https://github.com/ZiluM/sacpy
A Python Package for Statistical Analysis of Climate
https://github.com/ZiluM/sacpy
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
A Python Package for Statistical Analysis of Climate
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/ZiluM/sacpy
- Owner: ZiluM
- License: mit
- Created: 2022-07-22T13:48:34.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-05T19:48:22.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-06-11T10:47:32.616Z (6 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Size: 101 MB
- Stars: 62
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 15
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- License: License.txt
Awesome Lists containing this project
- open-sustainable-technology - Sacpy - An effecient Statistical Analysis tool (e.g. regression, EOF, MCA) for Climate and Meteorology data. (Climate Change / Climate Data Processing and Analysis)
README
# SACPY -- A Python Package for Statistical Analysis of Climate
**Sacpy**, an effecient Statistical Analysis tool for Climate and Meteorology data.
Author : Zilu Meng
e-mail : zilumeng@uw.edu
github : https://github.com/ZiluM/sacpy
pypi : https://pypi.org/project/sacpy/
Document: https://zilum.github.io/sacpy/
version : 0.0.20
## Why choose Sacpy?
### Fast!
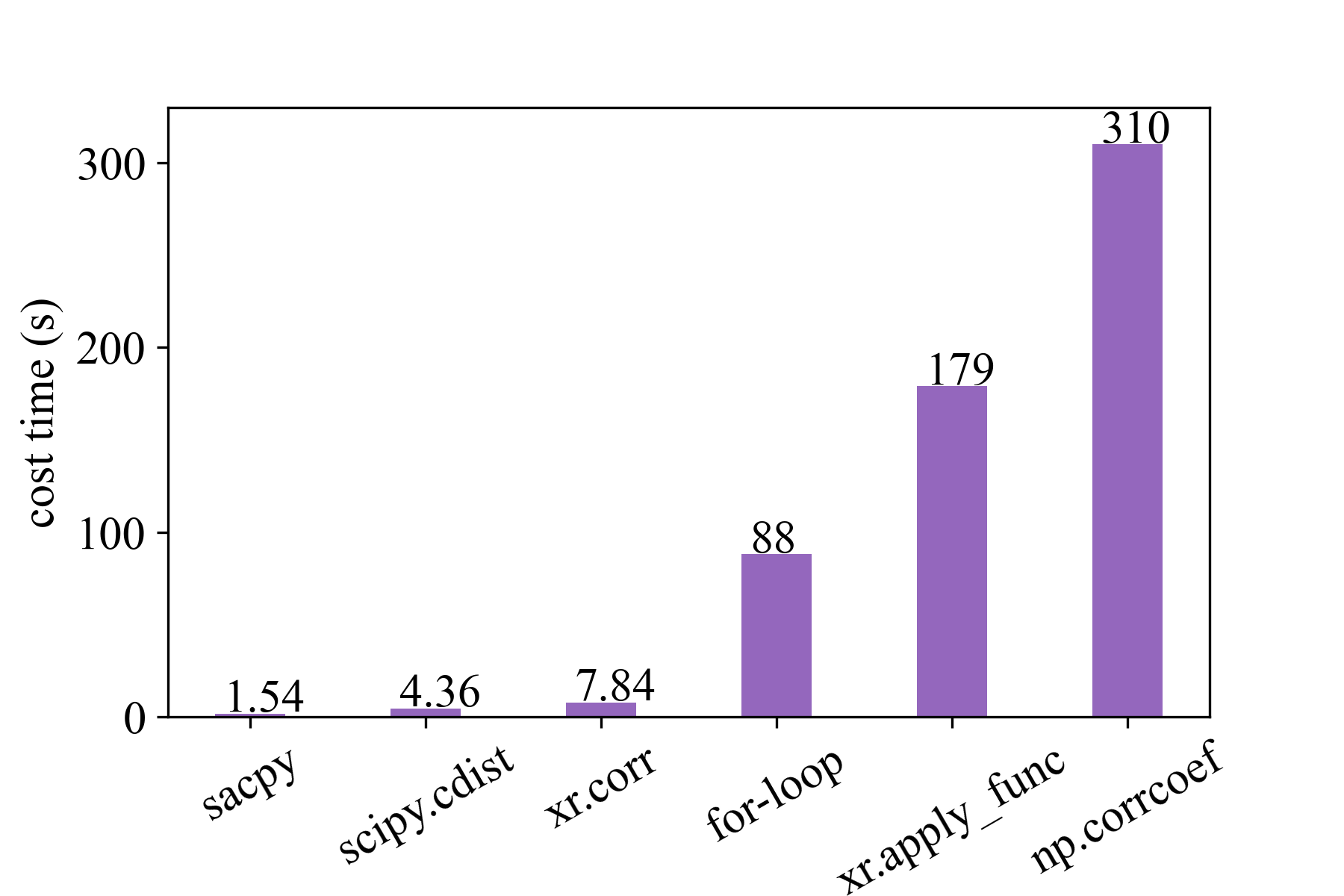
For example, Sacpy is more than 60 times faster than the traditional regression analysis with Python (see **speed test**). The following is the time spent performing the same task. Sacpy is fastest.
### Turn to climate data customization!
Compatible with commonly used meteorological calculation libraries such as numpy and xarray.
### Concise code
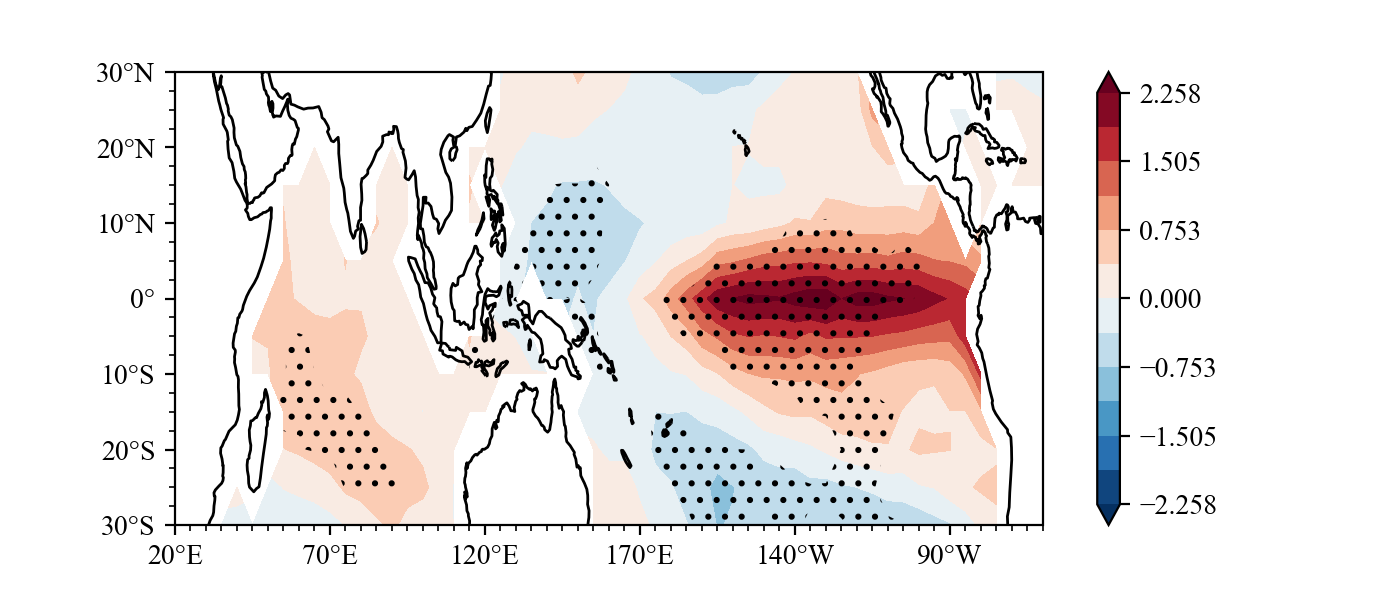
You can finish drawing a following figure with just seven lines of code. see **examples of concise**.
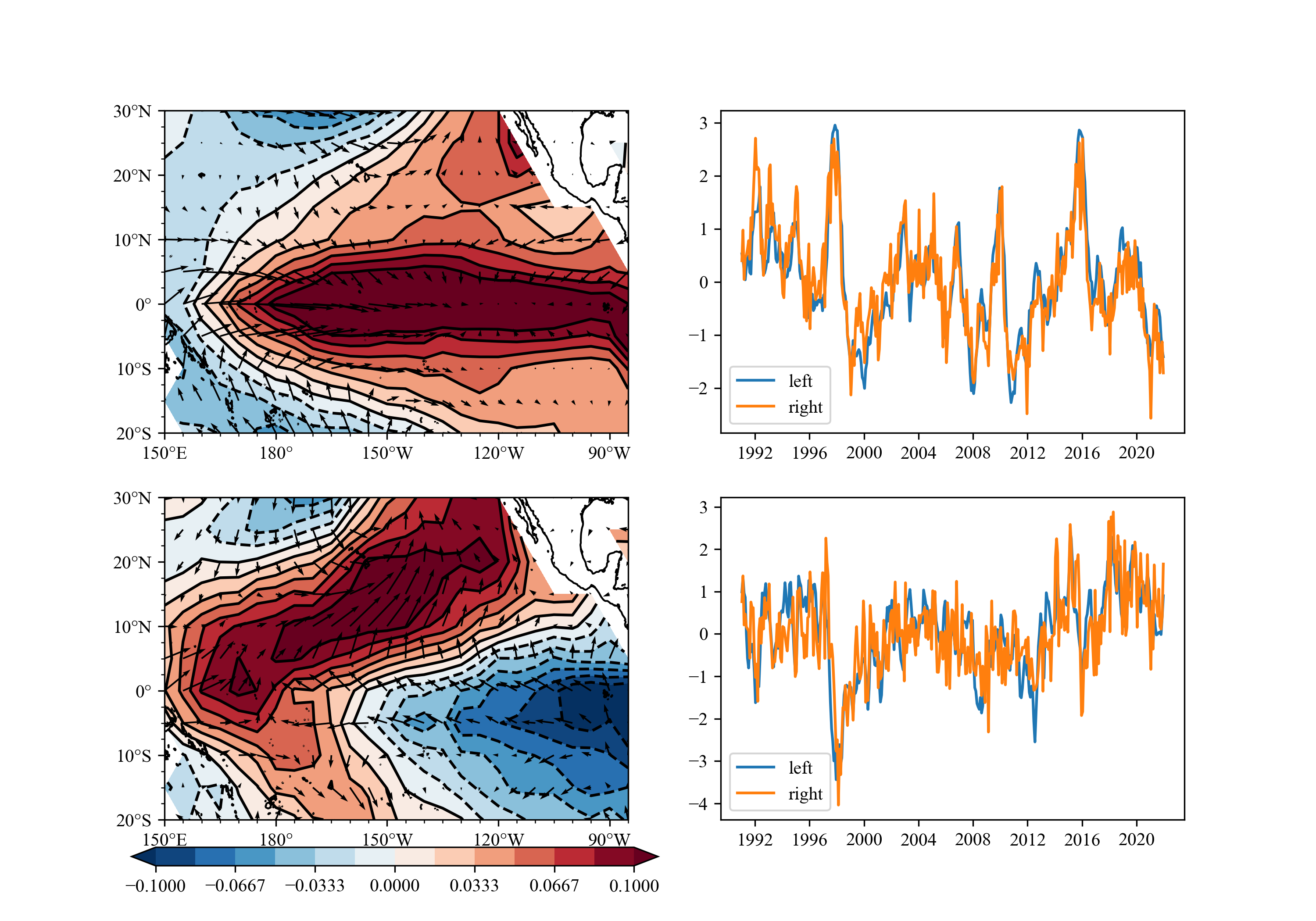
You can use SVD/MCA to get the image below easily.
## Install and update
You can use pip to install.
pip install sacpy
Or you can visit https://gitee.com/zilum/sacpy/tree/main/dist to download **.whl file**, then
pip install .whl_file
update:
pip install --upgrade sacpy
or you can download **.whl** file and then install use ` pip install .whl_file`.
## Speed
As a comparison, we use the **corr** function in the xarray library, **corrcoef** function in numpy library, cdist in scipy, apply_func in xarray and **for-loop**. The time required to calculate the correlation coefficient between SSTA and nino3.4 for 50 times is shown in the figure below.
It can be seen that we are four times faster than scipy cdist, five times faster than xarray.corr, 60 times faster than forloop, 110 times faster than xr.apply_func and 200 times faster than numpy.corrcoef.
Moreover, xarray and numpy can not return the **p value**. We can simply check the pvalue attribute of sacpy to get the p value.
All in all, if we want to get p-value and correlation or slope, we only to choose **Sacpy is 60 times faster than before**.

## Example
### example1
Calculate the correlation between SST and nino3.4 index
```Python
import numpy as np
import scapy as scp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sacpy.Map # need cartopy or you can just not import
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
# load sst
sst = scp.load_sst()['sst']
# get ssta (method=1, Remove linear trend;method=0, Minus multi-year average)
ssta = scp.get_anom(sst,method=1)
# calculate Nino3.4
Nino34 = ssta.loc[:,-5:5,190:240].mean(axis=(1,2))
# regression
linreg = scp.LinReg(Nino34,ssta)
# plot
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[7, 3])
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))
lon ,lat = ssta.lon , ssta.lat
# shading
m = ax.scontourf(lon,lat,linreg.corr)
# significant plot
n = ax.sig_plot(lon,lat,linreg.p_value,color="k",marker="..")
# initialize map
ax.init_map(stepx=50, ysmall=2.5)
# colorbar
plt.colorbar(m)
# save
plt.savefig("../pic/nino34.png",dpi=200)
```
Result(For a detailed drawing process, see **example**):
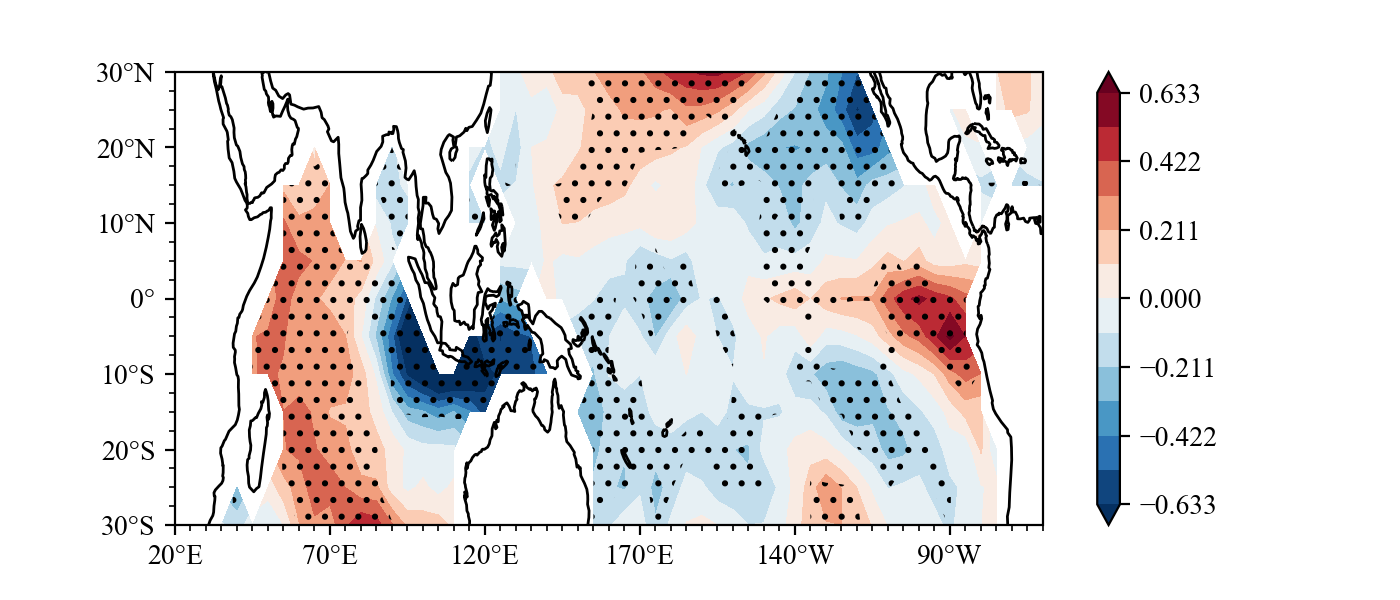
### example2
multiple linear regression on Nino3.4 IOD Index and ssta pattern
```Python
import numpy as np
import scapy as scp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# load sst
sst = scp.load_sst()['sst']
# get ssta (method=1, Remove linear trend;method=0, Minus multi-year average)
ssta = scp.get_anom(sst,method=1)
# calculate Nino3.4
Nino34 = ssta.loc[:,-5:5,190:240].mean(axis=(1,2))
# calculate IODIdex
IODW = ssta.loc[:,-10:10,50:70].mean(axis=(1,2))
IODE = ssta.loc[:,-10:0,90:110].mean(axis=(1,2))
IODI = +IODW - IODE
# get x
X = np.vstack([np.array(Nino34),np.array(IODI)]).T
# multiple linear regression
MLR = scp.MultLinReg(X,ssta)
# plot IOD's effect
import sacpy.Map
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[7, 3])
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))
lon ,lat = ssta.lon , ssta.lat
m = ax.scontourf(lon,lat,MLR.slope[1])
# significant plot
n = ax.sig_plot(lon,lat,MLR.pv_i[1],color="k",marker="..")
# initialize map
ax.init_map(stepx=50, ysmall=2.5)
plt.colorbar(m)
plt.savefig("../pic/MLR.png",dpi=200)
```
Result(For a detailed drawing process, see **example**):
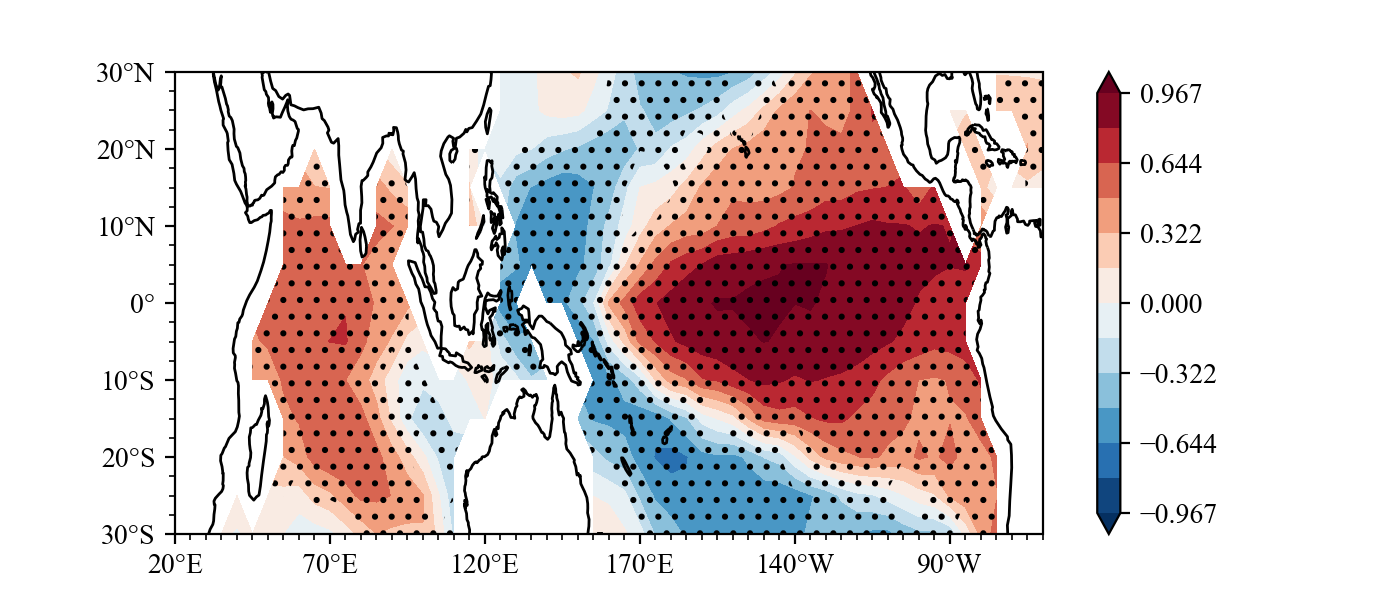
### example3
What effect will ENSO have on the sea surface temperature in the next summer?
```Python
import numpy as np
import sacpy as scp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import xarray as xr
# load sst
sst = scp.load_sst()['sst']
ssta = scp.get_anom(sst)
# calculate Nino3.4
Nino34 = ssta.loc[:,-5:5,190:240].mean(axis=(1,2))
# get DJF mean Nino3.4
DJF_nino34 = scp.XrTools.spec_moth_yrmean(Nino34,[12,1,2])
# get JJA mean ssta
JJA_ssta = scp.XrTools.spec_moth_yrmean(ssta, [6,7,8])
# regression
reg = scp.LinReg(DJF_nino34[:-1], JJA_ssta)
# plot
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import sacpy.Map
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[7, 3])
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))
lon ,lat = np.array(ssta.lon) , np.array(ssta.lat)
m = ax.scontourf(lon,lat,reg.slope)
n = ax.sig_plot(lon,lat,reg.p_value,color="k",marker="///")
ax.init_map(stepx=50, ysmall=2.5)
plt.colorbar(m)
plt.savefig("../pic/ENSO_Next_year_JJA.png",dpi=300)
```
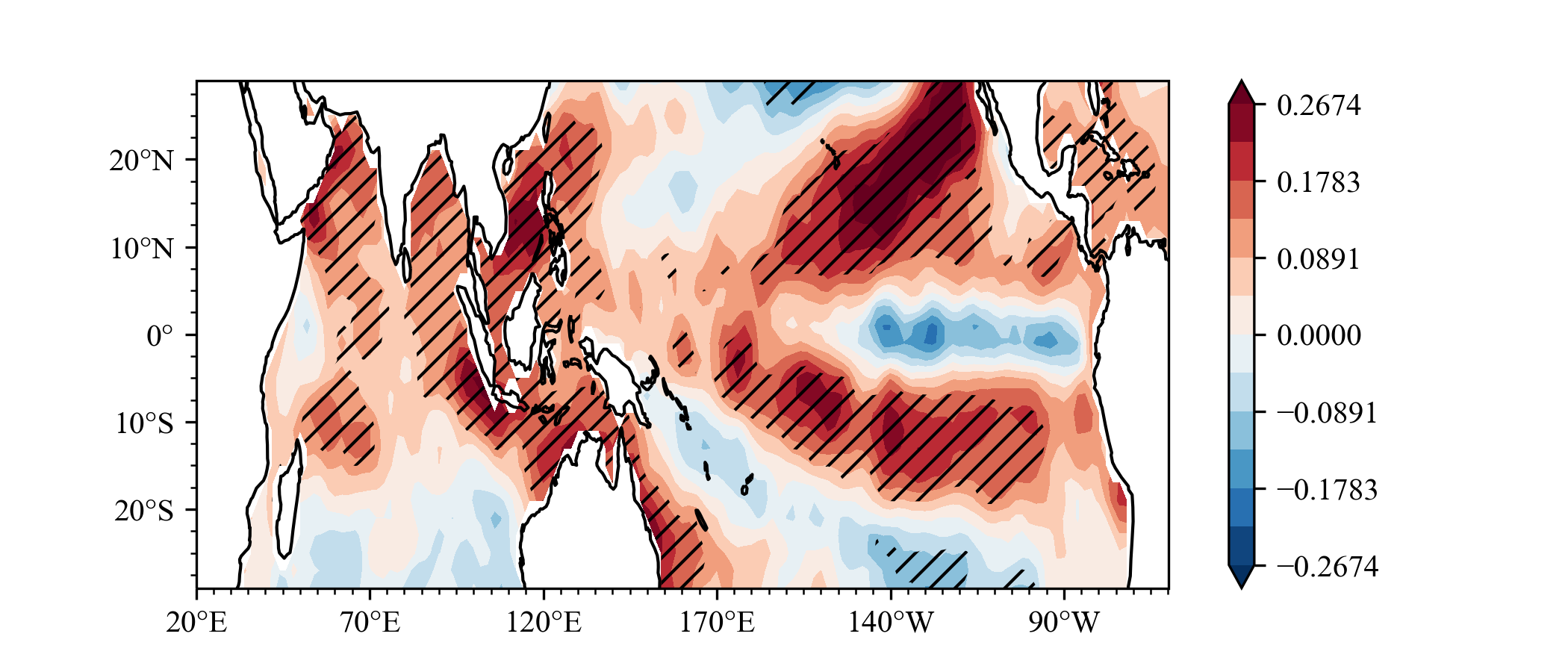
Same as **Indian Ocean Capacitor Effect on Indo–Western Pacific Climate during the Summer following El Niño** (Xie et al.), the El Nino will lead to Indian ocean warming in next year JJA.
### example4
EOF analysis
```Python
import sacpy as scp
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# get data
sst = scp.load_sst()["sst"].loc[:, -20:30, 150:275]
ssta = scp.get_anom(sst)
# EOF
eof = scp.EOF(np.array(ssta))
eof.solve()
# get spartial pattern and pc
pc = eof.get_pc(npt=2)
pt = eof.get_pt(npt=2)
# plot
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import sacpy.Map
lon , lat = np.array(ssta.lon) , np.array(ssta.lat)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[15,10])
ax = fig.add_subplot(221,projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))
m1 = ax.scontourf(lon,lat,pt[0,:,:],cmap='RdBu_r',levels=np.linspace(-0.75,0.75,15),extend="both")
ax.scontour(m1,colors="black")
ax.init_map(ysmall=2.5)
# plt.colorbar(m1)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(222)
ax2.plot(sst.time,pc[0])
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(223,projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))
m2 = ax3.scontourf(lon,lat,pt[1,:,:],cmap='RdBu_r',levels=np.linspace(-0.75,0.75,15),extend="both")
ax3.scontour(m2,colors="black")
ax3.init_map(ysmall=2.5)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(224)
ax4.plot(sst.time,pc[1])
cb_ax = fig.add_axes([0.1,0.06,0.4,0.02])
fig.colorbar(m1,cax=cb_ax,orientation="horizontal")
plt.savefig("../pic/eof_ana.png",dpi=300)
```
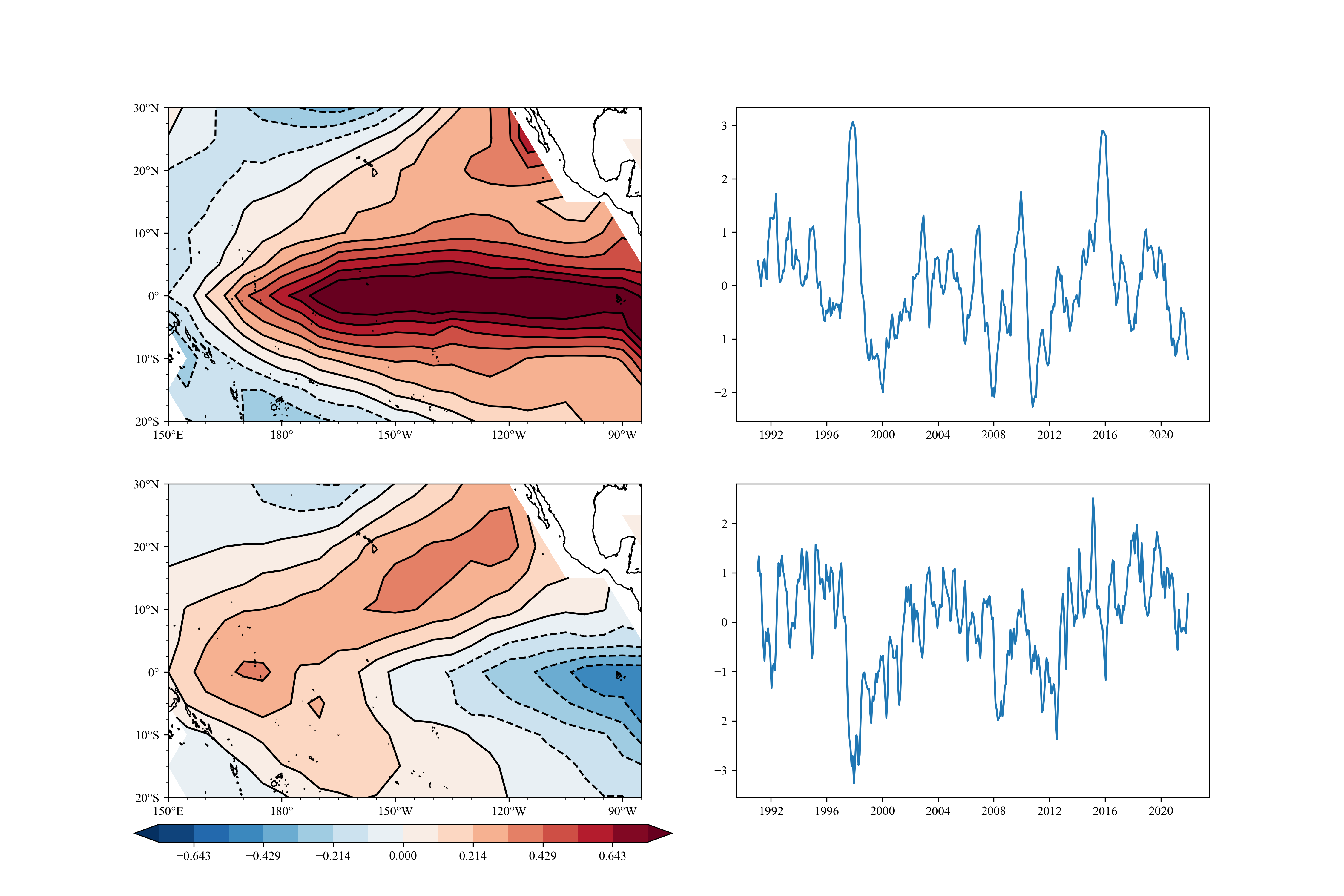
## example5
Mean value (Composite Analysis) t-test for super El Nino (DJF Nino3.4 > 1)
```Python
import sacpy as scp
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sst = scp.load_sst()["sst"]
ssta = scp.get_anom(sst, method=0)
# get Dec Jan Feb SSTA
ssta_djf = scp.XrTools.spec_moth_yrmean(ssta,[12,1,2])
Nino34 = ssta_djf.loc[:, -5:5, 190:240].mean(axis=(1, 2))
# select year of Super El Nino
select = Nino34 >= 1
ssta_sl = ssta_djf[select]
mean, pv = scp.one_mean_test(ssta_sl)
# plot
import sacpy.Map
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[7, 3])
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))
lon ,lat = np.array(ssta.lon) , np.array(ssta.lat)
m = ax.scontourf(lon,lat,mean)
n = ax.sig_plot(lon,lat,pv,color="k",marker="..")
ax.init_map(stepx=50, ysmall=2.5)
plt.colorbar(m)
plt.savefig("../pic/one_test.png")
```
Result:

## example6
SVD(MCA) analysis.
```Python
import sacpy as scp
import xarray as xr
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from xmca import array
import sacpy.Map
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
# load data
sst = scp.load_sst()['sst'].loc["1991":"2021", -20:30, 150:275]
ssta = scp.get_anom(sst)
u = scp.load_10mwind()['u']
v = scp.load_10mwind()['v']
uua = scp.get_anom(u)
vua = scp.get_anom(v)
uv = np.concatenate([np.array(uua)[...,np.newaxis],np.array(vua)[...,np.newaxis]],axis=-1)
# calculation
svd = scp.SVD(ssta,uv,complex=False)
svd.solve()
ptl, ptr = svd.get_pt(3)
pcl,pcr = svd.get_pc(3)
upt ,vpt = ptr[...,0] , ptr[...,1]
sst_pt = ptl
# plot progress, see example/SVD.ipynb
```
result:

## examples of concise
If you want to plot example1's figure , you need write:
```Python
from cartopy.mpl.ticker import LongitudeFormatter, LatitudeFormatter
from matplotlib.ticker import MultipleLocator
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
plt.rc('font', family='Times New Roman', size=12)
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))
m = ax.contourf(ssta.lon,ssta.lat,linreg.corr,
cmap="RdBu_r",
levels=np.linspace(-1, 1, 15),
extend="both",
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
n = plt.contourf(ssta.lon,ssta.lat,linreg.p_value,
levels=[0, 0.05, 1],
zorder=1,
hatches=['..', None],
colors="None",
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
xtk = np.arange(-180,181,60)
ax.set_xticks(xtk)
# ax.set_xticks(xtk,crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-50,51,20),crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(LatitudeFormatter())
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(LongitudeFormatter(zero_direction_label=True))
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(MultipleLocator(10))
ax.yaxis.set_minor_locator(MultipleLocator(5))
ax.coastlines()
ax.set_aspect("auto")
plt.colorbar(m)
```
**So troublesome!!!**
But if you `import sacpy.Map`, you can easily write:
```Python
import sacpy.Map
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[7, 3])
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))
lon ,lat = ssta.lon , ssta.lat
m = ax.scontourf(lon,lat,rvalue)
n = ax.sig_plot(lon,lat,p,color="k",marker="..")
ax.init_map(stepx=50, ysmall=2.5)
plt.colorbar(m)
```
How wonderful, how concise !
## Acknowledgements
Thank Prof. Feng Zhu (NUIST,https://fzhu2e.github.io/) for his guidance of this project.
Thank for Prof. Tim Li (University of Hawaii at Mānoa, http://iprc.soest.hawaii.edu/people/li.php) ,Prof. Lin Chen (NUIST, https://faculty.nuist.edu.cn/chenlin12/zh_CN/index.htm) and Dr. Ming Sun (NUIST) 's help.
Sepcial thanks: Lifei Lin (Sun Yat-sen University) 's `repr_html.py` to visualize class in jupyter!