https://github.com/twosixlabs/d3-force-reuse
Faster force-directed graph layouts by reusing force approximations
https://github.com/twosixlabs/d3-force-reuse
d3js graph visualization
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Faster force-directed graph layouts by reusing force approximations
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/twosixlabs/d3-force-reuse
- Owner: twosixlabs
- License: bsd-3-clause
- Created: 2018-11-14T20:10:12.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-07-29T14:36:24.000Z (almost 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-01T22:41:12.477Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: d3js, graph, visualization
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 197 KB
- Stars: 125
- Watchers: 13
- Forks: 5
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-d3 - d3-force-reuse - Faster force-directed graph layouts by reusing force approximations (Miscellaneous)
- awesome-d3 - d3-force-reuse - Faster force-directed graph layouts by reusing force approximations (Miscellaneous)
README
# d3-force-reuse
This module includes `d3.forceManyBodyReuse()`, a faster version of the repulsive force algorithm in d3-force. In practice, `d3.forceManyBodyReuse()` can decrease force-directed graph layout runtimes by 10% to 90% depending on the graph without a decrease in layout quality (as measured by graph layout quality metrics).
How does it achieve the performance speedup? The standard D3 algorithm uses the [Barnes–Hut approximation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barnes–Hut_simulation) to speed up the force calculations, which bases the force approximations on a quadtree that is recalculated after every tick of the layout algorithm. To reduce the runtime, `d3.forceManyBodyReuse()` only recalculates the quadtree once every 13 ticks. Experiments show that this is enough to achieve good quality graph layouts while still greatly speeding the algorithm.
[This blog post](https://www.twosixlabs.com/faster-force-directed-graph-layouts-by-reusing-force-approximations/) discusses this in more detail, and [the research paper](https://osf.io/wgzn5/) contains the details of the algorithm experiments and their results. For a different approach to speeding up force layouts, see also [d3-force-sampled](https://github.com/twosixlabs/d3-force-sampled).
If you use this module, please cite the following research paper:
Robert Gove. "It Pays to Be Lazy: Reusing Force Approximations to Compute Better Graph Layouts Faster." In Proceedings of the 11th Forum Media Technology (2018), pp. 43-51. [Preprint PDF.](https://osf.io/wgzn5/)
## Credit
This module heavily uses code from [d3-force](https://github.com/d3/d3-force). Many thanks to Mike Bostock for making this resource available open source!
## Installing
If you use NPM, `npm install d3-force-reuse`. Otherwise, download the [latest release](https://github.com/twosixlabs/d3-force-reuse/releases/latest). AMD, CommonJS, and vanilla environments are supported.
## Usage
`d3.forceManyBodyReuse()` extends the `d3.forceManyBody()` API, and therefore can be used as a drop-in replacement for `d3.forceManyBody()`. The following is a simple example:
```html
var simulation = d3.forceSimulation(nodes)
.force("link", d3.forceLink().id(function(d) { return d.id; }))
.force("charge", d3.forceManyBodyReuse());
```
For full usage examples, see the [simple example of d3-force-reuse](https://bl.ocks.org/rpgove/98820c49a3d7fd0d4d628402536aa60b) or the [d3-force-reuse speed comparison](https://bl.ocks.org/rpgove/ecee35052e3e81126dcefff134c06dae):
[ ](http://bl.ocks.org/rpgove/98820c49a3d7fd0d4d628402536aa60b)[
](http://bl.ocks.org/rpgove/98820c49a3d7fd0d4d628402536aa60b)[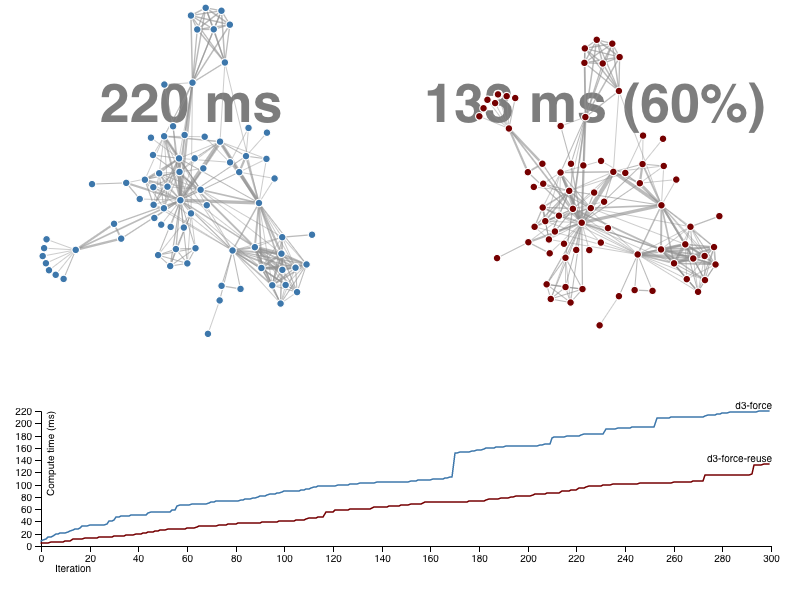 ](http://bl.ocks.org/rpgove/ecee35052e3e81126dcefff134c06dae)
](http://bl.ocks.org/rpgove/ecee35052e3e81126dcefff134c06dae)
## API Reference
### Many-Body Reuse
The many-body (or *n*-body) force applies mutually amongst all [nodes](#simulation_nodes). It can be used to simulate gravity (attraction) if the [strength](#manyBodyReuse_strength) is positive, or electrostatic charge (repulsion) if the strength is negative. This implementation uses quadtrees and the [Barnes–Hut approximation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barnes–Hut_simulation) to greatly improve performance; the accuracy can be customized using the [theta](#manyBodyReuse_theta) parameter. In addition, the quadtree is only updated once every 13 ticks of the simulation. Research shows that this reduces running time while also preserving graph layout quality. The updating behavior can be controlled using the [update](#manyBody_update) parameter.
Unlike links, which only affect two linked nodes, the charge force is global: every node affects every other node, even if they are on disconnected subgraphs.
# d3.forceManyBodyReuse() [<>](https://github.com/twosixlabs/d3-force-reuse/blob/master/src/manyBodyReuse.js "Source")
Creates a new many-body force with the default parameters.
# manyBodyReuse.update([update]) [<>](https://github.com/twosixlabs/d3-force-reuse/blob/master/src/manyBodyReuse.js#L152 "Source")
If *update* is specified, sets the update function to the specified closure and returns this force. (A closure is a function that returns another function.) The outer function takes two parameters: the current iteration number *i*, which is a nonzero integer, and *nodes*, which is the array of nodes used by the many-body force simulation. The inner function returns true if a new quadtree should be calculated, and false otherwise. If *update* is not specified, returns the current closure, which defaults to following uniform distribution (i.e. evenly spaced intervals):
```js
function () {
return function (i, nodes) {
if (i % 13 === 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
};
}
```
To accelerate computation, this force only updates the quadtree used by the [Barnes–Hut approximation](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barnes–Hut_simulation) once every 13 ticks of the simulation. Calculating the quadtree runs in O(n log n) time, so reducing the number of times the algorithm calculates a quadtree can greatly reduce the overall running time.
Note that *update* must be a closure, which allows the update function to maintain state. This allows users to specific update functions like the following, which updates the quadtree with decreasing frequency as the simulation progresses (although note that research shows the uniform function performs better):
```js
var force = d3.forceManyBodyReuse().update(
function () {
var next = 1;
return function (i, nodes) {
var curr = Math.floor(4 * Math.log(i));
if (curr !== next) {
next = curr;
return true;
}
return false;
};
}
)
```
# manyBodyReuse.strength([strength]) [<>](https://github.com/twosixlabs/d3-force-reuse/blob/master/src/manyBodyReuse.js#L136 "Source")
If *strength* is specified, sets the strength accessor to the specified number or function, re-evaluates the strength accessor for each node, and returns this force. A positive value causes nodes to attract each other, similar to gravity, while a negative value causes nodes to repel each other, similar to electrostatic charge. If *strength* is not specified, returns the current strength accessor, which defaults to:
```js
function strength() {
return -30;
}
```
The strength accessor is invoked for each node in the simulation, being passed the *node* and its zero-based *index*. The resulting number is then stored internally, such that the strength of each node is only recomputed when the force is initialized or when this method is called with a new *strength*, and not on every application of the force.
# manyBodyReuse.theta([theta]) [<>](https://github.com/twosixlabs/d3-force-reuse/blob/master/src/manyBodyReuse.js#L148 "Source")
If *theta* is specified, sets the Barnes–Hut approximation criterion to the specified number and returns this force. If *theta* is not specified, returns the current value, which defaults to 0.9.
To accelerate computation, this force implements the [Barnes–Hut approximation](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barnes–Hut_simulation) which takes O(*n* log *n*) per application where *n* is the number of nodes. For each application, a [quadtree](https://github.com/d3/d3-quadtree) stores the current node positions; then for each node, the combined force of all other nodes on the given node is computed. For a cluster of nodes that is far away, the charge force can be approximated by treating the cluster as a single, larger node. The *theta* parameter determines the accuracy of the approximation: if the ratio *w* / *l* of the width *w* of the quadtree cell to the distance *l* from the node to the cell’s center of mass is less than *theta*, all nodes in the given cell are treated as a single node rather than individually.
# manyBodyReuse.distanceMin([distance]) [<>](https://github.com/twosixlabs/d3-force-reuse/blob/master/src/manyBodyReuse.js#L140 "Source")
If *distance* is specified, sets the minimum distance between nodes over which this force is considered. If *distance* is not specified, returns the current minimum distance, which defaults to 1. A minimum distance establishes an upper bound on the strength of the force between two nearby nodes, avoiding instability. In particular, it avoids an infinitely-strong force if two nodes are exactly coincident; in this case, the direction of the force is random.
# manyBodyReuse.distanceMax([distance]) [<>](https://github.com/twosixlabs/d3-force-reuse/blob/master/src/manyBodyReuse.js#L144 "Source")
If *distance* is specified, sets the maximum distance between nodes over which this force is considered. If *distance* is not specified, returns the current maximum distance, which defaults to infinity. Specifying a finite maximum distance improves performance and produces a more localized layout.