https://github.com/wagiminator/ch32x033-usb-nrf
USB controlled nRF24L01+ 2.4GHz Transceiver
https://github.com/wagiminator/ch32x033-usb-nrf
ch32x033 ch32x035 nrf24l01 rf-transceiver risc-v transceiver usb usb-cdc
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
USB controlled nRF24L01+ 2.4GHz Transceiver
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/wagiminator/ch32x033-usb-nrf
- Owner: wagiminator
- License: other
- Created: 2024-03-09T16:07:36.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-11-24T11:14:49.000Z (7 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-26T06:19:28.456Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: ch32x033, ch32x035, nrf24l01, rf-transceiver, risc-v, transceiver, usb, usb-cdc
- Language: C
- Homepage: https://oshwlab.com/wagiminator/ch32x033-usb2nrf
- Size: 780 KB
- Stars: 14
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# USB2NRF - USB Controlled 2.4GHz Transceiver
NRF2USB is a simple development tool designed specifically for wireless applications that utilize the low-cost nRF24L01+ 2.4GHz transceiver module. The integrated CH32X033 microcontroller provides a USB interface for communication with the module. The versatility of this tool makes it an ideal choice for a wide range of wireless applications.
Depending on the firmware, it can be used, for example, to transfer serial data wirelessly between two PCs (USB CDC - Communications Device Class) or as a receiver for wireless keyboards, mice or joysticks (USB HID - Human Interface Device). It is also possible to receive sensor data or control remote actuators. This makes it ideal for IoT (Internet of Things) applications where data collected from sensors needs to be transmitted wirelessly to a central device for analysis.
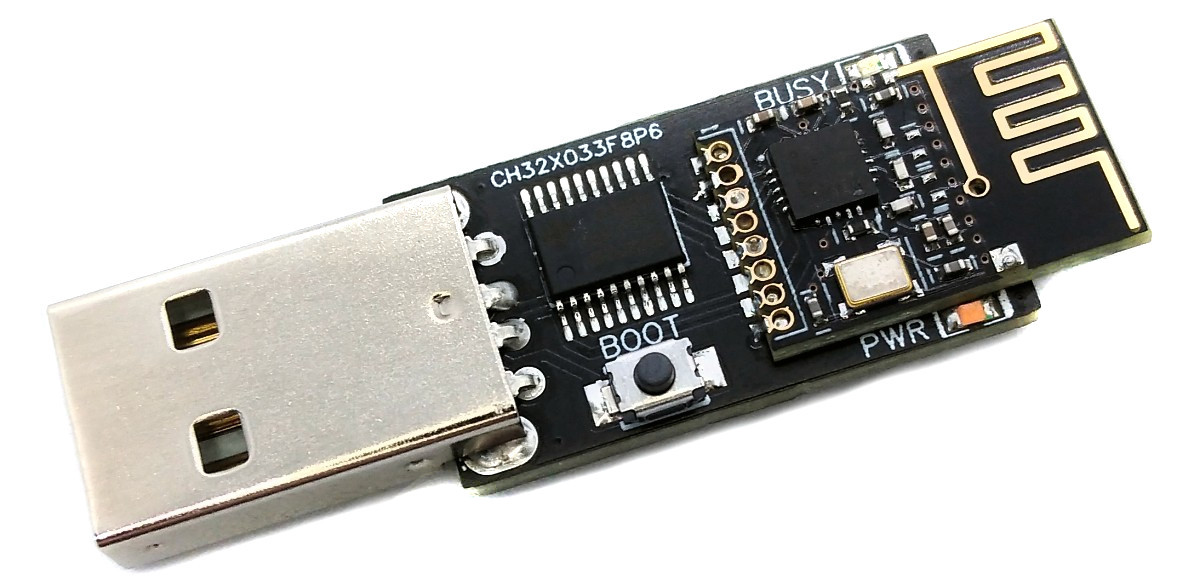
# Hardware
## Schematic
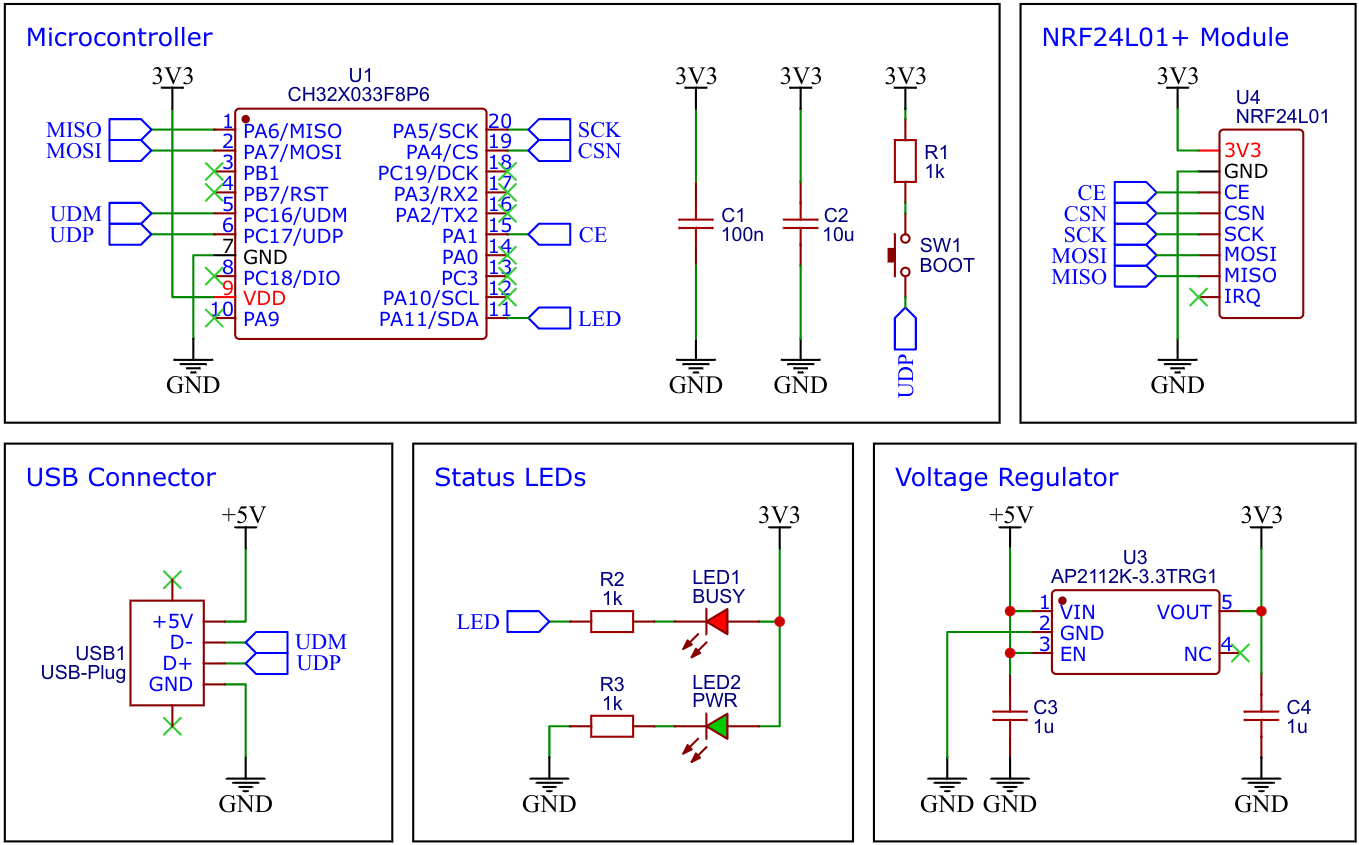
## CH32X033 32-bit RISC-V USB Microcontroller
CH32X033 is a low-cost microcontroller that utilizes the QingKe 32-bit RISC-V4C core, supporting the RV32IMAC instruction set along with self-extending instructions. This microcontroller comes with a built-in USB PHY and supports USB2.0 full-speed device functions. It features a programmable protocol I/O controller (PIOC), 2 groups of operational amplifiers (OPA) with programmable gain (PGA), 2 groups of analog comparators (CMP), a 12-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC), a 10-channel touch-key controller, 4 groups of USART, I2C, SPI, multiple timers, and various other peripheral resources. The device can operate at clock frequencies of up to 48MHz and is compatible with a supply voltage range of 2.0V to 5.5V. The CH32X033 includes 62KB of flash, 20KB of SRAM, and an embedded USB bootloader.
## nRF24L01+ 2.4GHz Transceiver Module
The nRF24L01+ is a highly integrated, ultra-low power (ULP) 2Mbps RF transceiver IC for the 2.4GHz ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band. It is designed to be used as a wireless communication module in a variety of applications, such as home automation, wireless gaming, and the Internet of Things (IoT). The module is equipped with an SPI interface, which makes it simple to connect to a variety of microcontrollers, such as the Arduino, Raspberry Pi, and others.
## Building Instructions
1. Take the Gerber files (the *zip* file inside the *hardware* folder) and upload them to a PCB (printed circuit board) manufacturer of your choice (e.g., [JLCPCB](https://jlcpcb.com/)). They will use these files to create the circuit board for your device and send it to you.
2. Once you have the PCB, you can start soldering the components onto it. Use the BOM (bill of materials) and schematic as a guide to make sure everything is connected correctly. You can find the corresponding files in the *hardware* folder.
3. Upload the firmware by following the instructions in the next section (see below).
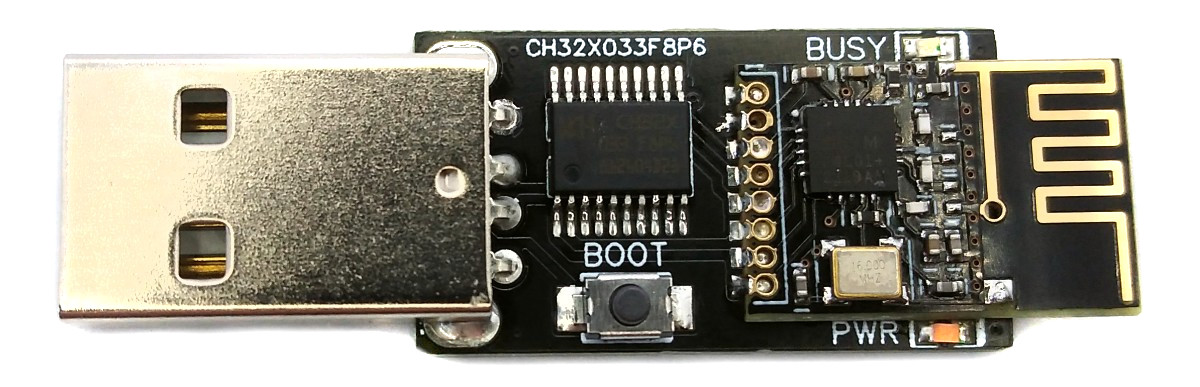

# Software
## Firmware Versions
### NRF to CDC
This firmware provides a serial interface for communication with the module via USB CDC. It can be used to transfer serial data wirelessly between two PCs, receive data from a remote sensor or trasmit commands to an actuator.
#### Operating Instructions:
Open a serial monitor and set the correct serial port (BAUD rate doesn't matter). Enter the text to be sent, terminated with a Newline (NL or '\ n'). A string that begins with an exclamation mark ('!') is recognized as a command. The command is given by the letter following the exclamation mark. Command arguments are appended as bytes in 2-digit hexadecimal directly after the command. The following commands can be used to set the NRF:
|Command|Description|Example|Example Description|
|-|:-|:-|:-|
|c|set channel|!c2A|set channel to 0x2A (0x00 - 0x7F)|
|t|set TX address|!t7B271F1F1F|addresses are 5 bytes, LSB first|
|r|set RX address|!r41C355AA55|addresses are 5 bytes, LSB first|
|s|set speed|!s02|data rate (00:250kbps, 01:1Mbps, 02:2Mbps)|
Enter just the exclamation mark ('!') for the actual NRF settings to be printed in the serial monitor.
### NRF to HID
- in development...
## USB Bootloader
### Installing Drivers for the Bootloader
On Linux you do not need to install a driver. However, by default Linux will not expose enough permission to upload your code with the USB bootloader. In order to fix this, open a terminal and run the following commands:
```
echo 'SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="4348", ATTR{idProduct}=="55e0", MODE="666"' | sudo tee /etc/udev/rules.d/99-ch55x.rules
echo 'SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="1a86", ATTR{idProduct}=="55e0", MODE="666"' | sudo tee -a /etc/udev/rules.d/99-ch55x.rules
sudo udevadm
```
For Windows you can use the [Zadig](https://zadig.akeo.ie/) tool to install the correct driver. Here, click "Options" -> "List All Devices" and select the USB module. Then install the libusb-win32 driver. To do this, the board must be connected and the microcontroller must be in bootloader mode.
### Entering Bootloader Mode
The bootloader must be started manually for new uploads. To do this, the board must first be disconnected from the USB port. Now press the BOOT button and keep it pressed while reconnecting the board to the USB port of your PC. The chip now starts in bootloader mode, the BOOT button can be released and new firmware can be uploaded via USB within the next couple of seconds.
## Compiling and Uploading Firmware using the Makefile
### Linux
Install the toolchain (GCC compiler, Python3, and chprog):
```
sudo apt install build-essential libnewlib-dev gcc-riscv64-unknown-elf
sudo apt install python3 python3-pip
pip install chprog
```
Open a terminal and navigate to the folder with the *makefile*. Press the BOOT button and keep it pressed while connecting the board to the USB port of your PC. Run the following command to compile and upload:
```
make flash
```
### Other Operating Systems
Follow the instructions on [CNLohr's ch32v003fun page](https://github.com/cnlohr/ch32v003fun/wiki/Installation) to set up the toolchain on your respective operating system (for Windows, use WSL). Also, install [Python3](https://www.pythontutorial.net/getting-started/install-python/) and [chprog](https://pypi.org/project/chprog/). Compile and upload with "make flash". Note that I only have Debian-based Linux and have not tested it on other operating systems.
## Compiling and Uploading Firmware using PlatformIO
- Install [PlatformIO](https://platformio.org) and [platform-ch32v](https://github.com/Community-PIO-CH32V/platform-ch32v). Follow [these instructions](https://pio-ch32v.readthedocs.io/en/latest/installation.html) to do so. Linux/Mac users may also need to install [pyenv](https://realpython.com/intro-to-pyenv).
- Click on "Open Project" and select the firmware folder with the *platformio.ini* file.
- Press the BOOT button and keep it pressed while connecting the board to the USB port of your PC. Then click "Upload".
## Uploading pre-compiled Firmware Binary
WCH offers the free but closed-source software [WCHISPTool](https://www.wch.cn/downloads/WCHISPTool_Setup_exe.html) to upload firmware with Windows via the USB bootloader. Press the BOOT button and keep it pressed while connecting the board to the USB port of your PC. Release the BOOT button, open the *.hex* file in the *bin* folder with WCHISPTool and upload it to the microcontroller.
If [Python3](https://www.pythontutorial.net/getting-started/install-python/) is installed, you can also use the platform-independent open-source command-line tool [chprog](https://pypi.org/project/chprog/) for uploading:
```
chprog bin/.bin
```
## Installing CDC driver
On Linux you do not need to install a CDC driver. On Windows you may need the [Zadig](https://zadig.akeo.ie/) tool to install the correct driver for the CDC device. Click "Options" and "List All Devices" to select the CDC device, then install the CDC driver.
# References, Links and Notes
- [EasyEDA Design Files](https://oshwlab.com/wagiminator)
- [MCU Templates](https://github.com/wagiminator/MCU-Templates)
- [MCU Flash Tools](https://github.com/wagiminator/MCU-Flash-Tools)
- [CH32X033 Datasheets](http://www.wch-ic.com/products/CH32X035.html)
- [nRF24L01+ Datasheet](https://www.sparkfun.com/datasheets/Components/SMD/nRF24L01Pluss_Preliminary_Product_Specification_v1_0.pdf)
- [ATtiny814 USB2NRF](https://github.com/wagiminator/ATtiny814-NRF2USB)
- [CH552G USB2NRF](https://github.com/wagiminator/CH552-USB-NRF)
- [nRF24L01+ on Aliexpress](http://aliexpress.com/wholesale?SearchText=nrf24l01+plus+smd)
# License

This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)