https://github.com/tweedegolf/mailcrab
Email test server for development, written in Rust
https://github.com/tweedegolf/mailcrab
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Email test server for development, written in Rust
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/tweedegolf/mailcrab
- Owner: tweedegolf
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2022-10-21T15:11:00.000Z (about 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-05-15T10:13:39.000Z (7 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-16T04:02:52.733Z (7 months ago)
- Language: Rust
- Size: 995 KB
- Stars: 862
- Watchers: 8
- Forks: 27
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-rust - tweedegolf/mailcrab
- awesome-opensource-email - MailCrab - Email test server for development, written in Rust - `Apache License`, `Rust` (Sending / SMTP Testing)
- awesome-rust - tweedegolf/mailcrab - Email test server for development. (Libraries / Email)
- fucking-awesome-rust - tweedegolf/mailcrab - Email test server for development. (Libraries / Email)
README

# MailCrab
Email test server for development, written in Rust.
Inspired by [MailHog](https://github.com/mailhog/MailHog) and [MailCatcher](https://mailcatcher.me/).
MailCrab was created as an exercise in Rust, trying out [Axum](https://github.com/tokio-rs/axum) and functional components with [Yew](https://yew.rs/), but most of all because it is really enjoyable to write Rust code.
## TLDR
```sh
docker run --rm -p 1080:1080 -p 1025:1025 marlonb/mailcrab:latest
```
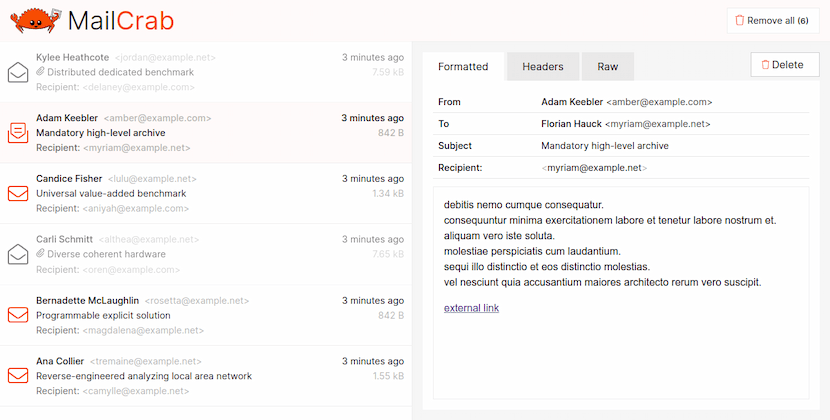
## Features
- Accept-all SMTP server
- Web interface to view and inspect all incoming email
- View formatted mail, download attachments, view headers or the complete raw mail contents
- Single binary
- Runs on all `amd64` and `arm64` platforms using docker
- Just a 7.77 MB docker image
## Related projects
- [CrabAlert](https://github.com/klr/crabalert) is a macOS status bar application that notifies you of incoming messages in MailCrab
## Technical overview
Both the backend server and the frontend are written in Rust. The backend receives email over an unencrypted connection on a configurable port. All email is stored in memory while the application is running. An API exposes all received email:
- `GET /api/messages` return all message metadata
- `GET /api/message/[id]` returns a complete message, given its `id`
- `POST /api/delete/[id]` deletes a message, given its `id`
- `POST /api/delete-all` deletes all messages
- `GET /api/version` returns version information about the executable
- `GET /ws` send email metadata to each connected client when a new email is received
The frontend initially performs a call to `/api/messages` to receive all existing email metadata and then subscribes for new messages using the websocket connection. When opening a message, the `/api/message/[id]` endpoint is used to retrieve the complete message body and raw email.
The backend also accepts a few commands over the websocket, to mark a message as opened, to delete a single message or delete all messages.
## Installation and usage
You can run MailCrab using docker. Start MailCrab using the following command:
```sh
docker run --rm -p 1080:1080 -p 1025:1025 marlonb/mailcrab:latest
```
Open a browser and navigate to [http://localhost:1080](http://localhost:1080) to view the web interface.
There are also (single) binary builds available, see https://github.com/tweedegolf/mailcrab/releases
### Ports
The default SMTP port is 1025, the default HTTP port is 1080. You can configure the SMTP and HTTP port using environment variables (`SMTP_PORT` and `HTTP_PORT`), or by exposing them on different ports using docker:
```sh
docker run --rm -p 3000:1080 -p 2525:1025 marlonb/mailcrab:latest
```
## Host
You can specify the host address MailCrab will listen on for HTTP request using
the `HTTP_HOST` environment variable. In the docker image the default
address is `0.0.0.0`, when running MailCrab directly using cargo or a binary, the default is `127.0.0.1`.
### TLS
You can enable TLS and authentication by setting the environment variable `ENABLE_TLS_AUTH=true`. MailCrab will generate a key-pair and print the self-signed certificate. Any username/password combination is accepted. For example:
```sh
docker run --rm --env ENABLE_TLS_AUTH=true -p 1080:1080 -p 1025:1025 marlonb/mailcrab:latest
```
It is also possible to provide your own certificate by mounting a key and a certificate to `/app/key.pem` and `/app/cert.pem`:
```sh
docker run --rm --env ENABLE_TLS_AUTH=true -v key.pem:/app/key.pem:ro -v cert.pem:/app/cert.pem:ro -p 1080:1080 -p 1025:1025 marlonb/mailcrab:latest
```
### Path prefix
You can configure a prefix path for the web interface by setting and environment variable named `MAILCRAB_PREFIX`, for example:
```sh
docker run --rm --env MAILCRAB_PREFIX=emails -p 1080:1080 -p 1025:1025 marlonb/mailcrab:latest
```
The web interface will also be served at [http://localhost:1080/emails/](http://localhost:1080/emails/)
### Reverse proxy
See [the reverse proxy guide](./reverse_proxy.md).
### Retention period
By default messages will be stored in memory until MailCrab is restarted. This might cause an OOM when MailCrab lives
long enough and receives enough messages.
By setting `MAILCRAB_RETENTION_PERIOD` to a number of seconds, messages older than the provided duration will
be cleared.
### Performance
MailCrab is fast, although there is a bottleneck in the throughput of the websocket connection
(between the server and the browser). If there are many messages sent at once (more than 100 per second)
a client can lag behind and messages can get lost. When dealing with many messages at once,
increasing the internal queue size can help to prevent losing messages.
Use the `QUEUE_CAPACITY` environment variable to set the queue size. De default
is 32, which means that MailCrab can handle 32 messages if the are all sent at the same time.
### docker compose
Usage in a `docker-compose.yml` file:
```yml
version: '3.8'
services:
mailcrab:
image: marlonb/mailcrab:latest
# environment:
# ENABLE_TLS_AUTH: true # optionally enable TLS for the SMTP server
# MAILCRAB_PREFIX: emails # optionally prefix the webinterface with a path
# volumes:
# key.pem:/app/key.pem:ro # optionally provide your own keypair for TLS, else a pair will be generated
# cert.pem:/app/cert.pem:ro
ports:
- '1080:1080'
- '1025:1025'
networks: [default]
```
## Kubernetes deployment
To deploy MailCrab to a Kubernetes cluster, you can use [Helm Chart](./charts/mailcrab/) by cloning this repository and running:
```sh
helm install mailcrab ./charts/mailcrab -f values.yaml
```
For more information on configuring the Helm Chart, see the chart [README](./charts/mailcrab/README.md).
## Sample messages
The `samples` directory contains a couple of test messages. These can be sent using by running:
```sh
cd backend/
cargo test send_sample_messages -- --ignored
```
Alternatively you can send messages using curl:
```sh
curl smtp://127.0.0.1:1025 --mail-from myself@example.com --mail-rcpt receiver@example.com --upload-file samples/normal.email
# with tls
curl -k --ssl-reqd smtps://127.0.0.1:1025 --mail-from myself@example.com --mail-rcpt receiver@example.com --upload-file samples/normal.email --user 'user:pass'
```
## Development
Install [Rust](https://www.rust-lang.org/learn/get-started) and [Trunk](https://trunkrs.dev/)
```sh
# Add wasm as target if it it not present after following the install instructions for Trunk
rustup target add wasm32-unknown-unknown
# clone the code
git clone git@github.com:tweedegolf/mailcrab.git
# start the backend
cd backend
cargo run
# serve the frontend (in a new terminal window)
cd ../frontend
trunk serve
# optionally send test messages in an interval
cd ../backend
cargo test
```