https://github.com/vriajs/vria
A Web-based Framework for Creating Immersive Analytics Experiences
https://github.com/vriajs/vria
augmented-reality charts data-visualization immersive-analytics virtual-reality visualization webxr
Last synced: 4 months ago
JSON representation
A Web-based Framework for Creating Immersive Analytics Experiences
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/vriajs/vria
- Owner: vriajs
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-10-16T19:24:26.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-06-17T12:48:50.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-30T22:18:54.651Z (about 1 year ago)
- Topics: augmented-reality, charts, data-visualization, immersive-analytics, virtual-reality, visualization, webxr
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage: https://vriajs.github.io/vria
- Size: 4.49 MB
- Stars: 48
- Watchers: 6
- Forks: 15
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- vr-resources - vria, A Web-based Framework for Creating Immersive Analytics Experiences
README
---

# VRIA
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/vria) [](https://github.com/vriajs/vria/blob/master/LICENSE)
A Web-Based Framework for Creating Immersive Analytics Experiences
Try it in your browser: https://vriajs.github.io/vria
## Contents
- [What is VRIA?](#what-is-vria)
- [VRIA Grammar](#vria-grammar)
- [What's in the package?](#whats-in-the-package)
- [Basic usage](#basic-usage)
- [VRIA `aframe-react` Component and API](#vria-aframe-react-component-and-api)
- [Props API Reference](#props-api-reference)
- [config](#config)
- [onConfigParsed](#onconfigparsed)
- [additionalFilters](#additionalfilters)
- [onFilter](#onfilter)
- [setFilters](#setfilters)
- [onSelection](#onselection)
- [setSelection](#setselection)
- [customMarks](#custommarks)
- [options](#options)
- [Config Validation](#config-validation)
- [VRIA Builder](#vria-builder)
- [VRIA Boilerplate](#vria-boilerplate)
- [Team](#team)
- [Publications](#publications)
- [Citation](#citation)
- [License](#license)
---
## What is VRIA?
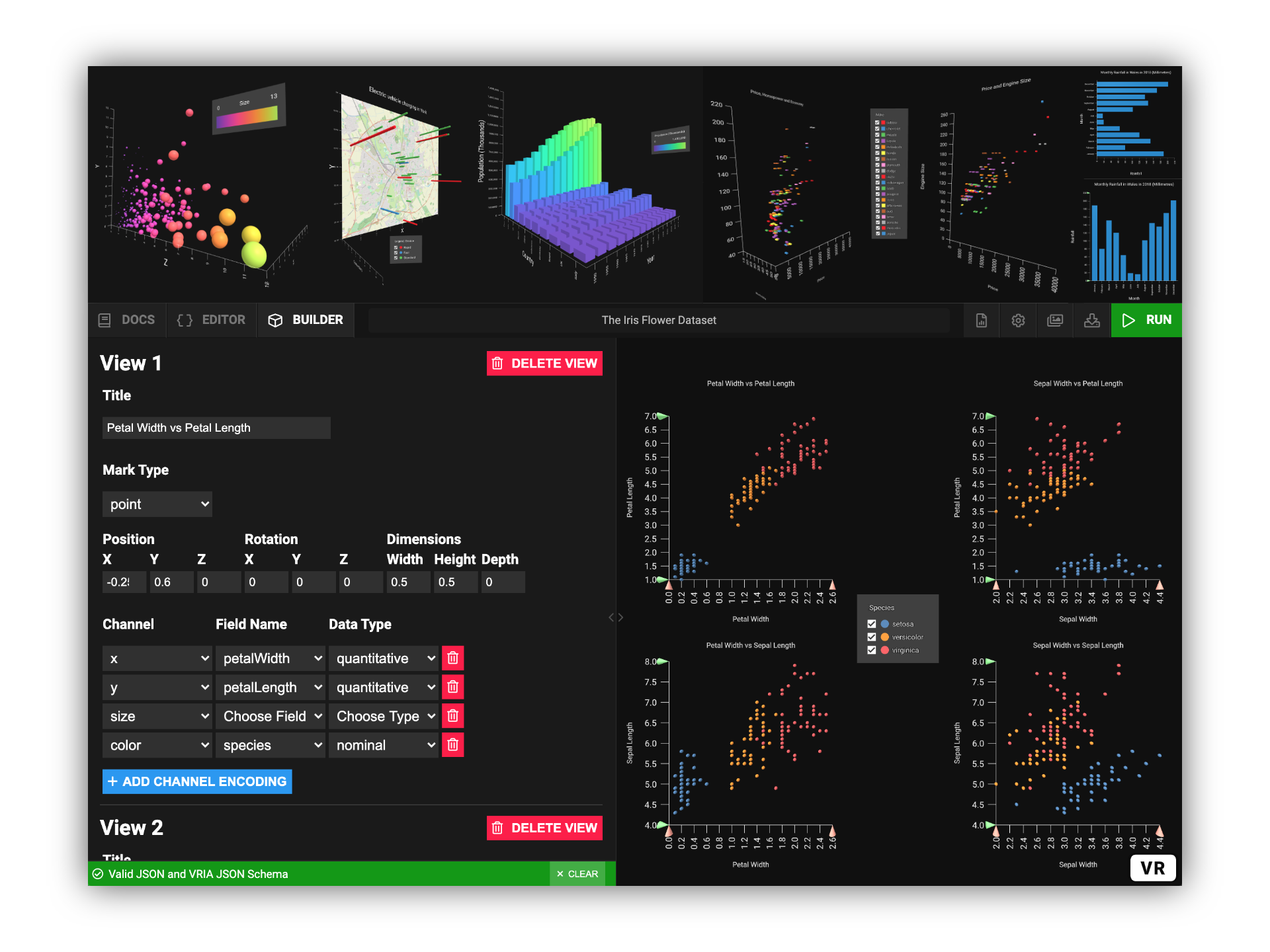
VRIA is a Web-based framework for creating Immersive Analytics experiences in virtual and augmented reality. Built with [React](https://reactjs.org), [A-Frame](https://aframe.io), and [D3](https://d3js.org), VRIA lets you rapidly create interactive, immersive data visualizations with a declarative grammar described in JSON. Powered by [WebXR](https://immersiveweb.dev/), the scenes you create with VRIA can be accessed immediately on a growing number of [supported devices](https://immersiveweb.dev/#supporttable) and [browsers](https://caniuse.com/webxr). Extra functionality can be added to immersive scenes with VRIA's API.
### VRIA Grammar
VRIA visualizations are defined with a declarative grammar described in JSON. VRIA's grammar is similar to those of [Vega-Lite](https://vega.github.io/vega-lite) and [DxR](https://github.com/ronellsicat/DxR).
Please refer to the [VRIA Grammar Definition](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1WdzG45G8_wPnhOeLuEgZEYGCOWJqBhzJeYFBL7Pbdf0) and/or the [VRIA JSON Schema](https://github.com/vriajs/vria/tree/master/src/grammar/schema/vria-schema-v1.0.json).
### What's in the package?
VRIA's NodeJS module is separated into three parts:
1. The VRIA `aframe-react` component and API. [[docs](#vria-aframe-react-component)]
2. The VRIA Builder: An end-to-end tool for learning and rapidly prototyping immersive Web-based visualizations. [[docs](#vria-builder)]
3. A boilerplate environment to create your first standalone VRIA application. [[docs](#vria-boilerplate)]
---
## Basic Usage
To get started with VRIA, you can experiment with the hosted version of the VRIA Builder online: https://vriajs.github.io/vria
To add VRIA to a new or existing project you will need:
- [NodeJS](https://nodejs.org) (>= v10.0).
- You will also need to install [`react`](https://npmjs.org/package/react) and [`react-dom`](https://npmjs.org/package/react-dom) if you haven't already. The easiest way to get started with a new React project is via [create-react-app](https://create-react-app.dev/docs/getting-started/) _(recommended)_.
- Alternatively, you can add React later and start off by installing VRIA on its own by cloning this repository and using the `boilerplate/` directory to create your first VRIA app [[docs](#vria-boilerplate)]. The VRIA Builder is also available to install locally in the `builder/` directory [[docs](#vria-builder)].
- Finally, you will need to include the A-Frame library script in the `` of your `index.html` file:
```html
```
### Installing VRIA
You can add VRIA to a new or existing application by installing it with [Yarn](https://yarnpkg.com) or [NPM](https://npmjs.org):
```bash
yarn add vria
```
or
```bash
npm install vria
```
You can then include VRIA in your project:
```jsx
import VRIA from 'vria';
```
### Run the development server
If you are using `create-react-app` you can run either `yarn start` or `npm start` to start the development server.
Your app will now be running at `localhost:3000`.
You can then include VRIA in your project, something like this:
```jsx
// index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Scene } from 'aframe-react';
import VRIA from 'vria';
const config = {
title: 'My first VRIA app',
data: {
values: [
{ a: 'A', b: 1 },
{ a: 'B', b: 2 }
]
},
mark: 'bar',
encoding: {
x: { field: 'a', type: 'nominal' },
y: { field: 'b', type: 'quantitative' }
}
};
const App = () => (
);
ReactDOM.render(, document.getElementById('root'));
```
### Create a production build
You can build your app for production to the `build/` directory by running either `yarn build` or `npm run build`.
---
## VRIA `aframe-react` Component and API
The VRIA `aframe-react` component is an A-Frame entity, wrapped up in a React component. It can be passed A-Frame props (e.g. `position` and `rotation` etc.), as well as props to access VRIA API features.
You can include other A-Frame components and assets inside the `` element. Entities can be added with [aframe-react](https://www.npmjs.com/package/aframe-react)'s `` component:
```jsx

```
In the above example the `config` prop is used to load a VRIA vis-config as JSON. The `config` prop is the only required prop, and all visualization functionality can be acheived with it. See [VRIA Grammar](#vria-grammar).
VRIA exposes a set of props that can be used to integrate a scene with other libraries and user-defined features. For example, additional filters can be added to other features of a multi-variate dataset with user-defined interaction components (e.g. buttons, sliders etc.).
### Props API Reference
- [config](#config)
- [onConfigParsed](#onconfigparsed)
- [additionalFilters](#additionalfilters)
- [onFilter](#onfilter)
- [setFilters](#setfilters)
- [onSelection](#onselection)
- [setSelection](#setselection)
- [customMarks](#custommarks)
- [options](#options)
#### `config`
_required_ **[object]**
The `config` prop contains a VRIA vis-config as JSON and must be supplied when the VRIA component is rendered. See [VRIA Grammar](#vria-grammar) for details on how to structure a VRIA vis-config.
#### `onConfigParsed`
_optional_ **[function]**
The `onConfigParsed` prop should be passed a function which will be called whenever VRIA compiles a vis-config update. This function will be passed an object containing the following:
| Property | Type | Description |
| ---------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------- |
| `compiledConfig` | _object_ | The compiled VRIA vis-config |
| `dataset` | _object array_ | The parsed dataset |
| `domainMap` | [_Map()_](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Map) | The state of visualization domain filters |
| `scales` | _object array_ | Scale functions from each VRIA view |
Example usage:
```jsx
{
// Do something once the vis-config is compiled
}}
/>
```
#### `additionalFilters`
_optional_ **[object array]**
The `additionalFilters` prop is used to list field names and domains of the dataset that the user would like to filter from the visualization. From this it is possible to create a custom filter component for each of these additional fields. Fields must not already be included in any of the encoding channels in the vis-config. Custom filters can have the following properties:
| Key | Required | Default | Possible Values | Description |
| -------- | -------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `field` | Yes | - | _string_: field name | A field of the dataset |
| `type` | Yes | - | _string_: `quantitative` \| `nominal` \| `ordinal` \| `temporal` | Field data type |
| `zero` | No | false | _boolean_ | Whether the domain should start from zero (quantitative only) |
| `domain` | No | For quantitative data types: extent [min, max] or [0, max] if `zero`ed. Other data types: complete set of values | _number array_ \| _string array_ | Set the domain of this field. This sets the filtered state of a field's domain. |
For example, a vis-config already containing the fields `horsepower` and `miles_per_gallon` can have `top_speed` and `cylinders` added as additional filters:
```jsx
```
Notice how `cylinders` has a domain specified. This would have the effect of filtering the dataset based on this domain whereas `top_speed` does not yet have a domain filter applied.
Additional filters are normally specified when a visualization is created so that they may later be filtered with the [`onFilter`](#onfilter) callback and [`setFilters`](#setfilters) function.
#### `onFilter`
_optional_ **[function]**
The `onFilter` prop should be passed a function that will be called whenever a filter is updated in a VRIA visualization or by a user-defined filter that is attached to the [`setFilters`](#setfilters) prop.
This function will be passed a [Map()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Map) containing the current state of all field domains in a VRIA visualization, including any domains that were specified in the [`additionalFilters`](#additionalFilters) prop.
This prop can be used to send the state of VRIA filters across the network in a multi-user environment, or for use in other parts of your application.
| Argument | Type | Description |
| ----------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
| `domainMap` | [_Map()_](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Map) | Current state of visualization filters by field=>domain. |
Example usage:
```jsx
{
// Do something with the current visualization filter state
}}
/>
```
#### `setFilters`
_optional_ **[Map()]**
The `setFilters` prop should be passed a [Map()](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Map) containing the updated state of all field domains in a VRIA visualization, including any domains that were specified in the [`additionalFilters`](#additionalFilters) prop. The latest filter state can be retrieved from the [`onFilter`](#onfilter) prop whenever the filter state changes.
This prop can be used to set the state of VRIA filters received from across the network in a multi-user environment, or to update the visualization filters from elsewhere in your application.
#### `onSelection`
_optional_ **[object]**
The `onSelection` prop should be passed a function that will be called whenever a selection is made in a VRIA visualization. The function will be passed an object containing the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
| --------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `data` | _array_ | An array of objects containing data points from the selection |
| `dataMap` | [_Map()_](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Map) | A mapping of each mark's class name to its respective data point in the selection. |
| `marks` | _array_ | An array of the class names of each mark in the selection |
This prop can be used to send the state of VRIA selections across the network in a multi-user environment, or for use in other parts of your application.
```jsx
{
// Do something with the current selection state
}}
/>
```
#### `setSelection`
_optional_ **[object]**
The `setSelection` prop should be passed an object containing details of a selection to be made in a VRIA visualization. It should match the structure of the object received from the [`onSelection`](#onselection) prop.
This prop can be used to set the state of VRIA selections from across the network in a multi-user environment, or to update the visualization selections from elsewhere in your application.
#### `customMarks`
_optional_ **[object]**
Custom marks can be added to visualizations via the vis-config and `customMarks` prop. Custom marks are A-Frame entities or models. A custom mark can make use of data from all encoding channels in a vis-config which are accessible to them as props. Here is an example of a custom mark:
```jsx
const customMark = (props) => (
);
```
This example makes use of the dimension and color encoding channels, but every encoding channel is available to use via props. To include this mark in a visualization, the name of the mark should be used in place of the mark type in the vis-config. More than one custom mark can be used at a time inside the `customMarks` prop object. Here's how the `customMarks` prop would look with our mark definition above.
```jsx
```
#### `options`
_optional_ **[object]**
The `options` prop is used to pass overrides for some general VRIA settings:
| Option | Default | Possible Values | Description |
| ------------- | ------- | ----------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `userHeight` | 1.6 | _number_ | The height of the user in the scene in metres |
| `handedness` | both | _string_: `left` \| `right` \| `both` \| `none` | Which controllers to render |
| `multiSelect` | false | _boolean_ | Whether to accept single or multiple concurrent mark selections from a user |
| `chartColor` | #000000 | _string_ | The base color of all chart components |
| `selectColor` | #00FF00 | _string_ | The color a mark will change to when it is selected by the user |
For example, to change the `chartColor` to white and `selectColor` to red:
```jsx
```
### Config validation
Although VRIA will validate your vis-config at runtime, sometimes you may wish to valid a VRIA vis-config against the VRIA JSON Schema before passing it to VRIA. To do this you can run it through the validator with the `validateVisConfig` named export:
```jsx
import { validateVisConfig, schema } from 'vria';
import config from './config';
// Validate a vis-config
console.log(validateVisConfig(config));
```
This example also shows you how to access the VRIA JSON Schema if you wish to do your own validation.
---
## VRIA Builder
The VRIA Builder: An end-to-end tool for learning and rapidly prototyping immersive Web-based visualizations. It is available online at: https://vriajs.github.io/vria and as part of this package.
To use the VRIA builder locally, follow these instructions:
1. Clone or fork the VRIA Git repository
2. Navigate to `builder/`
3. Run `yarn install` or `npm install`
4. Run `yarn start` or `npm start`
The builder is now running at `localhost:3000`
Run `yarn build` or `npm run build` to create a production ready build of the VRIA builder to `builder/build`.
---
## VRIA Boilerplate
The VRIA Boilerplate is a way to quickly get started with VRIA without starting a new project from scratch. To use the boilerplate application, follow these instructions:
1. Clone or fork the VRIA Git repository
2. Navigate to `boilerplate/`
3. Run `yarn install` or `npm install`
4. Run `yarn start` or `npm start`
The boilerplate example is now running at `localhost:3000`
Run `yarn build` or `npm run build` to create a production ready build of your app to `boilerplate/build`.
---
## Team
VRIA is in ongoing development by the Visualization, Modeling and Graphics Research Group at Bangor University, UK, led by [Peter Butcher](https://twitter.com/pwsbutcher) and [Panagiotis Ritsos](https://twitter.com/ritsos_p).
---
## Publications
_VRIA: A Web-based Framework for Creating Immersive Analytics Experiences_
📃 Journal article available on IEEE Xplore: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8954824
Published in: [IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=2945) (Early Access) - Presented virtually at [IEEE VIS 2020](http://ieeevis.org/year/2020/welcome).
### Citation
```bib
@ARTICLE{8954824,
author={P. W. S. {Butcher} and N. W. {John} and P. D. {Ritsos}},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics},
title={VRIA: A Web-based Framework for Creating Immersive Analytics Experiences},
year={2020},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1-1},
}
```
---
## License
MIT © Copyright 2020 [Peter W. S. Butcher](https://twitter.com/pwsbutcher), [Nigel W. John](https://twitter.com/nigeljohn12) and [Panagiotis D. Ritsos](https://twitter.com/ritsos_p) - University of Chester, UK (Visualization, Interaction and Graphics Research Group) and Bangor University, UK (Visualization, Modeling and Graphics Research Group) - All rights reserved