https://github.com/typpo/quickchart-js
Javascript client for quickchart.io
https://github.com/typpo/quickchart-js
chart-api chartjs chartjs-node chartjs-to-image js-charts
Last synced: 11 months ago
JSON representation
Javascript client for quickchart.io
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/typpo/quickchart-js
- Owner: typpo
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-05-15T15:01:37.000Z (almost 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-02-10T18:47:29.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-13T00:48:15.973Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: chart-api, chartjs, chartjs-node, chartjs-to-image, js-charts
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage: https://quickchart.io
- Size: 959 KB
- Stars: 65
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 11
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
QuickChart for Javascript
---
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/quickchart-js)
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/quickchart-js)
[](https://travis-ci.com/typpo/quickchart-js)
This is a Javascript client for [quickchart.io](https://quickchart.io), a web service for generating static charts. View the main QuickChart repository [here](https://github.com/typpo/quickchart).
# Installation
If you are using npm:
```
npm install quickchart-js
```
# Usage
This library provides a **QuickChart** object. Import it, instantiate it, and set your [Chart.js](https://www.chartjs.org) config:
```js
const QuickChart = require('quickchart-js');
const myChart = new QuickChart();
myChart.setConfig({
type: 'bar',
data: { labels: ['Hello world', 'Foo bar'], datasets: [{ label: 'Foo', data: [1, 2] }] },
});
```
Use `getUrl()` on your quickchart object to get the encoded URL that renders your chart:
```js
console.log(myChart.getUrl());
// Prints: https://quickchart.io/chart?c=%7Btype%3A%27bar%27%2Cdata%3A%7Blabels%3A%5B%27Hello+world%27%2C%27Foo+bar%27%5D%2Cdatasets%3A%5B%7Blabel%3A%27Foo%27%2Cdata%3A%5B1%2C2%5D%7D%5D%7D%7D&w=500&h=300&bkg=transparent&f=png
```
If you have a large or complicated chart, use `getShortUrl()` on your quickchart object to get a fixed-length URL using the quickchart.io web service:
```js
const url = await myChart.getShortUrl();
console.log(url);
// Prints: https://quickchart.io/chart/render/f-a1d3e804-dfea-442c-88b0-9801b9808401
```
Or write it to disk:
```js
myChart.toFile('/tmp/mychart.png');
```
The URLs produce this chart image:
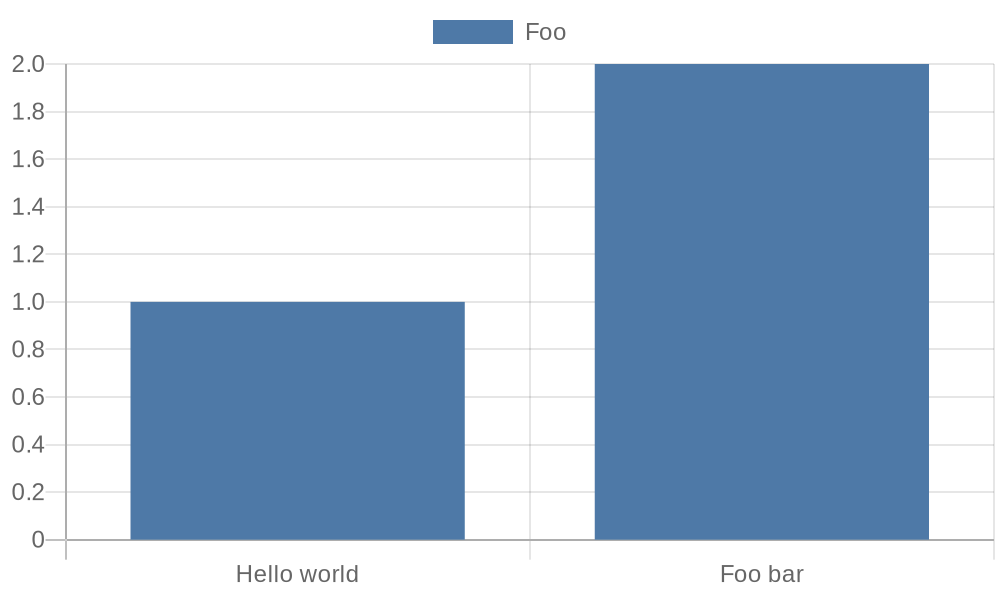
## Creating a QuickChart object
If you have an account ID and API key, authenticate using the QuickChart constructor:
```js
const qc = new QuickChart(apiKey, accountId);
```
To use the free (community) version, leave it blank:
```js
const qc = new QuickChart();
```
## Customizing your chart
### setConfig(chart: Object | string)
Use this config to customize the Chart.js config object that defines your chart. You must set this before generating a URL!
### setWidth(width: int)
Sets the width of the chart in pixels. Defaults to 500.
### setHeight(height: int)
Sets the height of the chart in pixels. Defaults to 300.
### setFormat(format: string)
Sets the format of the chart. Defaults to `png`. `svg` is also valid.
### setBackgroundColor(color: string)
Sets the background color of the chart. Any valid HTML color works. Defaults to `#ffffff` (white). Also takes `rgb`, `rgba`, and `hsl` values.
### setDevicePixelRatio(ratio: float)
Sets the device pixel ratio of the chart. This will multiply the number of pixels by the value. This is usually used for retina displays. Defaults to 1.0.
### setVersion(version: string)
Sets the Chart.js version to use (e.g. `2.9.4` or `3.4.0`). Valid options are shown in the [documentation](https://quickchart.io/documentation/#parameters).
### setHost(host: string)
Sets the host of generated URLs. `quickchart.io` by default.
### setScheme(scheme: string)
Sets the scheme of generated URLs. `https` by default.
## Getting outputs
There are two ways to get a URL for your chart object.
### getUrl(): string
Returns a URL that will display the chart image when loaded.
### getShortUrl(): Promise
Uses the quickchart.io web service to create a fixed-length chart URL that displays the chart image. The Promise resolves with a URL such as `https://quickchart.io/chart/render/f-a1d3e804-dfea-442c-88b0-9801b9808401`.
Note that short URLs expire after a few days for users of the free service. You can [subscribe](https://quickchart.io/pricing/) to keep them around longer.
### getSignedUrl(): string
Returns a URL that displays the chart image. It is signed with your user account to bypass rate limitations.
### toBinary(): Promise
Creates a binary buffer that contains your chart image.
### toDataUrl(): Promise
Returns a base 64 data URL beginning with `data:image/png;base64`.
### toFile(pathOrDescriptor: PathLike | FileHandle): Promise
Given a filepath string or a writable file handle, creates a file containing your chart image.
## More examples
Check out the `examples/` directory to see other usage. Here's a simple test that uses some of the custom parameters:
```js
const qc = new QuickChart();
qc.setConfig({
type: 'bar',
data: { labels: ['Hello world', 'Foo bar'], datasets: [{ label: 'Foo', data: [1, 2] }] },
});
qc.setWidth(500).setHeight(300).setBackgroundColor('transparent');
console.log(qc.getUrl());
// https://quickchart.io/chart?c=%7Btype%3A%27bar%27%2Cdata%3A%7Blabels%3A%5B%27Hello+world%27%2C%27Foo+bar%27%5D%2Cdatasets%3A%5B%7Blabel%3A%27Foo%27%2Cdata%3A%5B1%2C2%5D%7D%5D%7D%7D&w=500&h=300&bkg=transparent&f=png
```
Here's a more complicated chart that includes some Javascript:
```js
qc.setConfig({
type: 'bar',
data: {
labels: ['January', 'February', 'March', 'April', 'May'],
datasets: [
{
label: 'Dogs',
data: [50, 60, 70, 180, 190],
},
],
},
options: {
scales: {
yAxes: [
{
ticks: {
callback: function (value) {
return '$' + value;
},
},
},
],
},
},
});
qc.setWidth(500).setHeight(300).setBackgroundColor('#0febc2');
console.log(qc.getUrl());
// https://quickchart.io/chart?c=%7Btype%3A%27bar%27%2Cdata%3A%7Blabels%3A%5B%27January%27%2C%27February%27%2C%27March%27%2C%27April%27%2C%27May%27%5D%2Cdatasets%3A%5B%7Blabel%3A%27Dogs%27%2Cdata%3A%5B50%2C60%2C70%2C180%2C190%5D%7D%5D%7D%2Coptions%3A%7Bscales%3A%7ByAxes%3A%5B%7Bticks%3A%7Bcallback%3Afunction+%28value%29+%7B%0A++return+%27%24%27+%2B+value%3B%0A%7D%7D%7D%5D%7D%7D%7D&w=500&h=300&bkg=%230febc2&f=png
```
As we customize these charts, the URLs are getting a little long for my liking. There's a `getShortUrl` function that uses the QuickChart.io web service to generate a short(er), fixed-length URL:
```js
// Fill the chart with data from 0 to 100
const data = [...Array(100).keys()];
qc.setConfig({
type: 'bar',
data: { labels: ['Hello world', 'Foo bar'], datasets: [{ label: 'Foo', data }] },
});
async function printShortUrl() {
const url = await qc.getShortUrl();
console.log(url);
}
printShortUrl();
// https://quickchart.io/chart/render/f-a1d3e804-dfea-442c-88b0-9801b9808401
```
## Using built-in QuickChart functions
QuickChart has builtin functions: `getImageFill`, `getGradientFill`, `getGradientFillHelper`, and `pattern.draw`. These functions can be accessed via the `QuickChart` class. For example:
```js
const qc = new QuickChart();
qc.setConfig({
type: 'bar',
data: {
labels: ['Hello world', 'Foo bar'],
datasets: [
{
label: 'Foo',
data: [1, 2],
backgroundColor: QuickChart.getGradientFillHelper('horizontal', ['red', 'green']),
},
],
},
});
```
# Building the library
To build this library locally, run:
```
yarn build
```
To run tests:
```
yarn test
```
If you're editing the library and running examples, you may want to continuously build the library in the background:
```
yarn build:watch
# ...
node examples/simple_example.js
```