https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo
3D geographic visualization library
https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo
dataviz gis gps-coordinates terrain threejs
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
3D geographic visualization library
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo
- Owner: w3reality
- License: mit
- Created: 2018-09-02T21:14:13.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-02-25T08:20:32.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-11T04:09:12.551Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: dataviz, gis, gps-coordinates, terrain, threejs
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 11.2 MB
- Stars: 1,151
- Watchers: 32
- Forks: 190
- Open Issues: 29
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-gis - three-geo - Is a three.js based geographic visualization library (Javascript frontend frameworks and librairies / Map display libraries)
- awesome-gis - three-geo - Is a three.js based geographic visualization library (Front-end Framework)
README
# three-geo
[![NPM][npm-badge]][npm-url]
[![MIT licensed][mit-badge]][mit-url]
[![CI][actions-badge]][actions-url]
[npm-badge]: https://img.shields.io/npm/v/three-geo.svg
[npm-url]: https://www.npmjs.com/package/three-geo
[mit-badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/license-MIT-blue.svg
[mit-url]: https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo/blob/master/LICENSE
[actions-badge]: https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo/workflows/CI/badge.svg
[actions-url]: https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo/actions
**three-geo** is a [three.js](https://github.com/mrdoob/three.js) based geographic visualization library. Using three-geo, we can easily build satellite-textured 3D terrain models in near real-time by simply specifying GPS coordinates anywhere on the globe. The geometry of the terrain is based on the RGB-encoded DEM (Digital Elevation Model) provided by the Mapbox Maps API.
The terrain is represented by standard [THREE.Mesh](https://threejs.org/docs/#api/en/objects/Mesh) objects. This makes it easy for us to access underlying geometry/texture array and perform original GIS (Geographic Information System) experiments in JavaScript. (See Usage for how to programatically obtain those mesh objects).
Credits: this library has been made possible thanks to
- geo-related libraries ([mapbox](https://github.com/mapbox), [Turfjs](https://github.com/Turfjs/turf)) and [the Mapbox Maps API](https://www.mapbox.com/api-documentation/#maps).
- [peterqliu](https://github.com/peterqliu) for informative 3D terrain-related articles and implementation.
## Demo
### 1) examples/geo-viewer ([live](https://w3reality.github.io/three-geo/examples/geo-viewer/io/index.html) | [source code](https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo/tree/master/examples/geo-viewer))
This demo app includes features such as
- on-demand 3D terrain building (by a mouse click on the Leaflet map),
- real-time camera projection onto Leaflet (with oritentaion and HFoV indication),
- terrain interaction with a VR-like laser beam,
- measuring Euclidean distances between terrain points,
- auto camera orbiting around the custom z-axis.
Live:
-
[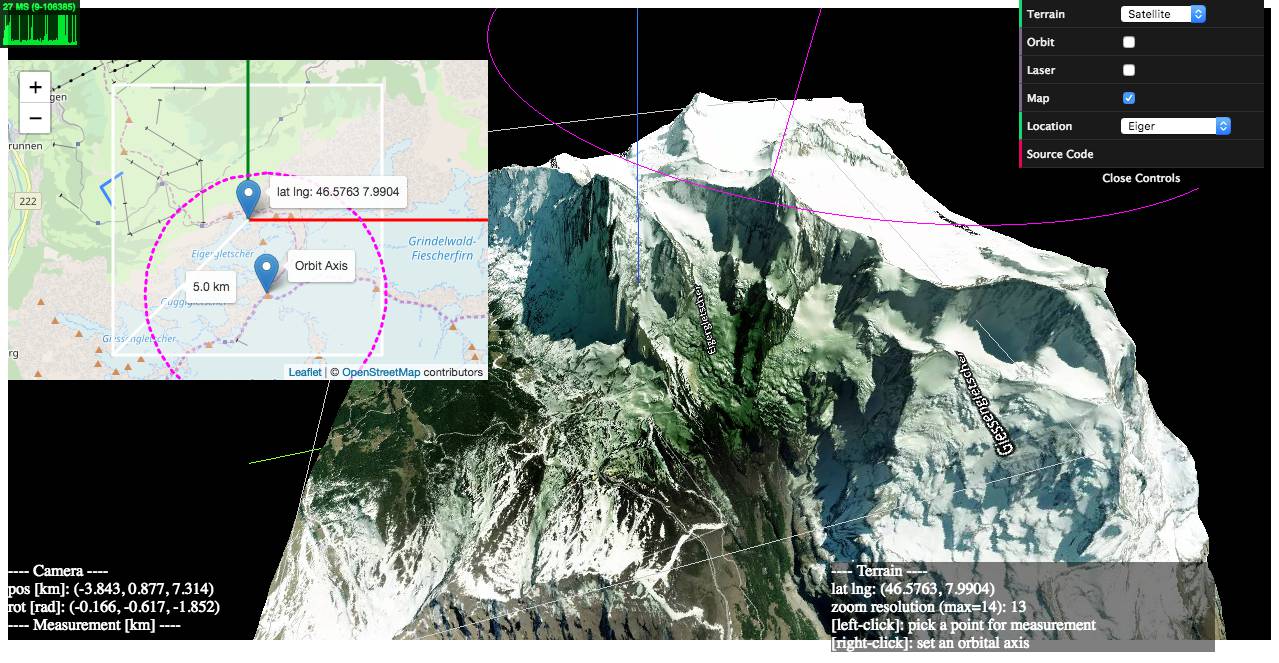](https://w3reality.github.io/three-geo/examples/geo-viewer/io/index.html?lat=46.5763&lng=7.9904&title=Eiger)
-
[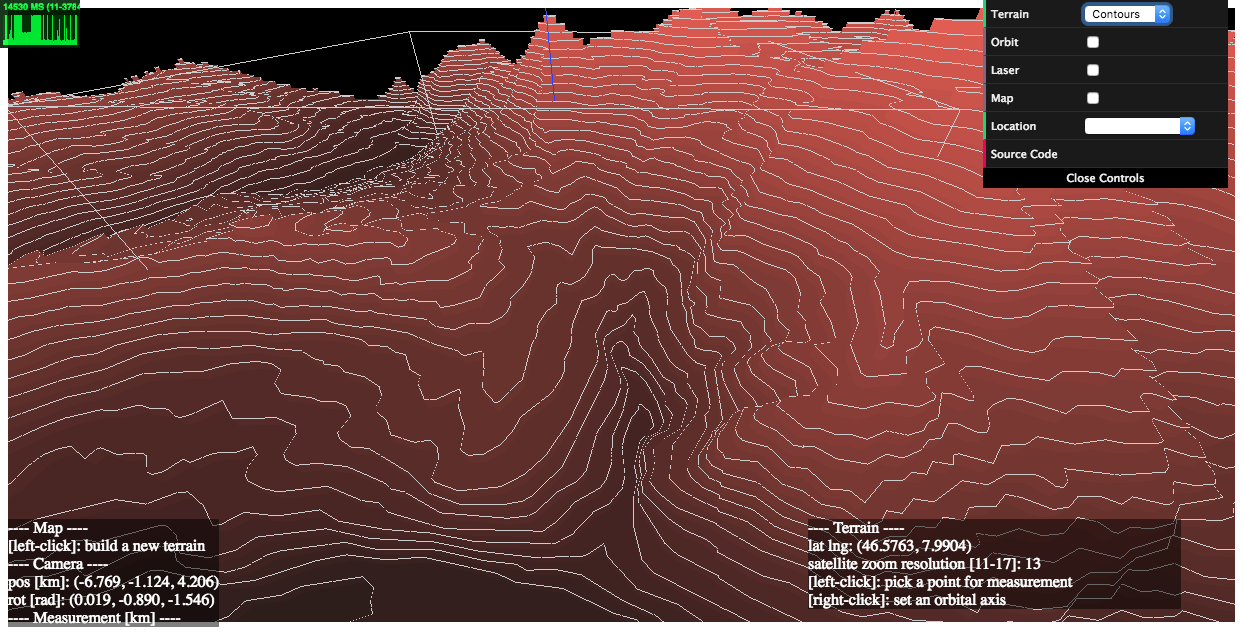](https://w3reality.github.io/three-geo/examples/geo-viewer/io/index.html?lat=46.5763&lng=7.9904&mode=contours&title=Eiger)
-
[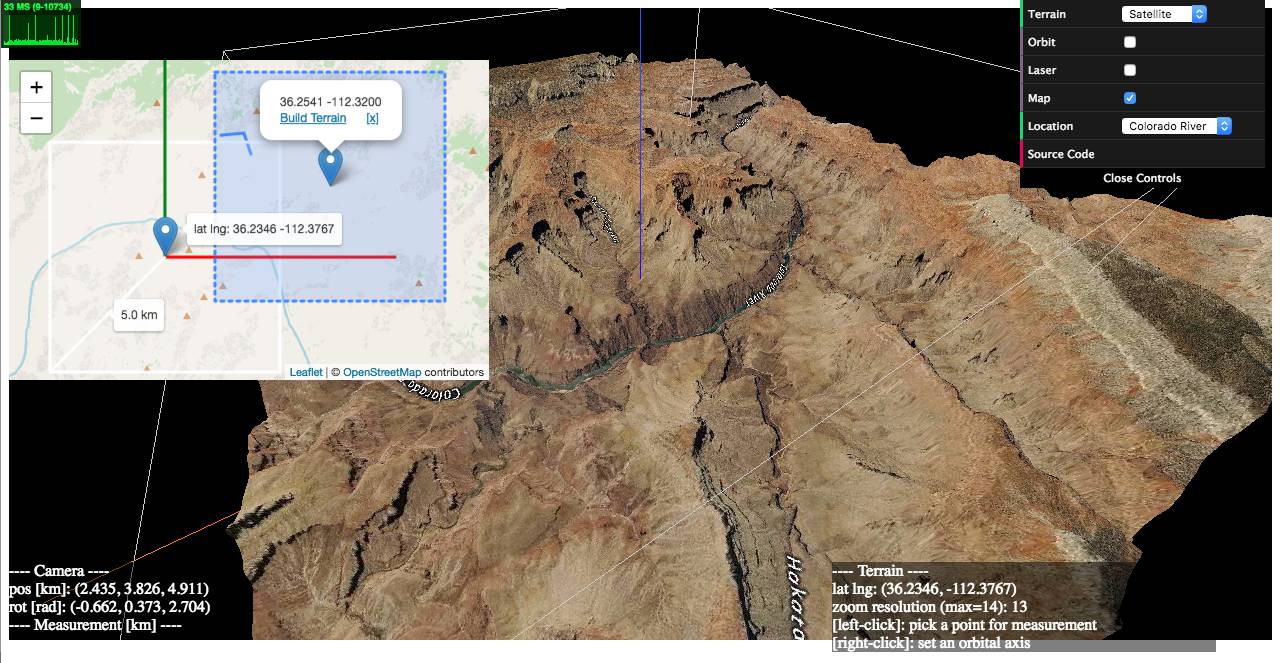](https://w3reality.github.io/three-geo/examples/geo-viewer/io/index.html?lat=36.2058&lng=-112.4413&title=Colorado_River)
### 2) examples/heightmaps ([live](https://w3reality.github.io/three-geo/examples/heightmaps/index.html) | [source code](https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo/tree/master/examples/heightmaps))
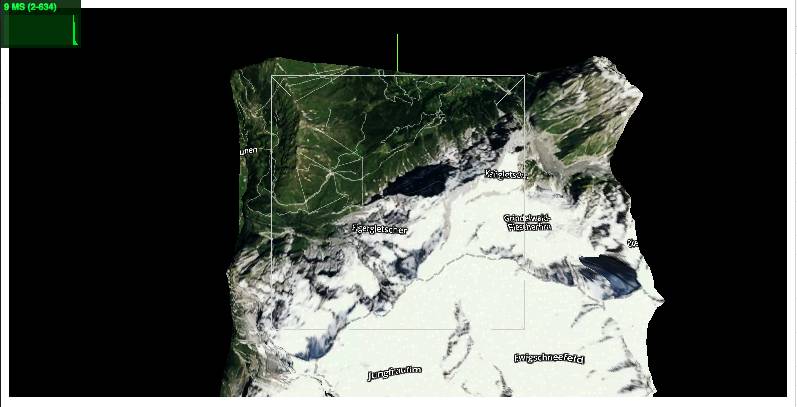
This demo illustrates the relationship between a reconstructed 3D terrain and its underlying satellite/DEM tiles.
[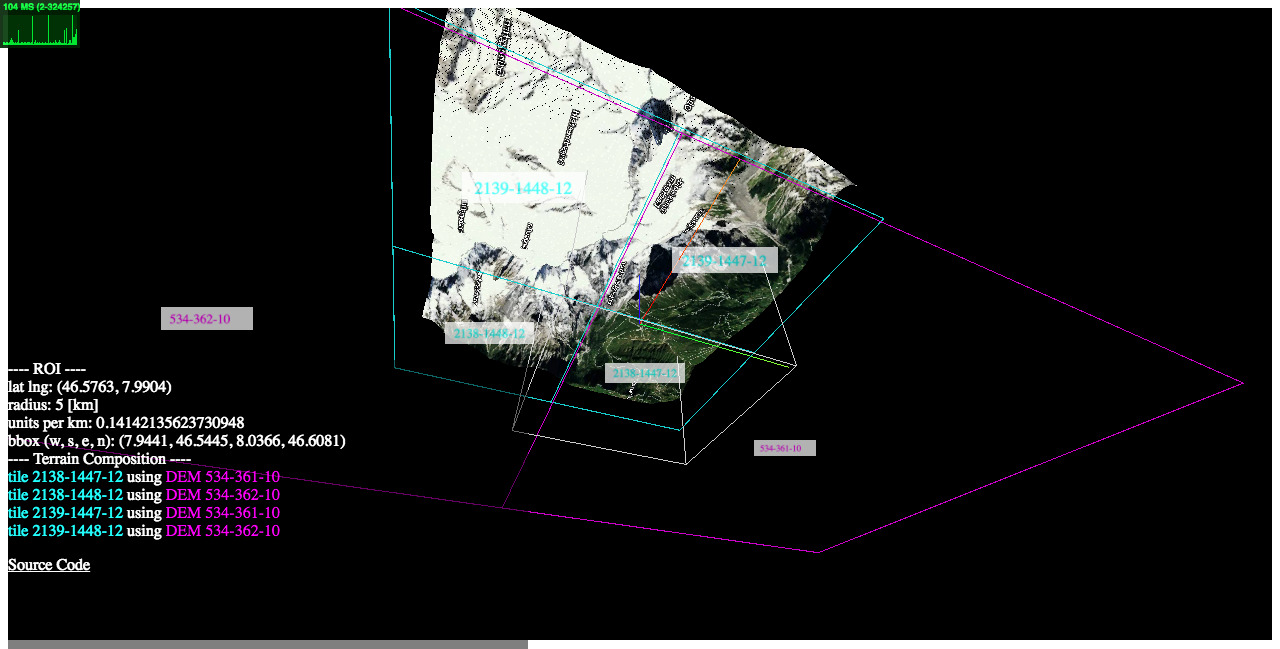](https://w3reality.github.io/three-geo/examples/heightmaps/index.html)
### 3) examples/flat ([live](https://w3reality.github.io/three-geo/examples/flat/index.html) | [source code](https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo/tree/master/examples/flat/index.html))
How to get a flattened view of the terrain by post-editing the underlying geometry.
### 4) examples/projection ([live](https://w3reality.github.io/three-geo/examples/projection/index.html) | [source code](https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo/tree/master/examples/projection/index.html))
How to register a new 3D object on top of the terrain based on its geographic location `[latitude, longitude, elevation]`.
## Setup
**Installation**
```
$ npm i three-geo
```
**Loading**
Script tag: use `ThreeGeo` after
```
```
ES6:
```
import ThreeGeo from 'dist/three-geo.esm.js';
```
## Usage
Here is an example of how to build a geographic terrain located at GPS coordinates (46.5763, 7.9904) in a 5 km radius circle. The terrain's satellite zoom resolution is set to 12. (The highest zoom value supported is 17.)
For standalone tests, use **examples/simple-viewer** ([source code](https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo/tree/master/examples/simple-viewer)).
For use with NodeJS, do enable [this `isNode` option](#note-nodejs) as well.
```js
const tgeo = new ThreeGeo({
tokenMapbox: '********', // <---- set your Mapbox API token here
});
const terrain = await tgeo.getTerrainRgb(
[46.5763, 7.9904], // [lat, lng]
5.0, // radius of bounding circle (km)
12); // zoom resolution
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.add(terrain);
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ canvas });
renderer.render(scene, camera);
```
[](https://w3reality.github.io/three-geo/examples/simple-viewer/index.html)
## Who is using `three-geo`?
- [jet-wasp](https://jet-wasp.glitch.me/) - Three-geo as A-Frame component ([source code](https://glitch.com/edit/#!/jet-wasp))
- [locus-pocus](https://locus-pocus.io/) - A webapp to visualise your area using three-geo
## API
In this section, we list `three-geo`'s public API methods, where `origin`, `radius`, and `zoom` are parameters common to them:
- `origin` **Array\** Center of the terrain represented as GPS coordinates `[latitude, longitude]`.
- `radius` **number** Radius of the circle that fits the terrain.
- `zoom` **number (integer)** Satellite zoom resolution of the tiles in the terrain. Select from {11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17}, where 17 is the highest value supported. For a fixed radius, higher zoom resolution results in more tileset API calls.
`ThreeGeo`
- `constructor(opts={})`
Create a ThreeGeo instance with parameters.
- `opts.tokenMapbox`=\"\" **string** Mapbox API token. This must be provided.
- `opts.unitsSide`=1.0 **number** The side length of the square that fits the terrain in WebGL space.
- `opts.isNode`=false **boolean** To use three-geo with NodeJS, you must explicitly set this option to `true`. [ Added in v1.4.5 ]
- `async getTerrainRgb(origin, radius, zoom)` [ Added in v1.4 ]
Return a **THREE.Group** object that represents a 3D surface of the terrain.
The group object contains an **Array\** as `.children`. Each mesh corresponds to a partial geometry of the terrain textured with satellite images.
- `async getTerrainVector(origin, radius, zoom)` [ Added in v1.4 ]
Return a **THREE.Group** object that represents a 3D contour map of the terrain.
The group object contains an **Array\** as `.children`. Each child object is either an extruded **THREE.Mesh** with `.name` attribute prefixed by `dem-vec-shade--`, or a **THREE.Line** with `.name` prefixed by `dem-vec-line--` (`` is the height of each contour in meters).
- `getProjection(origin, radius, unitsSide=1.0)` [ [Example](#ex-proj) ]
Return an object `{ proj, projInv, bbox, unitsPerMeter }` that includes transformation-related functions and parameters, where
- `proj(latlng)` is a function that maps geo coordinates `latlng` (an array `[lat, lng]`) to WebGL coordinates `[x, y]`.
- `projInv(x, y)` is a function that maps WebGL coordinates `[x, y]` to geo coordinates `[lat, lng]`.
- `bbox` is an array `[w, s, e, n]` that represents the computed bounding box of the terrain, where `w` (West) and `e` (East) are longitudinal limits; and `s` (South) and `n` (North) are latitudinal limits.
- `unitsPerMeter` is the length in WebGL-space per meter.
Legacy callback based API
- `getTerrain(origin, radius, zoom, callbacks={})`
- `callbacks.onRgbDem` **function (meshes) {}** Implement this to request the geometry of the terrain. Called when the entire terrain\'s geometry is obtained.
- `meshes` **Array\** All the meshes belonging to the terrain.
- `callbacks.onSatelliteMat` **function (mesh) {}** Implement this to request the satellite textures of the terrain. Called when the satellite texture of each mesh belonging to the terrain is obtained.
- `mesh` **THREE.Mesh** One of the meshes that's part of the terrain.
- `callbacks.onVectorDem` **function (objs) {}** Implement this to request the contour map of the terrain. Called when the contour map of the terrain is obtained.
- `objs` **Array\** Extruded meshes (**THREE.Mesh** objects with `.name` attribute prefixed by `dem-vec-shade--`) and lines (**THREE.Line** objects with `.name` attribute prefixed by `dem-vec-line--`), where `` is the height of each contour in meters.
## Build
After `git clone` and `cd` to the repository,
```
$ npm i
$ npm run build
```
### Building on Windows
While `npm run build` on Windows is confirmed to work (via GitHub's [workflow with some tweaks](https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo/blob/b8775e3a3e2d6b815fd550a96f7f45e441ff54a2/.github/workflows/nodejs.yml#L30-L32)), for better results, it is recommended to use WSL2 instead (thanks [@sonicviz](https://github.com/sonicviz) for [reporting this](https://github.com/w3reality/three-geo/issues/44#issuecomment-1482906468)).