https://github.com/wisconsinaivision/mixnmatch
Pytorch implementation of MixNMatch
https://github.com/wisconsinaivision/mixnmatch
deep-learning disentangled-representations fine-grained gans image-generation image-manipulation pytorch
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Pytorch implementation of MixNMatch
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/wisconsinaivision/mixnmatch
- Owner: WisconsinAIVision
- Created: 2019-11-26T02:40:22.000Z (almost 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2020-07-07T23:01:18.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-04T02:07:08.840Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: deep-learning, disentangled-representations, fine-grained, gans, image-generation, image-manipulation, pytorch
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 20.2 MB
- Stars: 973
- Watchers: 54
- Forks: 189
- Open Issues: 12
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# MixNMatch: Multifactor Disentanglement and Encoding for Conditional Image Generation
[[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11758)
[Yuheng Li](https://github.com/Yuheng-Li),
[Krishna Kumar Singh](http://krsingh.cs.ucdavis.edu/),
[Utkarsh Ojha](https://utkarshojha.github.io/),
[Yong Jae Lee](https://web.cs.ucdavis.edu/~yjlee/)
UC Davis
In [CVPR, 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11758)
**1/31/2020 update: Code and models released.**
## Demo Video
[](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w36vnkIbyjs)
This is our CVPR2020 presentation video [link](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MmFL59X-Xwg)
## Web Demo
For interactive web demo [click here](http://vision1.idav.ucdavis.edu:8005/). This web demo is created by Yang Xue.
## Requirements
- Linux
- Python 3.7
- Pytorch 1.3.1
- NVIDIA GPU + CUDA CuDNN
## Getting started
### Clone the repository
```bash
git clone https://github.com/Yuheng-Li/MixNMatch.git
cd MixNMatch
```
### Setting up the data
Download the formatted CUB data from this [link](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ardy8L7Cb-Vn1ynQigaXpX_JHl0dhh2M/view?usp=sharing) and extract it inside the `data` directory
### Downloading pretrained models
Pretrained models for CUB, Dogs and Cars are available at this [link](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1c4NtKyccBNDuh_vqB-KlzZpRv9cQxEI7?usp=sharing). Download and extract them in the `models` directory.
## Evaluating the model
In `code`
- Run `python eval.py --z path_to_pose_source_images --b path_to_bg_source_images --p path_to_shape_source_images --c path_to_color_source_images --out path_to_ourput --mode code_or_feature --models path_to_pretrained_models`
- For example `python eval.py --z pose/pose-1.png --b background/background-1.png --p shape/shape-1.png --c color/color.png --mode code --models ../models --out ./code-1.png`
- **NOTE**:(1) in feature mode pose source images will be ignored; (2) Generator, Encoder and Feature_extractor in models folder should be named as G.pth, E.pth and EX.pth
## Training your own model
In `code/config.py`:
- Specify the dataset location in `DATA_DIR`.
- **NOTE**: If you wish to train this on your own (different) dataset, please make sure it is formatted in a way similar to the CUB dataset that we've provided.
- Specify the number of super and fine-grained categories that you wish for FineGAN to discover, in `SUPER_CATEGORIES` and `FINE_GRAINED_CATEGORIES`.
- For the first stage training run `python train_first_stage.py output_name`
- For the second stage training run `python train_second_stage.py output_name path_to_pretrained_G path_to_pretrained_E`
- **NOTE**: output will be in `output/output_name`
- **NOTE**: `path_to_pretrained_G` will be `output/output_name/Model/G_0.pth`
- **NOTE**: `path_to_pretrained_E` will be `output/output_name/Model/E_0.pth`
- For example `python train_second_stage.py Second_stage ../output/output_name/Model/G_0.pth ../output/output_name/Model/E_0.pth`
## Results
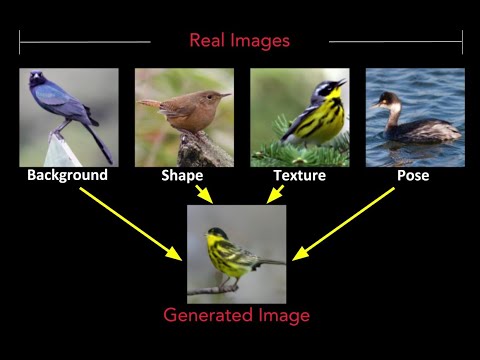
### 1. Extracting all factors from differnet real images to synthesize a new image

### 2. Comparison between the feature and code mode

### 3. Manipulating real images by varying a single factor

### 4. Inferring style from unseen data
Cartoon -> image | Sketch -> image
:-------------------------:|:-------------------------:
 |
| 
### 5. Converting a reference image according to a reference video

## Citation
If you find this useful in your research, consider citing our work:
```
@inproceedings{li-cvpr2020,
title = {MixNMatch: Multifactor Disentanglement and Encoding for Conditional Image Generation},
author = {Yuheng Li and Krishna Kumar Singh and Utkarsh Ojha and Yong Jae Lee},
booktitle = {CVPR},
year = {2020}
}
```