https://github.com/thu-nics/MoA
The official implementation of the paper <MoA: Mixture of Sparse Attention for Automatic Large Language Model Compression>
https://github.com/thu-nics/MoA
large-language-models model-compression sparse-attention
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
The official implementation of the paper <MoA: Mixture of Sparse Attention for Automatic Large Language Model Compression>
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/thu-nics/MoA
- Owner: thu-nics
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-06-19T06:31:47.000Z (11 months ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-11-12T03:20:54.000Z (6 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-12T04:23:05.733Z (6 months ago)
- Topics: large-language-models, model-compression, sparse-attention
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 505 KB
- Stars: 97
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 6
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- StarryDivineSky - thu-nics/MoA
README
# MoA: Mixture of Sparse Attention for Automatic Large Language Model Compression
**[[arXiv](https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.14909)]** **[[project page](https://thu-nics.github.io/MoA_project_page/)]**
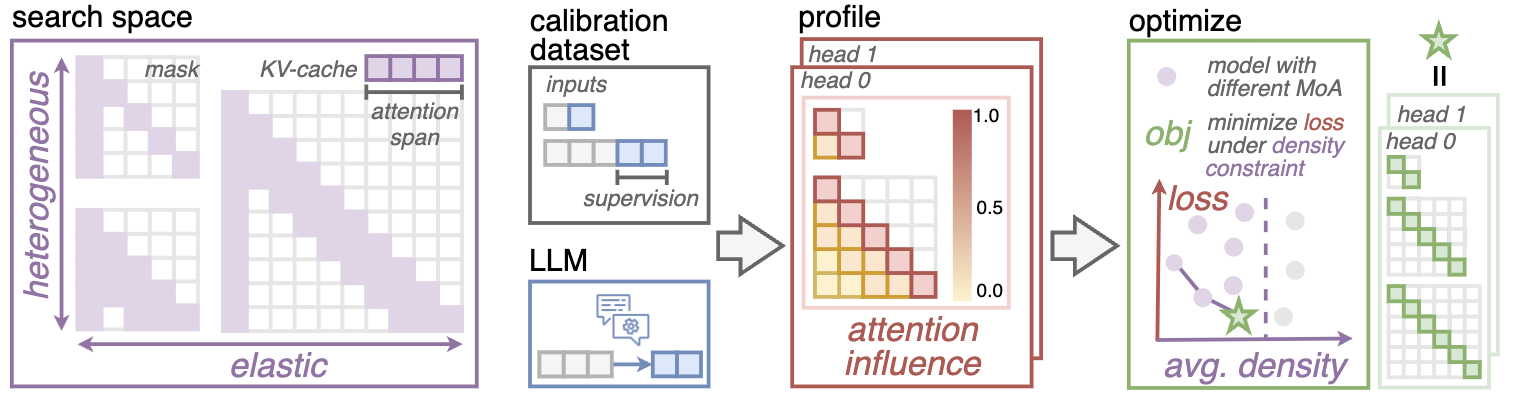
Compressing the attention operation is crucial for the efficiency of processing long inputs. Existing sparse attention methods (more specifically, local attention methods), such as StreamingLLM, adopt uniform and fixed attention masks across different attention heads. Nevertheless, some heads need to attend to more distant information than others; and as the input sequence gets longer, some heads might need to increase their span more than others. In this work, we propose MoA that overcomes the drawbacks of uniform sparse attention by searching heterogeneous elastic rules for each attention head using an automatic pipeline.

MoA achieves a 1.2-1.4x GPU memory reduction, boosting decode throughput by 6.6−8.2x and 1.7−1.9x compared to FlashAttention2 and vLLM, with minimal impact on performance.
If you find this repository or paper useful, you can cite
```
@misc{fu2024moa,
title={MoA: Mixture of Sparse Attention for Automatic Large Language Model Compression},
author={Tianyu Fu and Haofeng Huang and Xuefei Ning and Genghan Zhang and Boju Chen and Tianqi Wu and Hongyi Wang and Zixiao Huang and Shiyao Li and Shengen Yan and Guohao Dai and Huazhong Yang and Yu Wang},
year={2024},
eprint={2406.14909},
archivePrefix={arXiv}
}
```
## News
- [2024/10] MoA kernel is now available in [CUDA](https://github.com/thu-nics/MoA_Kernel), achieving faster inference speed.
## Environment Setup
First, create the Conda environment and install the relevant packages using the following commands:
```bash
conda create -n moa python=3.10
conda activate moa
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install -e .
```
Then, install the MoA kernel by following the instructions in the [MoA Kernel repository](https://github.com/thu-nics/MoA_Kernel).
## Kind Notes
### Cloning the Repository
If you have trouble cloning the repo, it is probably because the repo's git-lfs is too large. You can safely skip the downloading of git-lfs with `git clone --no-checkout `.
### Group Query Attention Models
If you are testing the accuracy of group query attention models with our kernel, please convert them to multi head attention models before profiling and inference. You can do so by running the `scripts/helper/gqa_to_mha.py` script.
## Quick Start: Use Pre-defined Plans
If you prefer not to perform the automatic compression plan search steps and want immediate results, we provide pre-compressed configurations for the `lmsys/vicuna-{size}-v1.5-16k` models (7B and 13B versions). These can be found in the `.json` files under the `examples` directory.
You can directly go to `Evaluation` section to evaluate the model with the plans.
If you want to compress other models, you can follow the `Automatic Search Pipeline` section to compress the model by yourself.
## Automatic Search Pipeline
The pipeline automatically compresses the LLM, beginning with the creation of a calibration dataset that includes long dependency and model alignment. This dataset is used for gradient-based profiling to assess the impact of each attention position on prediction loss. Following profiling, MoA optimizes sparse attention configurations for each model layer and attention head, aiming to minimize accuracy loss within specified density budgets.
### Calibration Dataset Generation
MoA creates the calibration dataset with long dependency and model alignment. We publish the calibration dataset at [this HuggingFace Repository](https://huggingface.co/datasets/nics-efc/MoA_Long_HumanQA) with human-written answers. To ensure "model alignment", we should generate the model answers from the original dense LLM.
This involves querying an LLM with original questions to collect its responses, which are then formatted into a standard Hugging Face `Dataset` item.
```bash
python scripts/pipeline/generate_calibration_dataset.py --model_path lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --model_name vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --output_path_base output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/dataset
```
### Profile
MoA employs a gradient based method to quantify the importance of the attention values. The `--response_mask` option specifies that only the model's responses are used as supervision. Given the calibration dataset, the profile process outputs the average attention influence tensor at a specific sequence length.
```bash
python scripts/pipeline/pipeline_profile.py --model_name lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --max_length 2048 --response_mask --dataset_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/dataset/multi_conversation_model/multi_news --grad_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/profile/profile_2k
python scripts/pipeline/pipeline_profile.py --model_name lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --max_length 4096 --response_mask --dataset_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/dataset/multi_conversation_model/multi_news --grad_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/profile/profile_4k
python scripts/pipeline/pipeline_profile.py --model_name lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --max_length 8192 --response_mask --dataset_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/dataset/multi_conversation_model/multi_news --grad_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/profile/profile_8k
```
### Optimize
MoA identifies Pareto front compression plans to minimize accuracy losses across various sequence lengths under density budget. The `--elastic_length` option specifies the sequence lengths for which profile are done, `--extend_length` determines the maximum length which we wish the compression plan to extend to, and `--density_bounds` sets the maximum allowable attention density for each length.
```bash
python scripts/pipeline/elastic_generate.py --output_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/optimize --elastic_length 2048 4096 8192 --extend_length 16384 --density_bounds 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 --importance_tensor_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/profile/ --output_length 4096 8192 12288 16384
```
You can set `--time_limit num` to specify the maximum duration (in seconds) for each single objective optimization. Also you might need to apply for the gurobi license on the [official website](https://www.gurobi.com/) to use the optimization library.
### Validate
MoA selects the plan that yields minimum loss at unseen length among the Pareto front plans.
To evaluate the loss of a certain plan on a specified length level, use the following command, replacing `{i}` with the actual plan ID:
```bash
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python scripts/pipeline/perplexity_evaluate.py --model_name lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --max_length 12288 --dataset_dir nics-efc/MoA_Long_HumanQA --split valid --response_mask --moa_config output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/optimize/moa_config_plan_{i}.json --result_path output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/validate/validate_0.csv
```
Alternatively, to evaluate all plans within a directory, run the following script:
```bash
scripts/pipeline/validate.sh
```
For example
```bash
scripts/pipeline/validate.sh output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/optimize/ output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/validate lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k
```
Replace with the number of plans under the directory.
## Evaluation
We provide the example compression plans under the `examples` directory. You can use them by setting the following `--moa_config` to the `.json` files under the directory.
### Apply MoA to LLM
Given the compression plan found by MoA, you can simply apply the plan to the model with few lines.
```python
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, pipeline
from MoA.models.interface import update_model_function
# Load the huggingface model
model_name = "lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
moa_config_path = "examples/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/moa_alpha_beta.json"
with open(moa_config_path, 'r') as f:
moa_config = json.load(f)
# Add mixture of sparse attention capability to the model
model = update_model_function(model, model_name)
model.model.set_mixture_of_attention(moa_config, permute_head=True)
# Now you can use the `model` for efficient inference like any regular huggingface model
# For example, you can use it in pipeline to chat with the model
pipe = pipeline(task="text-generation", tokenizer=tokenizer, model=model, trust_remote_code=True)
prompt = "Hi."
output = pipe(prompt)
```
### Retrieval
MoA aims to preserve the retrieval ability of the original dense model with a reduced impact on accuracy. To evaluate the retrieval performance of a specific plan at a given input length, use the following command, replacing `{i}` with the actual plan ID:
```bash
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python scripts/evaluate/retrieval_evaluate.py --model_name lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --moa_config output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/optimize/moa_config_plan_{i}.json --output_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/evaluate/retrieval --length_level 8
```
> Alternatively, you can use our example plans. When passing in multiple plans at different lengths, the correct length will be automatically selected according to the input length:
>
> ```bash
> CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python scripts/evaluate/retrieval_evaluate.py --model_name lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --moa_config examples/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/moa_alpha_beta.json --output_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/evaluate/retrieval --length_level 8
> ```
### LongBench
MoA strives to maintain the long-context understanding ability of the original dense model. To assess this capability using the [LongBench benchmark](https://github.com/THUDM/LongBench), execute the following command, substituting `{i}` with the actual plan ID:
```bash
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python scripts/evaluate/longbench_evaluate.py --model_name lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --max_length 3500 --eval longbench_fast --longbench_e --longbench_result_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/evaluate/longbench --longbench_length_range 0-4k --moa_config output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/optimize/moa_config_plan_{i}.json
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python scripts/evaluate/longbench_evaluate.py --model_name lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --max_length 7500 --eval longbench_fast --longbench_e --longbench_result_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/evaluate/longbench --longbench_length_range 4-8k --moa_config output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/optimize/moa_config_plan_{i}.json
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python scripts/evaluate/longbench_evaluate.py --model_name lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --max_length 15500 --eval longbench_fast --longbench_e --longbench_result_dir output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/evaluate/longbench --longbench_length_range 8k+ --moa_config output/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/optimize/moa_config_plan_{i}.json
```
> Alternatively, you can use our example plans.
### Chat Demo
To chat with the model using the example plans, run the following command:
```bash
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python scripts/evaluate/chat_demo.py --model_name lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k --moa_config examples/lmsys--vicuna-7b-v1.5-16k/moa_alpha_beta.json --batch_size 16
```
> Currently, the input prompt should have at least 64 tokens.
## TODOs
- [ ] Support padding in batch inference
- [ ] Support prefill with past_key_values (use Key-Value cache in multi-round conversation)