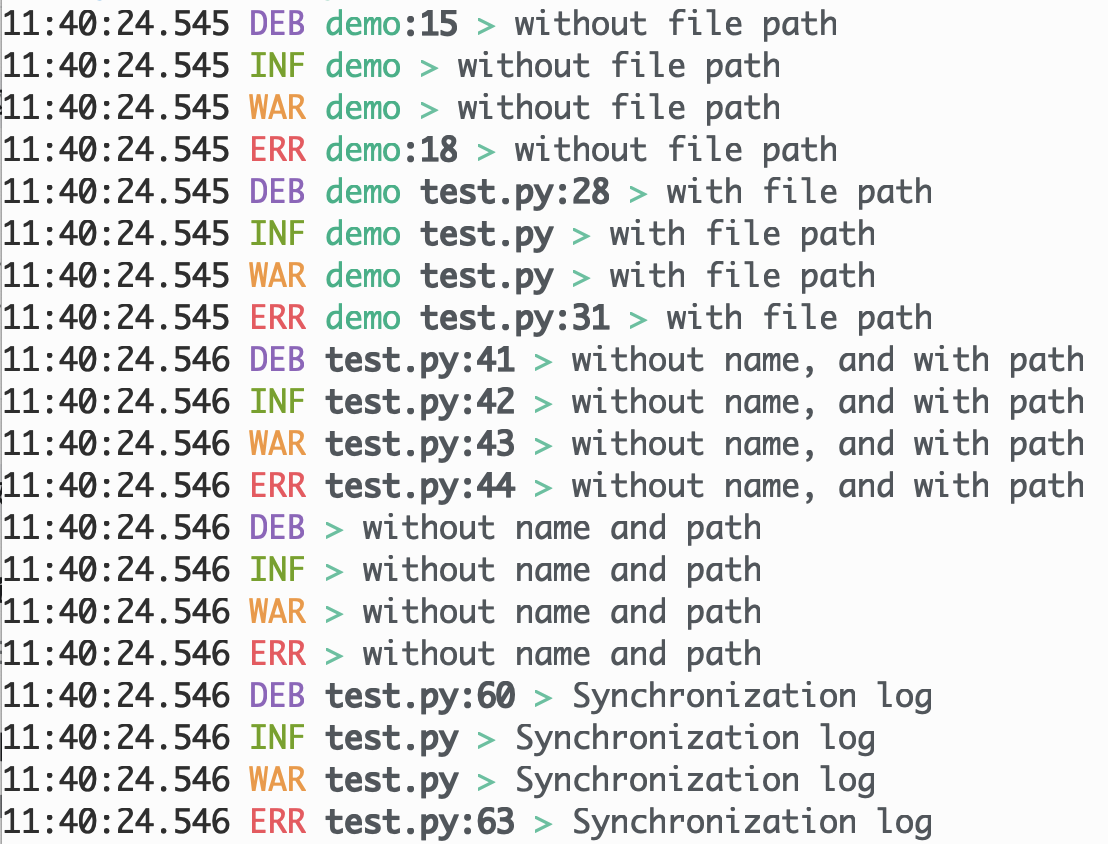
def demo_logger(to_file=False):
file = "test_%d.log"
l1 = get_logger(
"demo",
DEBUG,
add_file_path=False,
disable_line_number_filter=False,
file_path=file % 1 if to_file else None,
)
with l1:
l1.debug("without file path")
l1.info("without file path")
l1.warning("without file path")
l1.error("without file path")
l2 = get_logger(
"demo",
DEBUG,
add_file_path=True,
disable_line_number_filter=False,
file_path=file % 2 if to_file else None,
)
with l2:
l2.debug("with file path")
l2.info("with file path")
l2.warning("with file path")
l2.error("with file path")
l3 = get_logger(
None,
DEBUG,
add_file_path=True,
disable_line_number_filter=True,
file_path=file % 3 if to_file else None,
)
with l3:
l3.debug("without name, and with path")
l3.info("without name, and with path")
l3.warning("without name, and with path")
l3.error("without name, and with path")
l4 = get_logger(
None,
DEBUG,
add_file_path=False,
disable_line_number_filter=True,
file_path=file % 4 if to_file else None,
)
with l4:
l4.debug("without name and path")
l4.info("without name and path")
l4.warning("without name and path")
l4.error("without name and path")
l5 = get_logger(None, DEBUG, asynchronous=False)
l5.debug("Synchronization log")
l5.info("Synchronization log")
l5.warning("Synchronization log")
l5.error("Synchronization log")
```
There may be unexpected behavior when logging outside of the `with` statement.
Contents of the log file `./test.log` (example, inconsistent with the image above):
```
[90m10:09:33.146[0m [35mDEB[0m [36mdemo[0m[1m:26[0m [96m-[0m without file path
[90m10:09:33.146[0m [32mINF[0m [36mdemo[0m [96m-[0m without file path
[90m10:09:33.146[0m [33mWAR[0m [36mdemo[0m [96m-[0m without file path
[90m10:09:33.146[0m [91mERR[0m [36mdemo[0m[1m:29[0m [96m-[0m without file path
```
The log file does not contain color logs by default.
To save color logs to a file, set `file_colorful` to `True`. In this example, color logs are saved.
The only purpose of the color log file is to view logs in real-time in the terminal:
- Unix
```shell
tail -f test.log
# or
cat test.log
```
- Windows
```powershell
Get-Content -Path -Wait test.log
```
##### Synchronous
If you don't want to log asynchronously, you can create a synchronous logger by passing `asynchronous=False`. In the example above, `l5` is a synchronous logger. When using a synchronous logger, you don't need to wrap the logs in a `with` statement.
#### 3 Child Logger
After defining a `logger`, I want to use all the parameters of this `logger` except for `name` to output logs. You need to use the `child_logger` method to generate a child logger. The child logger needs to be executed inside the `with` statement of the parent logger:
```python
from colorful_logger import get_logger, DEBUG
# parent logger
logger = get_logger(name="sample_logger", level=DEBUG, file_path="./test.log")
with logger:
logger.error("parent error")
l1 = logger.child("l1")
l1.error("l1 error")
l1.fatal("l1 fatal")
```
The child logger is the same as the parent logger except for the name. It will not log third-party libraries.
Executing the child logger inside the `with` statement of the parent logger does not mean it has to be called directly inside the `with`. It can be executed inside a function in the `with` statement:
```python
# log.py
from colorful_logger import get_logger, DEBUG
logger = get_logger(name="sample_logger", level=DEBUG, file_path="./test.log")
```
```python
# main.py
from log import logger
from other_file import test
with logger:
test()
```
```python
# other_file.py
test_logger = logger.child("test_logger")
def test():
test_logger.error("test error")
```


