Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/tyson0314/leetcode
https://github.com/tyson0314/leetcode
Last synced: about 23 hours ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/tyson0314/leetcode
- Owner: Tyson0314
- Created: 2019-04-10T08:36:34.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-08-01T14:21:29.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-10T16:36:20.685Z (about 2 months ago)
- Language: Java
- Size: 742 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
- [动态规划](#%E5%8A%A8%E6%80%81%E8%A7%84%E5%88%92)
- [最长上升子序列](#%E6%9C%80%E9%95%BF%E4%B8%8A%E5%8D%87%E5%AD%90%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97)
- [最大子数组和](#%E6%9C%80%E5%A4%A7%E5%AD%90%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E5%92%8C)
- [买卖股票的最佳时机](#%E4%B9%B0%E5%8D%96%E8%82%A1%E7%A5%A8%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E4%BD%B3%E6%97%B6%E6%9C%BA)
- [最长公共子序列](#%E6%9C%80%E9%95%BF%E5%85%AC%E5%85%B1%E5%AD%90%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97)
- [不同路径II](#%E4%B8%8D%E5%90%8C%E8%B7%AF%E5%BE%84ii)
- [接雨水](#%E6%8E%A5%E9%9B%A8%E6%B0%B4)
- [分割回文串](#%E5%88%86%E5%89%B2%E5%9B%9E%E6%96%87%E4%B8%B2)
- [最长回文子串](#%E6%9C%80%E9%95%BF%E5%9B%9E%E6%96%87%E5%AD%90%E4%B8%B2)
- [单词拆分](#%E5%8D%95%E8%AF%8D%E6%8B%86%E5%88%86)
- [不同的二叉搜索树](#%E4%B8%8D%E5%90%8C%E7%9A%84%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%A0%91)
- [解码方法](#%E8%A7%A3%E7%A0%81%E6%96%B9%E6%B3%95)
- [三角形最小路径和](#%E4%B8%89%E8%A7%92%E5%BD%A2%E6%9C%80%E5%B0%8F%E8%B7%AF%E5%BE%84%E5%92%8C)
- [乘积最大子数组](#%E4%B9%98%E7%A7%AF%E6%9C%80%E5%A4%A7%E5%AD%90%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84)
- [无重复字符的最长子串](#%E6%97%A0%E9%87%8D%E5%A4%8D%E5%AD%97%E7%AC%A6%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E9%95%BF%E5%AD%90%E4%B8%B2)
- [二叉树的最近公共祖先](#%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E8%BF%91%E5%85%AC%E5%85%B1%E7%A5%96%E5%85%88)
- [数组中的第K个最大元素](#%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E7%AC%ACk%E4%B8%AA%E6%9C%80%E5%A4%A7%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0)
- [岛屿的数量](#%E5%B2%9B%E5%B1%BF%E7%9A%84%E6%95%B0%E9%87%8F)
- [相交链表](#%E7%9B%B8%E4%BA%A4%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8)
- [反转链表](#%E5%8F%8D%E8%BD%AC%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8)
- [反转链表II](#%E5%8F%8D%E8%BD%AC%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8ii)
- [K 个一组翻转链表](#k-%E4%B8%AA%E4%B8%80%E7%BB%84%E7%BF%BB%E8%BD%AC%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8)
- [二叉树的右视图](#%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E5%8F%B3%E8%A7%86%E5%9B%BE)
- [整数反转](#%E6%95%B4%E6%95%B0%E5%8F%8D%E8%BD%AC)
- [二叉树的直径](#%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E7%9B%B4%E5%BE%84)
- [验证二叉搜索树](#%E9%AA%8C%E8%AF%81%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%A0%91)
- [二叉树的最大深度](#%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E5%A4%A7%E6%B7%B1%E5%BA%A6)
- [回文链表](#%E5%9B%9E%E6%96%87%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8)
- [LRU](#lru)
- [字符串相加](#%E5%AD%97%E7%AC%A6%E4%B8%B2%E7%9B%B8%E5%8A%A0)
- [两数之和](#%E4%B8%A4%E6%95%B0%E4%B9%8B%E5%92%8C)
- [三数之和](#%E4%B8%89%E6%95%B0%E4%B9%8B%E5%92%8C)
- [买卖股票的最佳时机 II](#%E4%B9%B0%E5%8D%96%E8%82%A1%E7%A5%A8%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E4%BD%B3%E6%97%B6%E6%9C%BA-ii)
- [二叉树锯齿形层次遍历](#%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E9%94%AF%E9%BD%BF%E5%BD%A2%E5%B1%82%E6%AC%A1%E9%81%8D%E5%8E%86)
- [多数元素](#%E5%A4%9A%E6%95%B0%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0)
- [合并区间](#%E5%90%88%E5%B9%B6%E5%8C%BA%E9%97%B4)
- [对称的二叉树](#%E5%AF%B9%E7%A7%B0%E7%9A%84%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91)
- [用栈实现队列](#%E7%94%A8%E6%A0%88%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97)
- [最小栈](#%E6%9C%80%E5%B0%8F%E6%A0%88)
- [二叉树的完全性检验](#%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%8C%E5%85%A8%E6%80%A7%E6%A3%80%E9%AA%8C)
- [排序链表](#%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8)
- [最长连续序列](#%E6%9C%80%E9%95%BF%E8%BF%9E%E7%BB%AD%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97)
- [字符串转换整数*](#%E5%AD%97%E7%AC%A6%E4%B8%B2%E8%BD%AC%E6%8D%A2%E6%95%B4%E6%95%B0)
- [回文数](#%E5%9B%9E%E6%96%87%E6%95%B0)
- [盛最多水的容器](#%E7%9B%9B%E6%9C%80%E5%A4%9A%E6%B0%B4%E7%9A%84%E5%AE%B9%E5%99%A8)
- [电话号码的组合](#%E7%94%B5%E8%AF%9D%E5%8F%B7%E7%A0%81%E7%9A%84%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88)
- [四数之和](#%E5%9B%9B%E6%95%B0%E4%B9%8B%E5%92%8C)
- [删除链表倒数第n个节点](#%E5%88%A0%E9%99%A4%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E5%80%92%E6%95%B0%E7%AC%ACn%E4%B8%AA%E8%8A%82%E7%82%B9)
- [有效的括号](#%E6%9C%89%E6%95%88%E7%9A%84%E6%8B%AC%E5%8F%B7)
- [括号生成](#%E6%8B%AC%E5%8F%B7%E7%94%9F%E6%88%90)
- [两两交换链表中的节点](#%E4%B8%A4%E4%B8%A4%E4%BA%A4%E6%8D%A2%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E8%8A%82%E7%82%B9)
- [合并两个有序列表](#%E5%90%88%E5%B9%B6%E4%B8%A4%E4%B8%AA%E6%9C%89%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E8%A1%A8)
- [删除排序数组的重复项](#%E5%88%A0%E9%99%A4%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E7%9A%84%E9%87%8D%E5%A4%8D%E9%A1%B9)
- [两数相除](#%E4%B8%A4%E6%95%B0%E7%9B%B8%E9%99%A4)
- [下一个排列](#%E4%B8%8B%E4%B8%80%E4%B8%AA%E6%8E%92%E5%88%97)
- [在排序数组中查找第一个和最后一个位置](#%E5%9C%A8%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E4%B8%AD%E6%9F%A5%E6%89%BE%E7%AC%AC%E4%B8%80%E4%B8%AA%E5%92%8C%E6%9C%80%E5%90%8E%E4%B8%80%E4%B8%AA%E4%BD%8D%E7%BD%AE)
- [组合总和](#%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88%E6%80%BB%E5%92%8C)
- [移除元素](#%E7%A7%BB%E9%99%A4%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0)
- [字符串相乘](#%E5%AD%97%E7%AC%A6%E4%B8%B2%E7%9B%B8%E4%B9%98)
- [有效的数独](#%E6%9C%89%E6%95%88%E7%9A%84%E6%95%B0%E7%8B%AC)
- [全排列](#%E5%85%A8%E6%8E%92%E5%88%97)
- [全排列II](#%E5%85%A8%E6%8E%92%E5%88%97ii)
- [实现 strStr()](#%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0-strstr)
- [字母异位词分组](#%E5%AD%97%E6%AF%8D%E5%BC%82%E4%BD%8D%E8%AF%8D%E5%88%86%E7%BB%84)
- [pow(x, n)](#powx-n)
- [旋转图像](#%E6%97%8B%E8%BD%AC%E5%9B%BE%E5%83%8F)
- [跳跃游戏](#%E8%B7%B3%E8%B7%83%E6%B8%B8%E6%88%8F)
- [螺旋矩阵](#%E8%9E%BA%E6%97%8B%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5)
- [螺旋矩阵II](#%E8%9E%BA%E6%97%8B%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5ii)
- [第 k 个排列](#%E7%AC%AC-k-%E4%B8%AA%E6%8E%92%E5%88%97)
- [简化路径](#%E7%AE%80%E5%8C%96%E8%B7%AF%E5%BE%84)
- [矩阵置零](#%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5%E7%BD%AE%E9%9B%B6)
- [搜索二维矩阵](#%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E4%BA%8C%E7%BB%B4%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5)
- [颜色分类](#%E9%A2%9C%E8%89%B2%E5%88%86%E7%B1%BB)
- [组合](#%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88)
- [子集](#%E5%AD%90%E9%9B%86)
- [单词搜索](#%E5%8D%95%E8%AF%8D%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2)
- [删除排序数组的重复项](#%E5%88%A0%E9%99%A4%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E7%9A%84%E9%87%8D%E5%A4%8D%E9%A1%B9-1)
- [搜索旋转排序数组II](#%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%97%8B%E8%BD%AC%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84ii)
- [删除排序链表的重复元素](#%E5%88%A0%E9%99%A4%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%9A%84%E9%87%8D%E5%A4%8D%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0)
- [分隔链表](#%E5%88%86%E9%9A%94%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8)
- [格雷编码](#%E6%A0%BC%E9%9B%B7%E7%BC%96%E7%A0%81)
- [子集II](#%E5%AD%90%E9%9B%86ii)
- [复原ip](#%E5%A4%8D%E5%8E%9Fip)
- [从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树](#%E4%BB%8E%E5%89%8D%E5%BA%8F%E4%B8%8E%E4%B8%AD%E5%BA%8F%E9%81%8D%E5%8E%86%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E6%9E%84%E9%80%A0%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91)
- [将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树](#%E5%B0%86%E6%9C%89%E5%BA%8F%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E8%BD%AC%E6%8D%A2%E4%B8%BA%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%A0%91)
- [有序链表转换二叉搜索树](#%E6%9C%89%E5%BA%8F%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E8%BD%AC%E6%8D%A2%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E6%A0%91)
- [平衡二叉树](#%E5%B9%B3%E8%A1%A1%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91)
- [二叉树的最小深度](#%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E5%B0%8F%E6%B7%B1%E5%BA%A6)
- [二叉树展开为链表](#%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E5%B1%95%E5%BC%80%E4%B8%BA%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8)
- [杨辉三角II](#%E6%9D%A8%E8%BE%89%E4%B8%89%E8%A7%92ii)
- [验证回文串](#%E9%AA%8C%E8%AF%81%E5%9B%9E%E6%96%87%E4%B8%B2)
- [被围绕的区域](#%E8%A2%AB%E5%9B%B4%E7%BB%95%E7%9A%84%E5%8C%BA%E5%9F%9F)
- [单词接龙](#%E5%8D%95%E8%AF%8D%E6%8E%A5%E9%BE%99)
- [求根到叶子节点数字之和](#%E6%B1%82%E6%A0%B9%E5%88%B0%E5%8F%B6%E5%AD%90%E8%8A%82%E7%82%B9%E6%95%B0%E5%AD%97%E4%B9%8B%E5%92%8C)
- [克隆图](#%E5%85%8B%E9%9A%86%E5%9B%BE)
- [只出现一次的数字](#%E5%8F%AA%E5%87%BA%E7%8E%B0%E4%B8%80%E6%AC%A1%E7%9A%84%E6%95%B0%E5%AD%97)
- [复制带随机指针的链表](#%E5%A4%8D%E5%88%B6%E5%B8%A6%E9%9A%8F%E6%9C%BA%E6%8C%87%E9%92%88%E7%9A%84%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8)
- [环形链表](#%E7%8E%AF%E5%BD%A2%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8)
- [环形链表II](#%E7%8E%AF%E5%BD%A2%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8ii)
- [只出现一次的数字 II](#%E5%8F%AA%E5%87%BA%E7%8E%B0%E4%B8%80%E6%AC%A1%E7%9A%84%E6%95%B0%E5%AD%97-ii)
- [重排链表](#%E9%87%8D%E6%8E%92%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8)
- [对链表进行插入排序](#%E5%AF%B9%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E8%BF%9B%E8%A1%8C%E6%8F%92%E5%85%A5%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F)
- [逆波兰表达式求值](#%E9%80%86%E6%B3%A2%E5%85%B0%E8%A1%A8%E8%BE%BE%E5%BC%8F%E6%B1%82%E5%80%BC)
| 题目 | 题解 |
| ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| [环形链表II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/) | [DetectCycle](https://github.com/Tyson0314/leetcode/blob/master/src/leetcode/DetectCycle.java) |
| [重排链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reorder-list/) | [ReorderList](https://github.com/Tyson0314/leetcode/blob/master/src/leetcode/ReorderList.java) |
| [乘积最大子序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-product-subarray/) | [MaxProduct](https://github.com/Tyson0314/leetcode/blob/master/src/leetcode/MaxProduct.java) |
| [版本比较](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/compare-version-numbers/) | [CompareVersion](https://github.com/Tyson0314/leetcode/blob/master/src/leetcode/CompareVersion.java) |
| [最大数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/largest-number/) | [LargestNumber](https://github.com/Tyson0314/leetcode/blob/master/src/leetcode/LargestNumber.java) |
| [最大正方形](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximal-square/) | [MaximalSquare](https://github.com/Tyson0314/leetcode/blob/master/src/leetcode/MaximalSquare.java) |
## 动态规划
动态规划常常适用于有重叠子问题的问题。动态规划的基本思想:若要解一个给定问题,我们需要解其不同部分(即子问题),再根据子问题的解以得出原问题的解。
动态规划法试图仅仅解决每个子问题一次,一旦某个给定子问题的解已经算出,则将其记忆化存储,以便下次遇到同一个子问题的时候直接查表得到解。
动态规划的解题思路:1、状态定义;2、状态转移方程;3、初始状态。
### 最长上升子序列
```
输入: [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18]
输出: 4
解释: 最长的上升子序列是 [2,3,7,101],它的长度是 4。
```
[动态规划](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/solution/zui-chang-shang-sheng-zi-xu-lie-dong-tai-gui-hua-2/)
dp[i] 的值代表以nums[i]结尾的最大递增子序列的长度。
```
[10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18]
dp[5]:以nums[5],也就是7结尾的最大递增子序列(2 5 7或者2 3 7)的长度(3)
```
时间复杂度O(N2)。
```java
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) { //[]
return 0;
}
int len = nums.length;
//dp[i]:以nums[i]结尾的最大递增子序列的长度
int dp[] = new int[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
dp[i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
}
int maxLen = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
if (maxLen < dp[i]) {
maxLen = dp[i];
}
}
return maxLen;
}
}
```
### 最大子数组和
dp[i]表示以nums[i]结尾的子数组的最大和。`dp[i] = dp[i - 1] > 0 ? ( dp[i - 1] + nums[i]) : nums[i]`
dp[i+1]取决于dp[i]的值,不需要使用数组保存状态,只需要一个变量sum来保存上一个状态即可。
```java
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int max = nums[0];
int sum = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
if (sum > 0) {
sum += num;
} else {
sum = num;
}
max = Math.max(max, sum);
}
return max;
}
}
```
### 买卖股票的最佳时机
动态规划 前i天的最大收益 = max{前i-1天的最大收益,第i天的价格-前i-1天中的最小价格}
```java
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int minPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int maxProfit = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i] < minPrice) {
minPrice = prices[i];
}
maxProfit = Math.max(prices[i] - minPrice, maxProfit);
}
return maxProfit;
}
}
```
### 最长公共子序列
一个字符串的 子序列 是指这样一个新的字符串:它是由原字符串在不改变字符的相对顺序的情况下删除某些字符(也可以不删除任何字符)后组成的新字符串。
例如,"ace" 是 "abcde" 的子序列,但 "aec" 不是 "abcde" 的子序列。
动态规划。`dp[i][j]`表示text1以i-1结尾的子串和text2以j-1结尾的子串的最长公共子序列的长度。dp横坐标或纵坐标为0表示空字符串,`dp[0][j] = dp[i][0] = 0`,无需额外处理base case。

```java
class Solution {
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
char[] arr1 = text1.toCharArray();
char[] arr2 = text2.toCharArray();
//dp[0][x]和dp[x][0]表示有一个为空字符串
//dp[1][1]为text1第一个字符和text2第一个字符的最长公共子序列的长度
//dp[i][j]表示text1以i-1结尾的子串和text2以j-1结尾的子串的最长公共子序列的长度
int len1 = arr1.length;
int len2 = arr2.length;
int[][] dp = new int[len1 + 1][len2 + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < len1 + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < len2 + 1; j++) {
if (arr1[i - 1] == arr2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[len1][len2];
}
}
```
`dp[i][j]`表示text1以i结尾的子串和text2以j结尾的子串的最长公共子序列的长度。需要处理base case。
```java
class Solution {
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
char[] arr1 = text1.toCharArray();
char[] arr2 = text2.toCharArray();
int len1 = arr1.length;
int len2 = arr2.length;
//`dp[i][j]`表示text1以i结尾的子串和text2以j结尾的子串的最长公共子序列的长度。
int[][] dp = new int[len1][len2];
if (arr1[0] == arr2[0]) {
dp[0][0] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < len1; i++) {
if (arr1[i] == arr2[0]) {
dp[i][0] = 1;
} else {
dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < len2; i++) {
if (arr1[0] == arr2[i]) {
dp[0][i] = 1;
} else {
dp[0][i] = dp[0][i - 1];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < len1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < len2; j++) {
if (arr1[i] == arr2[j]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[len1 - 1][len2 - 1];
}
}
```
### 不同路径II
一个机器人位于一个 *m x n* 网格的左上角 。机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角。
考虑网格中有障碍物。那么从左上角到右下角将会有多少条不同的路径?网格中的障碍物和空位置分别用 `1` 和 `0` 来表示。
```java
class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
if (obstacleGrid == null || obstacleGrid.length == 0 || obstacleGrid[0].length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("array is null or array is empty");
}
if (obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1) { //[[1]]
return 0;
}
int rows = obstacleGrid.length;
int columns = obstacleGrid[0].length;
int[][] path = new int[rows][columns];
path[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < rows; i++) {
path[i][0] = (path[i - 1][0] == 1 && obstacleGrid[i][0] == 0) ? 1 : 0;
}
for (int j = 1; j < columns; j++) {
path[0][j] = (path[0][j - 1] == 1 && obstacleGrid[0][j] == 0) ? 1 : 0;
}
for (int m = 1; m < rows; m++) {
for (int n = 1; n < columns; n++) {
path[m][n] = obstacleGrid[m][n] == 0 ? path[m - 1][n] + path[m][n - 1] : 0;
}
}
return path[rows - 1][columns - 1];
}
}
```
### 接雨水
动态规划,使用两个数组空间。leftMax[i] 代表第 `i` 列左边(不包含自身)最高的墙的高度,rightMax[i] 代表第 `i` 列右边最高的墙的高度。
```java
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int len = height.length;
int res = 0;
int[] leftMax = new int[len];
int[] rightMax = new int[len];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
leftMax[i] = Math.max(leftMax[i - 1], height[i - 1]);
}
for (int j = len - 2; j > 0; j--) {
rightMax[j] = Math.max(rightMax[j + 1], height[j + 1]);
}
for (int i = 1; i < len - 1; i++) {
int min = Math.min(leftMax[i], rightMax[i]);
if (min > height[i]) {
res += min - height[i];
}
}
return res;
}
}
```
[双指针法,只需要两个变量存储状态](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/solution/jie-yu-shui-by-leetcode/327718/)
```java
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int maxLeft = 0, maxRight = 0;
int left = 0;
int right = height.length - 1;
int res = 0;
while (left <= right) {
if (maxLeft < maxRight) {
if (height[left] < maxLeft) {
res += (maxLeft - height[left]);
}
maxLeft = Math.max(maxLeft, height[left]);
left++;
} else {
if (height[right] < maxRight) {
res += (maxRight - height[right]);
}
maxRight = Math.max(maxRight, height[right]);
right--;
}
}
return res;
}
}
```
### 分割回文串
```
输入: "aab"
输出:
[
["aa","b"],
["a","a","b"]
]
```
[参考](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/solution/hui-su-you-hua-jia-liao-dong-tai-gui-hua-by-liweiw/)
使用动态规划预标记出哪一段属于回文串。
```java
class Solution {
public List> partition(String s) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
int len = s.length();
if (s == null || len == 0) {
return res;
}
boolean dp[][] = new boolean[len][len];
char[] charArr = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][i] = true;
}
for (int right = 1; right < len; right++) {
for (int left = 0; left < right; left++) {
dp[left][right] = charArr[left] == charArr[right] && (right - left <= 2 || dp[left + 1][right - 1]);
}
}
LinkedList path = new LinkedList<>();
dfs(s, 0, res, path, dp);
return res;
}
private void dfs(String s, int start, List> res, LinkedList path, boolean[][] dp) {
if (start == s.length()) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (dp[start][i]) {
path.addLast(s.substring(start, i + 1));
dfs(s, i + 1, res, path, dp);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
}
```
### 最长回文子串
从给定的字符串 `s` 中找到最长的回文子串的长度。
例如 `s = "babbad"` 的最长回文子串是 `"abba"` ,长度是 `4` 。
解题思路:
1. 定义状态。`dp[i][j]` 表示子串 `s[i..j]` 是否为回文子串
2. 状态转移方程:`dp[i][j] = (s[i] == s[j]) and dp[i + 1][j - 1]`
3. 初始化的时候,单个字符一定是回文串,因此把对角线先初始化为 `true`,即 `dp[i][i] = true` 。
4. 只要一得到 `dp[i][j] = true`,就记录子串的长度和起始位置
注意事项:总是先得到小子串的回文判定,然后大子串才能参考小子串的判断结果,即填表顺序很重要。

时间复杂度O(N2),空间复杂度O(N2),因为使用了二维数组。
```java
public class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
// 特判
int len = s.length();
if (len < 2) {
return s;
}
int maxLen = 1;
int begin = 0;
// dp[i][j] 表示 s[i, j] 是否是回文串
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len];
char[] charArray = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][i] = true;
}
for (int j = 1; j < len; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
if (charArray[i] != charArray[j]) {
dp[i][j] = false;
} else {
if (j - i < 3) {
dp[i][j] = true;
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1];
}
}
// 只要 dp[i][j] == true 成立,就表示子串 s[i..j] 是回文,此时记录回文长度和起始位置
if (dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > maxLen) {
maxLen = j - i + 1;
begin = i;
}
}
}
return s.substring(begin, begin + maxLen); //substring(i, j)截取i到j(不包含j)的字符串
}
}
```
### 单词拆分

```java
class Solution {
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List wordDict) {
int len = s.length(), maxw = 0;
//dp[i]表示前i个字母组成的字符串是否可以被拆分
boolean[] dp = new boolean[len + 1];
//状态转移方程初始化条件
dp[0] = true;
Set set = new HashSet();
for(String str : wordDict){
set.add(str);
maxw = Math.max(maxw, str.length());
}
for(int i = 1; i < len + 1; i++){
for(int j = i; j >= 0 && j >= i - maxw; j--){
if(dp[j] && set.contains(s.substring(j, i))){
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[len];
}
}
```
### 不同的二叉搜索树
给定一个整数 *n*,求以 1 ... *n* 为节点组成的二叉搜索树有多少种?
[动态规划解法](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/solution/bu-tong-de-er-cha-sou-suo-shu-by-leetcode/)
```java
class Solution {
public int numTrees(int n) {
int arr[] = new int[n + 1];
arr[0] = 1;
arr[1] = 1;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
arr[i] += arr[j - 1] * arr[i - j];
}
}
return arr[n];
}
}
```
### 解码方法
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/decode-ways/
```java
class Solution {
public int numDecodings(String s) {
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
if (arr[0] == '0') {
return 0;
}
int cur = 1;
int pre = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
int tmp = cur;
if (arr[i] == '0') {
if (arr[i - 1] == '1' || arr[i - 1] == '2') {
cur = pre;
} else {
return 0;
}
} else if (arr[i - 1] == '1' || (arr[i - 1] == '2' && arr[i] >= '0' && arr[i] <= '6')) {
cur += pre;
}
pre = tmp;
}
return cur;
}
}
```
### 三角形最小路径和
给定一个三角形,找出自顶向下的最小路径和。每一步只能移动到下一行中相邻的结点上。相邻的结点 在这里指的是 下标 与 上一层结点下标 相同或者等于 上一层结点下标 + 1 的两个结点。
```java
[
[2],
[3,4],
[6,5,7],
[4,1,8,3]
]
```
动态规划。
```java
class Solution {
public int minimumTotal(List> triangle) {
int size = triangle.size();
int[] minLen = new int[size + 1];//+1
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0 ; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
minLen[j] = Math.min(minLen[j], minLen[j + 1]) + triangle.get(i).get(j);
}
}
return minLen[0];
}
}
```
### 乘积最大子数组
动态规划。
```java
class Solution {
public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
int curMax = 1, curMin = 1;//保证i=1时,结果正确
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] < 0) {
int tmp = curMax;
curMax = curMin;
curMin = tmp;
}
curMax = Math.max(curMax, curMax * nums[i]);
curMin = Math.min(curMin, curMin * nums[i]);
max = Math.max(max, curMax);//[2,-2],当i=1时,curMax与curMin交换,curMax=1,max=2,故取max与curMax中最大值
}
return max;
}
}
```
## 回溯
回溯算法的基本思想是:从一条路往前走,能进则进,不能进则退回来,换一条路再试。
### 组合总和
给定一个**无重复元素**的数组 `candidates` 和一个目标数 `target` ,找出 `candidates` 中所有可以使数字和为 `target` 的组合。
示例:
```
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
输出:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
```
数组元素可能重复。使用回溯算法。
剪枝:

去重复组合:

```java
class Solution {
private List> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
if (candidates == null || candidates.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
Arrays.sort(candidates);//排序方便回溯剪枝
Deque path = new ArrayDeque<>();//作为栈来使用,效率高于Stack;也可以作为队列来使用,效率高于LinkedList;线程不安全
combinationSum2Helper(candidates, target, 0, path);
return ans;
}
public void combinationSum2Helper(int[] arr, int target, int start, Deque path) {
if (target == 0) {
ans.add(new ArrayList(path));
}
for (int i = start; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (target < arr[i]) {//剪枝
return;
}
if (i > start && arr[i] == arr[i - 1]) {//在一个层级,会产生重复
continue;
}
path.addLast(arr[i]);
combinationSum2Helper(arr, target - arr[i], i + 1, path);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
```
### 全排列
给定一个 **没有重复** 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
示例:
```
输入: [1,2,3]
输出:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
```
使用回溯。注意与组合总和的区别(数字有无顺序)。
```java
class Solution {
private List> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List> permute(int[] nums) {
boolean[] flag = new boolean[nums.length];
ArrayDeque path = new ArrayDeque<>();
permuteHelper(nums, flag, path);
return ans;
}
private void permuteHelper(int[] nums, boolean[] flag, ArrayDeque path) {
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (flag[i]) {
continue;//继续循环
}
path.addLast(nums[i]);
flag[i] = true;
permuteHelper(nums, flag, path);
path.removeLast();
flag[i] = false;
}
}
}
```
### 全排列II
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列,返回所有不重复的全排列。注意与组合总和的区别。
1、排序;2、同一层级相同元素剪枝。参考自:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations-ii/solution/hui-su-suan-fa-python-dai-ma-java-dai-ma-by-liwe-2/

```java
class Solution {
private List> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
ArrayDeque path = new ArrayDeque<>();
boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];
Arrays.sort(nums);//切记
dps(nums, used, path);
return ans;
}
private void dps(int[] nums, boolean[] used, ArrayDeque path) {
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
if ((i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) && !used[i - 1]) {//同一层相同的元素,剪枝
continue;//继续循环,不是return退出循环
}
path.addLast(nums[i]);
used[i] = true;
dps(nums, used, path);
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
```
### 子集
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 *nums*,返回该数组所有可能的子集。解集不能包含重复的子集。
回溯。
```java
class Solution {
public List> subsets(int[] nums) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>()); //空集
return res;
}
Stack queue = new Stack<>();
subsetsHelper(res, queue, 0, nums);
return res;
}
public void subsetsHelper(List> res, Stack queue, int index, int[] nums) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(queue));
for (int i = index; i < nums.length; i++) {
queue.push(nums[i]);
subsetsHelper(res, queue, i + 1, nums);
queue.pop();
}
}
}
```
### 括号生成
使用深度优先算法。
```java
class Solution {
private List ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List generateParenthesis(int n) {
if (n <= 0) {
return ans;
}
dfs("", n, n);
return ans;
}
//left左括号剩下可用数目,right右括号剩下可用数目
private void dfs(String s, int left, int right) {
if (left > right || left < 0 || right < 0) {//右括号剩下的少,说明组合无效
return;
}
if (left == 0 && right == 0) {
ans.add(s);
}
dfs(s + "(", left - 1, right);
dfs(s + ")", left, right - 1);
}
}
```
### 子集II
给定一个可能包含重复元素的整数数组 ***nums***,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
```java
class Solution {
private List> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
Stack subset = new Stack<>();
subsetsWithDupHelper(nums, 0, subset);
return res;
}
private void subsetsWithDupHelper(int[] nums, int index, Stack subset) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(subset));
if (index >= nums.length) {
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i > index && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) { //i > index
continue;
}
subset.push(nums[i]);
subsetsWithDupHelper(nums, i + 1, subset);
subset.pop();
}
}
}
```
### 单词搜索
给定一个二维网格和一个单词,找出该单词是否存在于网格中。
```java
board =
[
['A','B','C','E'],
['S','F','C','S'],
['A','D','E','E']
]
给定 word = "ABCCED", 返回 true
给定 word = "SEE", 返回 true
给定 word = "ABCB", 返回 false
```
注意避免同一元素多次使用([A B C],A->B->A)。
```java
class Solution {
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
if (board == null || board.length == 0 || board[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
if (existHelper(board, i, j, word, 0)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean existHelper(char[][] board, int row, int col, String word, int index) {
if (index == word.length()) {
return true;
}
if (row < 0 || col < 0 || row >= board.length || col >= board[0].length || board[row][col] != word.charAt(index)) {
return false;
}
if (board[row][col] == word.charAt(index)) {
index++;
}
char tmp = board[row][col];
board[row][col] = '#'; //防止回溯自身
boolean result = existHelper(board, row - 1, col, word, index) ||
existHelper(board, row + 1, col, word, index) ||
existHelper(board, row, col - 1, word, index) ||
existHelper(board, row, col + 1, word, index);
board[row][col] = tmp;
return result;
}
}
```
### 电话号码的组合
回溯是一种通过穷举所有可能情况来找到所有解的算法。如果一个候选解最后被发现并不是可行解,回溯算法会舍弃它,并在前面的一些步骤做出一些修改,并重新尝试找到可行解。
时间复杂度n3
```java
class Solution {
private List ans = new ArrayList<>();
private String[] strs = {"abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
public List letterCombinations(String digits) {
if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0) {
return ans;
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
letterCombinationsHelper(sb, digits, 0);
return ans;
}
private void letterCombinationsHelper(StringBuilder sb, String digits, int index) {
if (index == digits.length()) {
ans.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
int num = digits.charAt(index) - '0' - 2;//数字2到9,对应strs下标0到7
for (int i = 0; i < strs[num].length(); i++) {
sb.append(strs[num].charAt(i));
letterCombinationsHelper(sb, digits, index + 1);
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);//function forgot,剪枝
}
}
}
```
### 复原ip
```java
class Solution {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
public List restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
dfs(s, 0, 0, new StringBuilder());
return res;
}
private void dfs(String s, int start, int ipIndex, StringBuilder sb) {
if (ipIndex == 4) {
if (start == s.length()) {
res.add(sb.substring(0, sb.length() - 1).toString());
}
return; //长度为4则返回
}
for (int i = start; i < start + 3 && i < s.length(); i++) {
String subStr = s.substring(start, i + 1);
int num = Integer.parseInt(subStr);
if (num > 255) {
return;
}
sb.append(subStr).append(".");
dfs(s, i + 1, ipIndex + 1, sb);
sb.delete(sb.length() - (i - start + 2), sb.length());
if(s.charAt(start) == '0') { //允许0.0.0.0,其他以0开头的剪枝
return;
}
}
}
}
```
### 格雷编码
[参考解法](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/gray-code/solution/gray-code-jing-xiang-fan-she-fa-by-jyd/)
```java
class Solution {
public List grayCode(int n) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(0);
int head = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = res.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
res.add(head + res.get(j));
}
head <<= 1;
}
return res;
}
}
```
## 贪心算法
贪心算法,是寻找**最优解问题**的常用方法,这种方法模式一般将求解过程分成**若干个步骤**,但每个步骤都应用贪心原则,选取当前状态下**最好/最优的选择**(局部最有利的选择),并以此希望最后堆叠出的结果也是最好/最优的解。
**贪婪法的基本步骤:**
1. 从某个初始解出发;
2. 采用迭代的过程,当可以向目标前进一步时,就根据局部最优策略,得到一部分解,缩小问题规模;
3. 将所有解综合起来。
### 买卖股票的最佳时机 II
**题目描述**:
给你一个整数数组 prices ,其中 prices[i] 表示某支股票第 i 天的价格。
在每一天,你可以决定是否购买和/或出售股票。你在任何时候 最多 只能持有 一股 股票。你也可以先购买,然后在 同一天 出售。
返回 你能获得的 最大 利润 。
**示例**:
```java
输入:prices = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:4
解释:在第 1 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天 (股票价格 = 5)的时候卖出, 这笔交易所能获得利润 = 5 - 1 = 4 。
总利润为 4 。
```
思路:可以尽可能地完成更多的交易,但不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
```java
//输入: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
//输出: 7
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
int tmp = prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
if (tmp > 0) {
profit += tmp;
}
}
return profit;
}
}
```
### 跳跃游戏
**题目描述**
给定一个非负整数数组 `nums` ,你最初位于数组的 **第一个下标** 。
数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
判断你是否能够到达最后一个下标。
**示例**:
```java
输入:nums = [2,3,1,1,4]
输出:true
解释:可以先跳 1 步,从下标 0 到达下标 1, 然后再从下标 1 跳 3 步到达最后一个下标。
```
解题思路:
1. 如果某一个作为 起跳点 的格子可以跳跃的距离是 3,那么表示后面 3 个格子都可以作为 起跳点
2. 可以对每一个能作为 起跳点 的格子都尝试跳一次,把 能跳到最远的距离 不断更新
3. 如果可以一直跳到最后,就成功了
```java
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return true;
}
int maxIndex = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (maxIndex >= i) {
maxIndex = Math.max(maxIndex, i + nums[i]);
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
```
### 加油站
**题目描述**
在一条环路上有 n 个加油站,其中第 i 个加油站有汽油 gas[i] 升。
你有一辆油箱容量无限的的汽车,从第 i 个加油站开往第 i+1 个加油站需要消耗汽油 cost[i] 升。你从其中的一个加油站出发,开始时油箱为空。
给定两个整数数组 gas 和 cost ,如果你可以绕环路行驶一周,则返回出发时加油站的编号,否则返回 -1 。如果存在解,则 保证 它是 唯一 的。
**示例**
```java
输入: gas = [1,2,3,4,5], cost = [3,4,5,1,2]
输出: 3
解释:
从 3 号加油站(索引为 3 处)出发,可获得 4 升汽油。此时油箱有 = 0 + 4 = 4 升汽油
开往 4 号加油站,此时油箱有 4 - 1 + 5 = 8 升汽油
开往 0 号加油站,此时油箱有 8 - 2 + 1 = 7 升汽油
开往 1 号加油站,此时油箱有 7 - 3 + 2 = 6 升汽油
开往 2 号加油站,此时油箱有 6 - 4 + 3 = 5 升汽油
开往 3 号加油站,你需要消耗 5 升汽油,正好足够你返回到 3 号加油站。
因此,3 可为起始索引。
```
**思路**:
1. 遍历一周,总获得的油量少于要花掉的油量必然没有结果;
2. 先苦后甜,记录遍历时所存的油量最少的站点,由于题目有解只有唯一解,所以从当前站点的下一个站点开始是唯一可能成功开完全程的。
```java
class Solution {
public int canCompleteCircuit(int[] gas, int[] cost) {
int minIdx=0;
int sum=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int num=0;
for (int i = 0; i < gas.length; i++) {
num+=gas[i]-cost[i];
if(num 0) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return tmp.next;
}
}
```
### 三数之和
[题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/3sum/)
**题目描述**
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
**示例**
```java
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
```
**思路**:
- 首先对数组进行排序,排序后固定一个数 nums[i]nums[i],再使用左右指针指向 nums[i]nums[i]后面的两端,数字分别为 nums[L]nums[L] 和
- nums[R]nums[R],计算三个数的和 sumsum 判断是否满足为 00,满足则添加进结果集
- 如果 nums[i]nums[i]大于 00,则三数之和必然无法等于 00,结束循环
- 如果 nums[i]nums[i] == nums[i-1]nums[i−1],则说明该数字重复,会导致结果重复,所以应该跳过
- 当 sumsum == 00 时,nums[L]nums[L] == nums[L+1]nums[L+1] 则会导致结果重复,应该跳过,L++L++
- 当 sumsum == 00 时,nums[R]nums[R] == nums[R-1]nums[R−1] 则会导致结果重复,应该跳过,R--R−−
**参考代码**:
```java
class Solution {
public List> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > 0) { //最左边的数字大于0,则sum不会等于0,退出
break;
}
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) { //去重复
continue;
}
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (sum == 0) {
res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right])); ///array to list
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) {
left++;
}
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {
right--;
}
left++;
right--;
} else if (sum > 0) {
right--;
} else {
left++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
```
### 环形链表
[题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/)
**题目描述**
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
**示例**
```java
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
```
**思路**
快慢指针。快指针每次走两步,慢指针走一步,相当于慢指针不动,快指针每次走一步,如果是环形链表,则一定会相遇。
```java
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode quick = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (quick != null && quick.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
quick = quick.next.next;
if (slow == quick) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
```
### 环形链表II
[题目链接](https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
**题目描述**
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
**示例**
```java
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点
```
**解题思路**
方法一:头结点到入环结点的距离为a,入环结点到相遇结点的距离为b,相遇结点到入环结点的距离为c。然后,当fast以slow的两倍速度前进并和slow相遇时,fast走过的距离是s的两倍,即有等式:a+b+c+b = 2(a+b) ,可以得出 a = c ,所以说,让fast和slow分别从相遇结点和头结点同时同步长出发,他们的相遇结点就是入环结点。
```java
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (true) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return null;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
break;
}
}
fast = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
```
方法二:先算出环的大小n,快指针先走n步,然后快慢指针一起走,相遇的地方即是环的入口。
```java
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
//快慢指针找出环的大小
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (fast == slow) {
break;
}
}
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return null;
}
int cycleSize = 1;
while (fast.next != slow) {
cycleSize++;
fast = fast.next;
}
//快慢指针重新从链表首部出发,快指针先走sizeOfCycle步
//然后两个指针同时一起走,步长为1,相遇节点即是环的入口
fast = head;
slow = head;
while (cycleSize-- > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
```
## 无重复字符的最长子串
滑动窗口。
```java
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
int maxLen = 0;
int left = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < s.length(); j++) { //i是左指针,j是右指针
if (map.containsKey(s.charAt(j))) {//!!子串中有相同的元素,左指针右移。类似tcp收到确认
left = Math.max(left, map.get(s.charAt(j)) + 1); //相同元素落在子串范围内,则更新左指针;不在子串范围则不更新。类似tcp:确认落在发送窗口内,则更新左指针;在发送窗口外则不更新
}
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, j - left + 1);
map.put(s.charAt(j), j);
}
return maxLen;
}
}
```
## 二叉树的最近公共祖先
[后序遍历思路](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/solution/236-er-cha-shu-de-zui-jin-gong-gong-zu-xian-hou-xu/)
```java
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if (left != null && right != null) {
return root;
} else {
return left == null ? right : left;
}
}
}
```
## 数组中的第K个最大元素
利用快速排序,每次得到pivot的下标,与(arr.length-1)比较,相等则为所求元素。
```java
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
int index = nums.length - k;
while (left < right) {
int pivot = partition(nums, left, right);
if (pivot == index) {
return nums[pivot];
} else if (index > pivot) {
left = pivot + 1;
} else {
right = pivot - 1;
}
}
return nums[left];
}
private int partition(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
int i = left, j = right;
median3(nums, left, right);
int pivot = nums[left];
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && nums[j] >= pivot) {
j--;
}
while (i < j && nums[i] <= pivot) {
i++;
}
if (i < j) {
swap(nums, i, j);
} else {
break;
}
}
nums[left] = nums[j];
nums[j] = pivot;
return j;
}
private void median3(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[left] > nums[mid]) {
swap(nums, left, mid);
}
if (nums[left] > nums[right]) {
swap(nums, left, right);
}
if (nums[mid] > nums[right]) {
swap(nums, mid, right);
}
swap(nums, left, mid);
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}
```
## 岛屿的数量
深度优先遍历,使用isVisited数组记录元素是否被访问过。
```java
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0 || grid[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
boolean[][] isVisited = new boolean[grid.length][grid[0].length];
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1' && !isVisited[i][j]) {
dfs(grid, isVisited, i, j);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
private void dfs(char[][] grid, boolean[][] isVisited, int i, int j) {
if (i < 0 || i >= grid.length || j < 0 || j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] == '0') {
return;
}
if (!isVisited[i][j]) {
isVisited[i][j] = true;
dfs(grid, isVisited, i + 1, j);
dfs(grid, isVisited, i - 1, j);
dfs(grid, isVisited, i, j + 1);
dfs(grid, isVisited, i, j - 1);
}
}
}
```
## 相交链表
解法一:两个指针a和b,a指向headA,b指向headB,两个指针同时出发。假如a先走到尽头,则a重新指向headB。然后b走到尽头,b重新指向headA。如果是相交链表,则a和b会相遇,否则a/b最终会指向null。
解法二:算出headA和headB的长度lenA、lenB,假如lenA较大,则先让headA走(lenA - lenB)步,然后headA和headB同时走,最终两者会相遇或者都指向null。
```java
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode a = headA;
ListNode b = headB;
while (a != b) {
a = a == null ? headB : a.next;
b = b == null ? headA : b.next;
}
return a;
}
}
```
## 二叉树的右视图
层序遍历,保存最右边树节点。
```java
class Solution {
public List rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Queue queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size-- > 0) { //先取size的值,再自减
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
if (size == 0) { //最右边的节点
res.add(node.val);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
```
## 整数反转
注意 int32 位溢出、正负号问题。
解法一:
```java
class Solution {
public int reverse(int x) {
long out = 0;
while (x != 0) {
out = out * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
if (out > Integer.MAX_VALUE || out < Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
return 0;
}
}
return (int)out;
}
}
```
解法二:
```java
class Solution {
public int reverse(int x) {
int out = 0;
while (x != 0) {
int tmp = x % 10;
//先判断再做运算,防止溢出;注意正负号
if (out > Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 || (out == Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 && tmp > Integer.MAX_VALUE % 10)) {
return 0;
} else if (out < Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 || (out == Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 && tmp < Integer.MIN_VALUE % 10 )) {
return 0;
}
out = out * 10 + tmp;
x /= 10;
}
return out;
}
}
```
## 二叉树的直径
二叉树的直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值。这条路径可能穿过也可能不穿过根结点。
```java
class Solution {
private int max = 0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
depth(root);
return max;
}
private int depth(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = depth(node.left);
int right = depth(node.right);
max = Math.max(max, left + right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
}
```
## 验证二叉搜索树
利用中序遍历。
```java
class Solution {
long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE; //最左节点为Integer.MIN_VALUE
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
if (!isValidBST(root.left)) {
return false;
}
if (pre >= root.val) {
return false;
}
pre = root.val; //更新pre
return isValidBST(root.right);
}
}
```
## 二叉树的最大深度
```java
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
```
## 回文链表
```java
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
//找到中间节点
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//链表后半部分反转
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = slow;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
while (pre != null && head != null) {
if (pre.val != head.val) {
return false;
}
pre = pre.next;
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
}
```
## LRU
双链表+HashMap实现。get和put操作都是O(1)时间复杂度。
```java
class LRUCache {
DoubleList list;
int capacity;
Map map;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
list = new DoubleList();
map = new HashMap<>();
}
public int get(int key) {
Node node = map.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
list.remove(node);
list.addFirst(node);
return node.val;
}
public void put(int key, int val) {
Node node = map.get(key);
if (node == null) {
node = new Node(key, val);
if (map.size() >= capacity) {
Node last = list.removeLast();
map.remove(last.key);
}
list.addFirst(node);
map.put(key, node);
} else {
list.remove(node);
node.val = val;
list.addFirst(node);
}
}
}
class Node {
int key;
int val;
Node pre, next;
public Node(int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
class DoubleList {
Node head, tail;
public DoubleList() {
head = new Node(0, 0);
tail = new Node(0, 0);
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
}
public void remove(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
node.pre.next = node.next;
node.next.pre = node.pre;
}
public Node removeLast() {
Node node = tail.pre;
if (node != head) {
remove(node);
return node;
}
return null;
}
public void addFirst(Node node) {
Node firstNode = head.next;
head.next = node;
node.pre = head;
node.next = firstNode;
firstNode.pre = node;
}
}
```
如果 Node 结构中只存储 val,那么当链表长度超过阈值需要淘汰旧节点时,便无法知道对应的 key,从而无法删除 map 中的键,造成错误。
```java
if (map.size() >= capacity) {
Node last = list.removeLast();
map.remove(last.key);
}
```
使用LinkedList不符合要求,因为remove(Object o)方法时间复杂度为O(N),需要遍历链表找到对应的元素再删除。传入remove的节点o不一定是链表内部的节点,故需要遍历链表进行比较,找到相等的节点。
```java
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
```
## 字符串相加
```java
class Solution {
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int tmp = 0;
int i = num1.length() - 1;
int j = num2.length() - 1;
while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || tmp > 0) {
int a = i >= 0 ? (num1.charAt(i--) - '0') : 0;
int b = j >= 0 ? (num2.charAt(j--) - '0') : 0;
int sum = a + b + tmp;
sb.append(sum % 10);
tmp = sum / 10;
}
return sb.reverse().toString(); //reverse()
}
}
```
## 两数之和
```java
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] result = new int[2];
Map map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
result[0] = map.get(nums[i]);
result[1] = i;
return result;
}
map.put(target - nums[i], i);
}
return result;
}
}
```
## 二叉树锯齿形层次遍历
使用两个栈实现。
```java
class Solution {
public List> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
//判空
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Stack s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack s2 = new Stack<>();
s1.push(root);
while (!s1.isEmpty() || !s2.isEmpty()) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
if (!s1.isEmpty()) {
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = s1.pop();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
s2.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
s2.push(node.right);
}
}
} else {
while (!s2.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = s2.pop();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.right != null) {
s1.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
s1.push(node.left);
}
}
}
res.add(list);
}
return res;
}
}
```
## 多数元素
投票算法。
```java
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int count = 1;
int maj = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (count == 0) {
maj = nums[i];
}
if (maj == nums[i]) {
count++;
} else {
count--;
}
}
return maj;
}
}
```
## 合并区间
给出一个区间的集合,请合并所有重叠的区间。
```
输入: intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
输出: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
解释: 区间 [1,3] 和 [2,6] 重叠, 将它们合并为 [1,6].
```
先对区间左边界排序 `Array.sort(arr, (i1, i2) -> i1[0] - i2[0])`,然后新建数组进行合并。
```java
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
if (intervals == null || intervals.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("array is null or array is empty");
}
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]); //lambda表达式写法,返回值是int
int index = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {
if (intervals[index][1] < intervals[i][0]) {
intervals[++index] = intervals[i]; //++index,先自增,再取值
} else {
intervals[index][1] = Math.max(intervals[i][1], intervals[index][1]);
}
}
return Arrays.copyOf(intervals, index + 1); //第二个参数是数组长度
}
}
```
## 对称的二叉树
```java
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
return isMirror(root.left, root.right);
}
public boolean isMirror(TreeNode node1, TreeNode node2) {
if (node1 == null && node2 == null) {
return true;
}
if (node1 == null || node2 == null || node1.val != node2.val) {
return false;
}
return isMirror(node1.left, node2.right) && isMirror(node1.right, node2.left);
}
}
```
## 用栈实现队列
```java
class MyQueue {
private Stack s1;
private Stack s2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
s1 = new Stack<>();
s2 = new Stack<>();
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if (!s2.isEmpty()) {
return s2.pop();
}
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
return s2.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
if (!s2.isEmpty()) {
return s2.peek();
}
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
return s2.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty();
}
}
```
## 最小栈
使用两个栈实现,data存放数据,minHelper存放最小值。当入栈的数据小于或等于minHelper栈顶的数据时,将该数据放进minHelper。
```java
class MinStack {
private Stack data;
private Stack minHelper;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
data = new Stack<>();
minHelper = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
data.push(x);
if (minHelper.isEmpty() || minHelper.peek() >= x) { //minHelper栈顶与x相等,也入栈(0,1,0)
minHelper.push(x);
}
}
public void pop() {
if (!data.isEmpty()) {
int x = data.pop();
if (x == minHelper.peek()) {
minHelper.pop();
}
}
}
public int top() {
if (!data.isEmpty()) {
return data.peek();
}
throw new RuntimeException("栈为空");
}
public int getMin() {
if (!data.isEmpty()) {
return minHelper.peek();
}
throw new RuntimeException("栈为空");
}
}
```
## 二叉树的完全性检验
层序遍历,当且仅当存在两个相邻节点:前一个为null,后一个不为null时,则不是完全二叉树。
```java
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 6
层序遍历序列为:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, null, 6],其中 null 出现在了6前面,所以不是完全二叉树
```
```java
class Solution {
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode pre = root;
TreeNode cur = root;
list.addLast(root);
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
cur = list.removeFirst();
if (cur != null) {
if (pre == null) {
return false;
}
list.addLast(cur.left);
list.addLast(cur.right);
}
pre = cur;
}
return true;
}
}
```
## 排序链表
归并排序。
```java
//输入: 4->2->1->3
//输出: 1->2->3->4
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return mergeSort(head);
}
public ListNode mergeSort(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode rHead = slow.next;
slow.next = null; //断开链表
ListNode l = mergeSort(head);
ListNode r = mergeSort(rHead);
return merge(l, r);
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode l, ListNode r) {
ListNode tmp = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = tmp;
while (l != null && r != null) {
if (l.val > r.val) {
cur.next = r;
r = r.next;
} else {
cur.next = l;
l = l.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = l == null ? r : l;
return tmp.next;
}
}
```
[排序链表快速排序](https://www.cnblogs.com/morethink/p/8452914.html)
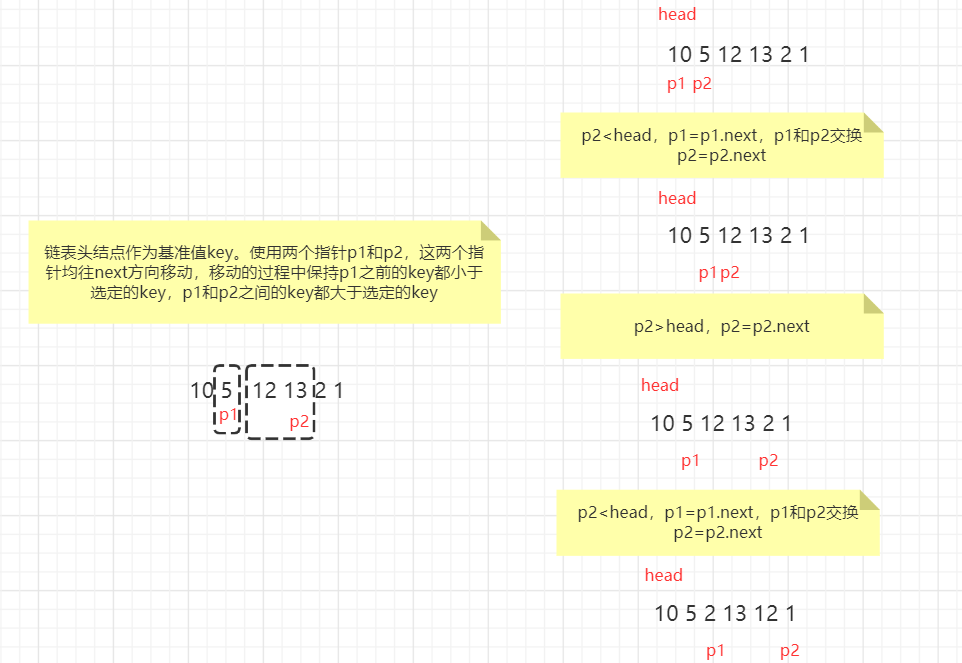
```java
//快速排序
//链表头结点作为基准值key。使用两个指针p1和p2,这两个指针均往next方向移动,移动的过程中保持p1之前的key都小于选定的key,p1和p2之间的key都大于选定的key,那么当p2走到末尾时交换p1与key值便完成了一次切分。
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return quickSort(head, null);
}
private ListNode quickSort(ListNode head, ListNode tail) {
if (head != tail) {
ListNode node = quickSortHelper(head, tail);
quickSort(head, node);
quickSort(node.next, tail);
}
return head;
}
private ListNode quickSortHelper(ListNode head, ListNode tail) {
ListNode p1 = head, p2 = head.next;
while (p2 != tail) {
if (p2.val < head.val) {
p1 = p1.next;
int tmp = p1.val;
p1.val = p2.val;
p2.val = tmp;
}
p2 = p2.next;
}
if (p1 != head) {
int tmp = p1.val;
p1.val = head.val;
head.val = tmp;
}
return p1;
}
}
```
## 最长连续序列
```java
输入:nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
输出:4
解释:最长数字连续序列是 [1, 2, 3, 4]。它的长度为 4。
```
将数组存入set。遍历数组,对`num[i]`前后连续的数字进行计数,并将set中的这些数字移除,避免重复计算。
比如`[10, 9, 8, 7, 11, 14]`,存入set。遍历第一个元素10,set移除10,10前面有7-8-9,后面有11,连续序列长度为5,将set中的7-8-9-11移除,后续遍历到7-8-9-11,直接跳过。
```java
class Solution {
public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
Set set = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : nums) {
set.add(num);
}
int len = 0;
int maxLen = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
len = 1;
if (set.remove(num)) {
int cur = num;
while (set.remove(--cur)) {
len++;
}
cur = num;
while (set.remove(++cur)) {
len++;
}
maxLen = maxLen > len ? maxLen : len;
}
}
return maxLen;
}
}
```
## 字符串转换整数*
```
"4193 with words" 4193
" -42" -42
"words and 987" 0
```
注意边界,空格,int 32位最大值最小值。
```java
class Solution {
public int myAtoi(String str) {
if (str == null || str.trim().length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
str = str.trim();
if (str.charAt(0) != '-' && str.charAt(0) != '+' &&
!Character.isDigit(str.charAt(0))) {
return 0;
}
boolean positive = str.charAt(0) == '-' ? false : true;
int i = Character.isDigit(str.charAt(0)) ? 0 : 1;
long out = 0;
while (i < str.length() && Character.isDigit(str.charAt(i))) {
out = out * 10 + (str.charAt(i++) - '0');
if (positive && out > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
if (!positive && out > 1L + Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
}
return positive ? (int)out : (int)(-1 * out);
}
}
```
## 回文数
将数字后半段反转,跟数字前半段相比即可。
```java
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
//排除负数和整十的数
if (x < 0 || (x % 10 == 0 && x != 0)) {
return false;
}
int reverseNum = 0;
//反转x的后半段数字,再做比较即可
while(x > reverseNum) {
reverseNum = reverseNum * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
//x为奇数位时,转换后reverseNum会比x多一位
//如x为1234321,转换后reverseNum为1234,x为123
return x == reverseNum || x == reverseNum / 10;
}
}
```
## 盛最多水的容器

左右指针,数字小的指针往数字大的指针移动,面积才有可能变大。注意左右指针数字相同的情况。
```java
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int maxArea = 0;
int left = 0;
int right = height.length - 1;
while(left < right) {
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, Math.min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left));
if(height[left] > height[right]) {
right--;
} else {
left++;
}
}
return maxArea;
}
}
```
## 四数之和
时间复杂度n3
```java
class Solution {
public List> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length < 4) {
return ans;
}
int len = nums.length;
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) { // forgot, 去重复
continue;
}
for (int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) {//j大于i+1才去重复
continue;
}
int left = j + 1;
int right = len - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (sum == target) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right]));
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) {
left++;//去重复
}
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {
right--;//去重复
}
left++;//forgot
right--;//forgot
} else if (sum < target) {
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
```
## 有效的括号
使用栈实现。
```java
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
switch (s.charAt(i)) {
case '(':
stack.push(')');//存进相反符号
break;
case '[':
stack.push(']');
break;
case '{':
stack.push('}');
break;
default:
if (stack.isEmpty() || s.charAt(i) != stack.pop()) {
return false;
}
break;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
```
## 两两交换链表中的节点
使用递归实现。
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode left = head;
ListNode right = head.next;
if (right == null) {
right = left;
} else {
left.next = swapPairs(right.next);
right.next = left;
}
return right;
}
}
```
## 合并两个有序列表
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode ans = new ListNode(0);
ListNode tmp = ans;
while (l1 != null && l2!= null) {
if (l1.val > l2.val) {
tmp.next = l2; //tmp.next = new ListNode(l2.val); 没必要这么做
l2 = l2.next;
} else {
tmp.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
tmp.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return ans.next;
}
}
```
## 删除排序数组的重复项
使用快慢指针。
```java
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int slow = 0;
for (int fast = 1; fast < nums.length; fast++) {
if (nums[slow] != nums[fast]) {
slow++;
nums[slow] = nums[fast];
}
}
return slow + 1;
}
}
```
## 两数相除
Integer.MIN_VALUE 转为正数会溢出,故将 dividend 和 divisor 都转化为负数。**两个负数相加溢出会大于0。**
```java
class Solution {
//dividend / divisor
public int divide(int dividend, int divisor) {
if (dividend == Integer.MIN_VALUE && divisor == -1) {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
if (divisor == 1) { //不加上会超时
return dividend;
}
int sign = 1;
if ((dividend < 0 && divisor > 0) || (dividend > 0 && divisor < 0)) {
sign = -1;
}
int a = dividend > 0 ? -dividend : dividend;
int b = divisor > 0 ? -divisor : divisor;
if (a > b) {
return 0;
}
int ans = divideHelper(a, b);
return sign > 0 ? ans : -ans;
}
private int divideHelper(int a, int b) {
if (a > b) {
return 0;
}
int count = 1;
int tmp = b;
while (tmp + tmp >= a && tmp + tmp < 0) { //两个负数相加溢出会大于0
tmp += tmp;
count += count;
}
return count + divideHelper(a - tmp, b);
}
}
```
## 下一个排列
将给定数字序列重新排列成字典序中下一个更大的排列。如果不存在下一个更大的排列,则将数字重新排列成最小的排列(即升序排列)。
```
1,2,3 → 1,3,2
3,2,1 → 1,2,3
1,1,5 → 1,5,1
```
思路:
1、从后往前找到a[i-1] < a[i];
2、找到a[j] > a[i - 1]> a[j - 1];
3、调换a[i - 1] 和 a[j] 位置;
4、翻转a[i]以后的数组;
特殊情况:数组降序排列,返回升序的数组。

```java
class Solution {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length <= 1) {
return;
}
int i = nums.length - 1;
while (i > 0 && nums[i] <= nums[i - 1]) {//注意等号
i--;
}
if (i == 0) {
reverse(nums, 0);
return;
}
int j = i;
for (; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i - 1] >= nums[j]) {//注意等号
break;
}
}
j--;//取前一个元素
swap(nums, i - 1, j);
reverse(nums, i);
}
public void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
public void reverse(int[] nums, int i) {
int j = nums.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
swap(nums, i++, j--);
}
}
}
```
## 在排序数组中查找第一个和最后一个位置
给定一个按照升序排列的整数数组 `nums`,和一个目标值 `target`。找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。算法时间复杂度必须是 *O*(log *n*) 级别。
```java
//输入: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8
//输出: [3,4]
class Solution {
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
int left = searchRangeHelper(nums, target);
int right = searchRangeHelper(nums, target + 1);//复用代码
if (left == nums.length || nums[left] != target) {//left==nums.length数组元素比target小
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
return new int[]{left, right - 1};
}
private int searchRangeHelper(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length;//特殊情况[1] 1
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return left;
}
}
```
## 移除元素
给你一个数组 *nums* 和一个值 *val*,你需要 **[原地](https://baike.baidu.com/item/原地算法)** 移除所有数值等于 *val* 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。仅使用 O(1) 额外空间。
```
给定 nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2,
函数应该返回新的长度 5, 并且 nums 中的前五个元素为 0, 1, 3, 0, 4。
```
前后双指针。
```java
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int start = 0;
int end = nums.length - 1;
while (start < end) {
if (nums[start] == val) {
nums[start] = nums[end];
end--;
} else {
start++;
}
}
return nums[start] == val ? start : start + 1;//需判断start处元素
}
}
```
## 字符串相乘
参考自:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/multiply-strings/solution/you-hua-ban-shu-shi-da-bai-994-by-breezean/

```java
class Solution {
public String multiply(String num1, String num2) {
if (num1.equals("0") || num2.equals("0")) { //乘0
return "0";
}
int[] arr = new int[num1.length() + num2.length()];
for (int i = num1.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int m = num1.charAt(i) - '0';
for (int j = num2.length() - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
int n = num2.charAt(j) - '0';
int sum = arr[i + j + 1] + m * n;
arr[i + j + 1] = sum % 10;
arr[i + j] += sum / 10; //+=,不能忘了原先的数
}
}
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder("");
if (arr[0] != 0) {
ans.append(arr[0]);
}
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
ans.append(arr[i]);
}
return ans.toString();
}
}
```
## 有效的数独
判断一个 9x9 的数独是否有效。只需要根据以下规则,验证已经填入的数字是否有效即可。
数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。
关键在于找到子数独的规律:`box_index = (row / 3) * 3 + columns / 3`
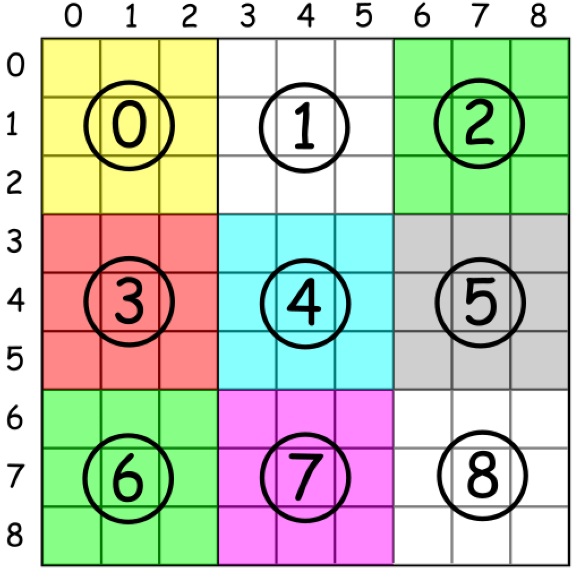
```java
class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
int[][] row = new int[9][9]; //二维数组初始化
int[][] column = new int[9][9];
int[][] box = new int[9][9];
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
continue;
}
int num = board[i][j] - '1';//数字1-9对应下标0-8
int boxIndex = (i/3)*3 + j/3;
if (row[i][num] > 0 || column[j][num] > 0 || box[boxIndex][num] > 0) {
return false;
}
row[i][num] = 1;
column[j][num] = 1;
box[boxIndex][num] = 1;
}
}
return true;
}
}
```
## 实现 strStr()
给定一个 haystack 字符串和一个 needle 字符串,在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串出现的第一个位置 (从0开始)。如果不存在,则返回 -1。
kmp算法,参考自:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-strstr/solution/kmp-suan-fa-xiang-jie-by-labuladong/
```java
class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
if (needle.equals("")) {
return 0;
}
if (needle.length() > haystack.length()) {
return -1;
}
int len = needle.length();
int[][] next = new int[len][256];
next[0][needle.charAt(0)] = 1;
int X = 0;
//构建状态转移图
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
for (int c = 0; c < 256; c++) {
if (needle.charAt(i) == c) {
next[i][c] = i + 1;//推进状态
} else {
next[i][c] = next[X][c];
}
}
X = next[X][needle.charAt(i)];//更新影子状态
}
int m = 0;//needle初始态
for (int i = 0; i < haystack.length(); i++) {
m = next[m][haystack.charAt(i)];//计算needle下一状态
//到达终止态
if (m == len) {
return i - len + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
```
## 字母异位词分组
将字符串转化成字符数组并排序。

```java
class Solution {
public List> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) {
return new ArrayList();
}
Map ans = new HashMap<>();
for (String s : strs) {
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(arr);
String key = String.valueOf(arr);
if (!ans.containsKey(key)) {
ans.put(key, new ArrayList());
}
ans.get(key).add(s);
}
return new ArrayList(ans.values());//没有<>
}
}
```
## pow(x, n)
快速幂算法。
```java
class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 1.0;
}
if (n == -1) {//负数边界
return 1 / x;
}
double res = myPow(x, n / 2);
double ans = 0;
if (n % 2 == 0) {
ans = res * res;
} else {
ans = n > 0 ? res * res * x : res * res / x;
}
return ans;
}
}
```
## 旋转图像
给定一个 *n* × *n* 的二维矩阵表示一个图像。将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。
先转置,然后翻转每一行。
```java
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length <= 1) {
return;
}
//转置
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < matrix.length; j++) {
int tmp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
matrix[j][i] = tmp;
}
}
//翻转每一行
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.length / 2; j++) {
int tmp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i][matrix.length - j - 1];
matrix[i][matrix.length - j - 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
```
## 螺旋矩阵
```
输入:
[
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5, 6 ],
[ 7, 8, 9 ]
]
输出: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
```
定义上下左右四个边界。注意边界判断。
```java
class Solution {
public List spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
int top = 0;
int bottom = matrix.length - 1;
int left = 0;
int right = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (true) {
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
ans.add(matrix[top][i]);
}
if (++top > bottom) {
break;
}
for (int j = top; j <= bottom; j++) {
ans.add(matrix[j][right]);
}
if (--right < left) {
break;
}
for (int m = right; m >= left; m--) {
ans.add(matrix[bottom][m]);
}
if (--bottom < top) {
break;
}
for (int n = bottom; n >= top; n--) {
ans.add(matrix[n][left]);
}
if (++left > right) {
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
```
## 螺旋矩阵II
给定一个正整数 *n*,生成一个包含 1 到 *n*2 所有元素,且元素按顺时针顺序螺旋排列的正方形矩阵。
```
输入: 3
输出:
[
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 8, 9, 4 ],
[ 7, 6, 5 ]
]
```
定义上下左右边界。
```java
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
int top = 0;
int bottom = n - 1;
int[][] ans = new int[n][n];
int num = 1;
while (true) {
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
ans[top][i] = num++;//注意下标顺序
}
if (++top > bottom) {
break;
}
for (int j = top; j <= bottom; j++) {
ans[j][right] = num++;
}
if (--right < left) {
break;
}
for (int m = right; m >= left; m--) {
ans[bottom][m] = num++;
}
if (--bottom < top) {
break;
}
for (int k = bottom; k >= top; k--) {
ans[k][left] = num++;
}
if (++left > right) {
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
```
## 第 k 个排列
给出集合 [1,2,3,…,n],其所有元素共有 n! 种排列。
按大小顺序列出所有排列情况,并一一标记,当 n = 3 时, 所有排列如下:
"123"
"132"
"213"
"231"
"312"
"321"
给定 n 和 k,返回第 k 个排列。
[参考代码](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutation-sequence/comments/)
```java
class Solution {
/**
直接用回溯法做的话需要在回溯到第k个排列时终止就不会超时了, 但是效率依旧感人
可以用数学的方法来解, 因为数字都是从1开始的连续自然数, 排列出现的次序可以推
算出来, 对于n=4, k=15 找到k=15排列的过程:
1 + 对2,3,4的全排列 (3!个)
2 + 对1,3,4的全排列 (3!个) 3, 1 + 对2,4的全排列(2!个)
3 + 对1,2,4的全排列 (3!个)-------> 3, 2 + 对1,4的全排列(2!个)-------> 3, 2, 1 + 对4的全排列(1!个)-------> 3214
4 + 对1,2,3的全排列 (3!个) 3, 4 + 对1,2的全排列(2!个) 3, 2, 4 + 对1的全排列(1!个)
确定第一位:
k = 14(从0开始计数)
index = k / (n-1)! = 2, 说明第15个数的第一位是3
更新k
k = k - index*(n-1)! = 2
确定第二位:
k = 2
index = k / (n-2)! = 1, 说明第15个数的第二位是2
更新k
k = k - index*(n-2)! = 0
确定第三位:
k = 0
index = k / (n-3)! = 0, 说明第15个数的第三位是1
更新k
k = k - index*(n-3)! = 0
确定第四位:
k = 0
index = k / (n-4)! = 0, 说明第15个数的第四位是4
最终确定n=4时第15个数为3214
**/
public String getPermutation(int n, int k) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
List candidates = new ArrayList<>();
//阶乘
int[] arr = new int[n + 1];
arr[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) {
candidates.add(i);
arr[i] = arr[i - 1] * i;
}
k--;
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
int index = k / arr[j];
k -= arr[j] * index;
sb.append(candidates.remove(index));
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
```
## 简化路径
返回的规范路径必须始终以斜杠 / 开头,并且两个目录名之间必须只有一个斜杠 /。最后一个目录名(如果存在)不能以 / 结尾。此外,规范路径必须是表示绝对路径的最短字符串。
使用栈实现。
```java
//输入:"/a/./b/../../c/"
//输出:"/c"
class Solution {
public String simplifyPath(String path) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
String[] strs = path.split("/");
for (String s : strs) {
if ("..".equals(s)) {
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
stack.pop();
}
continue;//只要是"..",就执行下一个循环,不能放入栈
}
if (!"".equals(s) && !".".equals(s)) {
stack.push(s);
}
}
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return "/";
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int size = stack.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
sb.append("/").append(stack.get(i));//tips
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
```
## 矩阵置零
给定一个 *m* x *n* 的矩阵,如果一个元素为 0,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为 0。请使用**[原地](http://baike.baidu.com/item/原地算法)**算法。
[参考解法](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/set-matrix-zeroes/solution/ju-zhen-zhi-ling-by-leetcode/)
1. 遍历整个矩阵,如果 cell[i][j] == 0 就将第 i 行和第 j 列的第一个元素标记。
2. 第一行和第一列的标记是相同的,都是 cell[0][0],所以需要一个额外的变量告知第一列是否被标记,同时用 cell[0][0] 继续表示第一行的标记。
3. 然后,从第二行第二列的元素开始遍历,如果第 r 行或者第 c 列被标记了,那么就将 cell[r][c] 设为 0。这里第一行和第一列的作用就相当于方法一中的 row_set 和 column_set 。
4. 然后我们检查是否 cell[0][0] == 0 ,如果是则赋值第一行的元素为零。
5. 然后检查第一列是否被标记,如果是则赋值第一列的元素为零。
```java
class Solution {
public void setZeroes(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) {
return;
}
boolean isCol = false;
int rows = matrix.length;
int cols = matrix[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
if (matrix[i][0] == 0) {
isCol = true;
}
for (int j = 1; j < cols; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 0) {
matrix[i][0] = 0;
matrix[0][j] = 0;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < cols;j++) {
if (matrix[i][0] == 0 || matrix[0][j] == 0) {
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
if (matrix[0][0] == 0) {//顺序
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
matrix[0][j] = 0;
}
}
if (isCol) {//顺序
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
matrix[i][0] = 0;
}
}
}
}
```
## 搜索二维矩阵
- 每行中的整数从左到右按升序排列。
- 每行的第一个整数大于前一行的最后一个整数。
```java
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if (null == matrix || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
int rows = matrix.length;
int cols = matrix[0].length;
int left = 0;
int right = rows * cols - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) >> 1; //!
int val = matrix[mid / cols][mid % cols]; //cols!不是rows
if (target == val) {
return true;
} else if (target > val) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return false;
}
}
```
## 颜色分类
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色,一共 *n* 个元素的数组,**[原地](https://baike.baidu.com/item/原地算法)**对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
三指针。
```java
class Solution {
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return;
}
int p1 = 0, cur = 0, p2 = nums.length - 1;
while (cur <= p2) { //边界,nums全为1的情况
if (nums[cur] == 0) {
int tmp = nums[p1];
nums[p1++] = 0;
nums[cur++] = tmp; //cur++
} else if (nums[cur] == 2) {
int tmp = nums[p2];
nums[p2--] = 2;
nums[cur] = tmp; //nums[cur]可能为2,不自增
} else {
cur++;
}
}
}
}
```
## 组合
给定两个整数 *n* 和 *k*,返回 1 ... *n* 中所有可能的 *k* 个数的组合。回溯。剪枝优化。

```java
class Solution {
public List> combine(int n, int k) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (n <= 0 || k <= 0 || n < k) {
return res;
}
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
combineHelper(res, stack, 1, n, k);
return res;
}
public void combineHelper(List> res, Stack stack, int index,int n, int k) {
if (stack.size() == k) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(stack));
return;
}
// i 的极限值满足: n - i + 1 = (k - pre.size())。
// 【关键】n - i + 1 是闭区间 [i,n] 的长度。
// k - pre.size() 是剩下还要寻找的数的个数。
for (int i = index; i <= n - (k - stack.size()) + 1; i++) {
stack.push(i);
combineHelper(res, stack, i + 1, n, k);
stack.pop();
}
}
}
```
## 删除排序数组的重复项
给定一个排序数组,你需要在**[原地](http://baike.baidu.com/item/原地算法)**删除重复出现的元素,使得每个元素最多出现两次,返回移除后数组的新长度。双指针。
```java
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int left = 0;
int right = 1;
int count = 1;
while (right < nums.length) {
if (nums[right] == nums[left]) {
if (count < 2) {
nums[++left] = nums[right++];
} else {
right++;
}
count++;
} else {
count = 1;
nums[++left] = nums[right++];
}
}
return left + 1;
}
}
```
## 搜索旋转排序数组II
假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。编写一个函数来判断给定的目标值是否存在于数组中。
```java
class Solution {
public boolean search(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return false;
}
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return true;
}
if (nums[left] < nums[mid]) {
if (target >= nums[left] && target <= nums[mid]) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
} else if (nums[mid] < nums[right]) {
if (target >= nums[mid] && target <= nums[right]) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
} else {
if (nums[left] == nums[mid]) { //[3,1,1] 3
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
```
## 删除排序链表的重复元素
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode pre = head, cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == pre.val) {
cur = cur.next;
continue;
}
pre.next = cur;
cur = cur.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
pre.next = null; //末尾相同元素,断开尾巴 [1,1,2,3,3]
return head;
}
}
```
## 分隔链表
哑节点;断尾,避免环形链表。
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode left = new ListNode(0); //哑节点
ListNode right = new ListNode(0);
ListNode leftTmp = left, rightTmp = right;
while (head != null) {
if (head.val < x) {
leftTmp.next = head;
leftTmp = leftTmp.next;
} else {
rightTmp.next = head;
rightTmp = rightTmp.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
rightTmp.next = null; //断开尾巴,防止链表成环
leftTmp.next = right.next;
return left.next;
}
}
```
## 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
使用 map 存放下标。
```java
class Solution {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if (preorder == null || preorder.length == 0) {
return null;
}
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return buildTreeHelper(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode buildTreeHelper(int[] preorder, int pStart, int pEnd, int[] inorder, int iStart, int iEnd) {
if (preorder == null || preorder.length == 0 || pStart > pEnd) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[pStart]);
int index = map.get(preorder[pStart]);
int leftNum = index - iStart;
root.left = buildTreeHelper(preorder, pStart + 1, pStart + leftNum, inorder, iStart, index - 1);
root.right = buildTreeHelper(preorder, pStart + leftNum + 1, pEnd, inorder, index + 1, iEnd);
return root;
}
}
```
## 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
只返回一个可能的答案。
```java
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null) {
return null;
}
return buildTree(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return null;
}
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = buildTree(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = buildTree(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
}
```
## 有序链表转换二叉搜索树
快慢指针。
```java
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode mid = locateMidNode(head);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(mid.val);
if (mid == head) {
return root;
}
root.left = sortedListToBST(head);
root.right = sortedListToBST(mid.next);
return root;
}
public ListNode locateMidNode(ListNode node) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode slow = node;
ListNode fast = node;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
if (pre != null) {
pre.next = null;//从中点的前一个节点断开链表
}
return slow;
}
}
```
## 平衡二叉树
递归解法。
```java
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return height(root) != -1;
}
private int height(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = height(root.left);
int right = height(root.right);
if (left < 0 || right < 0 || Math.abs(left - right) > 1) {
return -1;
}
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
}
```
## 二叉树的最小深度
注意当左子树或者右子树不存在的情况,如[1, 2]。
```java
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = minDepth(root.left);
int right = minDepth(root.right);
return (root.left == null || root.right == null) ? left + right + 1 : Math.min(left, right) + 1; //[1, 2]
}
}
```
## 二叉树展开为链表
```java
1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
//找到 1 的左子树2的最右节点a,1 的右子树作为a的右子树
1
/
2
/ \
3 4
\
5
\
6
//左子树变右子树
1
\
2
/ \
3 4
\
5
\
6
//找到3的最右节点,2的右子树变成3的右子树
1
\
2
/
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
//2的左子树变成2的右子树
```
[参考题解](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/solution/xiang-xi-tong-su-de-si-lu-fen-xi-duo-jie-fa-by--26/)
```java
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
while (root != null) {
if (root.left == null) {
root = root.right;
} else {
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
while (tmp.right != null) {
tmp = tmp.right;
}
tmp.right = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
root = root.right;
}
}
}
}
```
## 杨辉三角II
给定一个非负索引 *k*,其中 *k* ≤ 33,返回杨辉三角的第 *k* 行,k 从0开始。

```java
class Solution {
public List getRow(int rowIndex) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(1);
int pre = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= rowIndex; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
int tmp = res.get(j);
res.set(j, tmp + pre);
pre = tmp;
}
res.add(1);
}
return res;
}
}
```
## 验证回文串
给定一个字符串,验证它是否是回文串,只考虑字母和数字字符,可以忽略字母的大小写。输入"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama",输出 true。
```java
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return true;
}
s = s.toLowerCase();//toLowerCase()
int left = 0;
int right = s.length() - 1;
while (left < right) {
while (left < s.length() && !isValidChar(s.charAt(left))) {
left++;
}
while (right > 0 && !isValidChar(s.charAt(right))) {
right--;
}
if (left < right && s.charAt(left) != s.charAt(right)) {
return false;
}
left++;//warn
right--;//warn
}
return true;
}
private boolean isValidChar(char c) {
return (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') || (c >= '0' && c <= '9');
}
}
```
## 被围绕的区域
给定一个二维的矩阵,包含 `'X'` 和 `'O'`。
找到所有被 `'X'` 围绕的区域,并将这些区域里所有的 `'O'` 用 `'X'` 填充。
```
X X X X
X O O X
X X O X
X O X X
```
深度优先搜索。将与边界连通的O替换为#,最后将其他与边界不连通的O替换为X,将#还原为O。
```java
class Solution {
public void solve(char[][] board) {
if (board == null || board.length == 0 || board[0].length == 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
boolean isEdge = i == 0 || j == 0 || i == board.length - 1 || j == board[0].length - 1;
if (isEdge) {
dfs(board, i, j);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'O') {
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
if (board[i][j] == '#') {
board[i][j] = 'O';
}
}
}
}
private void dfs(char[][] arr, int i, int j) {
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= arr.length || j >= arr[0].length || arr[i][j] == 'X' || arr[i][j] == '#') {
return;
}
arr[i][j] = '#';
dfs(arr, i - 1, j);
dfs(arr, i + 1, j);
dfs(arr, i, j - 1);
dfs(arr, i, j + 1);
}
}
```
## 单词接龙
```
输入:
beginWord = "hit",
endWord = "cog",
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
输出: 5 一个最短转换序列是 "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog",返回它的长度 5。
```
已知目标顶点的情况下,可以分别从起点和目标顶点(终点)执行广度优先遍历,直到遍历的部分有交集。这种方式搜索的单词数量会更小一些。
判断当前单词可以转换成哪些候选单词(未访问的单词),有两种思路:
1、遍历所有候选单词,判断当前单词是否可以转换成这个候选单词。
2、因为单词是由a~z这有限数量的字符组成的,可以遍历当前单词能转换成的所有单词,判断其是否包含在候选单词中。候选单词用HashSet保存,可以大大提高判断包含关系的性能。
当单词总数量庞大的时候,之前代码用到的思路1耗时就会很长。而当单词的字符串数量、单词长度很大时,思路2耗时就会更长。实际情况下,一般单词不会很长,字符也是固定的26个小写字母,因此思路2的性能会好很多。
**假如单词有10个字母,候选单词有500个。思路1需要10*500=5000次比较;思路2只需要26\*10=260次比较。**
采用思路2的话,则双向BFS可以从节点更少的一端遍历,优化性能。假如beginWord有5个单词,endWords有10个单词,则从beginWords端进行遍历,需要5\*26*10次比较;从endWords端进行遍历的话,需要10\*26\*10次比较。
```java
class Solution {
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List wordList) {
Set wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordList);
if (wordSet.size() == 0 || !wordSet.contains(endWord)) {
return 0;
}
int step = 1;
Set beginWords = new HashSet<>();
beginWords.add(beginWord);
Set endWords = new HashSet<>();
endWords.add(endWord);
Set visited = new HashSet<>();
visited.addAll(beginWords);
visited.addAll(endWords);
while (!beginWords.isEmpty() && !endWords.isEmpty()) {
if (beginWords.size() > endWords.size()) {
Set tmp = beginWords;
beginWords = endWords;
endWords = tmp;
}
Set nextLevelSet = new HashSet<>();
for (String word : beginWords) {
if (oneLetterDiff(word, endWords, wordSet, visited, nextLevelSet)) {
return step + 1;//需要加1
}
}
beginWords = nextLevelSet;//从nextLevelSet开始新的遍历
step++;
}
return 0;
}
private boolean oneLetterDiff(String word, Set endWords, Set wordSet, Set visited, Set nextLevelSet) {
char[] charArr = word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char originChar = charArr[i];
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {
if (originChar == c) {
continue;
}
charArr[i] = c;
String newWord = String.valueOf(charArr);//api
if (wordSet.contains(newWord)) {
if (endWords.contains(newWord)) {
return true;
}
if (!visited.contains(newWord)) {
nextLevelSet.add(newWord);
visited.add(newWord);
}
}
}
//回溯
charArr[i] = originChar;
}
return false;
}
}
```
## 求根到叶子节点数字之和
```java
// 输入: [1,2,3]
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// 输出: 25
class Solution {
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return sumNumbersHelper(root, 0);
}
private int sumNumbersHelper(TreeNode node, int sum) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
if (sum > Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 || (sum == Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 && node.val > Integer.MAX_VALUE % 10)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("exceed max int value");
}
sum = sum * 10 + node.val;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return sum;
}
return sumNumbersHelper(node.right, sum) + sumNumbersHelper(node.left, sum);
}
}
```
## 克隆图
深度优先搜索。
```java
class Solution {
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
Map lookup = new HashMap<>();
return dfs(node, lookup);
}
private Node dfs(Node node, Map lookup) {
if (node == null) return null;
if (lookup.containsKey(node)) return lookup.get(node);
Node clone = new Node(node.val, new ArrayList<>());
lookup.put(node, clone);
for (Node n : node.neighbors)clone.neighbors.add(dfs(n,lookup));
return clone;
}
}
```
广度优先搜索。遍历图的过程,未访问过的节点放入队列。
```java
class Solution {
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
return bfs(node, new HashMap());
}
private Node bfs(Node root, HashMap visitedMap) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
Queue queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(root);
Node cloneNode = new Node(root.val, new ArrayList<>());
visitedMap.put(root, cloneNode);
while (queue.size() != 0) {
Node node = queue.poll();
for (Node n : node.neighbors) {
Node tmp = visitedMap.get(n);
if (tmp == null) {
queue.offer(n); //未访问过的放入队列
tmp = new Node(n.val, new ArrayList<>());
visitedMap.put(n, tmp); //标记访问过
}
visitedMap.get(node).neighbors.add(tmp);
}
}
return visitedMap.get(root);
}
}
```
## 只出现一次的数字
异或运算:相同为0不同为1。两个相同数字的异或运算结果为00000000。
```java
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
res = res ^ num;
}
return res;
}
}
```
## 复制带随机指针的链表
方法1:回溯。在回溯的过程中记录已经访问过的节点,否则可能会进入死循环。
```java
class Solution {
Map visitedMap = new HashMap<>();
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) {
return head;
}
if (visitedMap.get(head) != null) {
return visitedMap.get(head);
}
Node node = new Node(head.val);
visitedMap.put(head, node);
node.next = copyRandomList(head.next);
node.random = copyRandomList(head.random);
return node;
}
}
```
方法2:1、复制节点并插入当前节点后面;2、再设定好random指针;3、最后分离出原链表与副本链表
如: 1->2->3->null => 1->1'->2->2'->3->3'->null ; 再分离出 1->2->3->null 与 1'->2'->3'->null
## 只出现一次的数字 II
方法1:每个数想象成32位的二进制,对于每一位的二进制的1和0累加起来必然是3N或者3N+1, 为3N代表目标值在这一位没贡献,3N+1代表目标值在这一位有贡献(=1),然后将所有有贡献的位|起来就是结果。这样做的好处是如果题目改成K个一样,只需要把代码改成cnt%k。
```java
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
int mask = 1 << i;
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
if ((nums[j] & mask) != 0) {
count++;
}
}
if (count % 3 != 0) {
res |= mask;
}
}
return res;
}
}
```
方法2:先排序。
```java
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i += 3) {
if(nums[i] != nums[i + 1]) {
return nums[i];
}
}
return nums[nums.length - 1];
}
}
```
## 重排链表
1、找到中间节点,从中间节点断开;2、翻转右边链表;;右边链表插入到左边链表的间隙
```java
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return;
}
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
//找到中间节点
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode reverse = slow.next;
slow.next = null; //从中间断开
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = reverse;
//翻转链表
while (cur != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
ListNode l1 = head;
ListNode l2 = pre;
//l2插入l1间隙
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
ListNode tmp1 = l1.next;
ListNode tmp2 = l2.next;
l1.next = l2;
l2.next = tmp1;
l1 = tmp1;
l2 = tmp2;
}
}
}
```
## 对链表进行插入排序
- 需要一个指针指向当前已排序的最后一个位置,这里用的是head指针
- 需要另外一个指针pre,每次从表头循环,这里设置一个哑结点tmp。
- 每次拿出未排序的节点,先和前驱比较,如果大于或者等于前驱,就不用排序了,直接进入下一次循环
- 如果前驱小,则进入内层循环,依次和pre指针比较,插入对应位置即可。
```java
class Solution {
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
ListNode tmp = new ListNode(0);
ListNode pre;
tmp.next = head;
while (head != null && head.next != null) {
if (head.val <= head.next.val) {
head = head.next;
continue;
}
pre = tmp;
while (pre.next.val < head.next.val) {
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode cur = head.next;
head.next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre.next;
pre.next = cur;
}
return tmp.next;
}
}
```
## 逆波兰表达式求值
```
输入: ["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]
输出: 9
解释: 该算式转化为常见的中缀算术表达式为:((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
```
```java
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
Integer num1, num2;
for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++) {
switch (tokens[i]) {
case "+":
stack.push(stack.pop() + stack.pop());
break;
case "-":
num1 = stack.pop();
num2 = stack.pop();
stack.push(num2 - num1);
break;
case "*":
stack.push(stack.pop() * stack.pop());
break;
case "/":
num1 = stack.pop();
num2 = stack.pop();
stack.push(num2 / num1);
break;
default:
stack.push(Integer.valueOf(tokens[i]));
break;
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
}
```