Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/vzhou842/faster.js
faster.js is a Babel plugin that compiles idiomatic Javascript to faster, micro-optimized Javascript.
https://github.com/vzhou842/faster.js
babel babel-plugin fasterjs fastjs javascript optimization
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
faster.js is a Babel plugin that compiles idiomatic Javascript to faster, micro-optimized Javascript.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/vzhou842/faster.js
- Owner: vzhou842
- License: mit
- Created: 2018-02-27T22:35:59.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-12-30T18:29:36.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-04-26T08:47:16.764Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: babel, babel-plugin, fasterjs, fastjs, javascript, optimization
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage: https://www.npmjs.com/package/faster.js
- Size: 135 KB
- Stars: 436
- Watchers: 8
- Forks: 11
- Open Issues: 6
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-babel - faster.js - Transforms native `Array` methods into faster equivalents. 🔧 (Plugins / Optimization)
README
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/faster.js)
[](https://travis-ci.org/vzhou842/faster.js)
# faster.js
faster.js is a [Babel](https://babeljs.io/) plugin that compiles idiomatic Javascript to faster, micro-optimized Javascript.
Read **[the blog post](https://victorzhou.com/blog/avoid-premature-optimization/)** on faster.js!
## Installation
[Setup Babel](https://babeljs.io/docs/setup) for your project if you haven't already. Then install faster.js:
```bash
npm install --save-dev faster.js
```
## Usage
##### .babelrc
```json
{
"plugins": ["faster.js"]
}
```
##### Babel CLI
```bash
babel-cli --plugins faster.js script.js
```
##### webpack.config.js (Webpack 4)
```js
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.js$/,
exclude: /(node_modules)/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
plugins: [require('faster.js')]
}
}
}]
}
```
## What faster.js does
faster.js rewrites common `Array` method calls to faster code that does the same thing (usually - see [When NOT to use faster.js](#warning-when-not-to-use-fasterjs)). This results in performance boosts (especially on code that relies heavily on `Array` methods) while maintaining code readability, but comes at the cost of a slightly larger bundle size. If having a small Javascript bundle size is much more important for you than performance is, you should not use faster.js.
### Supported `Array` methods
faster.js will rewrite the following `Array` methods when possible:
- `.every()`
- `.filter()`
- `.forEach()`
- `.map()`
- `.reduce()`
- `.reduceRight()`
- `.some()`
### Demo
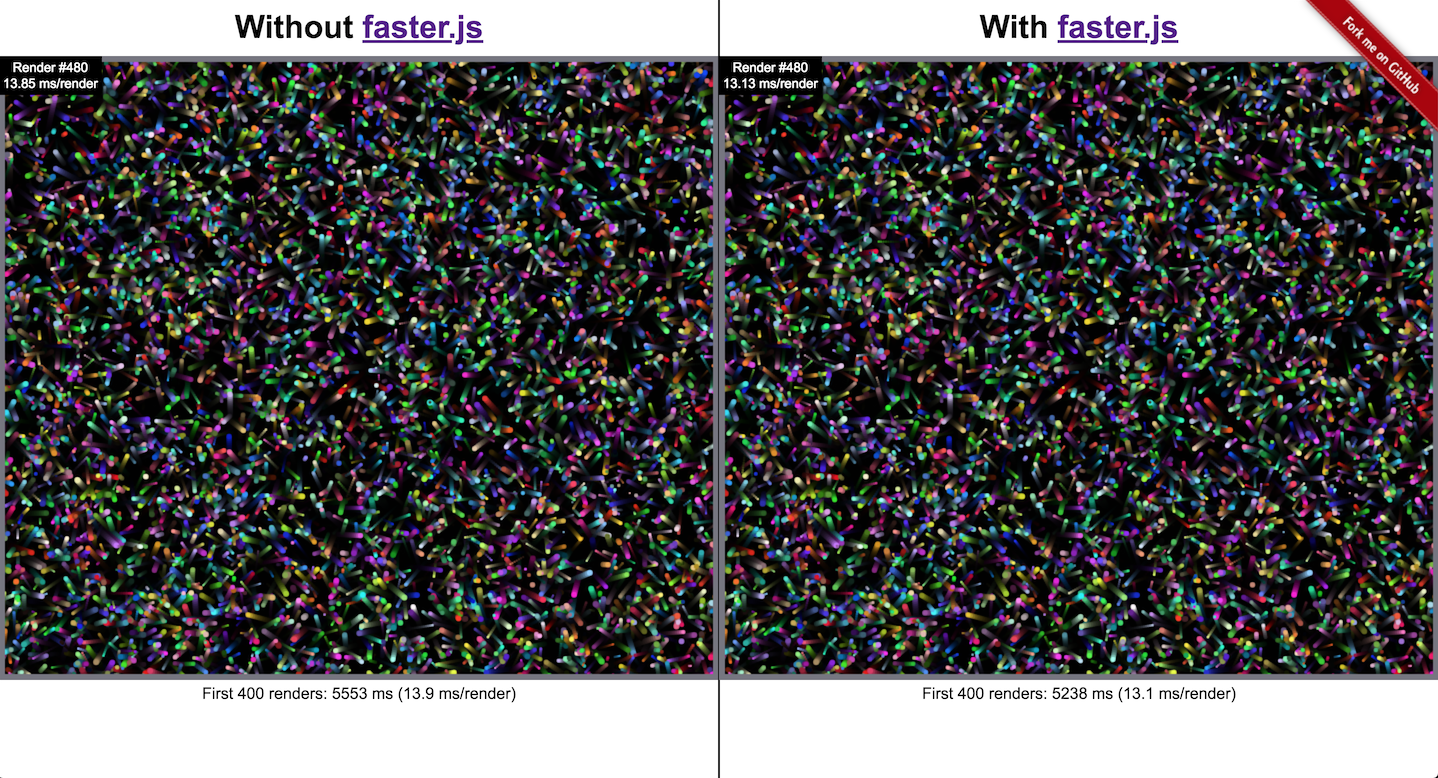
Try it yourself: https://fasterjs-demo.victorzhou.com
Demo Github repo: https://github.com/vzhou842/faster.js-demo
## :warning: When NOT to use faster.js
faster.js makes two critical assumptions that **MUST** be true about your codebase:
#### 1. [Sparse Arrays](#what-is-a-sparse-array) are never used.
Code compiled with faster.js may produce incorrect results when run on sparse arrays.
#### 2. Restricted methods are only ever called on native Javascript arrays:
faster.js assumes any restricted method call is done on a native Javascript array. Any new classes you write should not include methods with restricted names.
Restricted method names are the names of methods that faster.js will attempt to rewrite - see [Supported `Array` methods](#supported-array-methods).
```js
// OK
const a = [1, 2, 3].map(e => 2 * e);
// BAD
class Foo {
constructor(map) {
this._map = map;
}
map() {
return this._map;
}
}
const f = new Foo({});
const map = f.map(); // .map() is a restricted method
```
## How faster.js works
faster.js exploits the fact that native Javascript `Array` methods are slowed down by having to support seldom-used edge cases like [sparse arrays](#what-is-a-sparse-array). Assuming no sparse arrays, there are often simple ways to rewrite common `Array` methods to improve performance.
#### Example: Array.prototype.forEach()
```js
// Original code
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const results = arr.map(e => 2 * e);
```
roughly compiles to
```js
// Compiled with faster.js
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const results = new Array(arr.length);
const _f = (e => 2 * e);
for (let _i = 0; _i < arr.length; _i++) {
results[_i] = _f(arr[_i], _i, arr);
}
```
## Benchmarks
#### Example benchmark output (condensed)
```bash
$ npm run bench
array-every large
✓ native x 2,255,548 ops/sec ±0.46% (57 runs sampled)
✓ faster.js x 10,786,892 ops/sec ±1.25% (56 runs sampled)
faster.js is 378.2% faster (0.351μs) than native
array-filter large
✓ native x 169,237 ops/sec ±1.42% (55 runs sampled)
✓ faster.js x 1,110,629 ops/sec ±1.10% (59 runs sampled)
faster.js is 556.3% faster (5.008μs) than native
array-forEach large
✓ native x 61,097 ops/sec ±3.66% (43 runs sampled)
✓ faster.js x 200,459 ops/sec ±0.52% (55 runs sampled)
faster.js is 228.1% faster (11.379μs) than native
array-map large
✓ native x 179,800 ops/sec ±1.00% (58 runs sampled)
✓ faster.js x 1,706,593 ops/sec ±0.25% (56 runs sampled)
faster.js is 849.2% faster (4.976μs) than native
array-reduce large
✓ native x 200,425 ops/sec ±1.01% (55 runs sampled)
✓ faster.js x 1,694,350 ops/sec ±1.52% (55 runs sampled)
faster.js is 745.4% faster (4.399μs) than native
array-reduceRight large
✓ native x 49,784 ops/sec ±0.38% (58 runs sampled)
✓ faster.js x 1,756,352 ops/sec ±0.99% (59 runs sampled)
faster.js is 3428.0% faster (19.517μs) than native
array-some large
✓ native x 2,968,367 ops/sec ±0.56% (56 runs sampled)
✓ faster.js x 11,591,773 ops/sec ±1.29% (54 runs sampled)
faster.js is 290.5% faster (0.251μs) than native
```
The benchmark example above was run on Node 8. Later versions of Node include improvements / optimizations that may make some features in faster.js obsolete. View full benchmark examples here: [Node 8](https://gist.github.com/vzhou842/6f22cf3c18391a7f0c0bbcfb2abdaa1a), [Node 10](https://gist.github.com/vzhou842/fa06751ca54f1dad9613c00307ac5b0f), [Node 12](https://gist.github.com/vzhou842/eee22267e1cb5172a83a504cf9809ac3).
## FAQ
#### What is a sparse array?
Sparse arrays are arrays that contain holes or empty slots.
```js
const sparse1 = [0, , 1]; // a sparse array literal
console.log(sparse1.length); // 3
const sparse2 = [];
sparse2[5] = 0; // sparse2 is now a sparse array
console.log(sparse2.length); // 6
```
It is generally recommended to avoid using sparse arrays.