https://github.com/wessberg/cjstoesm
A tool that can transform CommonJS to ESM
https://github.com/wessberg/cjstoesm
api cjs cli commonjs compiler es6 esm modules rollup transformer treeshake typescript webpack
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
A tool that can transform CommonJS to ESM
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/wessberg/cjstoesm
- Owner: wessberg
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-04-30T20:36:38.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-12-09T17:45:04.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-05-01T22:50:46.131Z (over 1 year ago)
- Topics: api, cjs, cli, commonjs, compiler, es6, esm, modules, rollup, transformer, treeshake, typescript, webpack
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 5.53 MB
- Stars: 376
- Watchers: 6
- Forks: 16
- Open Issues: 19
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
- License: LICENSE.md
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-github-star - cjstoesm
README
> A tool that can transform CommonJS to ESM
## Description
This is a tool that converts [CommonJS modules](https://requirejs.org/docs/commonjs.html) into tree-shakeable [ES Modules](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/import).
This allows you to not only bundle CommonJS modules for the browser, but also makes it possible for you to bundle them in modern tools such as [Rollup](https://rollupjs.org/).
It can also be used as a tool for migrating a CommonJS-based codebase to one based on ES-modules via a simple [CLI](#cli-usage).
`cjstoesm` can be used from the [Command Line](#cli-usage), as [a JavaScript library](#api-usage), and as a [TypeScript Custom Transformer](#usage-with-typescripts-compiler-apis).
Prior art such as [babel-plugin-transform-commonjs](https://github.com/tbranyen/babel-plugin-transform-commonjs) and [rollup-plugin-commonjs](https://github.com/rollup/rollup-plugin-commonjs) exists, but this Custom Transformer aims at producing code that is just as tree-shakeable as equivalent code written
natively with ES Modules. Additionally, it aims to be as clean as possible, with no _"wrappers"_ around modules as can be seen in other similar solutions.
For example, here's how `cjstoesm` may rewrite a CommonJS module:
**Input**
```typescript
exports.foo = function foo() {};
```
**Output**
```typescript
export function foo() {}
```
Here's another example:
**Input**
```typescript
module.exports = {
foo() {
return 2 + 2;
},
bar: 3,
baz: new RegExp("")
};
```
**Output**
```typescript
export function foo() {
return 2 + 2;
}
export const bar = 3;
export const baz = new RegExp("");
export default {foo, bar, baz};
```
The same goes for `require(...)` calls:
**Input:**
```typescript
const {foo: bar} = require("./my-module");
```
**Output:**
```typescript
import {foo as bar} from "./my-module.js";
```
And for complex require calls such as:
**Input:**
```typescript
const {
foo: {bar: baz}
} = require("./my-module").something("bar");
```
**Output:**
```typescript
import {something} from "./my-module.js";
const {
foo: {bar: baz}
} = {something}.something("bar");
```
As you can see, this transformer will attempt to produce code that generates as granular imports and exports as possible.
It includes Import Attributes too! And out of the box, these are added where relevant and necessary:
**Input**
```typescript
const pkg = require("./package.json");
```
**Output**
```typescript
import pkg from "./package.json" with {type: "json"};
```
### Features
- Transformation of CommonJS to ESM
- Tree-shaking friendly
- Clean, idiomatic output
- Automatic and configurable addition of file extensions to module specifiers
- Automatic and configurable addition of import attributes to relevant import declarations
- No wrappers
- Low-level implementation that can be used as the foundation for other tools such as Loaders, Plugins, CLIs, and Linters.
- CLI integration, enabling you to convert a project from CJS to ESM from the command line.
- API support, enabling you to convert a project from CJS to ESM programmatically.
## Backers
### Patreon
## Table of Contents
- [Description](#description)
- [Features](#features)
- [Backers](#backers)
- [Patreon](#patreon)
- [Table of Contents](#table-of-contents)
- [Install](#install)
- [npm](#npm)
- [Yarn](#yarn)
- [pnpm](#pnpm)
- [Run once with npx](#run-once-with-npx)
- [Peer Dependencies](#peer-dependencies)
- [Engine](#engine)
- [File extension handling](#file-extension-handling)
- [Import Attributes handling](#import-attributes-handling)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [CLI usage](#cli-usage)
- [API Usage](#api-usage)
- [API options](#api-options)
- [Usage with TypeScript's Compiler APIs](#usage-with-typescripts-compiler-apis)
- [Usage with Rollup](#usage-with-rollup)
- [Usage with @rollup/plugin-typescript](#usage-with-rollupplugin-typescript)
- [Usage with Webpack](#usage-with-webpack)
- [Usage with awesome-typescript-loader](#usage-with-awesome-typescript-loader)
- [Usage with ts-loader](#usage-with-ts-loader)
- [Custom Transformer Options](#custom-transformer-options)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
- [FAQ](#faq)
- [Is conditional require(...) syntax converted into dynamic imports?](#is-conditional-require-syntax-converted-into-dynamic-imports)
- [License](#license)
## Install
### npm
```
$ npm install cjstoesm
```
### Yarn
```
$ yarn add cjstoesm
```
### pnpm
```
$ pnpm add cjstoesm
```
### Run once with npx
First, add the peer dependency `typescript` as a dependency to the package from which you're going to run `cjstoesm`. Alternatively, if you want to run it from _anywhere_, you can also install it globally: `npm i -g typescript`. Now, you can simply run:
```
$ npx cjstoesm
```
You can also run `cjstoesm` along with its peer dependencies in one combined command:
```
$ npx -p typescript -p cjstoesm cjstoesm
```
### Peer Dependencies
`cjstoesm` depends on `typescript`, so you need to manually install this as well.
## Engine
`cjstoesm` requires Node.js v14.19.0 or newer to function correctly.
## File extension handling
The default behavior is to add file extensions to module specifiers to align with the implementation in [node.js](https://nodejs.org/dist/latest/docs/api/esm.html#esm_mandatory_file_extensions) and across browsers.
You can customize this with the `--preserve-module-specifiers` command line option, or with the `preserveModuleSpecifiers` API option. See the [API Options](#api-options) for documentation for the possible values you can pass to it.
## Import Attributes handling
The default behavior is to add Import Attributes to Import Declarations when necessary and relevant, such as for when referencing JSON files. This aligns with the implementation in [node.js](https://nodejs.org/dist/latest/docs/api/esm.html#import-attributes) and across browsers.
You can customize this with the `--import-attributes` command line option, or with the `importAttributes` API option. See the [API Options](#api-options) for documentation for the possible values you can pass to it.
## Usage
`cjstoesm` can be used in a variety of ways. The most straightforward usage is directly from the CLI:
### CLI usage
You can use this library as a CLI to convert your project files from using CommonJS to using ESM.
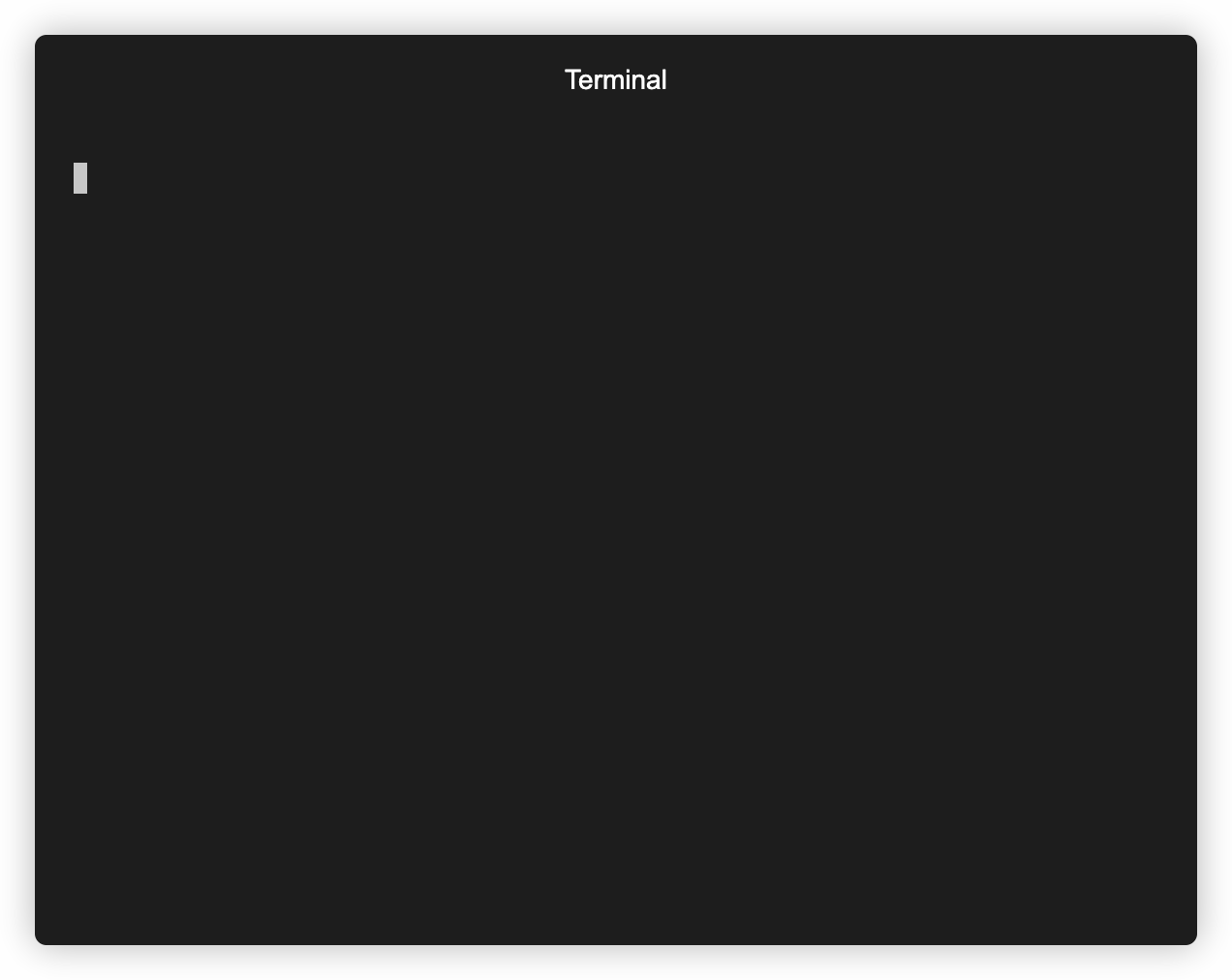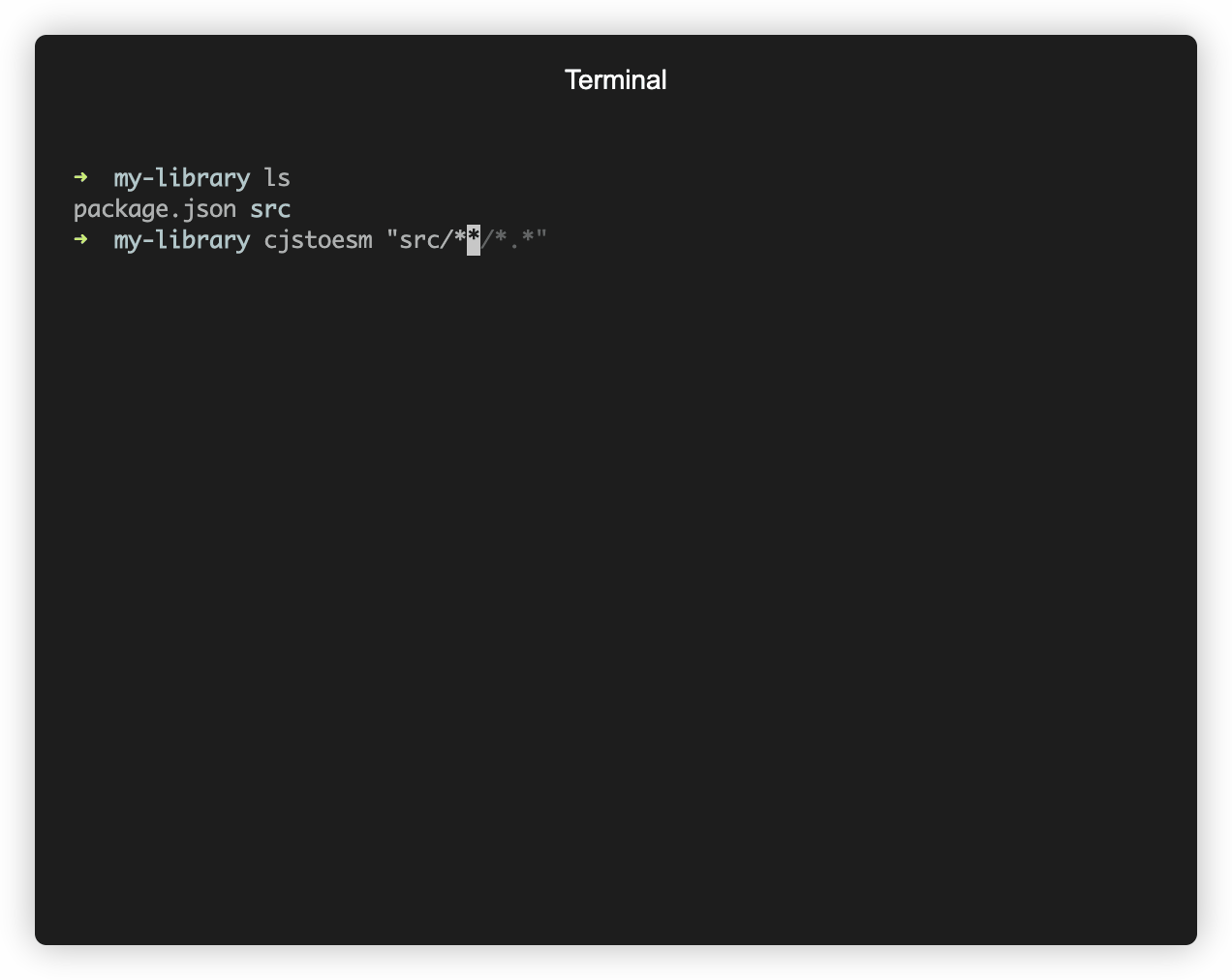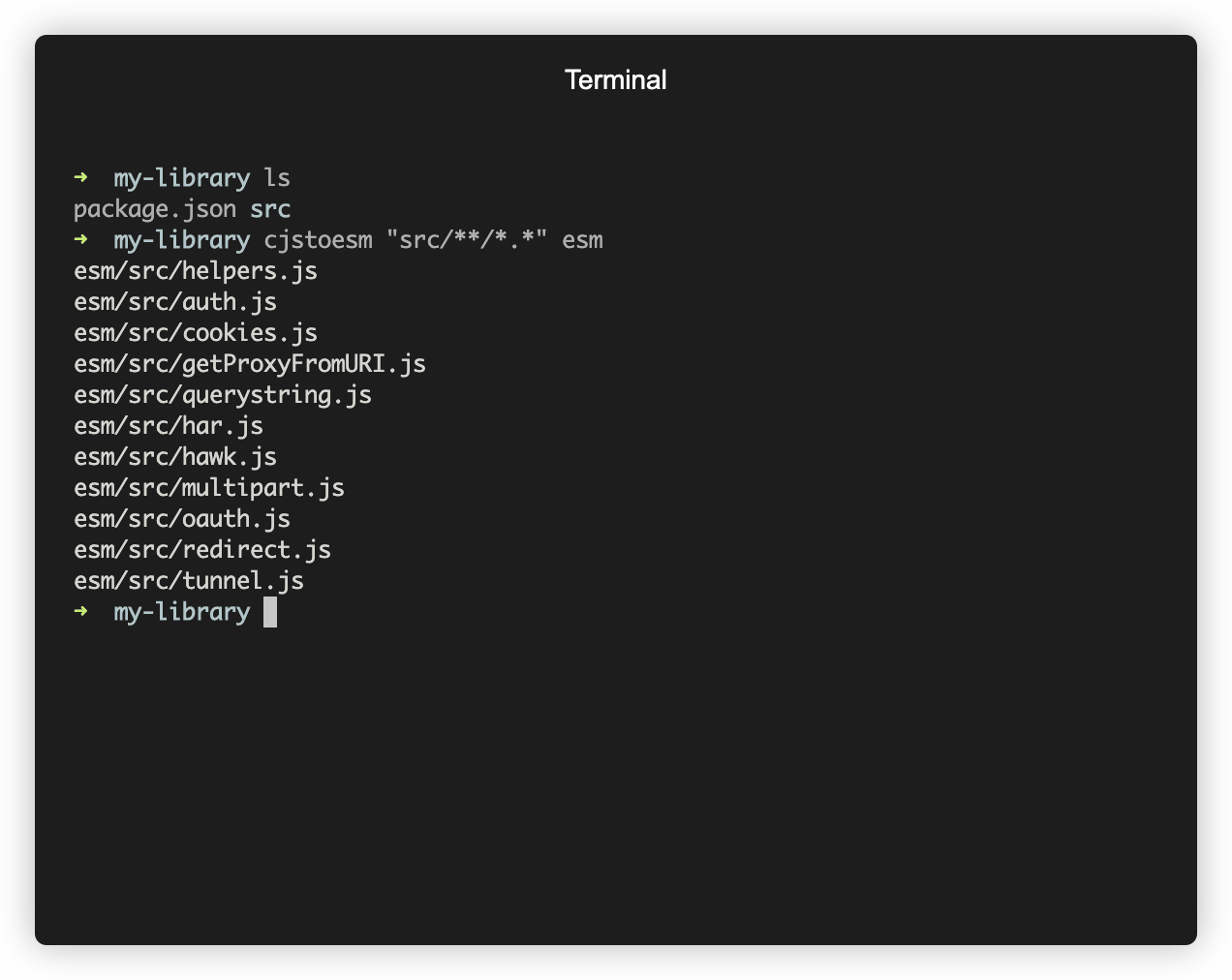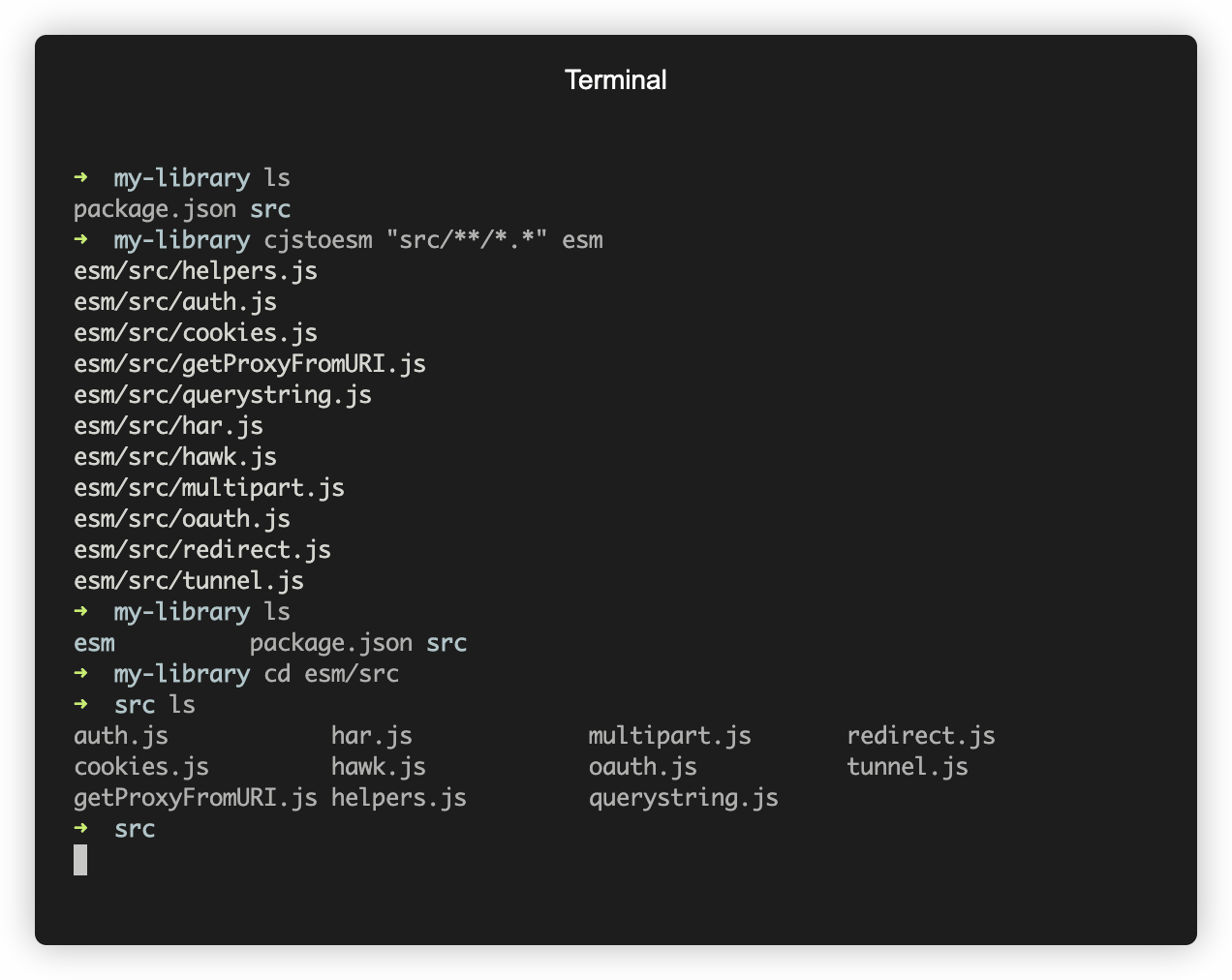
The following command transforms all files matched by the glob `**/*.*` and overwrites them in-place:
```
cjstoesm "**/*.*"
```
You can also just pass in a folder name, in which case all direct descendents of that folder will be transformed and overwritten:
```
cjstoesm "src"
```
You can also pass in a second argument, `outDir`, to avoid overwriting the source files. The following command transforms all files matched by the glob `**/*.*` and emits them to the folder `dist` from the current working directory:
```
cjstoesm "**/*.*" dist
```
Here's an overview of the options that can be passed via the CLI:
```
$ cjstoesm --help
Usage: cjstoesm [options]
Transforms CJS to ESM modules based on the input glob
Options:
-d, --debug [arg] Whether to print debug information
-v, --verbose [arg] Whether to print verbose information
-s, --silent [arg] Whether to not print anything
-c, --cwd [arg] Optionally which directory to use as the current working directory
-p, --preserve-module-specifiers [arg] Determines whether or not module specifiers are preserved. Possible values are: "external", "internal", "always", and "never" (default: "external")
-a, --import-attributes [arg] Determines whether or not Import Attributes are included where they are relevant. Possible values are: true and false (default: true)
-m, --dry [arg] If true, no files will be written to disk
-h, --help display help for command
```
### API Usage
You can also use this library programmatically:
```ts
import {transform} from "cjstoesm";
await transform({
input: "src/**/*.*",
outDir: "dist"
});
```
Alternatively, if you don't want the transform function to automatically write files to disk, you can pass `write: false` as an option and handle
it yourself:
```ts
import {transform} from "cjstoesm";
import {writeFileSync} from "fs";
const result = await transform({
input: "src/**/*.*",
write: false
});
// Write to disk
for (const {fileName, text} of result.files) {
writeFileSync(fileName, text);
}
```
#### API options
```typescript
interface TransformOptions {
/**
* The input glob(s) to match against the file system
*/
input: string[] | string;
/**
* Optionally, the output directory to use. Defaults to inheriting that of the matched input files`
*/
outDir?: string;
/**
* If write is false, no files will be written to disk
*/
write: boolean;
/**
* The FileSystem to use. Useful if you want to work with a virtual file system. Defaults to using the "fs" module
*/
fileSystem: FileSystem;
/**
* A logger that can print messages of varying severity depending on the log level
*/
logger: Loggable;
/**
* The base directory (defaults to process.cwd())
*/
cwd: string;
/**
* Determines how module specifiers are treated.
* - external (default): CommonJS module specifiers identifying libraries or built-in modules are preserved (default)
* - internal: CommonJS module specifiers identifying anything else than libraries or built-in modules are preserved
* - always: CommonJS module specifiers are never transformed.
* - never: CommonJS module specifiers are always transformed
* It can also take a function that is invoked with a module specifier and returns a boolean determining whether or not it should be preserved
*/
preserveModuleSpecifiers:
| "always"
| "never"
| "external"
| "internal"
| ((specifier: string) => boolean);
/**
* Determines whether or not to include import attributes when converting require() calls referencing JSON files to ESM.
* - true (default): Import attributes will always be added when relevant.
* - false: Import attributes will never be added.
* It can also take a function that is invoked with a module specifier and returns a boolean determining whether or not import attributes should be added
*/
importAttributes: boolean | ((specifier: string) => boolean);
/**
* If given, a specific TypeScript version to use
*/
typescript: typeof TS;
/**
* If true, debug information will be printed. If a function is provided, it will be invoked for each file name. Returning true from the function
* determines that debug information will be printed related to that file
*/
debug: boolean | string | ((file: string) => boolean);
}
```
### Usage with TypeScript's Compiler APIs
`cjstoesm` also provides its functionality as a [Custom Transformer](https://github.com/Microsoft/TypeScript/pull/13940) for Typescript.
This makes it possible for you to use it directly with TypeScript's Compiler APIs. **It works completely fine on JavaScript files, so long as you enable `allowJs` in your [CompilerOptions](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/compiler-options.html)**.
The simplest way of transpiling with Typescript would be with `transpileModule`:
```typescript
import {ModuleKind, transpileModule} from "typescript";
import {cjsToEsm} from "cjstoesm";
const result = transpileModule(`const {join} = require("path");`, {
transformers: cjsToEsm(),
compilerOptions: {
module: ModuleKind.ESNext
}
});
// 'import { join } from "path"' is printed to the console
console.log(result.outputText);
```
You may use this is conjunction with other Custom Transformers by importing `commonJsToEsmTransformerFactory` instead:
```typescript
import {ModuleKind, transpileModule} from "typescript";
import {cjsToEsmTransformerFactory} from "cjstoesm";
transpileModule(`const {join} = require("path");`, {
transformers: {
before: [cjsToEsmTransformerFactory(), someOtherTransformerFactory()],
after: [
// ...
],
afterDeclarations: [
// ...
]
},
compilerOptions: {
module: ModuleKind.ESNext
}
});
```
You can also use Custom Transformers with entire Typescript _Programs_:
```typescript
import {getDefaultCompilerOptions, createProgram, createCompilerHost} from "typescript";
import {cjsToEsm} from "cjstoesm";
const options = getDefaultCompilerOptions();
const program = createProgram({
options,
rootNames: ["my-file.js", "my-other-file.ts"],
host: createCompilerHost(options)
});
program.emit(undefined, undefined, undefined, undefined, cjsToEsm());
```
### Usage with Rollup
There are a few TypeScript plugins for Rollup that support Custom Transformers, and this tool can be easily integrated with them.
#### Usage with @rollup/plugin-typescript
Here's how you may integrate this tool with [@rollup/plugin-typescript](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@rollup/plugin-typescript):
```typescript
import ts from "@rollup/plugin-typescript";
import {cjsToEsm} from "cjstoesm";
export default {
input: "...",
output: [
/* ... */
],
plugins: [
ts({
transformers: program => cjsToEsm({program})
})
]
};
```
### Usage with Webpack
There are two popular TypeScript loaders for Webpack that support Custom Transformers:
- [awesome-typescript-loader](https://github.com/s-panferov/awesome-typescript-loader)
- [ts-loader](https://github.com/TypeStrong/ts-loader)
#### Usage with awesome-typescript-loader
```typescript
import {cjsToEsm} from "cjstoesm";
const config = {
// ...
module: {
rules: [
{
// Match .mjs, .js, .jsx, and .tsx files
test: /(\.mjs)|(\.[jt]sx?)$/,
loader: "awesome-typescript-loader",
options: {
// ...
getCustomTransformers: () => cjsToEsm()
}
}
]
}
// ...
};
```
#### Usage with ts-loader
```typescript
import {cjsToEsm} from "cjstoesm";
const config = {
// ...
module: {
rules: [
{
// Match .mjs, .js, .jsx, and .tsx files
test: /(\.mjs)|(\.[jt]sx?)$/,
loader: "ts-loader",
options: {
// ...
getCustomTransformers: () => cjsToEsm
}
}
]
}
// ...
};
```
### Custom Transformer Options
You can provide options to the `cjsToEsm` Custom Transformer to configure its behavior:
| Option | Description |
| --------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `debug` _(optional)_ | If `true`, errors will be thrown if unexpected or unhandled cases are encountered. Additionally, debugging information will be printed during transpilation. |
| `fileSystem` _(optional)_ | If given, the file system to use. Useful if you are using `cjstoesm` inside a virtual file system. |
| `preserveModuleSpecifiers` _(optional)_ | Determines whether or not module specifiers are preserved. Possible values are: "external", "internal", "always", and "never". See [API options](#api-options) for more details |
| `importAttributes` _(optional)_ | Determines whether or not Import Attributes are included where relevant. Possible values are: true and false. See [API options](#api-options) for more details |
| `typescript` _(optional)_ | If given, the TypeScript version to use internally for all operations. |
| `cwd` _(optional)_ | The directory to use as the current working directory. |
## Contributing
Do you want to contribute? Awesome! Please follow [these recommendations](./CONTRIBUTING.md).
## FAQ
### Is conditional require(...) syntax converted into dynamic imports?
No. For the input:
```typescript
const result = true ? require("./foo") : require("./bar");
```
The following may be the output, depending on the internal structure of the modules referenced by the `require` calls:
```typescript
import foo from "./foo.js";
import bar from "./bar.js";
const result = true ? foo : bar;
```
CommonJS `require()` syntax are _Expressions_, whereas ESM `import/export` syntax are _Declarations_, and to achieve the same expressiveness with ESM, dynamic imports are required.
However, these return `Promises` and as such cannot be transformed equivalently.
## License
MIT ©






