https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey
Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line
https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey
- Owner: chriskiehl
- License: mit
- Created: 2014-01-01T21:06:05.000Z (about 12 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-02-21T16:05:35.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-10-01T18:18:42.602Z (over 1 year ago)
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 4.07 MB
- Stars: 20,601
- Watchers: 282
- Forks: 1,018
- Open Issues: 168
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE.txt
Awesome Lists containing this project
- fucking-awesome-python-cn - Gooey
- awesome-python - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (GUI Development)
- awesome-repositories - chriskiehl/Gooey
- awesome-sciml - chriskiehl/Gooey: Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line
- awesome-list - Gooey - Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line. (Desktop App Development / Python Toolkit)
- awesome-python-zh - Gooey - 将命令行程序变成一行完整的GUI应用程序。 (GUI开发)
- my-awesome-github-stars - chriskiehl/Gooey - Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line (Python)
- awesome-python - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line (Command-line Tools)
- StarryDivineSky - chriskiehl/Gooey
- fucking_awesome_python - :octocat: Gooey - :star: 4169 :fork_and_knife: 212 - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line (Command-line Tools)
- python-awesome - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (GUI Development)
- awesome-python - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (GUI Development)
- awesome-starred - Gooey - Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line (Python)
- awesome-python-resources - GitHub - 19% open · ⏱️ 08.05.2022): (图形用户界面)
- awesome-starred - chriskiehl/Gooey - Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line (Python)
- awesome-hacking-lists - chriskiehl/Gooey - Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line (Python)
- awesome-starts - chriskiehl/Gooey - Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line (Python)
- awesome-python - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line (Command-line Tools)
- awesome-python - Gooey - Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line ` 📝 15 days ago ` (GUI Development [🔝](#readme))
- awesome-python - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (Command-line Tools)
- fucking-awesome-python - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (GUI Development)
- fucking-awesome-python - :octocat: Gooey - :star: 17711 :fork_and_knife: 945 - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (GUI Development)
- awesome-python - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (Command-line Tools)
- awesome-rainmana - chriskiehl/Gooey - Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line (Python)
- starred-awesome - Gooey - Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line (Python)
- awesome-python-cn - Gooey
- Awesome-Python - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (Command-line Tools)
- Python-Awesome - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line (Command-line Tools)
- awesome-python - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (GUI Development)
- awesome-python-tools - Gooey - line programs into a full-fledged GUI application with minimal code changes. (Web Development / Desktop Applications)
- awesome-python - Gooey - Turn (almost) any Python command line program into a full GUI application with one line (Awesome Python / Command-line Tools)
- awesome-python - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (GUI Development)
- awesome-drone - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (File Manipulation / HTTP Clients)
- git-github.com-vinta-awesome-python - Gooey - Turn command line programs into a full GUI application with one line. (Command-line Tools)
- awesome-tools - Gooey
README
# Gooey
Turn (almost) any Python 3 Console Program into a GUI application with one line

Table of Contents
-----------------
- [Gooey](#gooey)
- [Table of contents](#table-of-contents)
- [Latest Update](#latest-update)
- [Quick Start](#quick-start)
- [Installation Instructions](#installation-instructions)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [Examples](#examples)
- [What It Is](#what-is-it)
- [Why Is It](#why)
- [Who is this for](#who-is-this-for)
- [How does it work](#how-does-it-work)
- [Internationalization](#internationalization)
- [Global Configuration](#global-configuration)
- [Layout Customization](#layout-customization)
- [Run Modes](#run-modes)
- [Full/Advanced](#advanced)
- [Basic](#basic)
- [No Config](#no-config)
- [Menus](#menus)
- [Dynamic Validation](#dynamic-validation)
- [Lifecycle Events and UI control](#lifecycle-events-and-ui-control)
- [Showing Progress](#showing-progress)
- [Elapsed / Remaining Time](#elapsed--remaining-time)
- [Customizing Icons](#customizing-icons)
- [Packaging](#packaging)
- [Screenshots](#screenshots)
- [Contributing](#wanna-help)
- [Image Credits](#image-credits)
----------------
## Quick Start
### Installation instructions
The easiest way to install Gooey is via `pip`
pip install Gooey
Alternatively, you can install Gooey by cloning the project to your local directory
git clone https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey.git
run `setup.py`
python setup.py install
### Usage
Gooey is attached to your code via a simple decorator on whichever method has your `argparse` declarations (usually `main`).
from gooey import Gooey
@Gooey <--- all it takes! :)
def main():
parser = ArgumentParser(...)
# rest of code
Different styling and functionality can be configured by passing arguments into the decorator.
# options
@Gooey(advanced=Boolean, # toggle whether to show advanced config or not
language=language_string, # Translations configurable via json
auto_start=True, # skip config screens all together
target=executable_cmd, # Explicitly set the subprocess executable arguments
program_name='name', # Defaults to script name
program_description, # Defaults to ArgParse Description
default_size=(610, 530), # starting size of the GUI
required_cols=1, # number of columns in the "Required" section
optional_cols=2, # number of columns in the "Optional" section
dump_build_config=False, # Dump the JSON Gooey uses to configure itself
load_build_config=None, # Loads a JSON Gooey-generated configuration
monospace_display=False) # Uses a mono-spaced font in the output screen
)
def main():
parser = ArgumentParser(...)
# rest of code
See: [How does it Work](#how-does-it-work) section for details on each option.
Gooey will do its best to choose sensible widget defaults to display in the GUI. However, if more fine tuning is desired, you can use the drop-in replacement `GooeyParser` in place of `ArgumentParser`. This lets you control which widget displays in the GUI. See: [GooeyParser](#gooeyparser)
from gooey import Gooey, GooeyParser
@Gooey
def main():
parser = GooeyParser(description="My Cool GUI Program!")
parser.add_argument('Filename', widget="FileChooser")
parser.add_argument('Date', widget="DateChooser")
...
### Examples
Gooey downloaded and installed? Great! Wanna see it in action? Head over the the [Examples Repository](https://github.com/chriskiehl/GooeyExamples) to download a few ready-to-go example scripts. They'll give you a quick tour of all Gooey's various layouts, widgets, and features.
[Direct Download](https://github.com/chriskiehl/GooeyExamples/archive/master.zip)
What is it?
-----------
Gooey converts your Console Applications into end-user-friendly GUI applications. It lets you focus on building robust, configurable programs in a familiar way, all without having to worry about how it will be presented to and interacted with by your average user.
Why?
---
Because as much as we love the command prompt, the rest of the world looks at it like an ugly relic from the early '80s. On top of that, more often than not programs need to do more than just one thing, and that means giving options, which previously meant either building a GUI, or trying to explain how to supply arguments to a Console Application. Gooey was made to (hopefully) solve those problems. It makes programs easy to use, and pretty to look at!
Who is this for?
----------------
If you're building utilities for yourself, other programmers, or something which produces a result that you want to capture and pipe over to another console application (e.g. *nix philosophy utils), Gooey probably isn't the tool for you. However, if you're building 'run and done,' around-the-office-style scripts, things that shovel bits from point A to point B, or simply something that's targeted at a non-programmer, Gooey is the perfect tool for the job. It lets you build as complex of an application as your heart desires all while getting the GUI side for free.
How does it work?
-----------------
Gooey is attached to your code via a simple decorator on whichever method has your `argparse` declarations.
@Gooey
def my_run_func():
parser = ArgumentParser(...)
# rest of code
At run-time, it parses your Python script for all references to `ArgumentParser`. (The older `optparse` is currently not supported.) These references are then extracted, assigned a `component type` based on the `'action'` they provide, and finally used to assemble the GUI.
#### Mappings:
Gooey does its best to choose sensible defaults based on the options it finds. Currently, `ArgumentParser._actions` are mapped to the following `WX` components.
| Parser Action | Widget | Example |
|:----------------------|-----------|------|
| store | TextCtrl |  |
|
| store_const | CheckBox | |
|
| store_true | CheckBox |  |
|
| store_False | CheckBox|  |
|
| version | CheckBox|  |
|
| append | TextCtrl |  |
|
| count | DropDown |  |
|
| Mutually Exclusive Group | RadioGroup | 
|choice | DropDown |  |
|
### GooeyParser
If the above defaults aren't cutting it, you can control the exact widget type by using the drop-in `ArgumentParser` replacement `GooeyParser`. This gives you the additional keyword argument `widget`, to which you can supply the name of the component you want to display. Best part? You don't have to change any of your `argparse` code to use it. Drop it in, and you're good to go.
**Example:**
from argparse import ArgumentParser
....
def main():
parser = ArgumentParser(description="My Cool Gooey App!")
parser.add_argument('filename', help="name of the file to process")
Given then above, Gooey would select a normal `TextField` as the widget type like this:

However, by dropping in `GooeyParser` and supplying a `widget` name, you can display a much more user friendly `FileChooser`
from gooey import GooeyParser
....
def main():
parser = GooeyParser(description="My Cool Gooey App!")
parser.add_argument('filename', help="name of the file to process", widget='FileChooser')

**Custom Widgets:**
| Widget | Example |
|----------------|------------------------------|
| DirChooser, FileChooser, MultiFileChooser, FileSaver, MultiFileSaver |

|
| DateChooser/TimeChooser | 
Please note that for both of these widgets the values passed to the application will always be in [ISO format](https://www.wxpython.org/Phoenix/docs/html/wx.DateTime.html#wx.DateTime.FormatISOTime) while localized values may appear in some parts of the GUI depending on end-user settings.
|
| PasswordField | 
|
| Listbox |  |
| BlockCheckbox | 
The default InlineCheck box can look less than ideal if a large help text block is present. `BlockCheckbox` moves the text block to the normal position and provides a short-form `block_label` for display next to the control. Use `gooey_options.checkbox_label` to control the label text |
| ColourChooser | 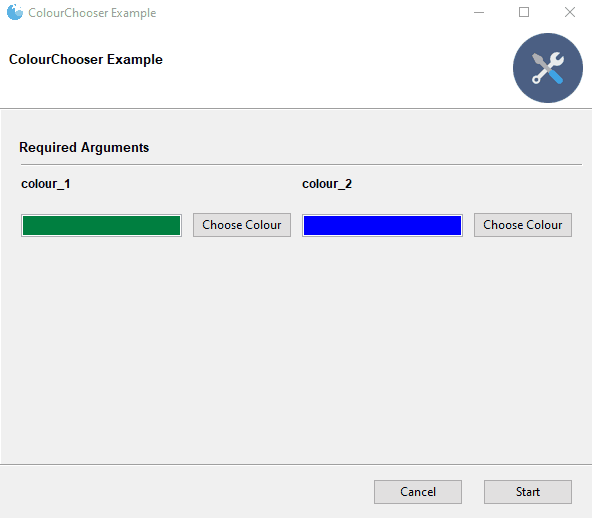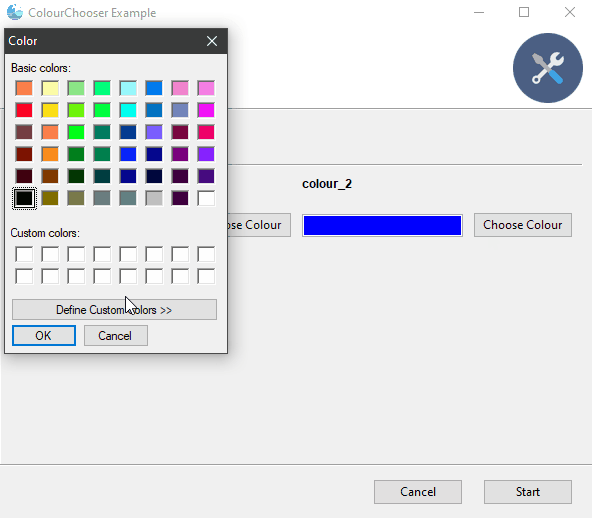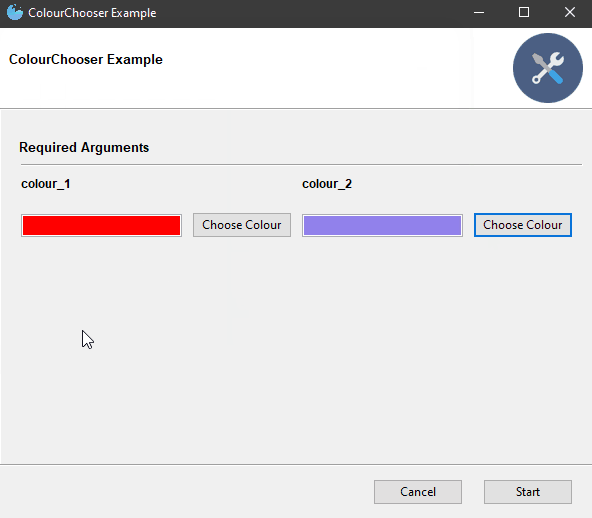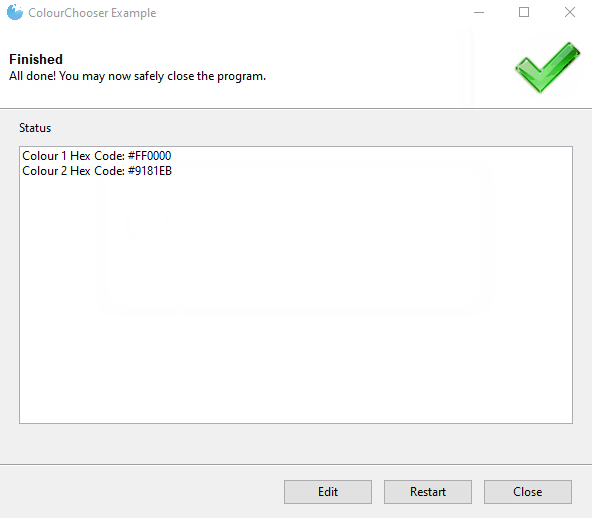
|
| FilterableDropdown | 
|
| IntegerField | 
|
| DecimalField | 
|
| Slider | 
|
Internationalization
--------------------

Gooey is international ready and easily ported to your host language. Languages are controlled via an argument to the `Gooey` decorator.
@Gooey(language='russian')
def main():
...
All program text is stored externally in `json` files. So adding new language support is as easy as pasting a few key/value pairs in the `gooey/languages/` directory.
Thanks to some awesome [contributors](https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey/graphs/contributors), Gooey currently comes pre-stocked with over 18 different translations!
Want to add another one? Submit a [pull request!](https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey/compare)
-------------------------------------------
Global Configuration
--------------------
Just about everything in Gooey's overall look and feel can be customized by passing arguments to the decorator.
| Parameter | Summary |
|-----------|---------|
| encoding | Text encoding to use when displaying characters (default: 'utf-8') |
| use_legacy_titles | Rewrites the default argparse group name from "Positional" to "Required". This is primarily for retaining backward compatibility with previous versions of Gooey (which had poor support/awareness of groups and did its own naive bucketing of arguments). |
| advanced | Toggles whether to show the 'full' configuration screen, or a simplified version |
| auto_start | Skips the configuration all together and runs the program immediately |
| language | Tells Gooey which language set to load from the `gooey/languages` directory.|
| target | Tells Gooey how to re-invoke itself. By default Gooey will find python, but this allows you to specify the program (and arguments if supplied).|
| suppress_gooey_flag | Should be set when using a custom `target`. Prevent Gooey from injecting additional CLI params |
|program_name | The name displayed in the title bar of the GUI window. If not supplied, the title defaults to the script name pulled from `sys.argv[0]`. |
| program_description | Sets the text displayed in the top panel of the `Settings` screen. Defaults to the description pulled from `ArgumentParser`. |
| default_size | Initial size of the window |
| fullscreen | start Gooey in fullscreen mode |
| required_cols | Controls how many columns are in the Required Arguments section
:warning: **Deprecation notice:** See [Layout Customization](https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey#layout-customization) for modern layout controls|
| optional_cols | Controls how many columns are in the Optional Arguments section
:warning: **Deprecation notice:** See [Layout Customization](https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey#layout-customization) for modern layout controls|
| dump_build_config | Saves a `json` copy of its build configuration on disk for reuse/editing |
| load_build_config | Loads a `json` copy of its build configuration from disk |
| monospace_display | Uses a mono-spaced font in the output screen
:warning: **Deprecation notice:** See [Layout Customization](https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey#layout-customization) for modern font configuration|
| image_dir | Path to the directory in which Gooey should look for custom images/icons |
| language_dir | Path to the directory in which Gooey should look for custom languages files |
| disable_stop_button | Disable the `Stop` button when running |
| show_stop_warning | Displays a warning modal before allowing the user to force termination of your program |
| force_stop_is_error | Toggles whether an early termination by the shows the success or error screen |
| show_success_modal | Toggles whether or not to show a summary modal after a successful run |
| show_failure_modal | Toggles whether or not to show a summary modal on failure |
| show_restart_button | Toggles whether or not to show the restart button at the end of execution |
| run_validators | Controls whether or not to have Gooey perform validation before calling your program |
| poll_external_updates | (Experimental!) When True, Gooey will call your code with a `gooey-seed-ui` CLI argument and use the response to fill out dynamic values in the UI (See: [Using Dynamic Values](#using-dynamic-values))|
| use_cmd_args | Substitute any command line arguments provided at run time for the default values specified in the Gooey configuration |
| return_to_config | When True, Gooey will return to the configuration settings window upon successful run |
| progress_regex | A text regex used to pattern match runtime progress information. See: [Showing Progress](#showing-progress) for a detailed how-to |
| progress_expr | A python expression applied to any matches found via the `progress_regex`. See: [Showing Progress](#showing-progress) for a detailed how-to |
| hide_progress_msg | Option to hide textual progress updates which match the `progress_regex`. See: [Showing Progress](#showing-progress) for a detailed how-to |
| disable_progress_bar_animation | Disable the progress bar |
| timing_options | This contains the options for displaying time remaining and elapsed time, to be used with `progress_regex` and `progress_expr`. [Elapsed / Remaining Time](#elapsed--remaining-time). Contained as a dictionary with the options `show_time_remaining` and `hide_time_remaining_on_complete`. Eg: `timing_options={'show_time_remaining':True,'hide_time_remaining_on_complete':True}` |
| show_time_remaining | Disable the time remaining text see [Elapsed / Remaining Time](#elapsed--remaining-time) |
| hide_time_remaining_on_complete | Hide time remaining on complete screen see [Elapsed / Remaining Time](#elapsed--remaining-time) |
| requires_shell | Controls whether or not the `shell` argument is used when invoking your program. [More info here](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3172470/actual-meaning-of-shell-true-in-subprocess#3172488) |
| shutdown_signal | Specifies the `signal` to send to the child process when the `stop` button is pressed. See [Gracefully Stopping](https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey/tree/master/docs) in the docs for more info. |
| navigation | Sets the "navigation" style of Gooey's top level window.
Options: TABBEDSIDEBAR 
 |
|
| sidebar_title |  Controls the heading title above the SideBar's navigation pane. Defaults to: "Actions" |
Controls the heading title above the SideBar's navigation pane. Defaults to: "Actions" |
| show_sidebar | Show/Hide the sidebar in when navigation mode == `SIDEBAR` |
| body_bg_color | HEX value of the main Gooey window |
| header_bg_color | HEX value of the header background |
| header_height | height in pixels of the header |
| header_show_title | Show/Hide the header title |
| header_show_subtitle | Show/Hide the header subtitle |
| footer_bg_color | HEX value of the Footer background |
| sidebar_bg_color | HEX value of the Sidebar's background |
| terminal_panel_color | HEX value of the terminal's panel |
| terminal_font_color | HEX value of the font displayed in Gooey's terminal |
| terminal_font_family | Name of the Font Family to use in the terminal |
| terminal_font_weight | Weight of the font (`constants.FONTWEIGHT_NORMAL`, `constants.FONTWEIGHT_XXX`) |
| terminal_font_size | Point size of the font displayed in the terminal |
| error_color | HEX value of the text displayed when a validation error occurs |
| richtext_controls | Switch on/off the console support for terminal control sequences (limited support for font weight and color). Defaults to : False. See [docs](https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey/tree/master/docs) for additional details |
| menus | Show custom menu groups and items (see: [Menus](#menus) |
| clear_before_run | When true, previous output will be cleared from the terminal when running program again |
Layout Customization
--------------------
You can achieve fairly flexible layouts with Gooey by using a few simple customizations.
At the highest level, you have several overall layout options controllable via various arguments to the Gooey decorator.
| `show_sidebar=True` | `show_sidebar=False` | `navigation='TABBED'` | `tabbed_groups=True` |
|---------------------|----------------------|----------------------|------------------------|
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
**Grouping Inputs**
By default, if you're using Argparse with Gooey, your inputs will be split into two buckets: `positional` and `optional`. However, these aren't always the most descriptive groups to present to your user. You can arbitrarily bucket inputs into logic groups and customize the layout of each.
With `argparse` this is done via `add_argument_group()`

```
parser = ArgumentParser()
search_group = parser.add_argument_group(
"Search Options",
"Customize the search options"
)
```
You can add arguments to the group as normal
```
search_group.add_argument(
'--query',
help='Base search string'
)
```
Which will display them as part of the group within the UI.
Run Modes
---------
Gooey has a handful of presentation modes so you can tailor its layout to your content type and user's level or experience.
### Advanced
The default view is the "full" or "advanced" configuration screen. It has two different layouts depending on the type of command line interface it's wrapping. For most applications, the flat layout will be the one to go with, as its layout matches best to the familiar CLI schema of a primary command followed by many options (e.g. Curl, FFMPEG).
On the other side is the Column Layout. This one is best suited for CLIs that have multiple paths or are made up of multiple little tools each with their own arguments and options (think: git). It displays the primary paths along the left column, and their corresponding arguments in the right. This is a great way to package a lot of varied functionality into a single app.

Both views present each action in the `Argument Parser` as a unique GUI component. It makes it ideal for presenting the program to users which are unfamiliar with command line options and/or Console Programs in general. Help messages are displayed along side each component to make it as clear as possible which each widget does.
**Setting the layout style:**
Currently, the layouts can't be explicitly specified via a parameter (on the TODO!). The layouts are built depending on whether or not there are `subparsers` used in your code base. So, if you want to trigger the `Column Layout`, you'll need to add a `subparser` to your `argparse` code.
It can be toggled via the `advanced` parameter in the `Gooey` decorator.
@gooey(advanced=True)
def main():
# rest of code
--------------------------------------------
### Basic
The basic view is best for times when the user is familiar with Console Applications, but you still want to present something a little more polished than a simple terminal. The basic display is accessed by setting the `advanced` parameter in the `gooey` decorator to `False`.
@gooey(advanced=False)
def main():
# rest of code

----------------------------------------------
### No Config
No Config pretty much does what you'd expect: it doesn't show a configuration screen. It hops right to the `display` section and begins execution of the host program. This is the one for improving the appearance of little one-off scripts.
To use this mode, set `auto_start=True` in the Gooey decorator.
```python
@Gooey(auto_start=True)
def main ():
...
```

--------------------------------------
### Menus

>Added 1.0.2
You can add a Menu Bar to the top of Gooey with customized menu groups and items.
Menus are specified on the main `@Gooey` decorator as a list of maps.
```
@Gooey(menu=[{}, {}, ...])
```
Each map is made up of two key/value pairs
1. `name` - the name for this menu group
2. `items` - the individual menu items within this group
You can have as many menu groups as you want. They're passed as a list to the `menu` argument on the `@Gooey` decorator.
```
@Gooey(menu=[{'name': 'File', 'items: []},
{'name': 'Tools', 'items': []},
{'name': 'Help', 'items': []}])
```
Individual menu items in a group are also just maps of key / value pairs. Their exact key set varies based on their `type`, but two keys will always be present:
* `type` - this controls the behavior that will be attached to the menu item as well as the keys it needs specified
* `menuTitle` - the name for this MenuItem
Currently, three types of menu options are supported:
* AboutDialog
* MessageDialog
* Link
* HtmlDialog

**About Dialog** is your run-of-the-mill About Dialog. It displays program information such as name, version, and license info in a standard native AboutBox.
Schema
* `name` - (_optional_)
* `description` - (_optional_)
* `version` - (_optional_)
* `copyright` - (_optional_)
* `license` - (_optional_)
* `website` - (_optional_)
* `developer` - (_optional_)
Example:
```
{
'type': 'AboutDialog',
'menuTitle': 'About',
'name': 'Gooey Layout Demo',
'description': 'An example of Gooey\'s layout flexibility',
'version': '1.2.1',
'copyright': '2018',
'website': 'https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey',
'developer': 'http://chriskiehl.com/',
'license': 'MIT'
}
```

**MessageDialog** is a generic informational dialog box. You can display anything from small alerts, to long-form informational text to the user.
Schema:
* `message` - (_required_) the text to display in the body of the modal
* `caption` - (_optional_) the caption in the title bar of the modal
Example:
```python
{
'type': 'MessageDialog',
'menuTitle': 'Information',
'message': 'Hey, here is some cool info for ya!',
'caption': 'Stuff you should know'
}
```
**Link** is for sending the user to an external website. This will spawn their default browser at the URL you specify.
Schema:
* `url` - (_required_) - the fully qualified URL to visit
Example:
```python
{
'type': 'Link',
'menuTitle': 'Visit Out Site',
'url': 'http://www.example.com'
}
```

**HtmlDialog** gives you full control over what's displayed in the message dialog (bonus: people can copy/paste text from this one!).
Schema:
* `caption` - (_optional_) the caption in the title bar of the modal
* `html` - (_required_) the html you want displayed in the dialog. Note: only a small subset of HTML is supported. [See the WX docs for more info](https://wxpython.org/Phoenix/docs/html/html_overview.html).
Example:
```python
{
'type': 'HtmlDialog',
'menuTitle': 'Fancy Dialog!',
'caption': 'Demo of the HtmlDialog',
'html': '''

Hello world!
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur
'''
}
```
**A full example:**
Two menu groups ("File" and "Help") with four menu items between them.
```python
@Gooey(
program_name='Advanced Layout Groups',
menu=[{
'name': 'File',
'items': [{
'type': 'AboutDialog',
'menuTitle': 'About',
'name': 'Gooey Layout Demo',
'description': 'An example of Gooey\'s layout flexibility',
'version': '1.2.1',
'copyright': '2018',
'website': 'https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey',
'developer': 'http://chriskiehl.com/',
'license': 'MIT'
}, {
'type': 'MessageDialog',
'menuTitle': 'Information',
'caption': 'My Message',
'message': 'I am demoing an informational dialog!'
}, {
'type': 'Link',
'menuTitle': 'Visit Our Site',
'url': 'https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey'
}]
},{
'name': 'Help',
'items': [{
'type': 'Link',
'menuTitle': 'Documentation',
'url': 'https://www.readthedocs.com/foo'
}]
}]
)
```
---------------------------------------
### Dynamic Validation

>:warning:
>Note! This functionality is experimental and likely to be unstable. Its API may be changed or removed altogether. Feedback/thoughts on this feature is welcome and encouraged!
>:warning:
>See [Release Notes]() for guidance on upgrading from 1.0.8 to 1.2.0
Before passing the user's inputs to your program, Gooey can optionally run a special pre-flight validation to check that all arguments pass your specified validations.
**How does it work?**
Gooey piggy backs on the `type` parameter available to most Argparse Argument types.
```python
parser.add_argument('--some-number', type=int)
parser.add_argument('--some-number', type=float)
```
In addition to simple builtins like `int` and `float`, you can supply your own function to the `type` parameter to vet the incoming values.
```python
def must_be_exactly_ten(value):
number = int(value)
if number == 10:
return number
else:
raise TypeError("Hey! you need to provide exactly the number 10!")
def main():
parser = ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--ten', type=must_be_exactly_ten)
```
**How to enable the pre-flight validation**
By default, Gooey won't run the validation. Why? This feature is fairly experimental and does a lot of intense Monkey Patching behind the scenes. As such, it's currently opt-in.
You enable to validation by telling Gooey you'd like to subscribe to the `VALIDATE_FORM` event.
```python
from gooey import Gooey, Events
@Gooey(use_events=[Events.VALIDATE_FORM])
def main():
...
```

Now, when you run Gooey, before it invokes your main program, it'll send a separate pre-validation check and record any issues raised from your `type` functions.
**Full Code Example**
```
from gooey import Gooey, Events
from argparse import ArgumentParser
def must_be_exactly_ten(value):
number = int(value)
if number == 10:
return number
else:
raise TypeError("Hey! you need to provide exactly the number 10!")
@Gooey(program_name='Validation Example', use_events=[Events.VALIDATE_FORM])
def main():
parser = ArgumentParser(description="Checkout this validation!")
parser.add_argument('--ten', metavar='This field should be 10', type=must_be_exactly_ten)
args = parser.parse_args()
print(args)
```
---------------------------------------
## Lifecycle Events and UI control
>:warning:
>Note! This functionality is experimental. Its API may be changed or removed altogether. Feedback on this feature is welcome and encouraged!
As of 1.2.0, Gooey now exposes coarse grain lifecycle hooks to your program. This means you can now take additional follow-up actions in response to successful runs or failures and even control the current state of the UI itself!
Currently, two primary hooks are exposed:
* `on_success`
* `on_error`
These fire exactly when you'd expect: after your process has completed.
**Anatomy of an lifecycle handler**:
Both `on_success` and `on_error` have the same type signature.
```python
from typing import Mapping, Any, Optional
from gooey.types import PublicGooeyState
def on_success(args: Mapping[str, Any], state: PublicGooeyState) -> Optional[PublicGooeyState]:
"""
You can do anything you want in the handler including
returning an updated UI state for your next run!
"""
return state
def on_error(args: Mapping[str, Any], state: PublicGooeyState) -> Optional[PublicGooeyState]:
"""
You can do anything you want in the handler including
returning an updated UI state for your next run!
"""
return state
```
* **args** This is the parsed Argparse object (e.g. the output of `parse_args()`). This will be a mapping of the user's arguments as existed when your program was invoked.
* **state** This is the current state of Gooey's UI. If your program uses subparsers, this currently just lists the state of the active parser/form. Whatever updated version of this state you return will be reflected in the UI!
**Attaching the handlers:**
Handlers are attached when instantiating the `GooeyParser`.
```python
parser = GooeyParser(
on_success=my_success_handler,
on_failure=my_failure_handler)
```
**Subscribing to the lifecycle events**
Just like [Validation](#dynamic-validation), these lifecycle events are opt-in. Pass the event you'd like to subscribe to into the `use_events` Gooey decorator argument.
```python
from gooey import Gooey, Events
@Gooey(use_events=[Events.ON_SUCCESS, Events.ON_ERROR])
def main():
...
```
-------------------------------------
## Showing Progress

Giving visual progress feedback with Gooey is easy! If you're already displaying textual progress updates, you can tell Gooey to hook into that existing output in order to power its Progress Bar.
For simple cases, output strings which resolve to a numeric representation of the completion percentage (e.g. `Progress 83%`) can be pattern matched and turned into a progress bar status with a simple regular expression (e.g. `@Gooey(progress_regex=r"^progress: (\d+)%$")`).
For more complicated outputs, you can pass in a custom evaluation expression (`progress_expr`) to transform regular expression matches as needed.
Output strings which satisfy the regular expression can be hidden from the console via the `hide_progress_msg` parameter (e.g. `@Gooey(progress_regex=r"^progress: (\d+)%$", hide_progress_msg=True)`.
**Regex and Processing Expression**
```python
@Gooey(progress_regex=r"^progress: (?P\d+)/(?P\d+)$",
progress_expr="current / total * 100")
```
**Program Output:**
```
progress: 1/100
progress: 2/100
progress: 3/100
...
```
There are lots of options for telling Gooey about progress as your program is running. Checkout the [Gooey Examples](https://github.com/chriskiehl/GooeyExamples) repository for more detailed usage and examples!
### Elapsed / Remaining Time
Gooey also supports tracking elapsed / remaining time when progress is used! This is done in a similar manner to that of the project [tqdm](https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm). This can be enabled with `timing_options`, the `timing_options` argument takes in a dictionary with the keys `show_time_remaining` and `hide_time_remaining_on_complete`. The default behavior is True for `show_time_remaining` and False for `hide_time_remaining_on_complete`. This will only work when `progress_regex` and `progress_expr` are used.
```python
@Gooey(progress_regex=r"^progress: (?P\d+)/(?P\d+)$",
progress_expr="current / total * 100",
timing_options = {
'show_time_remaining':True,
'hide_time_remaining_on_complete':True,
})
```
--------------------------------------
## Customizing Icons
Gooey comes with a set of six default icons. These can be overridden with your own custom images/icons by telling Gooey to search additional directories when initializing. This is done via the `image_dir` argument to the `Gooey` decorator.
@Gooey(program_name='Custom icon demo', image_dir='/path/to/my/image/directory')
def main():
# rest of program
Images are discovered by Gooey based on their _filenames_. So, for example, in order to supply a custom configuration icon, simply place an image with the filename `config_icon.png` in your images directory. These are the filenames which can be overridden:
* program_icon.png
* success_icon.png
* running_icon.png
* loading_icon.gif
* config_icon.png
* error_icon.png
## Packaging
Thanks to some [awesome contributors](https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey/issues/58), packaging Gooey as an executable is super easy.
The tl;dr [pyinstaller](https://github.com/pyinstaller/pyinstaller) version is to drop this [build.spec](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/chriskiehl/Gooey/master/docs/packaging/build-win.spec) into the root directory of your application. Edit its contents so that the `APPPNAME` and `name` are relevant to your project and the `pathex` value points to your applications root, then execute `pyinstaller -F --windowed build.spec` to bundle your app into a ready-to-go executable.
Detailed step by step instructions can be found [here](https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey/blob/master/docs/packaging/Packaging-Gooey.md).
Screenshots
------------
| Flat Layout | Column Layout |Success Screen | Error Screen | Warning Dialog |
|-------------|---------------|---------------|--------------|----------------|
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|
| Custom Groups | Tabbed Groups | Tabbed Navigation | Sidebar Navigation | Input Validation |
|-------------|---------------|---------------|--------------|----------------|
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|
----------------------------------------------
Wanna help?
-----------
Code, translation, documentation, or graphics? All pull requests are welcome. Just make sure to checkout [the contributing guidelines](https://github.com/chriskiehl/Gooey/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md) first.