https://github.com/trustly/bankapi
Secure Distributed Messaging Between Financial Institutions
https://github.com/trustly/bankapi
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
Secure Distributed Messaging Between Financial Institutions
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/trustly/bankapi
- Owner: trustly
- License: mit
- Archived: true
- Created: 2014-08-04T13:28:29.000Z (almost 11 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2014-11-01T14:56:53.000Z (over 10 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-04T04:05:24.425Z (9 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Size: 1.21 MB
- Stars: 779
- Watchers: 52
- Forks: 70
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- starred-awesome - bankapi - Secure Distributed Messaging Between Financial Institutions (Python)
README
# BankAPI
## What is it?
BankAPI is a secure decentralized messaging system to send files/messages between banks and other types of financial institutions.
There is a reference implementation of the protocol which can be used off-the-shelf, which is production grade quality and is not only for testing and demonstration, although it fulfils those two roles as well.
The BankAPI protocol relies on OpenPGP (RFC 4880) + SHA512 + HTTPS. That's it, there is nothing more to it.
BankAPI is only a transmission protocol, and makes no assumptions of what kind of messages or file types banks will want to transfer.
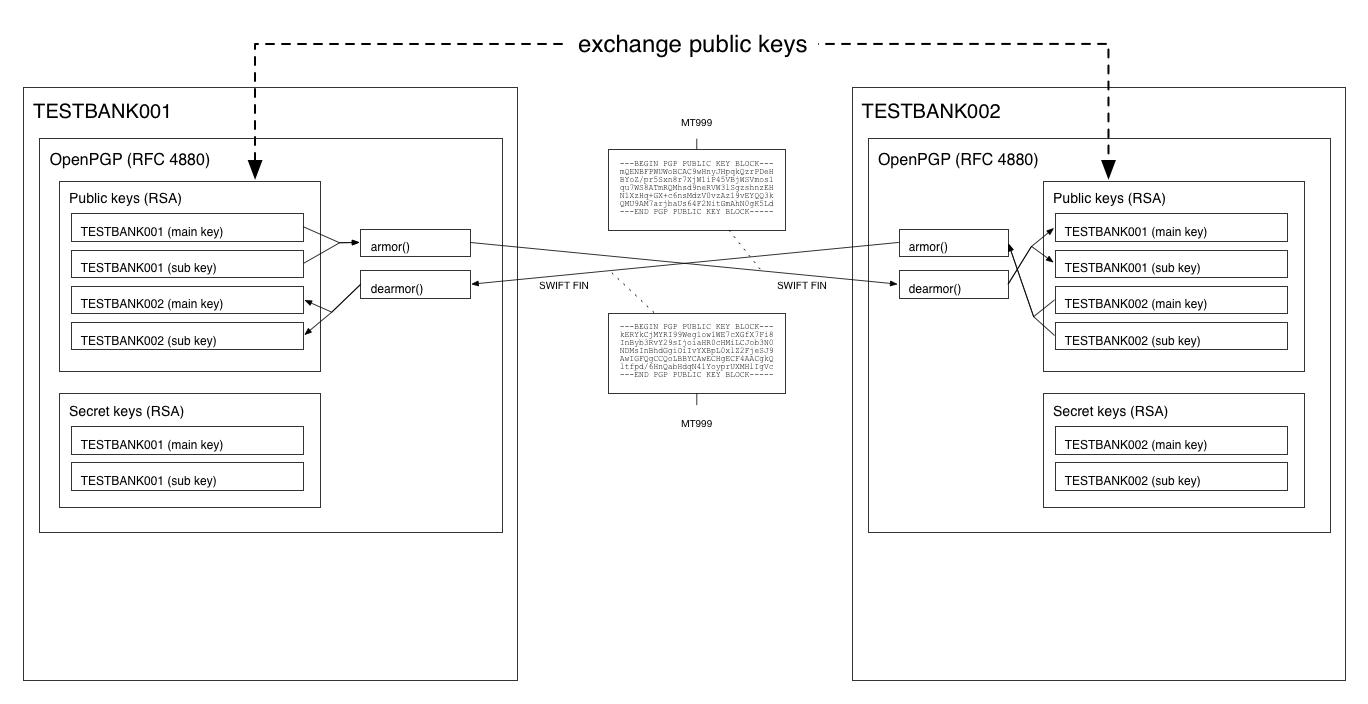
## Key exchange
## Protocol design

The protocol imposes certain restrictions on the details and choices of
algorithms used for generating the OpenPGP messages. The terminology used here
conforms to the one specified in [RFC2119](http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2119).
The details specific to OpenPGP are documented in
[RFC4880](http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4880).
1. All OpenPGP messages **MUST** be symmetrically encrypted messages, where the
session key is public-key encrypted. The _session key packet_ **MUST**
contain the _Key ID_ of the key used to encrypt the message. All messages
**MUST** contain a signature packet. Implementations **MAY** choose to
generate one-pass signatures.
2. All parties **MUST** use a key length of at least 2048 bits for their RSA
keys. Implementations **SHOULD** accept key sizes of 2048, 3072 and 4096
bits. Using 4096-bit keys is **RECOMMENDED**. DSA and Elgamal **MUST NOT**
be used.
3. The cipher algorithm **MUST** be one of AES128, AES192 and AES256.
4. If the OpenPGP message is a _compressed message_, the compression algorithm
**MUST** be ZIP or ZLIB.
5. The OpenPGP message **MAY** be _integrity protected_ via the _Modification
Detection Code packet_.
6. The _literal data_ inside the OpenPGP message **MUST** be marked to contain
binary data. If a text or UTF-8 message is received, an implementation
**MAY** choose to accept the message. An implementation **MUST NOT**
convert any _canonical line endings_ to their local counterpart.
7. The signature packet and (if present) the one-pass signature packet **MUST**
contain the _Key ID_ of the key used to sign the message. Implementations
**SHOULD** only sign a message using a single key. The hash algorithm used
for signatures **MUST** be SHA-512.
8. The _ASCII Armor_, including _Armor Headers_, **MUST** be valid UTF-8.
9. The _Armor Header_ "Comment", **MUST** be set to the message type.
## System design
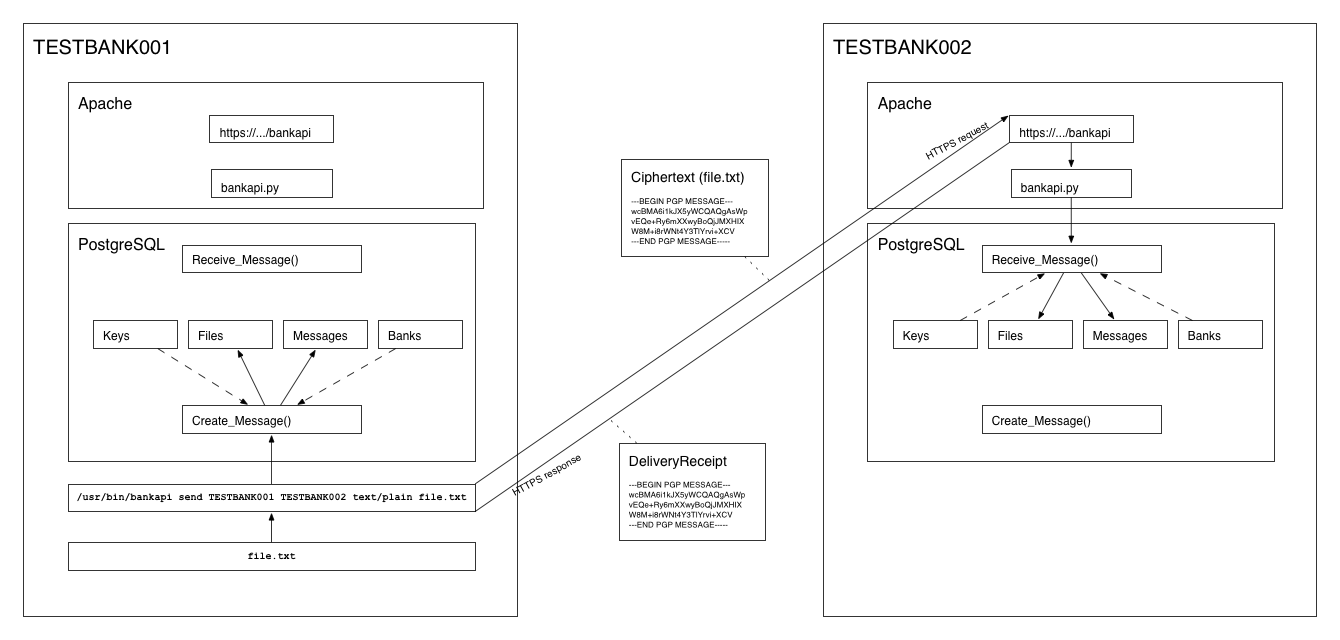
The system is built on top of PostgreSQL and uses its pgcrypto contrib module.
Messages are encrypted and signed using RSA public-key cryptography.
Each bank generates a RSA key-pair consisting of a public and a secret key.
The public keys and API URLs are exchanged between the banks.
The task of exchanging public keys and API URLs is preferrably done over the
SWIFT network, by sending them in a normal MT999 SWIFT FIN-message. This
allows banks to trust the validity of the public key and API URL, as the origin
of SWIFT messages can be trusted.
## Highlights
- RSA-encryption
- SHA512
- JSON-RPC / HTTPS
- Linux / PostgreSQL / Apache
- Open source / MIT-license
- Real-time request/response
- Instant delivery receipt
- Local archiving of files in PostgreSQL
## Overview of the interface
To send a message, the sending bank encrypts and signs a message using
Create\_Message(), and calls Get\_Message() to get the actual ciphertext
content of the message. The ciphertext is then delivered to the receiving bank
by calling its Receive\_Message() API method, accessible at the API URL
provided by the receiving bank. The API implementation must adhere to the
JSON-RPC standard and accept HTTPS POST.
The Receive\_Message() function returns a _delivery receipt_, which is a
cryptographic proof of the fact that the sender was able to verify the
signature contained within the message against the receiving bank's public key.
This allows the sender to be certain that the message was delivered and
decrypted successfully by the recipient.
The sending bank calls Decode\_Delivery\_Receipt() with the _delivery receipt_
as input to verify its validity.
## Database tables and columns
### Banks
- BankID : Unique identifier for the bank, preferrably the SWIFT BIC (PRIMARY KEY)
- Protocol : API procotol, example "https"
- Host : API host, Internet domain name, example "bank.com"
- Port : API port, Internet network port, example 443
- Path : API path, example "/api"
- Datestamp : Date/time when added to the table
### Files
- FileID : SHA512 hash of the Plaintext (PRIMARY KEY)
- Plaintext : The content of the file (UTF8)
- Datestamp : Date/time when added to the table
### Keys
- MainKeyID : Signature key (PRIMARY KEY)
- SubKeyID : Encryption key
- PublicKeyring : Contains public keys
- SecretKeyring : Contains secret keys (only set for your own bank, NULL for others)
- BankID : The BankID which the keys belong to
- Datestamp : Date/time when added to the table
- PrimaryKey : Only set to TRUE for one row per BankID, other keys are still valid, but this key is used when creating new messages
### Messages
- MessageID : SHA512 hash of the Cipherdata (PRIMARY KEY)
- FileID : The hash of the file send in the message
- FromBankID : The bank who sent the message
- ToBankID : The bank who received the message
- Cipherdata : The encrypted and signed message
- DeliveryReceipt : The encrypted and signed delivery receipt
- Datestamp : The date/time when the message was created
- Delivered : The date/time when the message was delivered
## Database functions
### Create\_Message(Plaintext, FromBankID, ToBankID)
Create\_Message() takes the plaintext context of a file as input and prepares
an encrypted _message_ signed by **FromBankID** which can be only decrypted by
**ToBankID**. If the _message_ already exists, the existing data is reused.
An error is returned if the _secret key_ of **FromBankID** or the _public key_
of **ToBankID** can not be located in the database.
The return value is the _message id_ of the message.
### Get\_Message(MessageID)
Given a _message id_ as input, Get\_Message() returns the ASCII armored PGP
message. This data can then be HTTPS POSTed to the Receive\_Message API method
of **ToBank**.
### Receive\_Message(Ciphertext text)
Receive\_Message() decrypts and verifies the signature of the input _message_.
The message's details are written to the _Messages_ table, and information
about the file and its plaintext contents are written into the _Files_ table.
This function will raise an error if:
1. The _secret key_ counterpart of the _public key_ used to encrypt the
message is not present in the table _Keys_.
2. The _public key_ counterpart of the _secret key_ used to sign the message
is not present in the table _Keys_.
3. The message is corrupt or the signature can not be verified.
The return value is a _delivery receipt_, which should be then used as the
contents of the response to the caller of the Receive\_Message API method.
### Decode\_Delivery\_Receipt(DeliveryReceipt text)
Decode\_Delivery\_Receipt() decrypts and verifies the given _delivery receipt_,
where the keys involved and the plaintext should match a row in Messages. If
so, the Message has been successfully delivered, and the
Messages.DeliveryReceipt and Messages.Delivered columns are set.
## Installing and building .deb packages for installation
The repository includes scripts for building debian/ubuntu packages for the
bankapi and the required pgcrypto extensions (in PostgreSQL) in order to run
the code.
If you are running a different version of PostgreSQL then 9.3 then replace the
version in the commands below with the appropriate version. If you are running
the default version in Debian you can omit the version extension of the
packages names.
- sudo apt-get -y build-dep postgresql-9.3
- sudo apt-get -y install postgresql-server-dev-9.3 postgresql-9.3 apache2 python-psycopg2 python-requests
- make
This should produce two deb files, one for bankapi and one for the pgcrypto
extension.
### bankapi-1.0.deb
Package contains the command line tools for sending messages
(/usr/bin/bankapi), SQL needed for creating the bankapi in postgres and
installes a CGI as an endpoint for receving incoming communication messages.
The installation of the module installs and activates the CGI script. It will
be available under http://localhost/bankapi .
The installation does not finish the installation of the database but leaves
this as a manual task. Follow the following steps for a default database
installation:
- cd /usr/share/bankapi
- sudo -u postgres createdb bankapi
- sudo -u postgres psql --dbname=bankapi --single-transaction --no-psqlrc --file=install.sql
- Make sure www-data user can connect to the bankapi database, this can for
instance be done by adding the following line where appropriate in the active
pg\_hba.conf file: local bankapi www-data peer
- To optionally install the test bank data: sudo -u postgres psql --dbname=bankapi --single-transaction --no-psqlrc --file=testdata/index.sql
### postgresql-pgcrypto-openpgp-9.3.deb
This is an extension to the pgcrypto PostgreSQL extension. The extension only
installs with the extended functions, all functions normally in pgcrypto is
still accessed from the standard pgcrypto extension. The extension is called
pgcrypto\_openpgp.