https://github.com/vladimirvivien/jmx-logger
JMX Logger for JUL and Log4J (old project & little support)
https://github.com/vladimirvivien/jmx-logger
Last synced: 8 months ago
JSON representation
JMX Logger for JUL and Log4J (old project & little support)
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/vladimirvivien/jmx-logger
- Owner: vladimirvivien
- Created: 2016-01-06T10:51:12.000Z (almost 10 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2016-01-06T11:26:57.000Z (almost 10 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-08T08:39:39.558Z (9 months ago)
- Language: Java
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.63 MB
- Stars: 3
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 10
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# jmx-logger
JmxLogger makes it easy to do realtime application log monitoring. The JmxLogger API provides both Java Util Logging Handler and a Log4J Appender classes for integration with your choice of logging technologies that you feel confortable with. You simply configure your logging framework, as you would normally do, and the JmxLogger automatically capture and braodcasts your event logs to any registered JMX client. It provides a built-in log console to monitor your log locally or remotely (no more tail -f server.log).
## Features
* Easy integration with your favorite logging framework
* Support for Java Util Logging API
* Support for the Log4J logging API
* No additional API coding required, configure your logging framework and that's it
* Leverages JMX client/agent infrastructure for logging/monitoring
* Support one or more logger running within same VM
* Design for performance / scalability
* dedicated log worker threads
* logged messages are quickly dispatched to dedicated work queue
* all log filtering occur on dedicated threads
* Specify and control the your log levels
* Set log filter at agent-side to save network chatter
* Expression language support for complex event filtering
* Set log filter expression using
* log event parameters (level, message, logger name, etc)
* log event statistics (log count, logger count, etc)
* system status (avail memory, runtime, thread count, etc)
* Multi-function JmxLogger GUI console to view logs
* Say bye to "tail -f server.log": monitor application log locally/remotely
* ability to connect, pause, resume JmxLoger connection
* control JmxLogger? log settings remotely
* change/update log levels directly from console
* change/update log filter expression
* color-coded log mesage based on level for readability
* consolidated message console for ease of use
* support secure/non-secure connection using JMX security settings
* Usage of JmxLogger is transparent to the developer.
* in your code, send your log events using your logging framework
* the JmxLogger (appender or handler class) then delegates propagation of your log events as JMX notifications using the JMX API.
## Getting Started
* Download the binary distribution zip
* Add jmxlogger-log4j-.x.x.x.jar (and log4j jar) to your classpath if you plan to use log4j for logging.
* Add jmxlogger-x.x.x.jar to classpath if you are using Java Logging Util.
* Add mvel2-x.x.x.jar to your classpath as well.
* Configure your application to use your favorite logging framework and run your application
* Start JmxLogger console (or JConsole) to monitor log via JMX
### Configure JmxLogger for Java Util Logging
If you are a user of the Java util Logging API, you should already be familiar with how to configure (declaratively or programmatically) the framwork for logging. The JmxLogger? handler is configured like any other Java Logging handler:
```
handlers=jmxlogger.integration.logutil.JmxLogHandler, java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler
# Default global logging level.
.level=INFO
# jmx log handler
jmxlogger.Handler.level=INFO
jmxlogger.Handler.objectName=jmxlogger:type=LogEmitter
# Console log handler
java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler.level = INFO
java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler.formatter = java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter
jmxlogger.Handler.objectName=jmxlogger:type=LogEmitter
```
The handler supports several attributes that are not provided and are automatically assigned a default value. In this configuration, we are declaring a JmxLogger with Level set to `INFO` The `SimpleFormatter` class will be used to format logs JMX `ObjectName` for remote monitoring is set to `jmxlogger:type=LogEmitter`.
#### Example Code
```Java
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.LogManager;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class SomeClassA {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(SomeClassA.class.getName());
public static void main(String[] args) {
logger.log(Level.INFO, "I am happy!");
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "I am concerned...");
logger.log(Level.SEVERE, "I am in trouble, something went wrong.");
logger.log(Level.FINE, "I am up, I am down, I am all around!");
}
}
```
### Configure JmxLogger for Log4J
`JmxLogger` also supports the `Log4J` logging framework. If you are a user of the Log4J framework, you should already be familiar with the configuration steps for Log4J appenders. The `JmxLogger` appender is configured as shown below:
```xml
```
#### Code Example
```java
import org.apache.log4j.Level;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
public class SomeClassB {
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(SomeClassB.class);
public static void main (String[] args) {
logger.log(Level.INFO, "I am happy!");
logger.log(Level.WARN, "I am concerned...");
logger.log(Level.ERROR, "I am in trouble, something went wrong.");
logger.log(Level.DEBUG, "I am up, I am down, I am all around!");
}
}
```
### Running the Code
You must provide several system properties to start your process with JMX remote connectivity & security enabled. For this example, we are only going to enable the remote port and turn off security
```console
java -cp your:class:path \
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote \
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=7070 \
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false
your.process.main.Class
```
When you start the process, it will setup JMX with remote connectivity. This will enable you to connect and see your log using the JmxLogger console (see below).
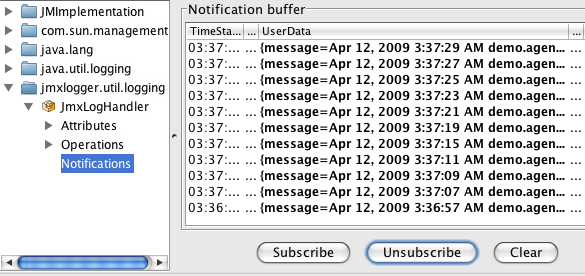
## Viewing Logs in JmxLoggerConsole and JConsole
Once you have started your process, you can view the log in realtime by connecting to the JmxLogger agent started by the logging framework. To start JmxLogger, do
`java -cp mvel2-mvel2-2.0.14.jar:jmxlogger-0.3.0.jar jmxlogger.tools.console.Main` This will start the console:
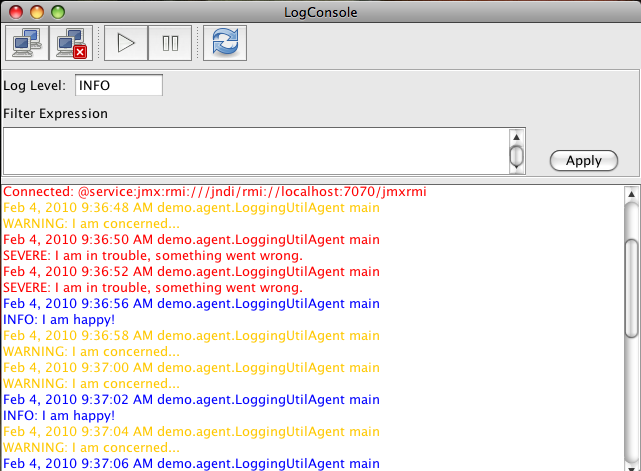
JmxLogger exposes several parameters which can be used in filter expressions at runtime.
Using JConsole, you can see these events as they are logged as well.
### JConsole
Since JmxLogger is based on the JMX standard Java API, all logs can also be viewed using JConsole: