https://github.com/xvertile/tcp-copy-benchmark
This project aims to benchmark various methods of copying data between TCP sockets, measuring both performance and CPU usage. The goal is to identify the fastest methods with the least amount of CPU overhead.
https://github.com/xvertile/tcp-copy-benchmark
golang-tcp io-benchmark proxy-server tcp tcp-benchmarking tcp-proxy
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
This project aims to benchmark various methods of copying data between TCP sockets, measuring both performance and CPU usage. The goal is to identify the fastest methods with the least amount of CPU overhead.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/xvertile/tcp-copy-benchmark
- Owner: xvertile
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-08-01T22:17:35.000Z (10 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-01T22:27:34.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-02T00:04:13.849Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: golang-tcp, io-benchmark, proxy-server, tcp, tcp-benchmarking, tcp-proxy
- Language: Go
- Homepage:
- Size: 153 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: readme.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# TCP Data Copy Benchmark
This project aims to benchmark various methods of copying data between TCP sockets, measuring both performance and CPU usage. The goal is to identify the fastest methods with the least amount of CPU overhead.
## Benchmark Methods
The benchmark tests the following methods:
1. **IoPipe**: Utilizes the `io.Pipe` function for data transfer.
2. **IoCopy**: Uses the `io.Copy` function.
3. **IoCopyBuffer**: Uses `io.CopyBuffer` for buffered copying.
4. **Syscall**: Direct system calls for data transfer.
5. **IoCopyDirect**: Direct copy using `io.Copy`.
6. **UnixSyscall**: Unix-specific system calls.
7. **Bufio**: Buffered I/O using `bufio` package.
8. **Splice**: Linux `splice` system call.
9. **Sendfile**: Uses the `sendfile` system call.
10. **ReadvWritev**: Vectorized I/O operations using `readv` and `writev`.
## Benchmark Setup
We are using the `net` package to create a TCP server and client for data transfer. The server listens on a specified port, and the client connects to the server to send and receive data.
the payload size is set to 10Kb, and the number of iterations is set to 5000.
```go
const (
address = "localhost:12345"
numClients = 5000
bufferSize = 32 * 1024
)
var (
message = generateRandomString(10240) // Generate a 10kb random string
messageLength = len(message)
)
```
## Benchmark Results
### notes
Tested on a base Hetzner instance with the following specifications:
- **CPU**: Intel Xeon (Skylake, IBRS, no TSX) (4) @ 2.099GHz
- **RAM**: 7747MiB
- **OS**: Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS x86_64
The benchmark results are summarized as follows:
- **Execution Times (ns/op)**:
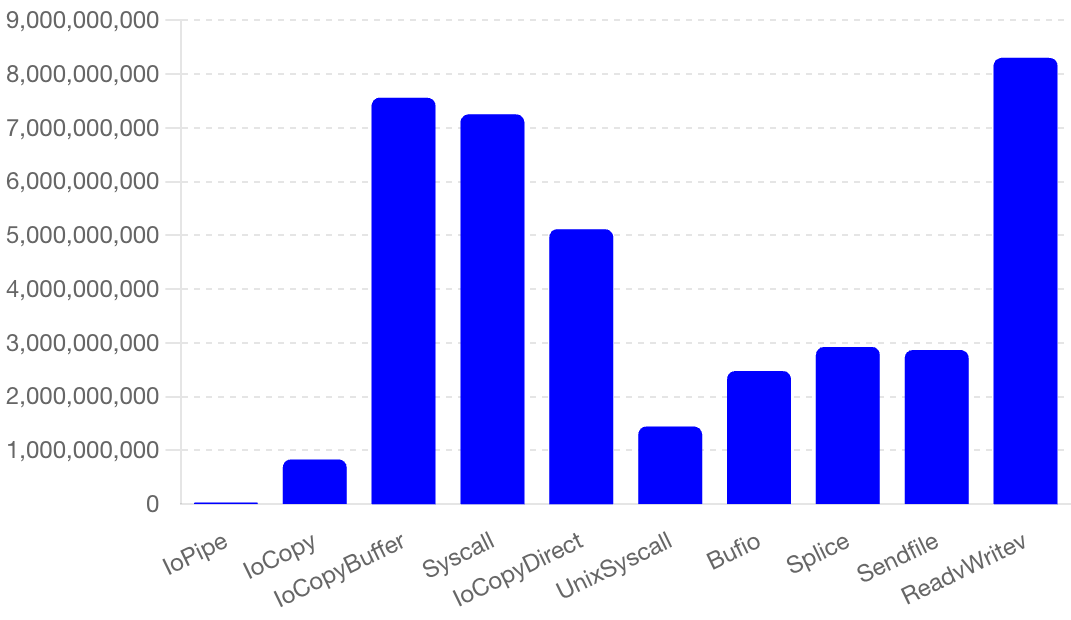
- **CPU Time (ms)**:
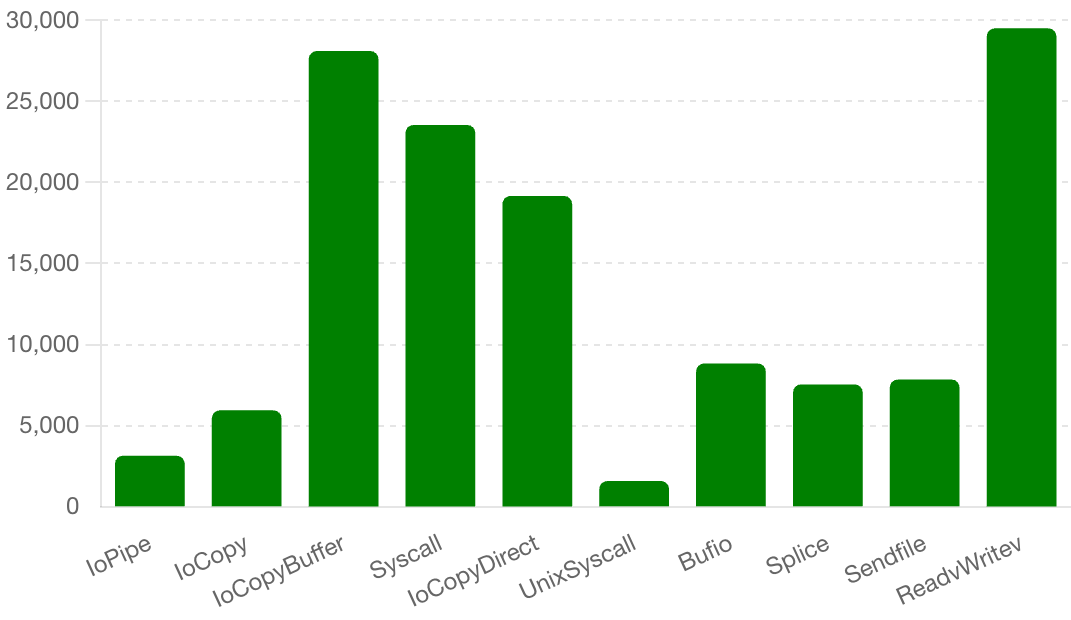
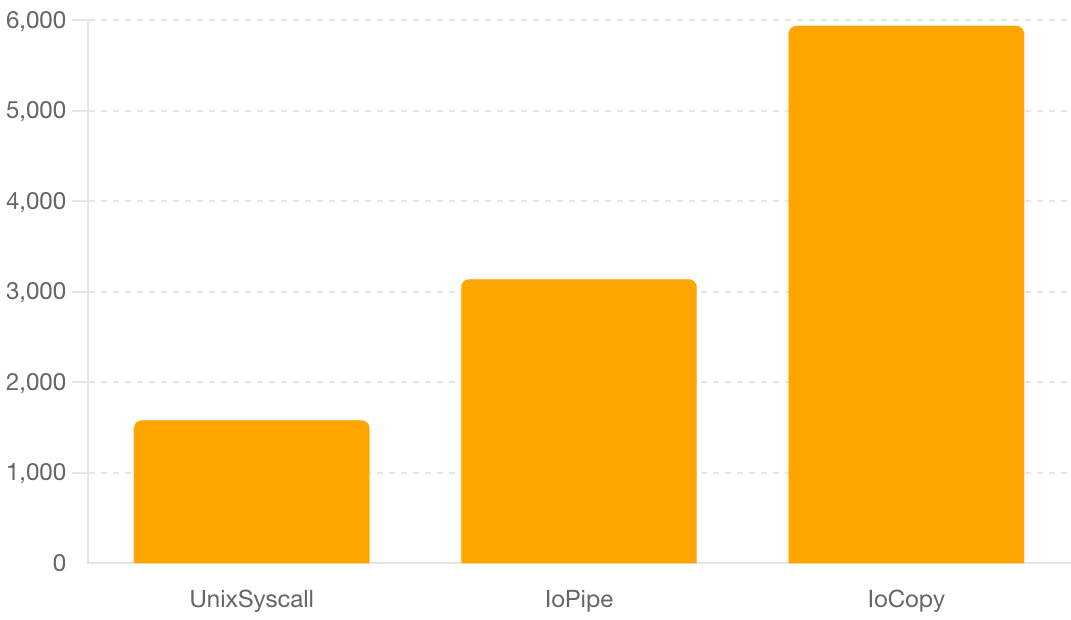
### Top 3 Methods with Least CPU Usage
1. **UnixSyscall**: 1580 ms
2. **IoPipe**: 3140 ms
3. **IoCopy**: 5940 ms
## Analysis
The `IoPipe` method stands out as a native solution working with the `net.Conn` interface, providing a balance between performance and CPU usage. However, methods such as `UnixSyscall` show the potential for further optimization by directly interfacing with the underlying system calls.
## How to Run
To execute the benchmarks and analyze the results, use the following commands:
```bash
go test -bench=. test/tcp_test.go && go run analyse.go
```
The above commands will run the benchmark tests and generate a detailed analysis of each method's performance.
## Conclusion
The native UnixSyscall method provides the best performance with the least CPU overhead. However, the IoPipe method is a close second and offers a more straightforward implementation. The choice of method depends on the specific requirements of the application, balancing performance and resource utilization.