Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/tienisto/rhttp
Make HTTP requests using Rust from Flutter.
https://github.com/tienisto/rhttp
Last synced: 4 days ago
JSON representation
Make HTTP requests using Rust from Flutter.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/tienisto/rhttp
- Owner: Tienisto
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-08-01T22:23:13.000Z (5 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-12-22T14:39:51.000Z (19 days ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-12-30T07:06:39.311Z (11 days ago)
- Language: Dart
- Homepage: https://pub.dev/packages/rhttp
- Size: 968 KB
- Stars: 129
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 13
- Open Issues: 15
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# rhttp
[](https://pub.dev/packages/rhttp)

[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
Make HTTP requests using Rust for Flutter developers.
## About
The default HTTP client in Dart is part of `dart:io`, which lacks configurability and performance compared to other HTTP clients.
Furthermore, HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 are either missing or not supported by default.
This package uses FFI with [flutter_rust_bridge](https://pub.dev/packages/flutter_rust_bridge) to call Rust code. This allows you to use a faster and more efficient HTTP client.
On Rust's side, the [reqwest](https://crates.io/crates/reqwest) crate is used to make the requests.
Why shouldn't I use [cronet_http](https://pub.dev/packages/cronet_http) or [cupertino_http](https://pub.dev/packages/cupertino_http)?
These packages for instance only support Android or iOS, while rhttp supports all platforms (except web currently) with a single configuration.
The APK size will increase by 2 MB on arm64 and 6 MB if compiled for all architectures (x64, arm32, arm64).
## Features
- ✅ HTTP/1, HTTP/1.1, HTTP/2, and HTTP/3 support
- ✅ TLS 1.2 and 1.3 support
- ✅ Connection pooling
- ✅ Interceptors
- ✅ Retry (optional)
- ✅ Certificate pinning
- ✅ Proxy support
- ✅ Custom DNS resolution
- ✅ Strong type safety
- ✅ DevTools support ([Network tab](https://docs.flutter.dev/tools/devtools/network))
- ✅ Compatible with [dart:io](https://api.dart.dev/stable/dart-io/HttpClient-class.html), [http](https://pub.dev/packages/http), and [dio](https://pub.dev/packages/dio)
## Benchmark
rhttp is much faster at downloading large files and a bit faster at downloading small files compared to the default HTTP client in Dart.
| Small Files (1 KB) | Large Files (10 MB) |
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 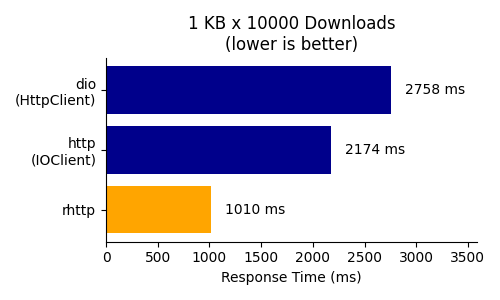 | 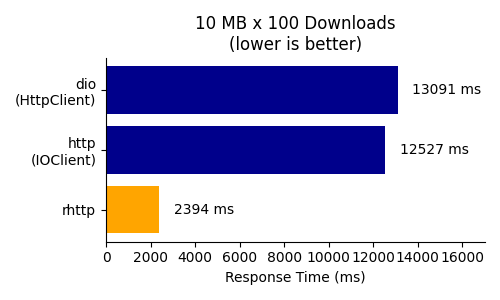 |
Referred packages: [dio](https://pub.dev/packages/dio) (5.5.0+1), [http](https://pub.dev/packages/http) (1.2.2), [rhttp](https://pub.dev/packages/rhttp) (0.3.0)
Checkout the benchmark code [here](https://github.com/Tienisto/rhttp/tree/main/benchmark).
## Table of Contents
- [Getting Started](#getting-started)
- [Request Basics](#request-basics)
- [HTTP methods](#-http-methods)
- [Request query parameters](#-request-query-parameters)
- [Request Headers](#-request-headers)
- [Request Body](#-request-body)
- [Response Body](#-response-body)
- [Request Lifecycle](#request-lifecycle)
- [Cancel Requests](#-cancel-requests)
- [Progress](#-progress)
- [Client Settings](#client-settings)
- [Connection Reuse](#-connection-reuse)
- [Keep-Alive](#-keep-alive)
- [Timeout](#-timeout)
- [Base URL](#-base-url)
- [HTTP version](#-http-version)
- [TLS version](#-tls-version)
- [TLS Server Name Indication (SNI)](#-tls-server-name-indication-sni)
- [Certificate Pinning](#-certificate-pinning)
- [Disable pre-installed root certificates](#-disable-pre-installed-root-certificates)
- [Client Authentication](#-client-authentication--mutual-tls)
- [Disable certificate verification](#-disable-certificate-verification)
- [Proxy](#-proxy)
- [Redirects](#-redirects)
- [DNS resolution](#-dns-resolution)
- [Intercept](#intercept)
- [Interceptors](#-interceptors)
- [RetryInterceptor](#-retryinterceptor)
- [Error Handling](#error-handling)
- [Exceptions](#-exceptions)
- [Throw on Status Code](#-throw-on-status-code)
- [Compatibility Layer](#compatibility-layer)
## Getting Started
### ➤ Installation
1. Install Rust via [rustup](https://rustup.rs/).
- Rust 1.80.0 or later is required.
2. For Android: Install [Command-line tools](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/68236007/i-am-getting-error-cmdline-tools-component-is-missing-after-installing-flutter)
- Make sure to have the latest NDK installed. [#44](https://github.com/Tienisto/rhttp/issues/44)
3. Add `rhttp` to `pubspec.yaml`:
```yaml
dependencies:
rhttp:
```
### ➤ Initialization
```dart
import 'package:rhttp/rhttp.dart';
void main() async {
await Rhttp.init(); // add this
runApp(MyApp());
}
```
### ➤ Usage
```dart
import 'package:rhttp/rhttp.dart';
void main() async {
await Rhttp.init();
// Make a GET request
HttpTextResponse response = await Rhttp.get('https://example.com');
// Read the response
int statusCode = response.statusCode;
String body = response.body;
}
```
Alternatively, you can use the `RhttpCompatibleClient` that implements the `Client` of the [http](https://pub.dev/packages/http) package.
For more information, see [Compatibility Layer](#compatibility-layer).
```dart
import 'package:rhttp/rhttp.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
void main() async {
await Rhttp.init();
http.Client client = await RhttpCompatibleClient.create();
http.Response response = await client.get(Uri.parse('https://example.com'));
print(response.statusCode);
print(response.body);
}
```
## Request Basics
### ➤ HTTP methods
You can make requests using different HTTP methods:
```dart
// Pass the method as an argument
await Rhttp.requestText(method: HttpMethod.post, url: 'https://example.com');
// Use the helper methods
await Rhttp.post('https://example.com');
```
### ➤ Request query parameters
You can add query parameters to the URL:
```dart
await Rhttp.get('https://example.com', query: {'key': 'value'});
```
### ➤ Request Headers
You can add headers to the request:
```dart
await Rhttp.post(
'https://example.com',
headers: const HttpHeaders.map({
HttpHeaderName.contentType: 'application/json',
}),
);
```
### ➤ Request Body
You can add a body to the request. There are different types of bodies you can use:
**Text**
Pass a string to the `HttpBody.text` constructor.
```dart
// Raw body
await Rhttp.post(
'https://example.com',
body: HttpBody.text('raw body'),
);
```
**JSON**
Pass a JSON data structure to the `HttpBody.json` constructor.
The Content-Type header will be set to `application/json` if not provided.
```dart
await Rhttp.post(
'https://example.com',
body: HttpBody.json({'key': 'value'}),
);
```
**Binary**
Pass a `Uint8List` to the `HttpBody.bytes` constructor.
```dart
await Rhttp.post(
'https://example.com',
body: HttpBody.bytes(Uint8List.fromList([0, 1, 2])),
);
```
**Stream**
Pass a `Stream>` to the `HttpBody.stream` constructor.
It is recommended to also provide a `length` to automatically set the `Content-Length` header.
```dart
await Rhttp.post(
'https://example.com',
body: HttpBody.stream(
Stream.fromIterable([[1, 2, 3]]),
length: 3,
),
);
```
**Form**
Pass a flat map to the `HttpBody.form` constructor.
The Content-Type header will be set to `application/x-www-form-urlencoded` if not provided.
```dart
await Rhttp.post(
'https://example.com',
body: HttpBody.form({'key': 'value'}),
);
```
**Multipart**
Pass a map of `MultipartItem` to the `HttpBody.multipart` constructor.
The Content-Type header will be overridden to `multipart/form-data` with a random boundary.
```dart
await Rhttp.post(
'https://example.com',
body: HttpBody.multipart({
'name': const MultipartItem.text(
text: 'Tom',
),
'profile_image': MultipartItem.bytes(
bytes: Uint8List.fromList(bytes),
fileName: 'image.jpeg',
),
}),
)
```
### ➤ Response Body
To let Rust do most of the work, you must specify the expected response body type before making the request.
```dart
HttpTextResponse response = await Rhttp.getText('https://example.com');
String body = response.body;
HttpBytesResponse response = await Rhttp.getBytes('https://example.com');
Uint8List body = response.body;
HttpStreamResponse response = await Rhttp.getStream('https://example.com');
Stream body = response.body;
```
## Request Lifecycle
### ➤ Cancel Requests
You can cancel a request by providing a `CancelToken`.
If the same `CancelToken` is used for multiple requests, all requests will be canceled.
If a canceled `CancelToken` is used for a request, the request will be canceled immediately.
```dart
final cancelToken = CancelToken();
final request = Rhttp.get(
'https://example.com',
cancelToken: cancelToken,
);
// Cancel the request
cancelToken.cancel();
// Will throw a `RhttpCancelException`
await request;
```
### ➤ Progress
You can observe the progress of the request, by providing `onSendProgress` and `onReceiveProgress` callbacks.
Please note that request and response bodies must be either `Stream` or `Uint8List`.
The parameter `total` can be `-1` if the total size is unknown.
It always emits the final value with `sent` / `received` and `total` being equal after the request is finished.
```dart
final request = Rhttp.post(
'https://example.com',
body: HttpBody.bytes(bytes),
onSendProgress: (sent, total) {
print('Sent: $sent, Total: $total');
},
onReceiveProgress: (received, total) {
print('Received: $received, Total: $total');
},
);
```
## Client Settings
### ➤ Connection Reuse
To improve performance, it is recommended to create a client and reuse it for multiple requests.
This allows you to reuse connections (with same servers).
Furthermore, it avoids the overhead of creating a new client for each request.
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create();
await client.get('https://example.com');
```
You can dispose the client when you are done with it:
```dart
client.dispose();
```
To create a client synchronously, use `RhttpClient.createSync`.
This should only be called during app start to avoid blocking the UI thread.
```dart
final client = RhttpClient.createSync();
```
### ➤ Keep-Alive
By default, connections are not kept alive. On HTTP/2, the same connection
is reused for multiple requests that are done on the same time, but the socket
is closed immediately after the last request is finished.
Setting `keepAliveTimeout` to a value greater than `0` will keep the socket
open when idle for the specified duration, both in HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/2.
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create(
settings: const ClientSettings(
timeoutSettings: TimeoutSettings(
keepAliveTimeout: Duration(seconds: 60),
keepAlivePing: Duration(seconds: 30),
),
),
);
```
### ➤ Timeout
You can specify the timeout for the request:
```dart
await Rhttp.get(
'https://example.com',
settings: const ClientSettings(
timeoutSettings: TimeoutSettings(
timeout: Duration(seconds: 10),
connectTimeout: Duration(seconds: 5),
),
),
);
```
### ➤ Base URL
Add a base URL to the client to avoid repeating the same URL or to change the base URL easily.
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create(
settings: const ClientSettings(
baseUrl: 'https://example.com',
),
);
```
### ➤ HTTP version
You can specify the HTTP version to use for the request.
HTTP/1, HTTP/1.1, HTTP/2, and HTTP/3 are currently supported.
```dart
await Rhttp.get(
'https://example.com',
settings: const ClientSettings(
httpVersionPref: HttpVersionPref.http3,
),
);
```
### ➤ TLS version
You can specify the TLS version to use for the request.
Only TLS 1.2 and 1.3 are currently supported.
```dart
await Rhttp.get(
'https://example.com',
settings: const ClientSettings(
tlsSettings: TlsSettings(
minTlsVersion: TlsVersion.tls12,
maxTlsVersion: TlsVersion.tls13,
),
),
);
```
### ➤ TLS Server Name Indication (SNI)
Controls the use of TLS server name indication.
This option is enabled by default.
```dart
await Rhttp.get(
'https://example.com',
settings: const ClientSettings(
tlsSettings: TlsSettings(
sni: false,
),
),
);
```
### ➤ Certificate Pinning
To improve security, you can specify the expected server certificate.
Due to limitations on Rust's side ([Github Issue](https://github.com/seanmonstar/reqwest/issues/298)),
you need to either provide the full certificate chain, or the root certificate.
```dart
await Rhttp.get(
'https://example.com',
settings: const ClientSettings(
tlsSettings: TlsSettings(
trustedRootCertificates: [
'''-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
some certificate
-----END CERTIFICATE-----''',
],
),
),
);
```
### ➤ Disable pre-installed root certificates
By default, the pre-installed root certificates are used.
You can disable this behavior by setting `trustRootCertificates` to `false`.
```dart
await Rhttp.get(
'https://example.com',
settings: const ClientSettings(
tlsSettings: TlsSettings(
trustRootCertificates: false,
),
),
);
```
### ➤ Client Authentication / mutual TLS
You can specify the client certificate and key to enable mutual TLS (mTLS).
```dart
await Rhttp.get(
'https://example.com',
settings: const ClientSettings(
tlsSettings: TlsSettings(
clientCertificate: ClientCertificate(
certificate: clientCert,
privateKey: clientKey,
),
),
),
);
```
### ➤ Disable certificate verification
This is very insecure and should only be used for testing purposes.
```dart
await Rhttp.get(
'https://example.com',
settings: const ClientSettings(
tlsSettings: TlsSettings(
verifyCertificates: false,
),
),
);
```
### ➤ Proxy
By default, the system proxy is enabled.
Disable system proxy:
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create(
settings: const ClientSettings(
proxySettings: ProxySettings.noProxy(),
),
);
```
Use a custom proxy:
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create(
settings: const ClientSettings(
proxySettings: ProxySettings.proxy('http://localhost:8080'),
),
);
```
Only proxy unencrypted HTTP traffic:
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create(
settings: const ClientSettings(
proxySettings: ProxySettings.static(
url: 'http://localhost:8080',
condition: ProxyCondition.onlyHttp,
),
),
);
```
Chain multiple proxies:
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create(
settings: const ClientSettings(
proxySettings: ProxySettings.list([
StaticProxy(
url: 'http://localhost:8080',
condition: ProxyCondition.onlyHttp,
),
StaticProxy(
url: 'http://localhost:8081',
condition: ProxyCondition.onlyHttps,
),
]),
),
);
```
### ➤ Redirects
By default, up to 10 redirects (e.g. HTTP 302) are followed.
Exceeding the maximum number of redirects will throw a `RhttpRedirectException`.
You can change the maximum number of redirects and whether to follow redirects:
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create(
settings: const ClientSettings(
redirectSettings: RedirectSettings.limited(5), // or RedirectSettings.none()
),
);
```
### ➤ DNS resolution
By default, the system DNS resolver is used.
You can override the mapping of hostnames to IP addresses:
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create(
settings: const ClientSettings(
dnsSettings: DnsSettings.static(
overrides: {
'example.com': ['127.0.0.1'],
},
),
)
);
```
For a more complex DNS resolution, you can construct a `DnsSettings.dynamic` object:
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create(
settings: ClientSettings(
dnsSettings: DnsSettings.dynamic(
resolver: (String host) async {
if (counter % 2 == 0) {
return ['127.0.0.1'];
} else {
return ['1.2.3.4'];
}
}
),
)
);
```
By default, the conventional port is used. You can override this behaviour by specifying the port:
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create(
settings: const ClientSettings(
dnsSettings: DnsSettings.static(
overrides: {
'example.com': ['127.0.0.1:8080'],
},
),
)
);
```
## Intercept
### ➤ Interceptors
You can add interceptors to the client to modify requests / responses, handle errors, observe requests, etc.
Any exception thrown by an interceptor that is not a subclass of `RhttpException`
will be caught and wrapped in a `RhttpInterceptorException`.
```dart
class TestInterceptor extends Interceptor {
@override
Future> beforeRequest(
HttpRequest request,
) async {
return Interceptor.next(request.addHeader(
name: HttpHeaderName.accept,
value: 'application/json',
));
}
@override
Future> afterResponse(
HttpResponse response,
) async {
return Interceptor.next();
}
@override
Future> onError(
RhttpException exception,
) async {
return Interceptor.next();
}
}
```
There are 4 termination methods:
- `Interceptor.next()`: Continue with the next interceptor.
- `Interceptor.stop()`: Stop the interceptor chain.
- `Interceptor.resolve()`: Resolve the request with the given response.
- `throw RhttpException`: Throw an exception. The stack trace will be preserved.
Instead of implementing the `Interceptor` class, you can use the `SimpleInterceptor` class:
```dart
final client = await RhttpClient.create(
interceptors: [
SimpleInterceptor(
onError: (exception) async {
if (exception is RhttpStatusCodeException && exception.statusCode == 401) {
// Log out
}
return Interceptor.next();
},
),
],
);
```
### ➤ RetryInterceptor
There is a built-in `RetryInterceptor` that retries the request if it fails.
During the retry, all interceptors except `RetryInterceptor` are called again.
```dart
class RefreshTokenInterceptor extends RetryInterceptor {
final Ref ref;
RefreshTokenInterceptor(this.ref);
@override
int get maxRetries => 1;
@override
bool shouldRetry(HttpResponse? response, RhttpException? exception) {
return exception is RhttpStatusCodeException &&
(exception.statusCode == 401 || exception.statusCode == 403);
}
@override
Future beforeRetry(
int attempt,
HttpRequest request,
HttpResponse? response,
RhttpException? exception,
) async {
ref.read(authProvider.notifier).state = await refresh();
return null;
}
}
```
Checkout this [example](https://github.com/Tienisto/rhttp/blob/main/rhttp/example/lib/interceptor_riverpod.dart)
to see how access tokens can be refreshed using Riverpod.
## Error Handling
### ➤ Exceptions
All exceptions are subclasses of `RhttpException`.
The following exceptions can be thrown:
| Exception | Description |
|------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------|
| `RhttpCancelException` | Request was canceled. |
| `RhttpTimeoutException` | Request timed out. |
| `RhttpRedirectException` | Too many redirects. |
| `RhttpStatusCodeException` | Response has 4xx or 5xx status code. |
| `RhttpInvalidCertificateException` | Server certificate is invalid. |
| `RhttpConnectionException` | Connection error. (no internet, server not reachable) |
| `RhttpClientDisposedException` | Client is already disposed. |
| `RhttpInterceptorException` | Interceptor threw an exception. |
| `RhttpUnknownException` | Unknown error occurred. |
### ➤ Throw on Status Code
By default, an exception is thrown if the response has a 4xx or 5xx status code.
You can disable this behavior by setting `throwOnStatusCode` to `false`.
```dart
await Rhttp.get(
'https://example.com',
settings: const ClientSettings(
throwOnStatusCode: false,
),
);
```
## Compatibility Layer
You can use the `RhttpCompatibleClient` that implements the `Client` of the [http](https://pub.dev/packages/http) package,
thereby exposing the same API as the default HTTP client in the Dart ecosystem.
This comes with some downsides, such as:
- inferior type safety due to the flaw that `body` is of type `Object?` instead of a sane supertype.
- body of type `Map` is implicitly interpreted as `x-www-form-urlencoded` that is only documented in StackOverflow (as of writing this).
- no support for cancellation
```dart
import 'package:rhttp/rhttp.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
void main() async {
await Rhttp.init();
http.Client client = await RhttpCompatibleClient.create();
http.Response response = await client.get(Uri.parse('https://example.com'));
print(response.statusCode);
print(response.body);
}
```
Because this client is compatible with [http](https://pub.dev/packages/http),
you can use [dio_compatibility_layer](https://pub.dev/packages/dio_compatibility_layer)
to use rhttp with the [dio](https://pub.dev/packages/dio) package.
```dart
Future createDioClient() async {
final dio = Dio();
final compatibleClient = await RhttpCompatibleClient.create(); // or createSync()
dio.httpClientAdapter = ConversionLayerAdapter(compatibleClient);
return dio;
}
```
If you are looking for a replacement for `HttpClient` of `dart:io`, you can use the `IoCompatibleClient`:
```dart
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:rhttp/rhttp.dart';
void main() async {
await Rhttp.init();
final client = await IoCompatibleClient.create();
final request = await client.getUrl(Uri.parse('https://example.com'));
final response = await request.close();
print(response.statusCode);
print(await response.transform(utf8.decoder).join());
}
```
## License
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2024 Tien Do Nam
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.