Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/utiasdsl/force_push
[RA-L 2024] Quasistatic robotic planar pushing with single-point contact using force feedback.
https://github.com/utiasdsl/force_push
control mobile-manipulation pushing robotics
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
[RA-L 2024] Quasistatic robotic planar pushing with single-point contact using force feedback.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/utiasdsl/force_push
- Owner: utiasDSL
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-03-01T18:41:08.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-06-25T16:14:21.000Z (7 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-06-25T18:03:39.884Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: control, mobile-manipulation, pushing, robotics
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.17517
- Size: 3.98 MB
- Stars: 3
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Force Push
Quasistatic robotic planar pushing with single-point contact using only force
feedback to sense the pushed object. The code in this repository accompanies
[this paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.17517) (see the citation below), and a
video of some of the experiments can be found
[here](http://tiny.cc/force-push).
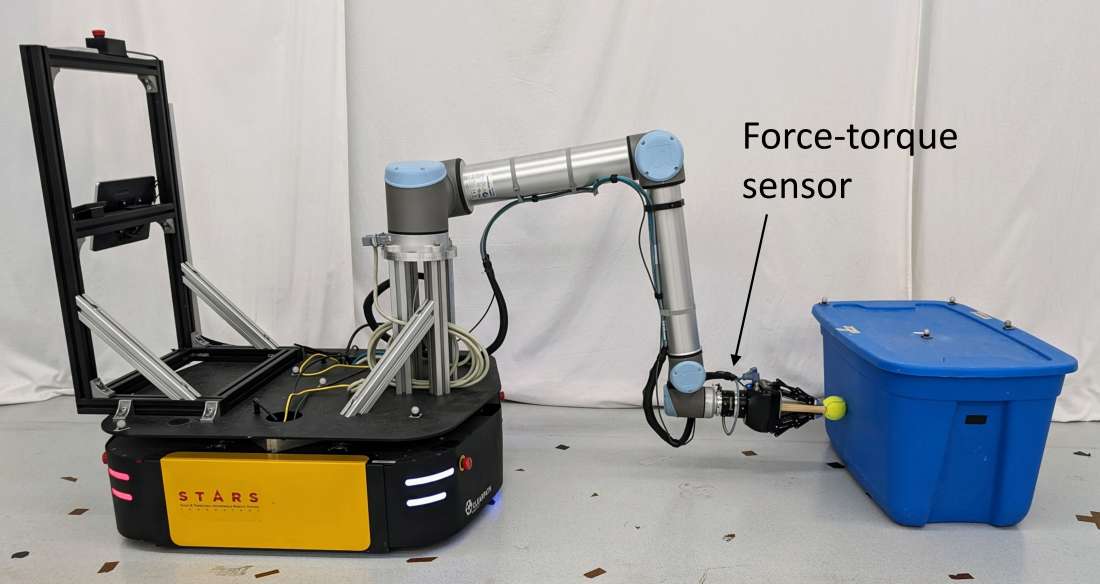
*Our mobile manipulator pushing a box based on contact force measurements.*
## Install
This code has been tested on Ubuntu 20.04 with ROS Noetic and Python 3.8.
Initialize your catkin workspace before proceeding.
First install
[mobile_manipulation_central](https://github.com/utiasDSL/mobile_manipulation_central)
into the catkin workspace.
Into the same catkin workspace, clone this repository:
```bash
cd ~/catkin_ws
git clone https://github.com/adamheins/force_push
```
Ensure all the Python dependencies in `requirements.txt` are satisfied (e.g.,
by doing something like `pip install -r requirements.txt`).
Build the workspace:
```bash
catkin build
```
## Simulation Experiments
Simulations are run in PyBullet. A small patch improving planar sliding
friction can be found
[here](https://github.com/bulletphysics/bullet3/pull/4539), which will require
you to build PyBullet from source:
```
# get patched version
git clone https://github.com/adamheins/bullet3
# build
cd bullet3
./build_cmake_pybullet_double.sh
# add this version to Python path
cd bullet3/build_cmake/examples/pybullet
export PYTHONPATH=$(pwd):$PYTHONPATH
```
Run the simulations using the script
`scripts/simulation/pyb_simulation_many.py`. The results can be saved as a
Python pickle and post-processed using `scripts/simulation/process_sim_results.py`
## Hardware Experiments
Experiments are done using utilities in mobile_manipulation_central.
### Arm
If it isn't already, connect to the arm and put it into the required home
position. Then turn it off:
```
roslaunch mobile_manipulation_central thing.launch
rosrun mobile_manipulation_central home.py --config (rospack find force_push)/config/home.yaml --arm-only pushing_diag
```
Grasp a tennis ball with the gripper in the "pinched" configuration.
### Base, gripper, F/T sensor, Vicon
After the initial positioning of the arm, these experiments use only the mobile
base; the arm can remain off. SSH into the robot and run:
```
rosrun robotiq_ft_sensor rq_sensor
```
This will take a few seconds to detect the FT sensor, and will then start
publishing the `/robotiq_ft_wrench` topic.
On the laptop, run
```
rosrun mobile_manipulation_central ridgeback_vicon.launch
```
for localization and control of the mobile base.
### Calibration
For best results, the offset between the origin of the base frame (i.e., the
point about which the base rotates) and the contact point (i.e., roughly the
front of the tennis ball) should be calibrated. This can be done by temporarily
placing a marker on the tennis ball, ensuring Tracking is off in the Vicon UI,
and running the script `calibrate_contact_point.py`. This script automatically
looks for a marker near the expected location, calculates the offset, and
outputs the results to a YAML file. To use this calibration subsequently, move
the YAML file to the `config` directory.
It is also desirable to calibrate the orientation of the FT sensor (see the
calibration notes in the `mobile_manipulation_central` repository and the
scripts in `scripts/experiment/calibration`).
### Pushing controller
To run the pushing controller, use the script
`scripts/experiments/push_control_node.py` with desired options.
## Tests
Some packages contain tests. Python tests use [pytest](https://pytest.org/).
Run `pytest .` inside a package's `test` directory to run the Python tests.
## Citation
If you find this work useful, feel free to cite the accompanying
[paper](https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2024.3414180):
```
@article{heins2024force,
title = {Force Push: Robust Single-Point Pushing With Force Feedback},
author = {Adam Heins and Angela P. Schoellig},
journal = {{IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters}},
volume = {9},
number = {8},
pages = {6856--6863},
doi = {10.1109/LRA.2024.3414180},
year = {2024},
}
```
## License
MIT - see the LICENSE file.