Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/toshikwa/rljax
A collection of RL algorithms written in JAX.
https://github.com/toshikwa/rljax
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
A collection of RL algorithms written in JAX.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/toshikwa/rljax
- Owner: toshikwa
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-09-24T15:34:43.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-07-05T04:06:02.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-07-13T14:44:38.310Z (4 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 621 KB
- Stars: 91
- Watchers: 7
- Forks: 19
- Open Issues: 4
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
**WARNING: Rljax is currently in a beta version and being actively improved. Any contributions are welcome :)**
# Rljax
Rljax is a collection of RL algorithms written in JAX.
## Setup
You can install dependencies simply by executing the following. To use GPUs, CUDA (10.0, 10.1, 10.2 or 11.0) must be installed.
```bash
pip install https://storage.googleapis.com/jax-releases/`nvcc -V | sed -En "s/.* release ([0-9]*)\.([0-9]*),.*/cuda\1\2/p"`/jaxlib-0.1.55-`python3 -V | sed -En "s/Python ([0-9]*)\.([0-9]*).*/cp\1\2/p"`-none-manylinux2010_x86_64.whl jax==0.2.0
pip install -e .
```
If you don't have a GPU, please execute the following instead.
```bash
pip install jaxlib==0.1.55 jax==0.2.0
pip install -e .
```
If you want to use a [MuJoCo](http://mujoco.org/) physics engine, please install [mujoco-py](https://github.com/openai/mujoco-py).
```bash
pip install mujoco_py==2.0.2.11
```
## Algorithm
Currently, following algorithms have been implemented.
|**Algorithm**|**Action**|**Vector State**|**Pixel State**|**PER**[[11]](#reference)|**D2RL**[[15]](#reference)|
| :-- | :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: |:--: |
| PPO[[1]](#reference) | Continuous | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - |
| DDPG[[2]](#reference) | Continuous | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
| TD3[[3]](#reference) | Continuous | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
| SAC[[4,5]](#reference) | Continuous | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
| SAC+DisCor[[12]](#reference)| Continuous | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: |
| TQC[[16]](#reference) | Continuous | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
| SAC+AE[[13]](#reference) | Continuous | - | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
| SLAC[[14]](#reference) | Continuous | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: |
| DQN[[6]](#reference) | Discrete | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - |
| QR-DQN[[7]](#reference) | Discrete | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - |
| IQN[[8]](#reference) | Discrete | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - |
| FQF[[9]](#reference) | Discrete | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - |
| SAC-Discrete[[10]](#reference)| Discrete | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - |
## Example
All algorithms can be trained in a few lines of code.
Getting started
Here is a quick example of how to train DQN on `CartPole-v0`.
```Python
import gym
from rljax.algorithm import DQN
from rljax.trainer import Trainer
NUM_AGENT_STEPS = 20000
SEED = 0
env = gym.make("CartPole-v0")
env_test = gym.make("CartPole-v0")
algo = DQN(
num_agent_steps=NUM_AGENT_STEPS,
state_space=env.observation_space,
action_space=env.action_space,
seed=SEED,
batch_size=256,
start_steps=1000,
update_interval=1,
update_interval_target=400,
eps_decay_steps=0,
loss_type="l2",
lr=1e-3,
)
trainer = Trainer(
env=env,
env_test=env_test,
algo=algo,
log_dir="/tmp/rljax/dqn",
num_agent_steps=NUM_AGENT_STEPS,
eval_interval=1000,
seed=SEED,
)
trainer.train()
```
MuJoCo(Gym)
I benchmarked my implementations in some environments from MuJoCo's `-v3` task suite, following [Spinning Up's benchmarks](https://spinningup.openai.com/en/latest/spinningup/bench.html) ([code](https://github.com/ku2482/rljax/blob/master/examples/mujoco)). In TQC, I set num_quantiles_to_drop to 0 for HalfCheetath-v3 and 2 for other environments. Note that I benchmarked with 3M agent steps, not 5M agent steps as in TQC's paper.




DeepMind Control Suite
I benchmarked SAC+AE and SLAC implementations in some environments from DeepMind Control Suite ([code](https://github.com/ku2482/rljax/blob/master/examples/dm_control)). Note that the horizontal axis represents the environment step, which is obtained by multiplying agent_step by action_repeat. I set action_repeat to 4 for cheetah-run and 2 for walker-walk.


Atari(Arcade Learning Environment)
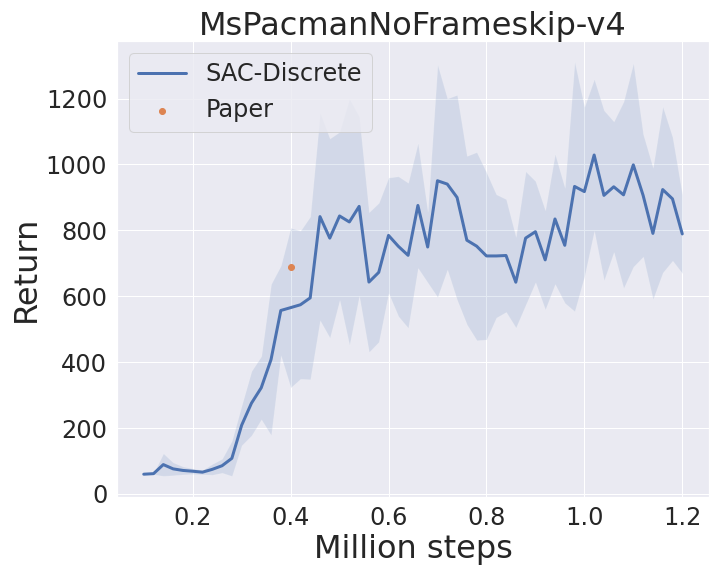
I benchmarked SAC-Discrete implementation in `MsPacmanNoFrameskip-v4` from the Arcade Learning Environment(ALE) ([code](https://github.com/ku2482/rljax/blob/master/examples/atari)). Note that the horizontal axis represents the environment step, which is obtained by multiplying agent_step by 4.
## Reference
[[1]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06347) Schulman, John, et al. "Proximal policy optimization algorithms." arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.06347 (2017).
[[2]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1509.02971) Lillicrap, Timothy P., et al. "Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:1509.02971 (2015).
[[3]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.09477) Fujimoto, Scott, Herke Van Hoof, and David Meger. "Addressing function approximation error in actor-critic methods." arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.09477 (2018).
[[4]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.01290) Haarnoja, Tuomas, et al. "Soft actor-critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor." arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.01290 (2018).
[[5]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.05905) Haarnoja, Tuomas, et al. "Soft actor-critic algorithms and applications." arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.05905 (2018).
[[6]](https://www.nature.com/articles/nature14236?wm=book_wap_0005) Mnih, Volodymyr, et al. "Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning." nature 518.7540 (2015): 529-533.
[[7]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10044) Dabney, Will, et al. "Distributional reinforcement learning with quantile regression." Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2018.
[[8]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.06923) Dabney, Will, et al. "Implicit quantile networks for distributional reinforcement learning." arXiv preprint. 2018.
[[9]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02140) Yang, Derek, et al. "Fully Parameterized Quantile Function for Distributional Reinforcement Learning." Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2019.
[[10]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.07207) Christodoulou, Petros. "Soft Actor-Critic for Discrete Action Settings." arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.07207 (2019).
[[11]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.05952) Schaul, Tom, et al. "Prioritized experience replay." arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.05952 (2015).
[[12]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.07305) Kumar, Aviral, Abhishek Gupta, and Sergey Levine. "Discor: Corrective feedback in reinforcement learning via distribution correction." arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.07305 (2020).
[[13]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.01741) Yarats, Denis, et al. "Improving sample efficiency in model-free reinforcement learning from images." arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.01741 (2019).
[[14]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.00953) Lee, Alex X., et al. "Stochastic latent actor-critic: Deep reinforcement learning with a latent variable model." arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.00953 (2019).
[[15]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.09163) Sinha, Samarth, et al. "D2RL: Deep Dense Architectures in Reinforcement Learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.09163 (2020).
[[16]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.04269) Kuznetsov, Arsenii, et al. "Controlling Overestimation Bias with Truncated Mixture of Continuous Distributional Quantile Critics." arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.04269 (2020).