https://github.com/vintasoftware/django-virtual-models
Improve performance and maintainability with a prefetching layer in your Django project
https://github.com/vintasoftware/django-virtual-models
django django-rest-framework orm performance python
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Improve performance and maintainability with a prefetching layer in your Django project
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/vintasoftware/django-virtual-models
- Owner: vintasoftware
- License: mit
- Created: 2022-09-16T22:38:37.000Z (almost 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-01-19T17:00:22.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-31T14:11:34.984Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: django, django-rest-framework, orm, performance, python
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://vintasoftware.github.io/django-virtual-models/
- Size: 657 KB
- Stars: 152
- Watchers: 8
- Forks: 4
- Open Issues: 32
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.rst
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
- Authors: AUTHORS.rst
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-django-performance - django-virtual-models - Improve performance and maintainability with a prefetching layer in your Django project. (Database / Tools)
- stars - vintasoftware/django-virtual-models - Improve performance and maintainability with a prefetching layer in your Django project (Python)
- stars - vintasoftware/django-virtual-models - Improve performance and maintainability with a prefetching layer in your Django project (Python)
README

Django Virtual Models
Improve performance and maintainability with a prefetching layer in your Django / Django REST Framework project
---
**Documentation**: https://vintasoftware.github.io/django-virtual-models/
**Example project**: https://github.com/vintasoftware/django-virtual-models/tree/main/example
**Source Code**: https://github.com/vintasoftware/django-virtual-models
---
Django Virtual Models introduces a new "prefetching layer" to Django codebases that assists developers to express complex read logic without sacrificing maintainability, composability and performance. A Virtual Model allows developers to declare all nesting they need along with all annotations, prefetches, and joins in a single declarative class.
When implementing Django REST Framework serializers, developers need to be careful to avoid causing the [*N+1 selects problem*](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/97197/what-is-the-n1-selects-problem-in-orm-object-relational-mapping) due to missing `prefetch_related` or `select_related` calls on the associated queryset. Additionaly, developers must not miss `annotate` calls for fields that are computed at queryset-level.
With Virtual Models integration with DRF, if you change a DRF Serializer, you won't forget to modify the associated queryset with additional annotations, prefetches, and joins. If you do forget to update the queryset, Django Virtual Models will guide you by raising friendly exceptions to assist you to write the correct Virtual Model for the serializer you're changing. This guidance will prevent N+1s and missing annotations in all serializers that use Virtual Models.
For example, imagine if you have following nested serializers starting from `MovieSerializer`:
```python
from movies.models import Nomination, Person, Movie
class AwardSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Nomination
fields = ["award", "category", "year", "is_winner"]
class PersonSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
awards = AwardSerializer(many=True)
nomination_count = serializers.IntegerField(read_only=True)
class Meta:
model = Person
fields = ["name", "awards", "nomination_count"]
class MovieSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
directors = PersonSerializer(many=True)
class Meta:
model = Movie
fields = ["name", "directors"]
```
For good performance and correct functionality, all nested serializers must have a corresponding `prefetch_related` on the queryset used by `MovieSerializer`. Also, the `nomination_count` field should be `annotate`d on it. Therefore, you'll need to write this complex chain of nested prefetches:
```python
from django.db.models import Prefetch
awards_qs = Nomination.objects.filter(is_winner=True)
directors_qs = Person.objects.prefetch_related(
Prefetch(
"nominations",
queryset=awards_qs,
to_attr="awards"
)
).annotate(
nomination_count=Count("nominations")
).distinct()
qs = Movie.objects.prefetch_related(
Prefetch(
"directors",
queryset=directors_qs
)
)
```
Conversely, you can declare Virtual Models for this read logic to easily reuse and customize those classes in multiple places of the codebase:
```python
import django_virtual_models as v
class VirtualAward(v.VirtualModel):
class Meta:
model = Nomination
def get_prefetch_queryset(self, **kwargs):
return Nomination.objects.filter(is_winner=True)
class VirtualPerson(v.VirtualModel):
awards = VirtualAward(lookup="nominations")
nomination_count = v.Annotation(
lambda qs, **kwargs: qs.annotate(
nomination_count=Count("nominations")
).distinct()
)
class Meta:
model = Person
class VirtualMovie(v.VirtualModel):
directors = VirtualPerson()
class Meta:
model = Movie
```
To configure your DRF view and serializer to use Virtual Models, inherit from the proper classes:
```python
import django_virtual_models as v
class MovieSerializer(v.VirtualModelSerializer):
...
class Meta:
...
virtual_model = VirtualMovie
class MovieList(v.VirtualModelListAPIView):
queryset = Movie.objects.all()
serializer_class = MovieSerializer
...
```
**Then the library will automatically do the right prefetches and annotations for you!**
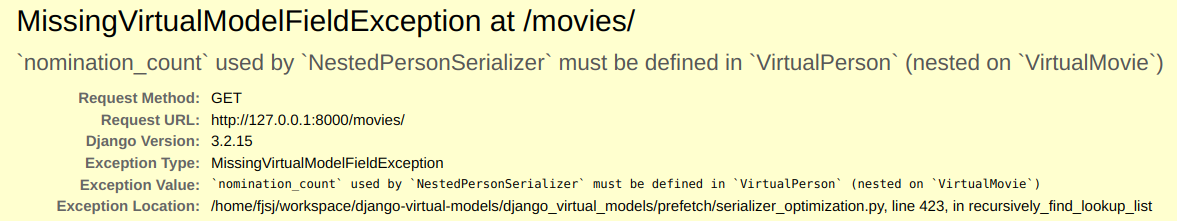
If, for example, you forget to add the `nomination_count` field on `VirtualPerson`, the following exception will appear when using `MovieSerializer`:
If you aren't using DRF serializers, you hydrate your queryset with *virtual fields* manually:
```python
qs = VirtualMovie().get_optimized_queryset(
Movie.objects.all(),
lookup_list=[
"directors__awards",
"directors__nomination_count",
]
)
```
To learn more, check the [Installation](https://vintasoftware.github.io/django-virtual-models/installation/) and the [Tutorial](https://vintasoftware.github.io/django-virtual-models/tutorial/).
Or the [example project](https://github.com/vintasoftware/django-virtual-models/tree/main/example).

