https://github.com/zeropointdynamics/zelos
A comprehensive binary emulation and instrumentation platform.
https://github.com/zeropointdynamics/zelos
binary binary-analysis emulation emulator linux malware malware-analysis vulnerability-analysis
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
A comprehensive binary emulation and instrumentation platform.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/zeropointdynamics/zelos
- Owner: zeropointdynamics
- License: agpl-3.0
- Created: 2020-03-02T17:22:51.000Z (almost 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-01-31T00:27:41.000Z (about 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-08-24T23:41:59.698Z (6 months ago)
- Topics: binary, binary-analysis, emulation, emulator, linux, malware, malware-analysis, vulnerability-analysis
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 23.2 MB
- Stars: 416
- Watchers: 25
- Forks: 50
- Open Issues: 22
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

[](https://dev.azure.com/kevin0853/zelos/_build/latest?definitionId=1&branchName=master)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/zeropointdynamics/zelos)
[](https://zelos.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)

[](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/agpl-3.0)

# Zelos
Zelos (**Z**eropoint **E**mulated **L**ightweight **O**perating **S**ystem) is a python-based binary emulation platform. One use of zelos is to quickly assess the dynamic behavior of binaries via command-line or python scripts. All syscalls are emulated to isolate the target binary. Linux x86_64 (32- and 64-bit), ARM and MIPS binaries are supported. [Unicorn](https://github.com/unicorn-engine/unicorn) provides CPU emulation.
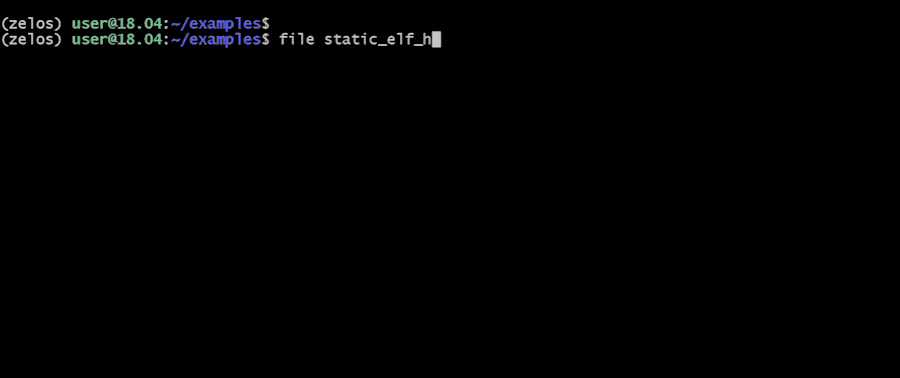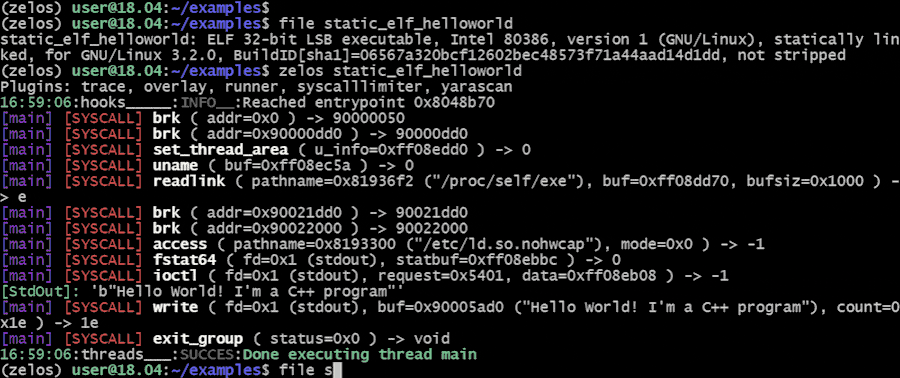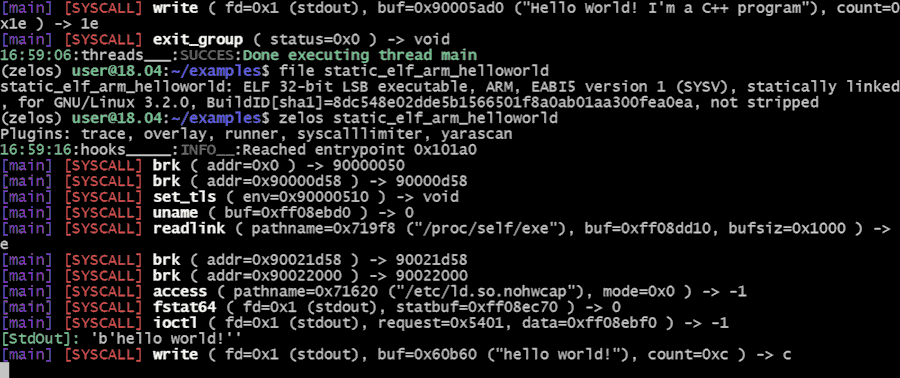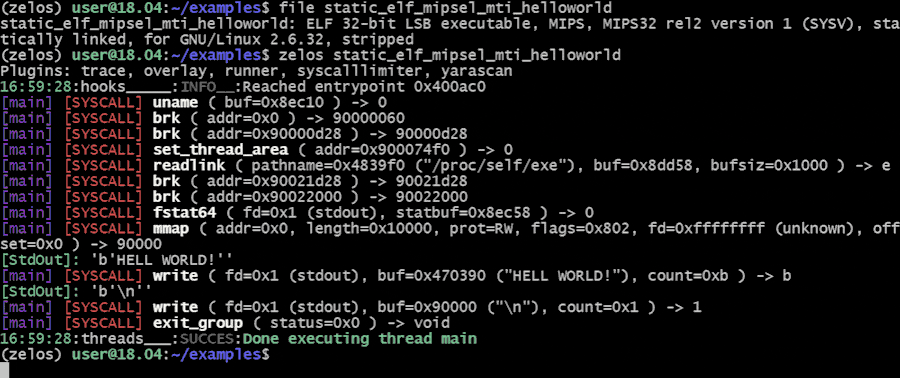
[Full documentation](https://zelos.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html) is available [here](https://zelos.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html).
## Installation
Use the package manager [pip](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/) to install zelos.
```bash
pip install zelos
```
## Basic Usage
### Command-line
To emulate a binary with default options:
```console
$ zelos my_binary
```
To view the instructions that are being executed, add the `--inst` flag:
```console
$ zelos --inst my_binary
```
You can print only the first time each instruction is executed, rather than *every* execution, using `--fasttrace`:
```console
$ zelos --inst --fasttrace my_binary
```
By default, syscalls are emitted on stdout. To write syscalls to a file instead, use the `--trace_file` flag:
```console
$ zelos --trace_file path/to/file my_binary
```
Specify any command line arguments after the binary name:
```console
$ zelos my_binary arg1 arg2
```
### Programmatic
```python
import zelos
z = zelos.Zelos("my_binary")
z.start(timeout=3)
```
## Plugins
Zelos supports first- and third-party [plugins](https://zelos.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorials/04_writing_plugins.html). Some notable plugins thus far:
- [crashd](https://github.com/zeropointdynamics/zelos-crashd) crash analyzer combining execution trace, dataflow and memory sanitization.
- [overlay (ida plugin)](https://zelos.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorials/06_snapshot_overlay.html): highlights `zelos` execution trace in IDA with instruction-level comments added.
- [angr integration](https://github.com/zeropointdynamics/angr-zelos-target): enables symbolic execution in `zelos`.
- [zdbserver](https://github.com/zeropointdynamics/zelos/tree/master/src/zelos/tools/zdbserver): remote control and debugging of emulated binaries.
- [syscall limiter](https://zelos.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorials/05_syscall_limit_plugin.html): demonstrates event hooking and provides syscall-based execution and termination options.
## Contributing
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
Please make sure to update tests as appropriate.
### Local Development Environment
First, create a new python virtual environment. This will ensure no package version conflicts arise:
```console
$ python3 -m venv ~/.venv/zelos
$ source ~/.venv/zelos/bin/activate
```
Now clone the repository and change into the `zelos` directory:
```console
(zelos) $ git clone git@github.com:zeropointdynamics/zelos.git
(zelos) $ cd zelos
```
Install an *editable* version of zelos into the virtual environment. This makes `import zelos` available, and any local changes to zelos will be effective immediately:
```console
(zelos) $ pip install -e '.[dev]'
```
At this point, tests should pass and documentation should build:
```console
(zelos) $ pytest
(zelos) $ cd docs
(zelos) $ make html
```
Built documentation is found in ``docs/_build/html/``.
Install zelos pre-commit hooks to ensure code style compliance:
```console
(zelos) $ pre-commit install
```
In addition to automatically running every commit, you can run them anytime with:
```console
(zelos) $ pre-commit run --all-files
```
#### Windows Development:
Commands vary slightly on Windows:
```console
C:\> python3 -m venv zelos_venv
C:\> zelos_venv\Scripts\activate.bat
(zelos) C:\> pip install -e .[dev]
```
## License
[AGPL v3](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/agpl-3.0.en.html)