https://github.com/tommikaikkonen/redux-orm-example
Example of redux-orm usage.
https://github.com/tommikaikkonen/redux-orm-example
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
Example of redux-orm usage.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/tommikaikkonen/redux-orm-example
- Owner: tommikaikkonen
- Created: 2015-12-14T09:13:17.000Z (over 9 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2015-12-26T12:21:43.000Z (over 9 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-06-14T04:06:07.781Z (about 1 month ago)
- Language: JavaScript
- Size: 1.46 MB
- Stars: 17
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 6
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# redux-orm Example App
This is a (visually very) crude non-async CRUD app that provides an example of redux-orm usage. It's not an ideal app in the sense that lots of things could be abstracted here - but the code should be relatively easy to digest to give you a sense of `redux-orm` and its possibilities.
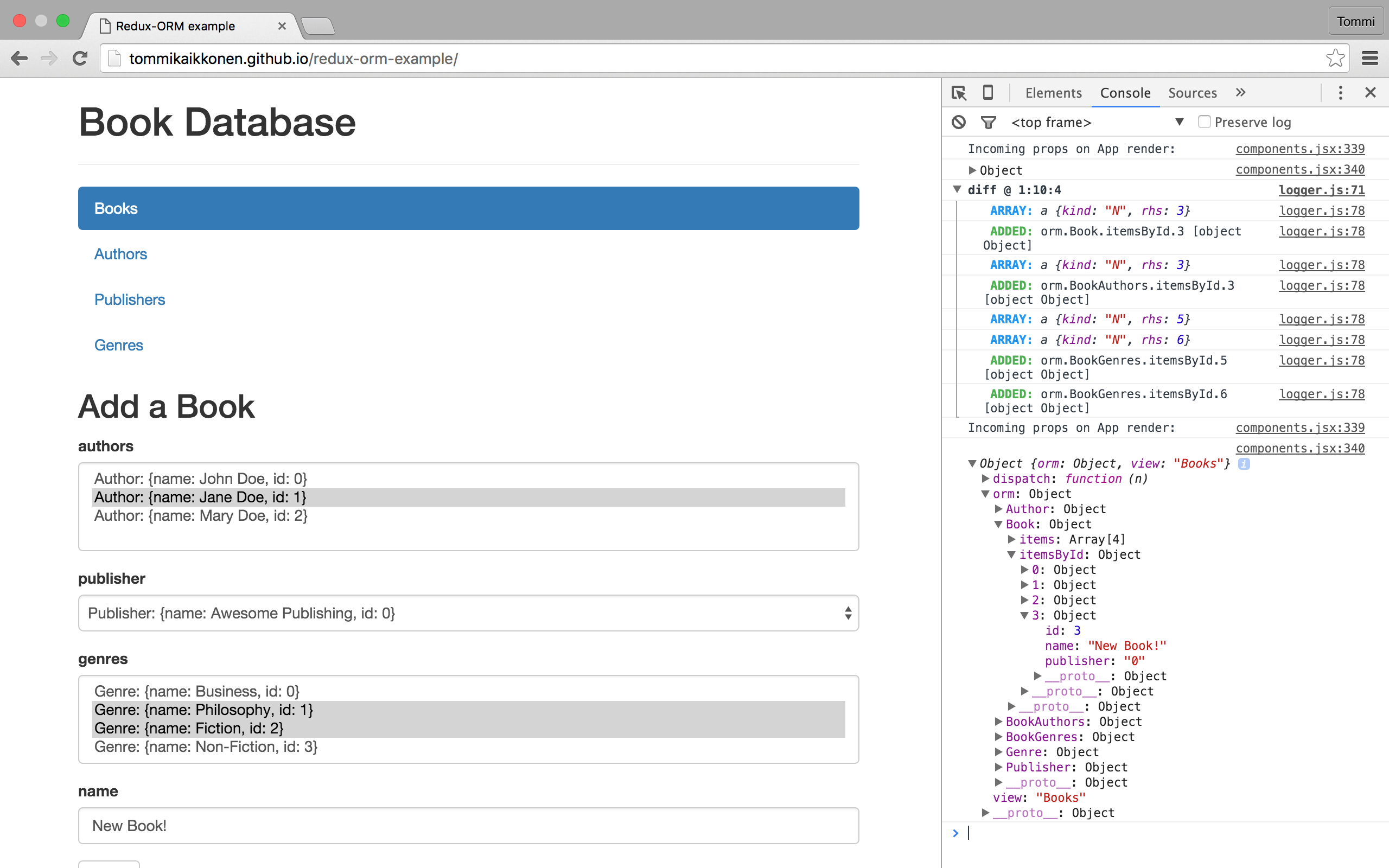
[Try the Example Book Database app in action](http://tommikaikkonen.github.io/redux-orm-example/). Open up the console to see the store diff and incoming App props after each dispatch.
## Reading the Source Code
The app is divided into `authors`, `books`, `genres` and `publishers` modules. Each have their own folder. Each module has models, components and selectors. You don't have to structure your apps like this, you could have one `models.js` file for the whole app if you prefer.
At the heart of `redux-orm` are the model declarations. They are declared in each module's `models.js`. You can use ES6 class inheritance to build your model definitions; just don't register your abstract models to the schema. This app uses one abstract model: `CRUDModel` found in [app/utils.js](app/utils.js). It defines a CRUD-enabled reducer that helps with boilerplate (each model takes three action types, create, update and remove. The action type is in the form `{{ action }}_{{ modelname }}`, for example `CREATE_BOOK`). `Book`, `Author`, `Genre` and `Publisher` models inherit from `CRUDModel`.
Each of the concrete models has a `validate` classmethod. This doesn't relate to `redux-orm` at all; it provides no validation services. We just call the `validate` classmethod in the app forms. Models are a convenient place to put business logic closely related to them.
The concrete models define their fields. `Book` has many `Author`s, many `Genre`s and one `Publisher`. They define some helping methods. For example, `Author` has a `writesGenres` method, that returns an array of all the genres his or her books are included in. Likewise `Publisher` has an `authors` method that returns a `QuerySet` of all the authors that have published a book with that `Publisher` instance. [app/schema.js](app/schema.js) registers the models to a new `Schema` instance.
You can use other reducers normally with `redux-orm`, see the one simple reducer defined in [app/reducers.js](app/reducers.js). It manages the current view (Books, Authors, Publishers, Genres) of the app.
To pass data to React components, we specify selectors in each modules `selectors.js` file. They take the ORM state branch as an input and output plain JS. When a selector runs for the first time, it checks which Models' state branches were accessed. On subsequent runs, the selector first checks if those branches have changed -- if not, it just returns the previous result. This way you can use the `PureRenderMixin` in your React components for great performance.
React components are declared in each modules `components.jsx`, and the app component in [app/components.jsx](app/components.jsx). `react-bootstrap` is utilized for presentational components. [app/ModelForm.jsx](app/ModelForm.jsx) declares a form component suitable for editing model instances.
The main `App` component in [app/components.jsx](app/components.jsx) renders the navigation sidebar, and the main content by using a switch statement on the current view name, and calling the correct sub-render method (`renderItems('Book')`, `renderItems('Publisher')` etc.).
Each of the sub-render methods pass on the dispatch-calling functions (onCreate, onEdit, onDelete).
[app/index.js](app/index.js) bootstraps the `redux-orm` state with initial data, creates the root Redux reducer and store, applies middleware.