https://github.com/zyn3rgy/LdapRelayScan
Check for LDAP protections regarding the relay of NTLM authentication
https://github.com/zyn3rgy/LdapRelayScan
Last synced: 8 months ago
JSON representation
Check for LDAP protections regarding the relay of NTLM authentication
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/zyn3rgy/LdapRelayScan
- Owner: zyn3rgy
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2022-01-16T06:50:44.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-11-19T21:11:53.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-19T22:24:18.187Z (over 1 year ago)
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 325 KB
- Stars: 464
- Watchers: 8
- Forks: 70
- Open Issues: 7
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-hacking-lists - zyn3rgy/LdapRelayScan - Check for LDAP protections regarding the relay of NTLM authentication (Python)
README
# LDAP Relay Scan
A tool to check Domain Controllers for LDAP server protections regarding the relay of NTLM authentication. If you're interested in the specifics of the error-based enumeration, see [below](https://github.com/zyn3rgy/LdapRelayScan#error-based-enumeration-specifics). For details regarding what can be done when you identify a lack of LDAP protections, see the [references section](https://github.com/zyn3rgy/LdapRelayScan#references).
## Summary
There are a couple server-side protections when attempting to relay NTLM authentication LDAP on Domain Controllers. The LDAP protections this tools attempts to enumerate include:
- LDAPS - [channel binding](https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/use-the-ldapenforcechannelbinding-registry-entry-to-make-ldap-authentication-over-ssl-tls-more-secure-e9ecfa27-5e57-8519-6ba3-d2c06b21812e)
- LDAP - [server signing requirements](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/security-policy-settings/domain-controller-ldap-server-signing-requirements)
The enforcement of channel binding for LDAP over SSL/TLS can be determined from an **unauthenticated** perspective. This is because the error associated with an LDAP client lacking the ability to conduct channel binding properly will occur before credentials are validated during the LDAP bind process.
However, to determine if the server-side protection of standard LDAP is enforced (server signing integrity requirements) the clients credential's must first be validated during the LDAP bind. The potential error identifying the enforcement of this protection is identified from an **authenticated** perspective.
#### TL;DR - LDAPS can be checked unauthenticated, but checking LDAP requires authentication.
## Installation
It is recommended to use either Docker or a Python virtual environment when running this project.
### Docker
1) Ensure [docker is installed](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/debian/) on your machine
2) Clone the repository and change directory
- `git clone https://github.com/zyn3rgy/LdapRelayScan.git && cd LdapRelayScan`
3) Build the Docker container
- `docker build -f docker/Dockerfile -t ldaprelayscan .`
4) [optionally] Ensure the script executes properly
- `docker run ldaprelayscan -h`
### Python Virtual Environment
1) Ensure [python virtualenv](https://packaging.python.org/en/latest/guides/installing-using-pip-and-virtual-environments/) is installed on your machine
2) Clone the repository and change directory
- `git clone https://github.com/zyn3rgy/LdapRelayScan.git && cd LdapRelayScan`
3) Create a Python virtual environment for the project
- `virtualenv env`
4) Activate the Python virtual environment
- `source venv/bin/activate`
5) Install exact requirement version dependencies
- `python3 -m pip install -r requirements_exact.txt`
6) [optionally] Ensure the script executes properly
- `python3 LdapRelayScan.py -h`
## Usage
> **NOTE**: DNS needs to resolve properly. If you are routing through SOCKS or running on a non-domain-joined host, ensure this is working.
The tool has two methods, **LDAPS** (the default), and **BOTH**. LDAPS only requires a domain controller IP address, because this check can be preformed unauthenticated. The BOTH method will require a username and password or NT hash. The Active Directory domain is not required, it will be determine via anonymous LDAP bind.
```
arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-method method LDAPS or BOTH - LDAPS checks for channel binding, BOTH checks for LDAP signing and LDAP channel binding [authentication required]
-dc-ip DC_IP DNS Nameserver on network. Any DC's IPv4 address should work.
-u username Domain username value.
-timeout timeout The timeout for MSLDAP client connection.
-p password Domain username value.
-nthash nthash NT hash of password
```
## Examples
### Basic / Virtual Environment Usage Examples
```
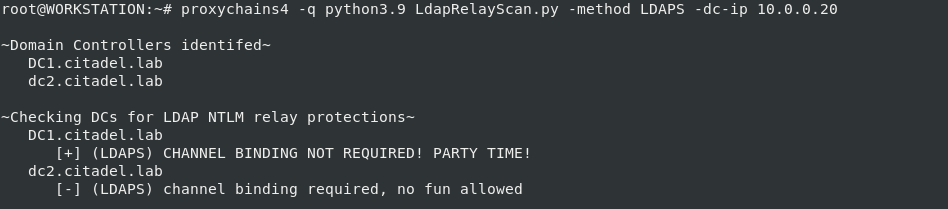
python3 LdapRelayScan.py -method LDAPS -dc-ip 10.0.0.20
python3 LdapRelayScan.py -method BOTH -dc-ip 10.0.0.20 -u domainuser1
python3 LdapRelayScan.py -method BOTH -dc-ip 10.0.0.20 -u domainuser1 -p badpassword2
python3 LdapRelayScan.py -method BOTH -dc-ip 10.0.0.20 -u domainuser1 -nthash e6ee750a1feb2c7ee50d46819a6e4d25
```

### Docker Usage Examples
> **NOTE**: The ability to use SOCKS is passed in using a `PROXY_CONFIG` environment variable. If SOCKS is required, the `--network=host` flag will also need to be used to correctly route traffic. See examples below.
```
docker run ldaprelayscan -h
docker run ldaprelayscan -dc-ip 10.0.0.20
docker run ldaprelayscan -dc-ip 10.0.0.20 -method BOTH -u domainuser1 -p secretpass
docker run -e PROXY_CONFIG='socks5 127.0.0.1 9050' --network=host ldaprelayscan -dc-ip 10.0.0.20 -method BOTH -u domainuser1 -p secretpass
```
## Error-Based Enumeration Specifics
### [LDAPS] Channel Binding Token Requirements
On a Domain Controller that has been patched since [CVE-2017-8563](https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2017-8563), the capability to enforce LDAPS channel binding has existed. The specific policy is called `Domain Controller: LDAP server channel binding token requirements` and can be set to either `Never`, `When supported`, or `Always`. This is also [not required by default](https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-us/vulnerability/ADV190023) (at the time of writing this).
Decrypting and monitoring LDAP over SSL/TLS traffic on a Domain Controller allowed for the identification of a difference in errors during bind attempts when channel binding is enforced versus when it's not. When attempting a bind to LDAP over SSL/TLS using invalid credentials, you will recieve the expected [resultCode 49](https://ldapwiki.com/wiki/LDAP_INVALID_CREDENTIALS), and in the error message contents you will see `data 52e`. However, when channel binding is enforced and the LDAP client does not calculate and include the Channel Binding Token (CBT), the resultCode will still be 49, but the error message contents will contain `data 80090346` meaning `SEC_E_BAD_BINDINGS` or that [the client's Supplied Support Provider Interface (SSPI) channel bindings were incorrect](https://ldapwiki.com/wiki/Common%20Active%20Directory%20Bind%20Errors).

> **NOTE**: Mentions of the `data 8009034` error during LDAP over SSL/TLS binding [[1]](http://gary-nebbett.blogspot.com/2020/01/ldap-channel-binding.html) [[2]](https://ldapwiki.com/wiki/Common%20Active%20Directory%20Bind%20Errors) [[3]](https://kb.vmware.com/s/article/77093) [[4]](https://kb.netapp.com/Advice_and_Troubleshooting/Data_Storage_Software/ONTAP_OS/ONTAP_is_unable_to_create_CIFS_server_with_AcceptSecurityContext_error_data_80090346) [[5]](https://github.com/fox-it/BloodHound.py/issues/55)
#### "Never" vs "When supported" vs "Always"
This specific error makes it easy enough to account for when the `Domain Controller: LDAP server channel binding token requirements` policy is set to `Always`. Simply attempt an NTLM-based LDAPS bind using a client that does not support channel binding and look for the `data 80090346` within the error in response. But what about when the policy is not set to `Always`, what about when it's set to `When supported`? The answer is: bind to LDAPS with NTLM-based authentication and purposefully miscalculate the channel binding information.
First, we need an LDAP client that supports channel binding. [SkelSec's](https://twitter.com/skelsec?lang=en) implementation of this in [msldap](https://github.com/skelsec/msldap) will be used to implement a PoC. Channel binding appears as an [AV_PAIR](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/openspecs/windows_protocols/ms-nlmp/83f5e789-660d-4781-8491-5f8c6641f75e) value during the NTLM challenge/response process, specifically within the Type 3 or [AUTHENTICATE_MESSAGE](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/openspecs/windows_protocols/ms-nlmp/033d32cc-88f9-4483-9bf2-b273055038ce). Here's another look at some decrypted LDAPS traffic on a Domain Controller to see what a bind attempt from a client supporting channel binding will look like:
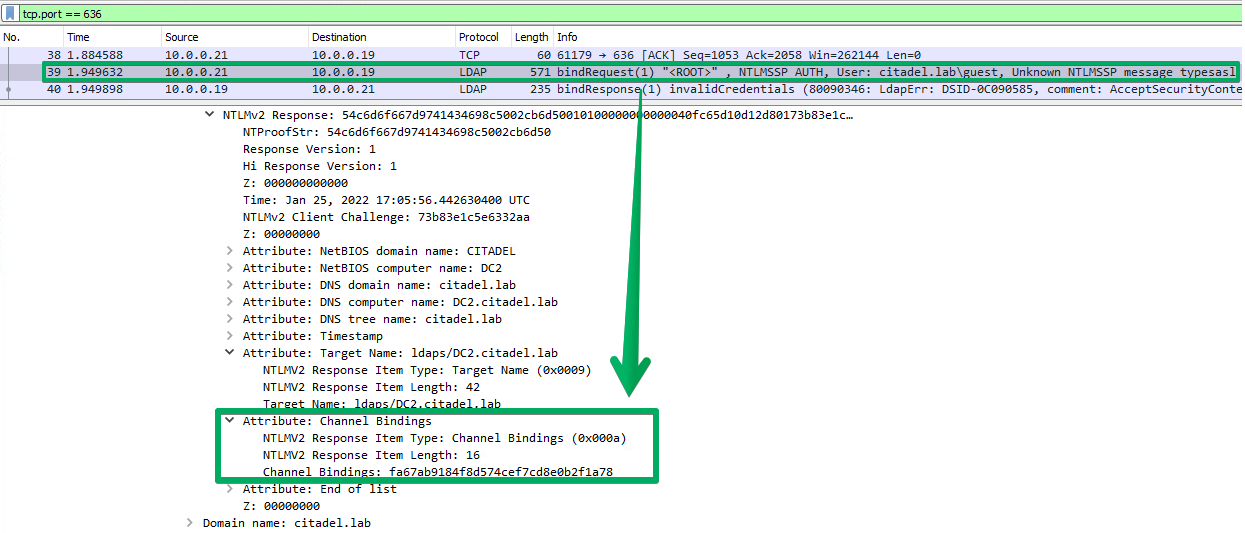
Intentionally miscalculating this value, when the policy in question is set to `When supported`, will produce the same `data 80090346` error. This gives us the ability to differentiate between all possible settings for this policy as it currently exists, from an unauthenticated perspective. How this value is purposefully miscalculated is important, because just manually replacing the value during challenge/response will invalidate the [MIC](https://en.hackndo.com/ntlm-relay/#mic---message-integrity-code).
### [LDAP] Server Signing Requirements
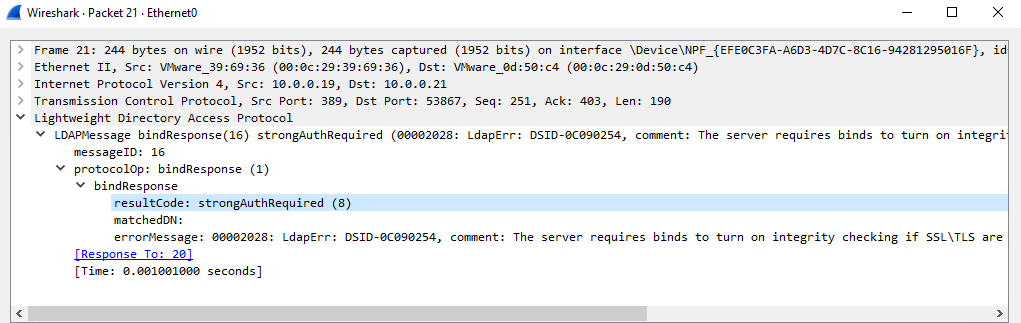
On a Domain Controller, the policy called ```Domain Controller: LDAP server signing requirements``` is set to `None`, `Require signing`, or it's just not defined. When not defined, it defaults to not requiring signing (at the time of writing this). The error which identifies this protection as required is when a [sicily NTLM](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/openspecs/windows_protocols/ms-adts/e7d814a5-4cb5-4b0d-b408-09d79988b550) or [simple](https://ldapwiki.com/wiki/Simple%20Authentication) bind attempt responds with a [resultCode of 8](https://ldap.com/ldap-result-code-reference-core-ldapv3-result-codes/#rc-strongerAuthRequired), signifying `strongerAuthRequired`. This will only occur if credentials during the LDAP bind are validated.
## References
A few invaluable resources for contextualization of this material and how it fits into common attack scenarios.
- [@HackAndDo](https://twitter.com/HackAndDo) - [NTLM relay](https://en.hackndo.com/ntlm-relay/)
- [@_nwodtuhs](https://twitter.com/_nwodtuhs) - [NTLM relay mindmap](https://twitter.com/_nwodtuhs/status/1424433914752421898?s=20)
- [@_dirkjan](https://twitter.com/_dirkjan) - [PrivExchange](https://dirkjanm.io/abusing-exchange-one-api-call-away-from-domain-admin/), the [ADCS ESC8 write up](https://dirkjanm.io/ntlm-relaying-to-ad-certificate-services/), the [NTLM relay for RBCD write up](https://dirkjanm.io/worst-of-both-worlds-ntlm-relaying-and-kerberos-delegation/), and more
- [@domchell](https://twitter.com/domchell) - implementation of [Farmer](https://github.com/mdsecactivebreach/Farmer) and [explanation](https://www.mdsec.co.uk/2021/02/farming-for-red-teams-harvesting-netntlm/)
- [@elad_shamir](https://twitter.com/elad_shamir) - thorough [explanations of abusing RBCD](https://shenaniganslabs.io/2019/01/28/Wagging-the-Dog.html) in [multiple scenarios](https://eladshamir.com/2019/08/08/Lock-Screen-LPE.html), and [shadow credentials](https://posts.specterops.io/shadow-credentials-abusing-key-trust-account-mapping-for-takeover-8ee1a53566ab)
- [@tifkin_](https://twitter.com/tifkin_) & [@topotam77](https://twitter.com/topotam77) - NTLM authentication coercion methods
- [@skelsec](https://twitter.com/skelsec?lang=en) - [msldap](https://github.com/skelsec/msldap) w/ support for channel binding