Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/uezo/aiproxy
🦉AIProxy is a reverse proxy for ChatGPT API that provides monitoring, logging, and filtering requests and responses.
https://github.com/uezo/aiproxy
chatgpt chatgpt-api
Last synced: 4 months ago
JSON representation
🦉AIProxy is a reverse proxy for ChatGPT API that provides monitoring, logging, and filtering requests and responses.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/uezo/aiproxy
- Owner: uezo
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2023-12-02T19:06:36.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-05-06T23:57:15.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-10-17T01:49:25.790Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: chatgpt, chatgpt-api
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 153 KB
- Stars: 42
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 5
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
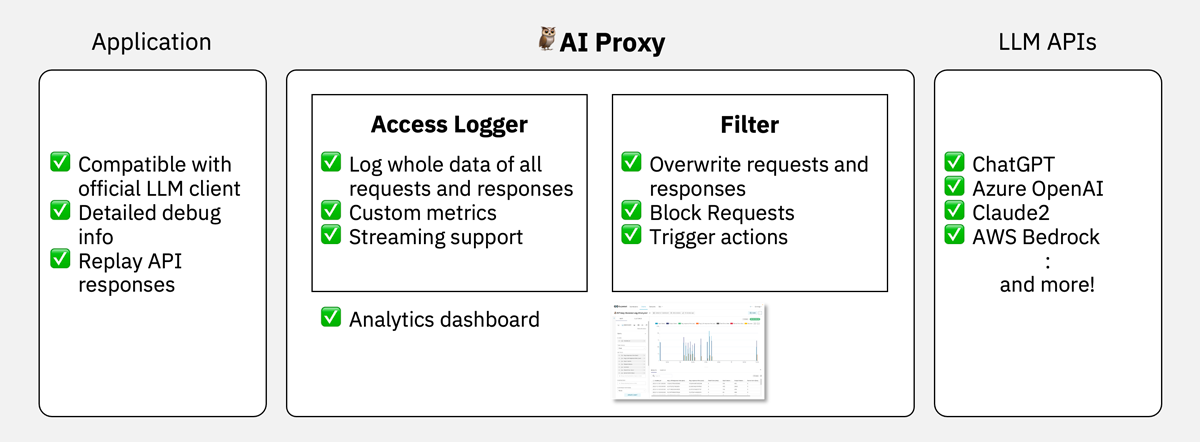
# 🦉 AIProxy
🦉 **AIProxy** is a Python library that serves as a reverse proxy LLM APIs including ChatGPT and Claude2. It provides enhanced features like monitoring, logging, and filtering requests and responses. This library is especially useful for developers and administrators who need detailed oversight and control over the interaction with LLM APIs.
- ✅ Streaming support: Logs every bit of request and response data with token count – never miss a beat! 💓
- ✅ Custom monitoring: Tailor-made for logging any specific info you fancy. Make it your own! 🔍
- ✅ Custom filtering: Flexibly blocks access based on specific info or sends back your own responses. Be in control! 🛡️
- ✅ Multiple AI Services: Supports ChatGPT (OpenAI and Azure OpenAI Service), Claude2 on AWS Bedrock, and is extensible by yourself! 🤖
- ✅ Express dashboard: We provide template for [Apache Superset](https://superset.apache.org) that's ready to use right out of the box – get insights quickly and efficiently! 📊
## 🚀 Quick start
Install.
```sh
$ pip install aiproxy-python
```
Run.
```sh
$ python -m aiproxy [--host host] [--port port] [--openai_api_key OPENAI_API_KEY]
```
Use.
```python
import openai
client = openai.Client(base_url="http://127.0.0.1:8000/openai", api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
resp = client.chat.completions.create(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "hello!"}])
print(resp)
```
Enjoy😊🦉
## 🏅 Use official client libraries
You can use the official client libraries for each LLM by just changing API endpoint url.
### ChatGPT
Set `http|https://your_host/openai` as `base_url` to client.
```python
import openai
client = openai.Client(
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY",
base_url="http://127.0.0.1:8000/openai"
)
resp = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "hello!"}]
)
print(resp)
```
### Anthropic Claude
Set `http|https://your_host/anthropic` as `base_url` to client.
```python
from anthropic import Anthropic
client = Anthropic(
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY",
base_url="http://127.0.0.1:8000/anthropic"
)
resp = client.messages.create(
max_tokens=1024,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, Claude",}],
model="claude-3-haiku-20240307",
)
print(resp.content)
```
### Google Gemini (AI Studio)
API itself is compatible but client of `google.generativeai` doesn't support rewriting urls. Use httpx instead.
```python
import httpx
resp = httpx.post(
url="http://127.0.0.1:8000/googleaistudio/v1beta/models/gemini-1.5-pro-latest:generateContent",
json={
"contents": [{"role": "user", "parts":[{"text": "Hello, Gemini!"}]}],
"generationConfig": {"temperature": 0.5, "maxOutputTokens": 1000}
}
)
print(resp.json())
```
## 🛠️ Custom entrypoint
To customize **🦉AIProxy**, make your custom entrypoint first. You can customize the metrics you want to monitor, add filters, change databases, etc.
```python
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
import threading
from fastapi import FastAPI
from aiproxy import AccessLogWorker
from aiproxy.chatgpt import ChatGPTProxy
from aiproxy.anthropic_claude import ClaudeProxy
from aiproxy.gemini import GeminiProxy
# Setup access log worker
worker = AccessLogWorker(connection_str="sqlite:///aiproxy.db")
# Setup server application
@asynccontextmanager
async def lifespan(app: FastAPI):
# Start access log worker
threading.Thread(target=worker.run, daemon=True).start()
yield
# Stop access log worker
worker.queue_client.put(None)
app = FastAPI(lifespan=lifespan, docs_url=None, redoc_url=None, openapi_url=None)
# Proxy for ChatGPT
chatgpt_proxy = ChatGPTProxy(
api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY,
access_logger_queue=worker.queue_client
)
chatgpt_proxy.add_route(app)
# Proxy for Anthropic Claude
claude_proxy = ClaudeProxy(
api_key=ANTHROPIC_API_KEY,
access_logger_queue=worker.queue_client
)
claude_proxy.add_route(app)
# Proxy for Gemini on Google AI Studio (not Vertex AI)
gemini_proxy = GeminiProxy(
api_key=GOOGLE_API_KEY,
access_logger_queue=worker.queue_client
)
gemini_proxy.add_route(app)
```
Run with uvicorn with some params if you need.
```sh
$ uvicorn run:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
```
## 🔍 Monitoring
By default, see `accesslog` table in `aiproxy.db`. If you want to use other RDBMS like PostgreSQL, set SQLAlchemy-formatted connection string as `connection_str` argument when instancing `AccessLogWorker`.
And, you can customize log format as below:
This is an example to add `user` column to request log. In this case, the customized log are stored into table named `customaccesslog`, the lower case of your custom access log class.
```python
from sqlalchemy import Column, String
from aiproxy.accesslog import AccessLogBase, AccessLogWorker
# Make custom schema for database
class CustomAccessLog(AccessLogBase):
user = Column(String)
# Make data mapping logic from HTTP headar/body to log
class CustomGPTRequestItem(ChatGPTRequestItem):
def to_accesslog(self, accesslog_cls: _AccessLogBase) -> _AccessLogBase:
accesslog = super().to_accesslog(accesslog_cls)
# In this case, set value of "x-user-id" in request header to newly added colmun "user"
accesslog.user = self.request_headers.get("x-user-id")
return accesslog
# Make worker with custom log schema
worker = AccessLogWorker(accesslog_cls=CustomAccessLog)
# Make proxy with your custom request item
proxy = ChatGPTProxy(
api_key=YOUR_API_KEY,
access_logger_queue=worker.queue_client,
request_item_class=CustomGPTRequestItem
)
```
NOTE: By default `AccessLog`, OpenAI API Key in the request headers is masked.
## 🛡️ Filtering
The filter receives all requests and responses, allowing you to view and modify their content. For example:
- Detect and protect from misuse: From unknown apps, unauthorized users, etc.
- Trigger custom actions: Doing something triggered by a request.
This is an example for custom request filter that protects the service from banned user. uezo will receive "you can't use this service" as the ChatGPT response.
```python
from typing import Union
from aiproxy import RequestFilterBase
class BannedUserFilter(RequestFilterBase):
async def filter(self, request_id: str, request_json: dict, request_headers: dict) -> Union[str, None]:
banned_user = ["uezo"]
user = request_json.get("user")
# Return string message to return response right after this filter ends (not to call ChatGPT)
if not user:
return "user is required"
elif user in banned_user:
return "you can't use this service"
# Enable this filter
proxy.add_filter(BannedUserFilter())
```
Try it.
```python
resp = client.chat.completions.create(model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=messages, user="uezo")
print(resp)
```
```sh
ChatCompletion(id='-', choices=[Choice(finish_reason='stop', index=0, message=ChatCompletionMessage(content="you can't use this service", role='assistant', function_call=None, tool_calls=None))], created=0, model='request_filter', object='chat.completion', system_fingerprint=None, usage=CompletionUsage(completion_tokens=0, prompt_tokens=0, total_tokens=0))
```
Another example is the model overwriter that forces the user to use GPT-3.5-Turbo.
```python
class ModelOverwriteFilter(RequestFilterBase):
async def filter(self, request_id: str, request_json: dict, request_headers: dict) -> Union[str, None]:
request_model = request_json["model"]
if not request_model.startswith("gpt-3.5"):
print(f"Change model from {request_model} -> gpt-3.5-turbo")
# Overwrite request_json
request_json["model"] = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
```
Lastly, `ReplayFilter` that retrieves content for a specific request_id from the histories. This is an exceptionally cool feature for developers to test AI-based applications.
```python
class ReplayFilter(RequestFilterBase):
async def filter(self, request_id: str, request_json: dict, request_headers: dict) -> Union[str, None]:
# Get request_id to replay from request header
request_id = request_headers.get("x-aiproxy-replay")
if not request_id:
return
db = worker.get_session()
try:
# Get and return the response content from histories
r = db.query(AccessLog).where(AccessLog.request_id == request_id, AccessLog.direction == "response").first()
if r:
return r.content
else:
return "Record not found for {request_id}"
except Exception as ex:
logger.error(f"Error at ReplayFilter: {str(ex)}\n{traceback.format_exc()}")
return "Error at getting response for {request_id}"
finally:
db.close()
```
`request_id` is included in HTTP response headers as `x-aiproxy-request-id`.
NOTE: **Response** filter doesn't work when `stream=True`.
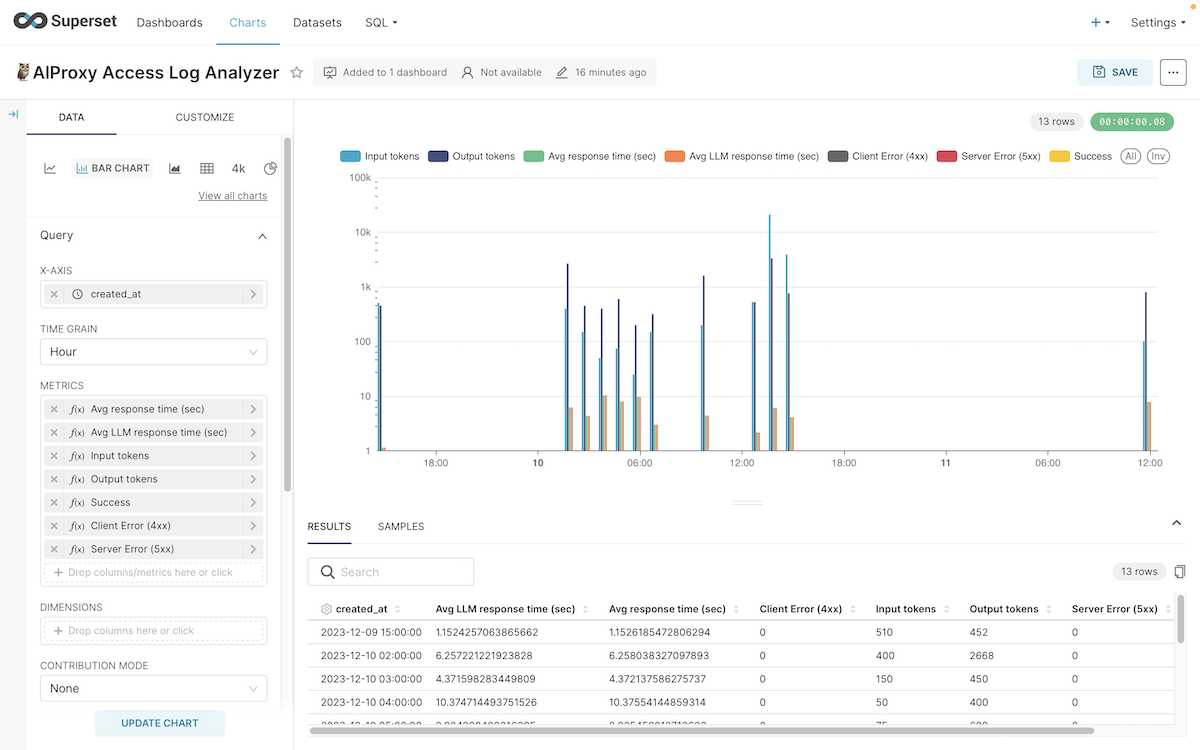
## 📊 Dashboard
We provide an Apache Superset template as our express dashboard. Please follow the steps below to set up.
Install Superset.
```sh
$ pip install apache-superset
```
Get dashboard.zip from release page and extract it to the same directory as aiproxy.db.
https://github.com/uezo/aiproxy/releases/tag/v0.3.0
Set required environment variables.
```sh
$ export SUPERSET_CONFIG_PATH=$(pwd)/dashboard/superset_config.py
$ export FLASK_APP=superset
```
Make database.
```sh
$ superset db upgrade
```
Create admin user. Change username and password as you like.
```sh
$ superset fab create-admin --username admin --firstname AIProxyAdmin --lastname AIProxyAdmin --email admin@localhost --password admin
```
Initialize Superset.
```sh
$ superset init
```
Import 🦉AIProxy dashboard template. Execute this command in the same directory as aiproxy.db. If you execute from a different location, open the Database connections page in the Superset after completing these steps and modify the database connection string to the absolute path.
```sh
$ superset import-directory dashboard/resources
```
Start Superset.
```sh
$ superset run -p 8088
```
Open and customize the dashboard to your liking, including the metrics you want to monitor and their conditions.👍
http://localhost:8088
📕 Superset official docs: https://superset.apache.org/docs/intro
## 💡 Tips
### CORS
Configure CORS if you call API from web apps. https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/cors/
### Database
You can use other RDBMS that is supported by SQLAlchemy. You can use them by just changing connection string. (and, install client libraries required.)
#### Example for PostgreSQL🐘
```sh
$ pip install psycopg2-binary
```
```python
# connection_str = "sqlite:///aiproxy.db"
connection_str = f"postgresql://{USER}:{PASSWORD}@{HOST}:{PORT}/{DATABASE}"
worker = AccessLogWorker(connection_str=connection_str)
```
#### Example for SQL Server or Azure SQL Database
This is a temporary workaroud from AIProxy >= 0.3.6. Set `AIPROXY_USE_NVARCHAR=1` to use NVARCHAR internally.
```sh
$ export AIPROXY_USE_NVARCHAR=1
```
Install ODBC driver (version 18 in this example) and `pyodbc` then set connection string as follows:
```python
# connection_str = "sqlite:///aiproxy.db"
connection_str = f"mssql+pyodbc:///?odbc_connect=DRIVER={ODBC Driver 18 for SQL Server};SERVER=YOUR_SERVER;PORT=1433;DATABASE=YOUR_DB;UID=YOUR_UID;PWD=YOUR_PWD"
worker = AccessLogWorker(connection_str=connection_str)
```
### Azure OpenAI
To use Azure OpenAI, use `AzureOpenAIProxy` instead of `ChatGPTProxy`.
```python
from aiproxy.chatgpt import AzureOpenAIProxy
aoai_proxy = AzureOpenAIProxy(
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY",
resource_name="YOUR_RESOURCE_NAME",
deployment_id="YOUR_DEPLOYMENT_ID",
api_version="2024-02-01", # https://learn.microsoft.com/ja-jp/azure/ai-services/openai/reference#chat-completions
access_logger_queue=worker.queue_client
)
aoai_proxy.add_route(app)
```
Clients do not need to be aware that it is Azure OpenAI; use the same code for ChatGPT API.
### Amazon Bedrock
To use Claude on Amazon Bedrock, use `BedrockClaudeProxy` instead of `ClaudeProxy`.
```python
from aiproxy.bedrock_claude import BedrockClaudeProxy
bedrock_claude_proxy = BedrockClaudeProxy(
aws_access_key_id="YOUR_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID",
aws_secret_access_key="YOUR_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY",
region_name="YOUR_REGION",
access_logger_queue=worker.queue_client
)
bedrock_claude_proxy.add_route(app)
```
Client side. We test API with `AnthropicBedrock`.
```python
# Make client with `base_url`
client = anthropic.AnthropicBedrock(
aws_secret_key="dummy_aws_secret_access_key",
aws_access_key="dummy_aws_access_key_id",
aws_region="dummy_region_name",
base_url="http://127.0.0.1:8000/bedrock-claude"
)
resp = client.messages.create(
model="anthropic.claude-3-haiku-20240307-v1:0",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": "こんにちは!"}]}],
max_tokens=512,
stream=True
)
for r in resp:
print(r)
```
## 🛟 Support
For support, questions, or contributions, please open an issue in the GitHub repository. Please contact me directly when you need an enterprise or business support😊.
## ⚖️ License
**🦉AIProxy** is released under the [Apache License v2](LICENSE).
Made with ❤️ by Uezo, the representive of Unagiken.