Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/trevorwslee/mcextension-dumbdisplay
DumbDisplay MakeCode Extension is a simple tool to extend your Micro:bit screen to your Android phone via Micro:bit built-in Bluetooth or USB Serial.
https://github.com/trevorwslee/mcextension-dumbdisplay
makecode-extension microbit
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
DumbDisplay MakeCode Extension is a simple tool to extend your Micro:bit screen to your Android phone via Micro:bit built-in Bluetooth or USB Serial.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/trevorwslee/mcextension-dumbdisplay
- Owner: trevorwslee
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-10-18T07:54:27.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-02-08T23:22:21.000Z (almost 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2023-05-16T01:27:44.441Z (over 1 year ago)
- Topics: makecode-extension, microbit
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage: https://trevorwslee.github.io/MCExtension-DumbDisplay/
- Size: 1.19 MB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# DumbDisplay MakeCode Extension (for Microbit V1)
DumbDisplay MakeCode Extension is a simple tool to extend your Micro:bit screen to your Android phone via Micro:bit (V1) built-in Bluetooth LE or USB Serial.
| Micro:bit | Turtle | LEDs + LCD |
|-----------|--------|------------|
||||
# Description
You explode your creativity with a little help from this extension, and use DumbDisplay to realize an enhanced Micro:bit virtual screen on your Android phone.
You can install the free DumbDisplay app (v0.3.2 or later) from Android Play Store -- https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=nobody.trevorlee.dumbdisplay
The app can accept connection via
* Bluetooth LE -- which is relatively slow (and memory hungry)
* USB (OTG) -- which is faster, but requires a cable and an adaptor (OTG)
In summary, this extension allows you to use DumbDisplay as a screen in place of the Micro:bit built-in screen
* customizable screen size
* customizable LED color
* many screen-related MakeCode Core-like commands
* can mix with a Turtle layer using many Turtle-like commands
* can create other types of layers like LED Grid layer and LCD layer
# Usage
For example, you can take advantage of your phone high-resolution screen to render drawings from your Micro:bit with Turtle-like operations.
You can also make use of DumbDisplay LED Grid / LCD layers for showing your experiment results, without the need to actualy attach real LEDs and/or LCD to your Micro:bit.
Your program can be interactivity; your drawings on the different layers can be according to Micro:bit different input mechanisms like
* push of buttont
* temperature
* compass direct
* etc
There should be many ways you can use DumbDisplay as a tool to realize your creativity.
# Sample Code
To start with, you should setup DumbDisplay (DD) like
// set a Micro:bit layer of size (5, 5)
ddmb.setup(5, 5)
- DumbDisplayMB `ddmb.setup(15, 9)` -- setup a DD screen layer similar to Micro:bit screen but with size 15x9
- DumbDisplayMB `ddmb.setupLikeLocal()` -- setup a DD screen layer similar to Micro:bit screen; additionally, most DumbDisplayMB commands will be replicated to Micro:bit internal screen
- DumbDisplayTurtle `ddturtle.setup(300, 200)` -- setup a DD screen layer with size 300x200
- notes:
* you can have 1 DumbDisplayMB screen layer + 1 DumbDisplayTurtle screen layer at the same time; the layer you setup first will be on top over the other layer
* setting up will wait for connection to DumbDisplay Android app; therefore, make sure your phone is ready to accept connection (Bluetooth or USB Serial)
* at any time, if you want to start again, press the reset button on the back of your Micro:bit
## Samples
| 1. Micro:bit | 2. Turtle | 3. LEDs + LCD | 4. "Bar Meter" | 5. Manual "pin" layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|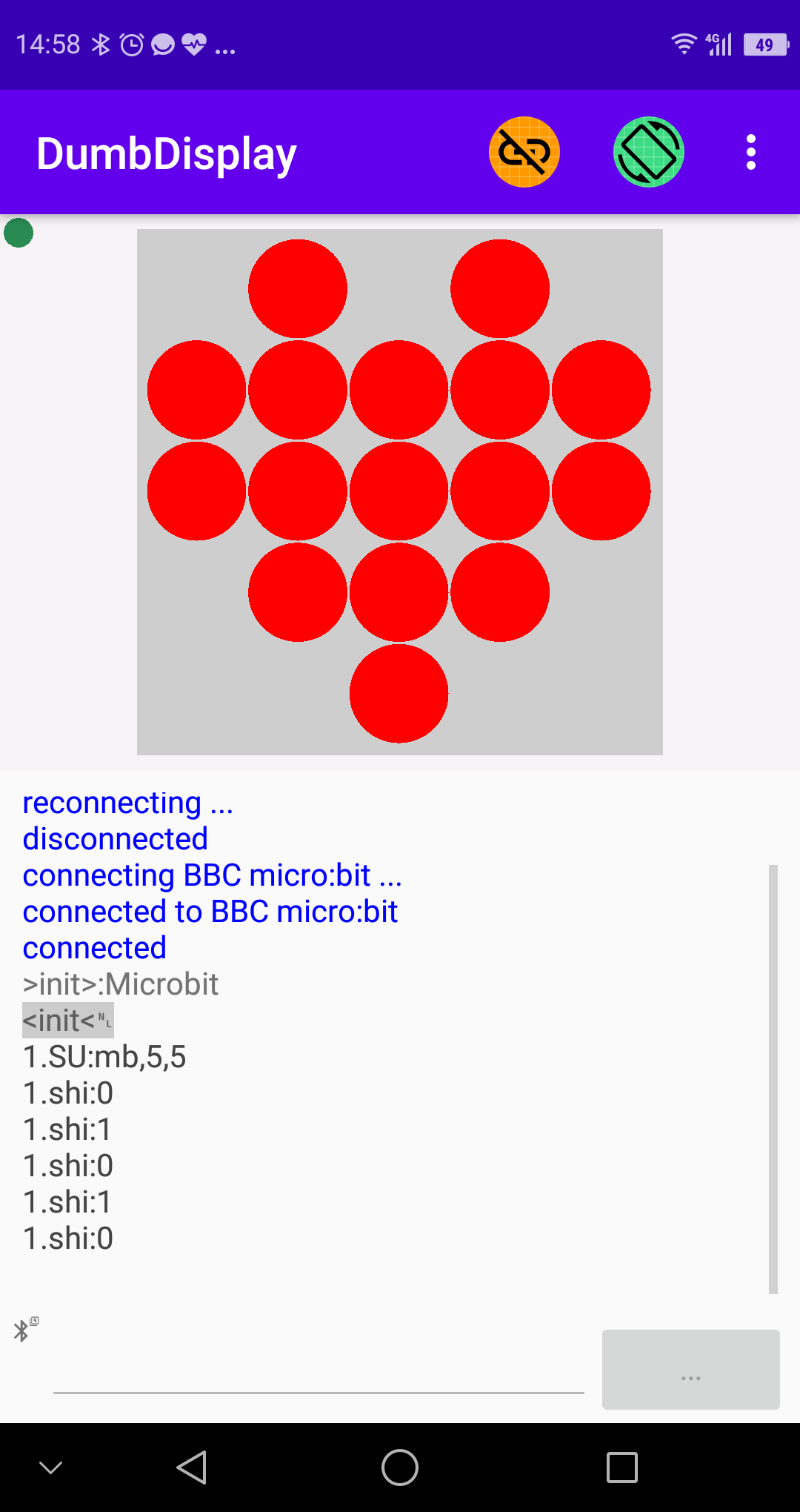|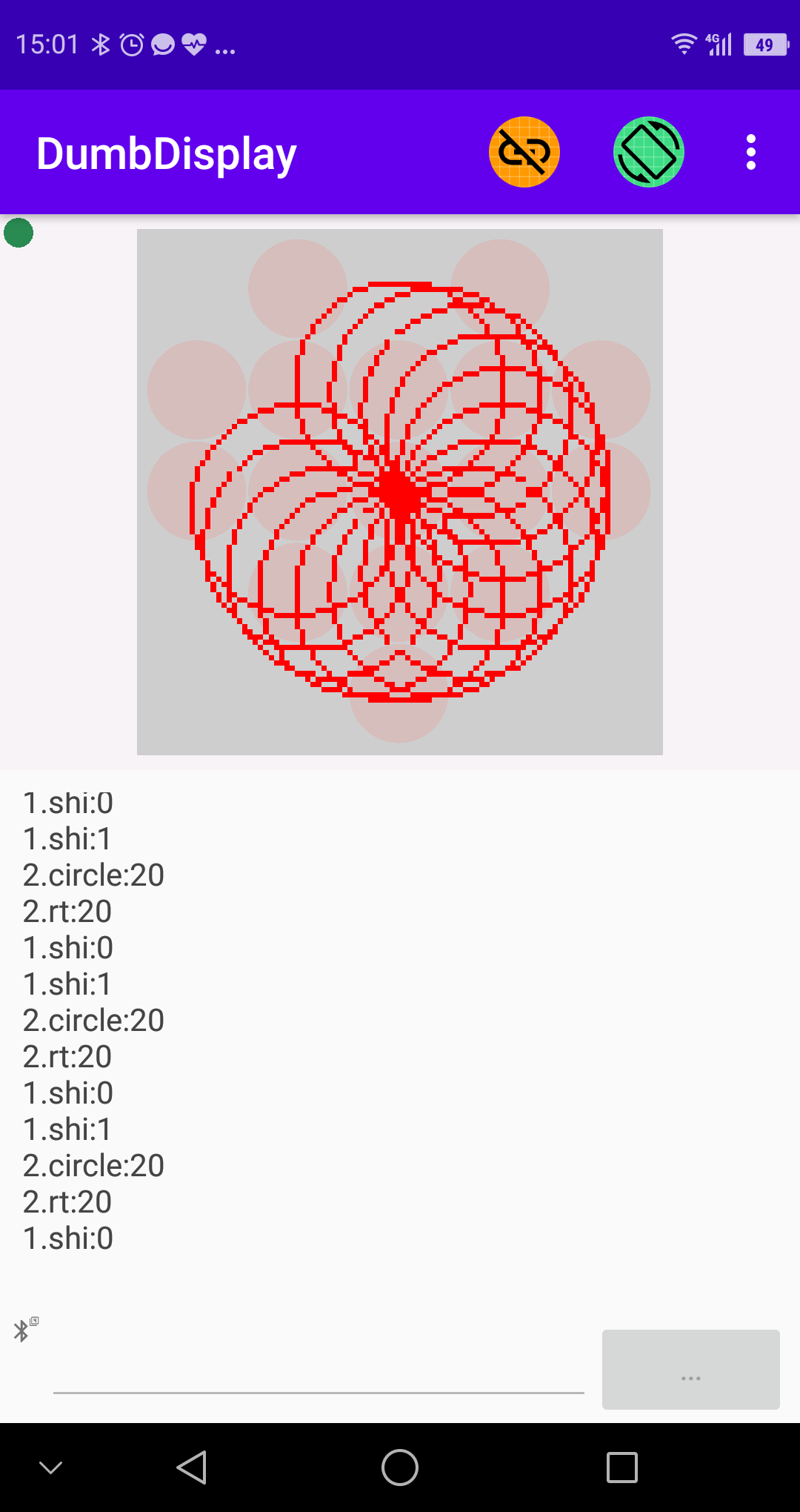|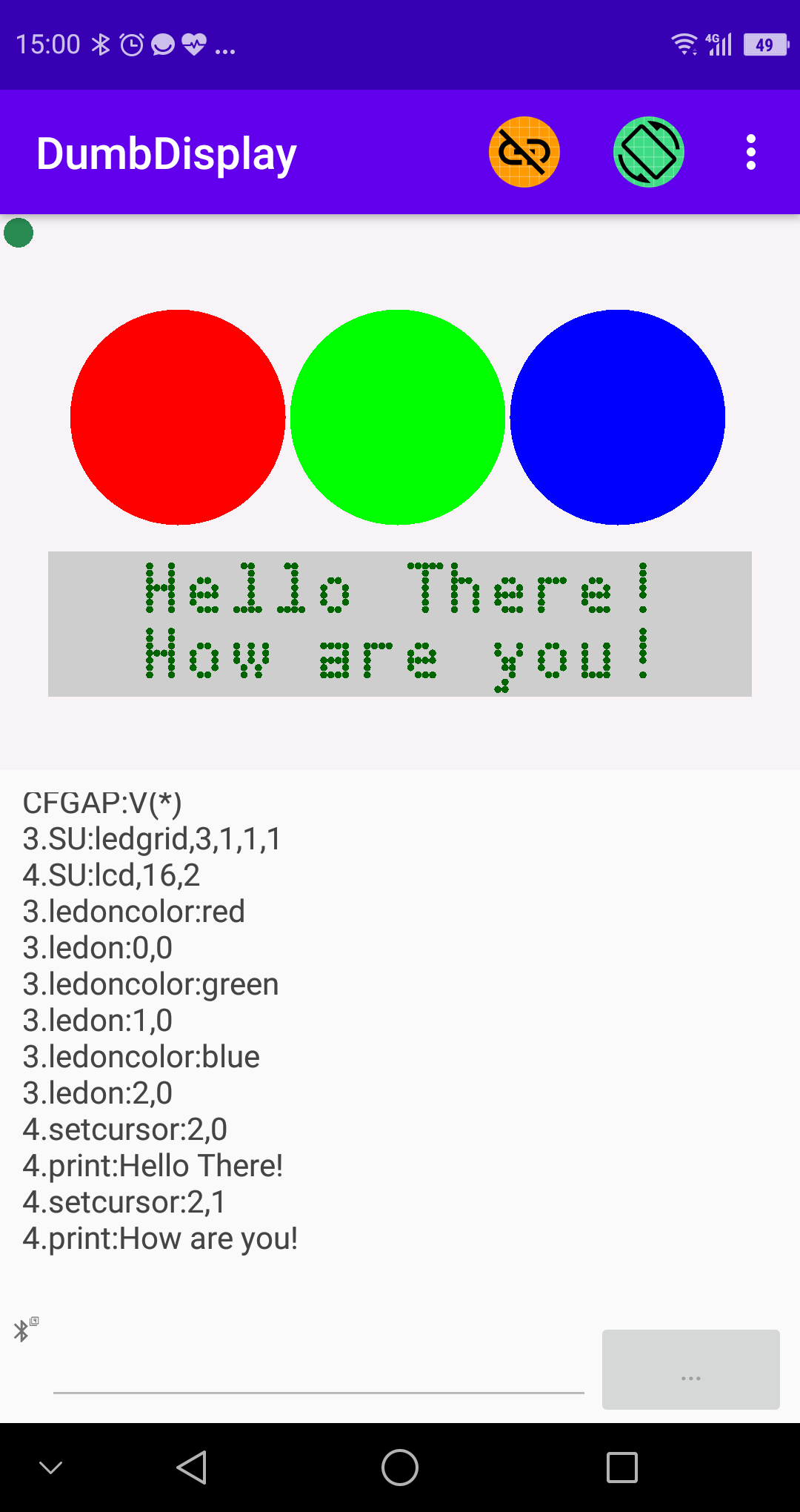|||
### Screenshot 1 -- *imitating your Micro:bit screen with your phone*
Then you can program something more interesting, like
// setup a Micro:bit layer of size (5, 5)
ddmb.setup(5, 5)
basic.forever(function () {
// draw a heart icon to Micro:bit layer
ddmb.showIcon(IconNames.Heart)
basic.pause(1000)
// draw a small heart icon to Micro:bit layer
ddmb.showIcon(IconNames.SmallHeart)
})
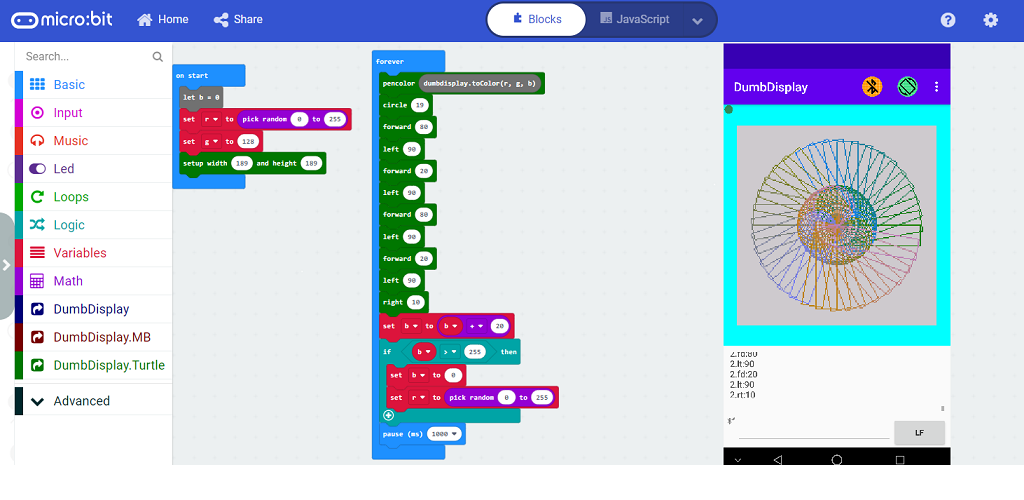
### Screenshot 2 -- *showing drawings rendered by Turtle-like operations (with Micro:bit icons as background)*
You can use Turtle-like operations to draw something interesting, like
// setup a Turtle layer of size (100, 100)
ddturtle.setup(100, 100)
// setup a Micro:bit layer of size (5, 5)
ddmb.setup(5, 5)
// set Micro:bit layer opacity to 20 (of 255)
ddmb.layer().layerOpacity(20)
basic.forever(function () {
// turtle draws a circle
ddturtle.circle(20)
// turtle turns right 20
ddturtle.right(20)
// draw a heart icon to Micro:bit layer
ddmb.showIcon(IconNames.Heart)
// pause a second
basic.pause(1000)
// draw a small heart icon to Micro:bit layer
ddmb.showIcon(IconNames.SmallHeart)
basic.pause(1000)
})
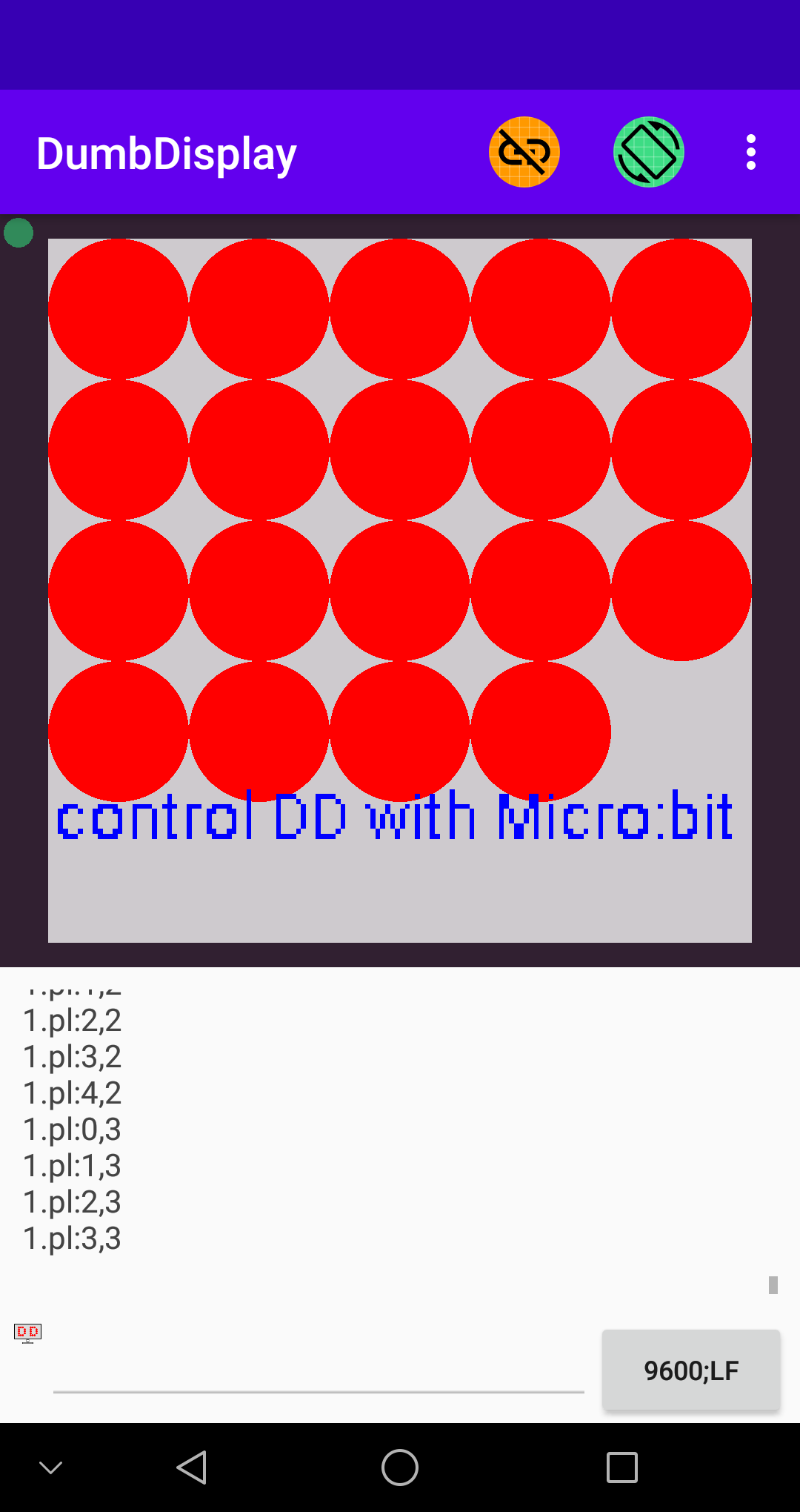
### Screenshot 3 -- *using LEDs and LCD ("auto pinning" the layers)*
By making use of LED / LCD layers, you can show experiment result values in various ways, like
// configure to "auto pin (layout) layers" in the vertical direction
dumbdisplay.configAutoPinLayers(AutoPinDirection.Vertical)
// create a LED layer
let ledLayer = dumbdisplay.setupLedGridLayer(3, 1)
// create a LCD layer
let lcdLayer = dumbdisplay.setupLcdLayer()
// turn on LEDs
ledLayer.ledOnColor("red")
ledLayer.ledOn(0, 0)
ledLayer.ledOnColor("green")
ledLayer.ledOn(1, 0)
ledLayer.ledOnColor("blue")
ledLayer.ledOn(2, 0)
// print messages to LCD
lcdLayer.setCursor(2, 0)
lcdLayer.print("Hello There!")
lcdLayer.setCursor(2, 1)
lcdLayer.print("How are you!")
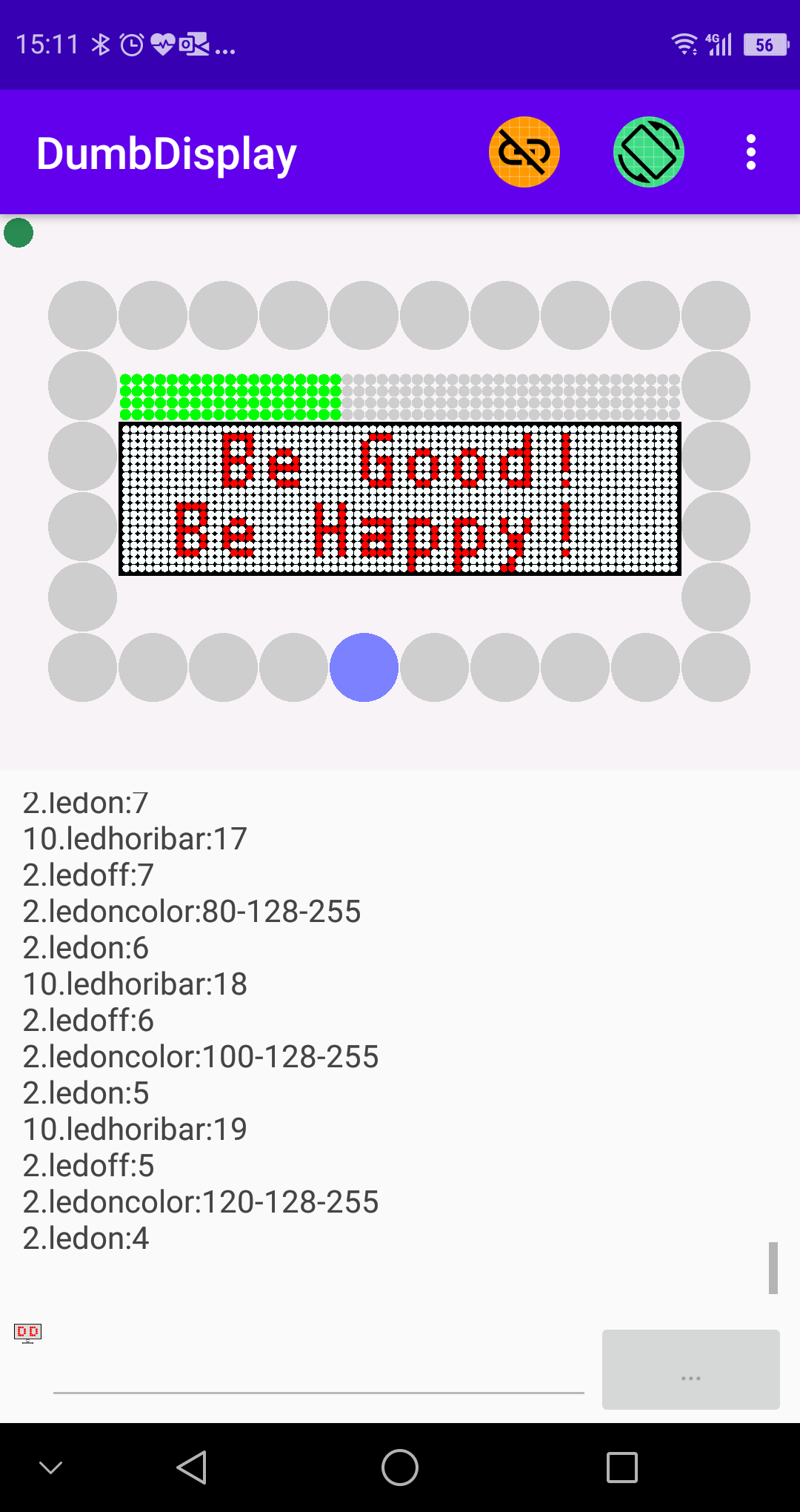
### Screenshot 4 -- *using LED Grid as Bar Meter*
In fact, you can use the LED grid layer as some sort of "Bar Meter" that shows meter values, like
// create a LED layer of size 10 by 1 (with sub-led size 1 by 5)
let horiBarMeter = dumbdisplay.setupLedGridLayer(10, 1, 1, 5)
// set colors
horiBarMeter.layerBackgroundColor("darkblue")
horiBarMeter.ledOnColor("green")
horiBarMeter.ledOffColor("lightgray")
// loop show bar of different values
basic.forever(function () {
for (let c = 1; c <= 10; c++) {
horiBarMeter.ledBar(c)
basic.pause(200)
}
})
### Screenshot 5 -- *"pinning" 3 LEDs in a more controlled way*
You can fine tune how different layers be "pinned", like
// configure the imaginary "pin frame" to be 3 units x 3 units
dumbdisplay.configPinLayers(3, 3)
// create 3 LED layers
let ledLayer1 = dumbdisplay.setupLedGridLayer()
let ledLayer2 = dumbdisplay.setupLedGridLayer()
let ledLayer3 = dumbdisplay.setupLedGridLayer()
// pin LED layer 1 to position (0, 0) with size (1, 1)
dumbdisplay.pinLayer(ledLayer1, 0, 0, 1, 1)
// pin LED layer 2 to position (1, 1) with size (1, 1)
dumbdisplay.pinLayer(ledLayer2, 1, 1, 1, 1)
// pin LED layer 3 to position (2, 2) with size (1, 1)
dumbdisplay.pinLayer(ledLayer3, 2, 2, 1, 1)
// turn on LEDs
ledLayer1.layerBackgroundColor("lightgray")
ledLayer2.layerBackgroundColor("lightgray")
ledLayer3.layerBackgroundColor("lightgray")
ledLayer1.ledOnColor("red")
ledLayer1.ledOn()
ledLayer2.ledOnColor("green")
ledLayer2.ledOn()
ledLayer3.ledOnColor("blue")
ledLayer3.ledOn()
# Reference
You largely do not need to use DumpDisplay package. Instead, you will mostly use DD.MB and/or DD.Turtle to render drawings on the corresponding layers.
### Micro:bit
DD.MB:
- `showIcon(name: IconNames)` -- similar to `Basic`
- `showArrow(name: ArrowNames)` -- similar to `Basic`
- `showString(str: string)` -- similar to `Basic`
- `showNumber(num: number)` -- similar to `Basic`
- `clearScreen()` -- similar to Basic
- `plot(x: number, y: number)` -- similary to `Led`
- `unplot(x: number, y: number)` -- similar to `Led`
- `toggle(x: number, y: number)` -- similar to `Led`
- `showLeds(leds: string)` -- similar to `Led`
- `ledColorNum(color: number)` -- set the color of the LEDs with a color number
- `ledColor(color: string)` -- set the color of the LEDs with a normal color name like "green", or a hex number (starting with "#")
- `createImage(leds: string)` / `showImage(offset: number)` / `scrollImage(offset: number, interval: number)` -- similar to Images
- `layer()` -- return the layer object to be used for some functions of DumbDisplay
- notes:
* unless "setup like local", which will replicate most commands to local Micro:bit, the DumbDisplayMB commands will be brief; in other words, you get to control the timing how long something is shown. For example, the text "Hello World!" can take a little while for `basic.showString()` to finish (since it will scroll the text), `ddmb.showString()` virtual takes no time to finish; you use `basic.pause()` to allow time for the string to scroll in DD virtual screen on your phone.
* `showLeds()` / `createImage()` input is a string -- an "image literal" or a normal string; if it is a normal string, some similar format should be followed
- char `#` -- ON
- char `.` -- OFF
- char `|` -- end of row
- e.g. `.####.||||#....#` represents 5 rows, with 1st row being `.####.` and last row being `#....#`
### Turtle
`DD.Turtle`:
- `forward(distance: number)` -- move forward
- `backward(distance: number)` -- move backward
- `right(angle: number)` -- turn right
- `left(angle: number)` -- turn left
- `setHeading(angle: number)` -- set heading direction
- `home()` -- move to home (center of screen)
- `goto(x: number, y: number)` -- go to a position of the screen
- `circle(radius: number)` -- draw a circle
- `centeredCircle(radius: number)` -- draw a circle with current position being the center
- `rectangle(width: number, height: number)` -- draw a rectangle
* it is similar to
```
forward(width)
left(90)
forward(height)
left(90)
forward(width)
left(90)
forward(height)
left(90)
```
- `centeredRectangle(width: number, height: number)` -- draw a rectangle with current position being the center
- `triangle(side1: number, angle: number, side2: number)` -- draw a triangle given SAS (side1, angle, side2)
- `isoscelesTriangle(side: number, angle: number)` -- draw an isosceles triangle given side and angle
- `polygon(side: number, vertexCount: number)` -- draw a polygon given side and number of vertices
- `centeredPolygon(radius: number, vertexCount: number)` -- draw a polygon with current position being the center (and surrounding an imaginary circle)
- `dot(size: number)` -- draw a dot (with certain pen size)
- `dotOfColorNum(size: number, color: number)` -- draw a dot (with certain pen size and pen color number)
- `dotOfColor(size: number, color: string)` -- draw a dot (with certain pen size and pen color name like "green")
- `write(text: string)` -- write text
- `drawText(text: string)` -- draw text (in the heading direction)
- `penup()` -- pen up
- `pendown()` -- pen down
- `penSize(size: number)` -- set pen size
- `penColorNum(color: number)` -- set pen color with color number
- `penColor(color: string)` -- set pen color with color name like "green", or a hex number (starting with "#")
- `fillColorNum(color: number)` -- set fill with color number
- `fillColor(color: string)` -- set fill color with color name like "green", or a hex number (starting with "#")
- `bgColorNum(color: number)` -- set background color with color number
- `bgColor(color: string)` -- set background color with color name like "green", or a hex number (starting with "#")
- `beginFill()`
- `endFill()`
- `clear()` -- clear the screen
- `jumpHome()` -- move to home (center of screen) without drawing
- `jumpTo(x: number, y: number)` -- go to a position on screen without drawing
- `penFilled(fillPen: boolean)` -- set whether pen filled (with fill color); note that when pen filled, drawn shape will be filled
- `penTextSize(size: number)` -- set the size of text (the default pen text size depends on your phone setting)
- `layer()` -- return the layer object -- "Layer" object have some common operations (refer to DDLayer below)
### DumbDisplay
`DumbDisplay`:
- `connect(enableBluetooth: boolean = true, enableSerial: boolean = true)` -- explicitly wait for connection, at the same time you also have an opportunity to override some default settings
* `enableBluetooth` -- set to false so that Bluetooth is not used (defaul to true)
; this will leave more memory for your program
* `enableSerial` -- set to false so that Serial is not used (defaul to true), and you can freely make use of Serial
- `configPinLayers(xUnitCount: number = 100, yUnitCount: number = 100)` -- configure the size of the virtual "pin frame" for pinning the layers (refer to pinLayer() below)
- `configAutoPinLayers(direction: AutoPinDirection)` -- configure to auto pin layers in either horizontal or vertical direction
- `setupLedGridLayer(numCols: number = 1, numRows: number = 1, numSubCols: number = 1, numSubRows: number = 1)` -- setup and create a LED Grid layer have numCols x numRows LEDs (with each LED composed of numSubCols by numSubRows sub-leds)
* note that sub-leds can make a LED looks rectangular ( like a bar)
- `setupLcdLayer(numCols: number = 16, numRows: number = 2)` -- setup and create a LCD layer capable of displaying numRows rows of numCols characters
- `pinLayer(layer: ddlayers.DDLayer, uLeft: number, uTop: number, uWidth: number, uHeight: number)` -- pin a layer on the virtual "pin frame" at position (uLeft, uTop) with size (uWidth x uHeight)
transparent; 255 being total opaque)
- `removeLayer(layer: Layer)` -- remove a layer; yes, you can setup the layer again
- `writeComment(msg: string)` -- write out some "comment", in a way that will not be harmful to the DD operations.
- `writeSerial(msg: string)` -- write out some "comment" to the serial port (without affecting DD operations)
- `toColor(r: number, g: number, b: number)` -- a helper operation that turns RGB into color name that you can use, say to set LED color
* in fact, the "color name" is simply the combine of the 3 RBG numbers -- e.g. R 100, B 0, G 200, will become "100-0-200"
-
### "Layers"
`DDLayer` -- "layer" operations (all layer objects including applicable to Micro:bit layer and Turtle layer):
- `layerVisible(visible: boolean)` -- set whether a layer is visible or not
- `layerOpacity(opacity: number)` -- set the opacity of a layer (0 to 255)
- `layerBackgroundColorNum(color: number)` -- set the background color of a layer with color number
- `layerBackgroundColor(color: number)` -- set the background color of a layer with color name like "green", or a hex number (starting with "#")
- `layerNoBackgroundColor()` -- set the background of a layer to no color (i.e. transparent)
- `layerClear()` -- clear the layer
### LedGridLayer
on top of `DDLayer`, additional `LedGridLayer` operations:
- `ledOn(x: number = 0, y: number = 0)` -- turn LED on
- `ledOff(x: number = 0, y: number = 0)` -- turn LED off
- `ledToggle(x: number = 0, y: number = 0)` -- toggle LED on / off
- `ledBar(count: number)` -- treat the LED Grid as a bar-meter, turning on a bar of count LEDs
- `ledOnColorNum(color: number)` -- set the LED on color with color number
- `ledOnColor(color: string)` -- set the LED on color with color name
- `ledOffColorNum(color: number)` -- set the LED off color with color number
- `ledOffColor(color: string)` -- set the LED off color with color name
### LcdLayer
on top of `DDLayer`, additional `LcdLayer` operations:
- `setCursor(x: number, y: number)` -- set cursor position; (0, 0) to start with
- `print(text: string)` -- print text to cursor position
- `home()` -- set cursor to (0, 0)
- `cursor()` -- show cursor on the LCD
- `noCursor()` -- no show cursor on the LCD
- `autoscroll()` -- auto scroll when print text
- `noAutoscroll()` -- no auto scroll when print text
- `display()` -- LCD will display
- `noDisplay()` -- LCD will not display
- `scrollDisplayLeft()` -- scroll LCD left
- `scrollDisplayRight()` -- scroll LCD right
- `writeLine(line: string, y: number = 0)` -- write text as a line to row y (note that the row will be erased first)
- `pixelColorNum(color: number)` -- set the color of the LCD pixels with color number
- `pixelColor(color: string)` -- set the color of the LCD pixels with color name
- `bgPixelColorNum(color: number)` -- set the color of the LCD "background / off" pixels with color number
- `bgPixelColor(color: string)` -- set the color of the LCD "background / off" pixels with color name
- `noBgPixelColor()` -- set the LCD "background / off" pixels to no color (i.e. not show)
### Reminder
A reminder -- DumbDisplay will make use of both your Micro:bit Bluetooth and USB Serial, therefore you should not be making use of them for your own purposes. However, if you really need to use any one of them, you can call DumbDisplay.connect() explicitly, and set to disallow DumbDisplay to use Bluetooth or USB Serial.
# Thank You!
Greeting from the author Trevor Lee:
> Be good! Be happy!
> Peace be with you!
> Jesus loves you!
# Supported target
PXT/microbit
# License
MIT