https://github.com/howtoautomateinth/awesome-aws
collection of aws resources
https://github.com/howtoautomateinth/awesome-aws
List: awesome-aws
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
collection of aws resources
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/howtoautomateinth/awesome-aws
- Owner: howtoautomateinth
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2019-08-05T04:01:29.000Z (almost 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2020-03-19T09:56:35.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-05-28T15:53:35.206Z (about 1 year ago)
- Homepage: http://www.howtoautomate.in.th
- Size: 578 KB
- Stars: 5
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 3
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- ultimate-awesome - awesome-aws - Collection of aws resources. (Other Lists / Julia Lists)
README
# Awesome AWS Collection
Categorize awesome things in AWS
## Elastic Compute Cloude (EC2)
#### Pricing
Three categories
- On-demand instance
- pay just for the usage on a flat hourly rate or per-second billing
- Reserved instance
- 75 percent discount compared to an on-demand instance
- have to know how many resources your workload is going to take and for how long (at least a year)
- Payment options
- up-front reserved
- partial up-front reserved
- no up-front reserved
- two subcategories of it
- standard reserved instance
- convertible reserved instance
- have ability and flexibility to exchange the instance from one class of family to another class if your computing need changes
- Spot instance
- biding
- you will not be charged for the partial hour that your instance has run. You are charged the Spot market price (not your bid price) for as long as the Spot Instance runs
- 90 percent discount compared to on-demand pricing
- great for workloads that can restart from where they failed (in other words, can interrupt job)
- Spot instance request type
- 
- one-time
- remains active until Amazon EC2 launches the Spot Instance, the request expires, or you cancel the request. If the Spot price exceeds your maximum price or capacity is not available, your Spot Instance is terminated and the Spot Instance request is closed
- persistent
- remains active until it expires or you cancel it, even if the request is fulfilled. If the Spot price exceeds your maximum price or capacity is not available, your Spot Instance is interrupted. After your instance is interrupted, when your maximum price exceeds the Spot price or capacity becomes available again, the Spot Instance is started if stopped or resumed if hibernated. If the Spot Instance is terminated, the Spot Instance request is opened again and Amazon EC2 launches a new Spot Instance
#### Placement Group
Three categories
- Cluster
- is a logical grouping of instances within a single Availability Zone
- To provide the lowest latency and the highest packet-per-second network performance for your placement group
- Partition
- spreads your instances across logical partitions such that groups of instances in one partition do not share the underlying hardware
- used by large distributed and replicated workloads, such as Hadoop, Cassandra, and Kafka
- Spread
- group of instances that are each placed on distinct racks, with each rack having its own network and power source
- reduces the risk of simultaneous failures that might occur when instances share the same racks
#### Life Cycle

- Launch
- Start and Stop
- lose any data on the instance store volumes
- Reboot
- Termination
- Retirement
## Virtual Private Cloud
### Amazon VPC Components
#### VPC
- first step of VPC is deciding the IP range by providing a Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) block, The allowed block size is between a /16 netmask (65,536 IP addresses) and /28 netmask (16 IP addresses)
- If you create a VPC with a small size and later realize that you need more IP addresses, you can create a new VPC with a bigger IP address range and then migrate your applications from the old VPC to the new one
- limited to a region
- It's not possible to modify the IP address range of an existing VPC or subnet. You must delete the VPC or subnet, and then create a new VPC or subnet with your preferred CIDR block.
- AWS will reserved five IP addresses
- For example, in a subnet with CIDR block 10.0.0.0/24 we won't use below IP
- 10.0.0.0 - 10.0.0.3 and 10.0.0.255
#### Subnet
- Subnet is short for subnetwork, With subnetting you can divide a network into multiple networks
- Subnet is tied to only one availability zone, If you have three AZs in a VPC, for example, you need to create a separate subnet in each AZ
#### Route Table
- route table is a table consisting of certain rules known as routes
- provide information to route when requested
- two columns
- Destination
- the destinations specifies the ip range that can be directed to the target
- Local destination, which indicates internal routing in VPC
- Target
- target is where the traffic is directed
#### Internet Gateway
- allows your VPC to communicate with the Internet
#### Network Address Translation (NAT)
> NAT device, you can enable any instance in a private subnet to connect to the Internet
- two types of NAT devices available withint AWS
- NAT instances
- in public subnet to allow private subnet through the internet
- created in a specific AZ, redundant NAT instances in different AZs
- each EC2 instance either sends or receives internet traffic. That is, it itself is the source and / or destination of the traffic. But, the NAT instance is neither the source nor the destination of the traffic. NAT Instances merely act as a gateway for the traffic. Thus, the Source/Destination checks need to be disabled on NAT instance so that the NAT instance can serve as a gateway and allow instances in a private subnets to securely connect to the internet
- NAT gateway
- same function as that of a NAT instance
- you must specify an elastic IP address
- created in a specific AZ, redundant NAT gateway in different AZs
- The NAT gateway sends the traffic to the internet gateway using the NAT gateway’s Elastic IP address as the source IP address
- use case: If you want to do some firmware updates in the database server or if you want to download some database patches, how do you download them? Network Address Translation (NAT) tries to solve that problem
#### Elastic IP Address (EIP)
> Every time you launch a new EC2 instance in AWS, you get a new IP address. Sometimes it becomes a challenge since you need to update all the applications every time there is an IP address change
- an EIP is a static IP address to address that issues
- There is no charge for using an EIP
- it will charge when it is allocated and associated with a stopped instance
#### Bastion
- bastion hosts in your VPC environment enables you to securely connect to your Linux instances without exposing your environment to the Internet
- through Secure Shell (SSH) connections on Linux
- Elastic IP addresses are associated with the bastion instances to make it easier to remember and allow these IP addresses from on-premises firewalls
- else should use auto-assigned Public IP address
#### VPC Endpoint
- VPC endpoint does is give you the ability to connect to VPC and AWS services directly using a private connection
#### Drecit Connect
- a dedicated private connection from your corporate data center to your VPC
#### VPC Peering
- VPC peering helps to connect one virtual private cloud to another and route the traffic across the virtual private clouds
- between two VPCs
- You can’t peer VPCs across regions
- one-to-one relationship two VPCs
- can not use transit point between VPC need to peering itself
#### VPC Flow Logs
- enable you to capture information about the IP traffic going to and from network interfaces in your VPC
#### ClassicLink
- allows EC2 instances in the EC2-Classic platform to communicate with instances in a VPC using private IP addresses
#### PrivateLink
- allows you to publish an "endpoint" that others can connect with from their own VPC. It's similar to a normal VPC Endpoint, but instead of connecting to an AWS service, people can connect to your endpoint. Think of it as a way to publish a private API endpoint without having to go via the Internet [Ref.](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57871544/what-is-difference-between-aws-vpc-private-link-and-vpc-peering)
#### VPC Monitoring
- Cloudwatch
- TunnelState Metric
- The state of the tunnel. For static VPNs, 0 indicates DOWN and 1 indicates UP
#### Accessing and Permission
##### Security Group
- virtual firewall applied at the instance level
- There are no deny rules, so the only way to block traffic is to not allow it
- stateful
- change inbound (ingress) also applied to outbound (egress)
##### Network Access Control list (NACL)
- firewall at a subnet level for your VPC
- default, each custom NACL denies all inbound and outbound traffic until you add rules
- able to denied IP, port
- denied rule should be infront of allow rule
- contain a numbered list of rules that are evaluated in order to decide whether the traffic is allowed to a particular subnet associated with the NACL
- starting with the lowest numbered rule
- recommend to start with number 100, highest number is 32766
- stateless
- have to create rule for inbound and outbound
- [Different Between Security Group and Network ACLs](https://medium.com/awesome-aws/aws-difference-between-security-groups-and-network-acls-adc632ea29ae)
## Storage on Cloud
The storage offerings of AWS can be divided into three major categories
- File
- Elastic File System (EFS)
- Object
- Simple Storage Services (S3)
- Glacier
- Block
- Instance Store on EC2
- Elastic Block Storage (EBS)
> [Different Between EBS, S3 and EFS](https://dzone.com/articles/confused-by-aws-storage-options-s3-ebs-amp-efs-explained)
#### ENCRYPTION
Two main ways of securing the data
- Data in transit
- HTTPS and use SSL-encrypted
- Data at rest
- S3 Encryption
- EBS Encryption
- Encrypted by Default
- Encryption by default has no effect on existing EBS volumes or snapshots
- Encrypted EBS Volume from Unencrypted Volume with Existing data on it
- Create a Snapshot from unencrypted volume
- Copy Unencrypted Snapshot to change it to an Encrypted Snapshot
- Create Encrypted EBS Volume from the Encrypted Snapshot
#### BLOCK STORAGE
- Considering information before using block storage type (SSD = Random & HDD = Sequential)
- [Random VS Sequential 1](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27180409/what-is-a-sequential-write-and-what-is-random-write?noredirect=1&lq=1)
- [Random VS Sequential 2](https://insightsblog.violinsystems.com/blog/understanding-io-random-vs-sequential)
- Block Storage Type
- EC2 instance store
- the instance store is ephemeral
- all the data stored in the instance store is gone when EC2 instance is shut down.
- no snapshot support for instance store
- available in a solid-state drive (SSD) or hybrid hard dive (HDD)
- EBS SSD-backed volume
- 2 major categories
- SSD-backed storage
- random IO
- transactional workloadssuch as database and boot volumes
- General-Purpose SSD (gp2)
- Provisioned IOPS SSD (Provisioned IOPS)
- for IO-intense workload such as database
- HDD-backed storage
- sequential IO
- throughput-intensive workloads such as log processing and mapreduce
- Throughput-Optimized HDD (st1)
- for big data, data warehouses
- Cold HDD (sc1)
- for noncritical support infrequently accessed
##### EBS Performance
- RAID
- RAID 0
- When I/O performance is more important than fault tolerance; for example, as in a heavily used database
- RAID 1
- When fault tolerance is more important than I/O performance
- RAID 5 and RAID 6 are not recommended for Amazon EBS because the parity write operations of these RAID modes consume some of the IOPS available to your volumes
##### EBS Snapshot
> Snapshots are incremental backups, which means that only the blocks on the device that have changed after your most recent snapshot are saved
- Snapshots occur asynchronously so the EBS volume able to use all the time during snapshot

#### FILE STORAGE
> a file system interface and file system semantics to Amazon EC2 instances
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) provides shared access to data via multiple Amazon EC2 instances, with low latencies
##### Interesting Feature
- Shared storage
- shared across thousands of EC2 instances
- Elastic and Scalable
- can grows to petabyte scale and don't need to specify a provisioned size up front
#### STORAGE TOOLS
- AWS Snowball
- AWS Import / Export tool, provides a petabyte-scale data transfer service
- Help transfer TB highspeed to Amazon S3
- AWS Storage Gateway
- The AWS Storage Gateway service enables hybrid cloud storage between on-premises environments and the AWS Cloud
- File Gateway
- such as NFS
- 
- Tape Gateway
- iSCSI virtual tape library (VTL) interface
- 
- Volume Gateway
- cached mode
- primary data is written to S3, while retaining your frequently accessed data locally in a cache for low-latency access 
- stored mode
- primary data is stored locally and your entire dataset is available for low-latency access while asynchronously backed up to AWS 
#### OBJECT
##### AWS Simple Storage Services (S3)
- S3 Encryption
- SSE with Amazon S3 Key Management (SSE-SE)
- S3 will manage encryption keys for you. Each object is encrypted using a per-object key
- SSE with customer-provided keys (SSE-C)
- Custom will send encryption key in your upload request,S3 doesn’t store your encryption key anywhere
- SSE with AWS Key Management Service KMS (SSE-KMS)
- S3 will manage encryption keys in KMS, can seperate permissions in KMS additional layer of control
- S3 Access Control
- Access Policies
- IAM policy helps you control who can access your data stored in S3
- Assign that policy to user,group or a role
- Bucket Policies
- Also can create at bucket level, which is called a bucket policy
- Any object from a particular object will be applied
- Access Control List
- Each bucket and and object inside the bucket has an ACL associated
- Can apply on bucket level and also object level
- Coarse-grained control, permissions only to other AWS accounts not users in your account
- S3 Storage Class
- Standard
- default storage
- fault tolerance
- The files in Amazon S3 Standard are synchronously copied across three facilities and designed to sustain the loss of data in two facilities
- 99.999999999 percent durability (11 nines)
- 99.99 percent availability
- Standard Infrequent Access
- much cheaper than standard
- same durability with standard
- 99.9 percent availability
- Reduced Redundancy Storage (RRS)
- storage option that is used to store noncritical, nonproduction data
- 99.99 percent durability
- 99.99 percent availability
- S3 One Zone-Infrequent Access
- accessed less frequently, but requires rapid access when needed
- single AZ so not fault tolerance
- Glacier
- mainly used for data archiving
- same durability with standard
- three main options for retrieving data
- expedited
- quick retrieval of data in the range of one to five minutes
- standard
- standard takes about three to five hours to retrieve the data
- bulk retrievals
- retrieve large amounts of data such as petabytes of data in a day (five to twelve hours)
- S3 Object Lifecycle Management
- Transition action
- objects can be transitioned to another storage class
- Expiration action
- define what is going to happen when the objects expire
- S3 Cross-Region Replication (CRR)
- replicate the objects in an S3 bucket to a different region
- use case: compliance requirement and disaster recovery considerations to keep copies of critical data that are hundreds of miles apart
##### S3 Characteristic
- Read-after-write consistency for PUTS of new objects in your S3 bucket
- For all other objects (apart from new ones), S3 is an eventually consistent system
- Also support for HTTP range request to get information in HTTP header [1](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/en_us/AmazonS3/latest/API/API_GetObject.html),[2](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Range_requests)
##### S3 Performance
> Amazon S3 bucket is going to exceed 100 PUT/LIST/DELETE requests per second or 300 GET requests per second
S3 is partitioning based on the key prefix
- Reverse the key name string
- Normally when doing massive uploads from your application we will increase the sequence by 1 so to prevent partition issues we should reverse the key so it will not be the same
- Adding a hex hash prefix to a key name
- [Optimized Performance S3 Naming](https://btuanexpress.net/optimized-performance-s3-naming/)
- 4-character hex hash will provide 65,536 list so have to aware this too
#### Tools
- AWS Data Pipeline
- is a web service that helps you reliably process and move data between different AWS compute and storage services, as well as on-premises data sources, at specified intervals. With AWS Data Pipeline, you can regularly access your data where it’s stored, transform and process it at scale, and efficiently transfer the results to AWS services such as Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon EMR.
- from a DynamoDB table to a file in an Amazon S3 bucket
## Identity and Access Management and Security (IAM)
offers the following authentication features
- Managing users and their access
- Managing federated users and their access
- Single sign-on (SSO)
- using the credentials of your corporate directory
- Support Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)
- identity provider (IdP)
- Google, Facebook, Amazon and many others
- corporate directory
### Authorization
- authorization is mainly done using IAM policies written in JavaSCript Object Notation (JSON)
- policy can be attached to any IAM entity such as a user, group, or role
- a policy, you can either allow or deny access to any resource for any IAM entity
- all permissions are implicitly denied by default
### Auditing
- CloudTrail log every API call and related event made
- ensure compliance with internal policies and regulatory standards
- CloudTrail service records activity made on your account and delivers log files to yourr Amazon S3 bucket
- AWS KMS is integrated with AWS CloudTrail, a service that provides a record of actions performed by a user, role, or an AWS service in AWS KMS
### Temporary Security Credentials
- AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS) These temporary security credentials won’t be stored with a user
- Dynamically generated whenever a user requests them
- Web Identity Federation
- you don't need to create custom sign-in code or manage your own user identities. Instead, users of your app can sign in using a well-known external identity provider (IdP), such as Login with Amazon, Facebook, Google, or any other OpenID Connect (OIDC)-compatible IdP
- with AWS STS enables you to create apps where users can sign in using a web-based identity provider like Login
- Once the credentials expire, you won’t be able to use them
- LDAP is a protocol for querying a directory
- SAML is a protocol for supplying security tokens for single sign on
- [LDAP & SAML Discussion](https://acloud.guru/forums/aws-certified-solutions-architect-associate/discussion/-KaXoTgYNh8TBNtuhVtc/which-technique-can-be-used-to-integrate-aws-iam-identity-and-access-management-)
### IAM Component
- User
- IAM Users
- permanent identity
- Federated users
- don't have permanent identities
- Groups
- Role
- Federated users don not have permanent identities the way you control their permission is by creating a role
- Using roles you can define a set of permissions to access the resources that a user or service needs, but the permissions are not attached to an IAM user or group
- create a role, you need to specify two policies
- trust policy
- who can assume the role
- access policy
- what resources and action is assuming the role is allowed access
- always use IAM roles to delegate cross-account access, to delegate access within an account, and to provide access for federated users
- no need to share security credentials or store long-term credentials
- IAM roles for EC2 instances make it easier for your applications and command-line tools to securely access AWS service APIs from EC2 instances
#### IAM Plugin
- IAM Authentication
- IAM database authentication, you use an authentication token when you connect to your DB cluster. An authentication token is a string of characters that you use instead of a password. After you generate an authentication token, it's valid for 15 minutes before it expires. If you try to connect using an expired token, the connection request is denied.
## Database on AWS
### Amazon RDS
> RDS fully manages the host, operating system, and database version you are running on
- have limited ability to modify the configuration that is normally managed on the host operating system
- choose if you want to focus on tasks that bring value to your business
#### High Availability on RDS
- deploy a database in a multi-AZ architecture
- master database
- data on the primary database is synchronously replicated to the storage in the standby configuration
- standby database
- does not remain open when it acts as a standby database
- the failover happens, the standby is automatically propagated to the master
#### Scaling on RDS
- Changing the instance type
- Read Replica
- is a read-only copy of your master database that is kept in sync with your master database
- offload the read-only queries to it
- up to 15 read replicas
- replication is not synchronous, it is asynchronous so if you promote a read replica to a master, there could be some data loss
- read replica
- same region
- intra-region
- additional read replicas within the same AWS region, but in the same or different availability zones from your master database
- different region
- called a cross-regional read replica
#### Security on RDS
- database in the private subnet
- data enryption
- data-at-rest encryption
- AES-256 encryption algorithm to encrypt your data on the server
- a default key for RDS is created in the Key Management Service (KMS)
#### Backups, Restores, and Snapshots
- Database backup is scheduled for every day
- Aurora, you don’t have to back up manually since everything is automatically backed up continuously to the S3 bucket
- retained for 35 days
- Creating a snapshot
- there is a temporary I/O suspension that can last from a few seconds to a few minutes
- created in S3
### Amazon Aurora
> cloud-optimized, MySQL- and PostgreSQL-compatible
- There is a separate storage layer that is automatically replicated across six different storage nodes in three different availability zones
- no additional cost
- data mirroring happens synchronously no data loss
- grows up to 64TB
- supports up to 15 copies of read replica
- data replication happens at the storage level in a synchronous
- Aurora is no concept of standby database, and the read replica is prompted to a master or primary database node when the primary node goes down
### Amazon Redshift
> managed data warehouse soltion
- data warehouses are very much read-oriented systems
#### Amazon Redshift Architecture
- Redshift cluster consists of
- Leader node
- performs a few roles. It acts as a SQL endpoint for the applications
- communicates with the compute nodes for processing any query
- Compute node
- Able to span to x regions by using Amazon Kinesis setup in x regions and Redshift using that subscriber
- Cross-region snapshots to the other regions provide rebuild [1](https://aws.amazon.com/th/blogs/aws/automated-cross-region-snapshot-copy-for-amazon-redshift/)
##### Encryption
- If the encryption is enabled in a cluster, it becomes immutable which means you can't disable
- If at a later phase you decide to encrypt the data, then the only way is to unload your data from the existing cluster and reload it in a new cluster with the encryption setting
### Amazon DynamoDB
> fully managed NoSQL database service that provides fast and predictable performance with seamless scalability
- can be used in advertising for capturing browser cookie state, in mobile applications for storing application data and session state, in gaming applications for storing user preferences and application state and for storing players’ game state, in consumer “voting” applications for reality TV contests, in Super Bowl commercials, in large-scale
- Local development
- The downloadable version of DynamoDB lets you write and test applications without accessing the DynamoDB web service
- Benefits of Amazon DynamoDB
- Scalable
- running a larger NoSQL cluser.DynamoDB is scalable and can automatically scale up and down depending on your application request
- DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
> is a fully managed, highly available, in-memory cache for DynamoDB that delivers up to a 10x performance improvement
### Amazon ElasticCache
> is a web service that makes it easy to deploy, operate, and scale an in-memory cache in the cloud
- caching to significantly improve latency and throughput for many read-heavy application workloads
- Two engine in elasticcache
- Memcached
- Redis
- support replication for multi-AZ redundancy
## Auto Scaling
> the ability to spin servers up when your workloads require additional resources and spin them back down when demand drops
### Auto Scaling Components
#### Launch Configuration
> stores all the information about instance such as AMI,instance type,key pair, security group
- create and link it with an Auto Scaling group
- 1-to-Many, Many Auto Scaling group can use 1 Launch Configuration
- Once you create an Auto Scaling group, you can’t edit the launch configuration tied up with it
#### Auto Scaling Groups
> where you define the logic for scaling up and scaling down. It has all the rules and policies that govern how the EC2 instances will be terminated or started
##### Schedule
- set your own scaling schedule for predictable load changes. For example, every week the traffic to your web application starts to increase on Wednesday, remains high on Thursday, and starts to decrease on Friday
##### Manual
- you can change the size of an existing Auto Scaling group manually. You can either update the desired capacity of the Auto Scaling group, or update the instances that are attached to the Auto Scaling group
##### Life Cycle Hook
- The Auto Scaling group responds to scale-out events by launching instances and scale-in events by terminating instances.
##### Dynamic
- three types of scaling policies
- Simple Scaling
- select an alarm, which can be CPU utilization, disk read, disk write, network in or network out, and so on, and then scale up or down
- also define how long to wait before starting or stopping a new instance. This waiting period is also called the cooldown period
- Simple Scaling with Steps
- same with Simple Scaling but can step it up due to condition
- Target-tracking Scaling
- can select a predetermined metric or you choose your own metric and then set it to a target value
- use case: set target 50 percent of CPU then Auto Scaling will automatically scale up or scale down the EC2 instances to maintain a 40 percent CPU utilization
- Termination Policy
- decide how exactly you are going to terminate the EC2 servers when you have to scale down
- default, will select AZ have the most instances, and at least one instance that is not protected from scale in
### Elastic Load Balancing
> the load balancers that you are going to use will be always deployed across multiple AZs. Internally, there will be multiple load balancers deployed in a separate ELB VPC, spanning multiple AZs to provide a highly available architecture
Three main load balancers
> Auto Scaling and ELB, it is recommended that you use multiple AZs whenever possible
- Network Load Balancer
- acts in layer 4 the OSI Model
- supports both TCP and SSL
- no X-Forwarded-For headers since it does not make any changes or touch the packet
- Application Load Balancer
- acts in layer 7 of the OSI Model
- supports HTTP and HTTPS
- the headers might be modified
- X-Forwarded-For header containing the client IP address
- Ability to do
- host-based routing
- path-based routing
- Classic Load Balancer
- Supports the classic EC2 instances
- Operates on layer 4 as well as on layer 7 of the OSI model
- X-Forwarded-For header containing the client IP address
- Support for SSL Termination
- HTTPS encryption and decryption process (generally known as SSL termination) to be handled by an Elastic Load Balancer
#### Monitor Load Balance
- CloudWatch metrics
- Elastic Load Balancing publishes data points to Amazon CloudWatch about your load balancers and back-end instances
- Elastic Load Balance Access Log
- The access logs for Elastic Load Balancing capture detailed information for requests made to your load balancer and stores them as log files in the Amazon S3 bucket that you specify. Each log contains details such as the time a request was received, the client's IP address, latencies, request path, and server responses
- CloudTrail logs
- Enables you to keep track of the calls made to the Elastic Load Balancing API by or on behalf of your AWS account
- [ALB vs NLB](https://medium.com/containers-on-aws/using-aws-application-load-balancer-and-network-load-balancer-with-ec2-container-service-d0cb0b1d5ae5)
- [OSI Model Layer](https://medium.com/@madhavbahl10/osi-model-layers-explained-ee1d43058c1f) of seven layers
#### Core Component Of The Load Balancer
- Listeners
- define the protocol and port on which the load balancer listens for incoming connections
- Target Groups and Target
- logical groupings of targets behind a load balancer
- Rules
- link between listeners and target groups and consist of conditions and actions
- Rules can forward requests to a specified target group
- Each rule has a priority attached to it
- The rule with the highest priority will be executed first
- Health Check
- run a health check, which is going to check the target or target group at a certain interval of time defined by you to make sure the target or the target group is working fine
- With the health check request, you specify the port, protocol, and ping path
- if the instance keep failing it will be replaced by a new EC2 instance
#### Cross-zone load balancing
> distributes the requests evenly across multiple availability zones
- enabled by default in an application load balancer
- cross-zone load balancing happens across the targets and not at the AZ level
## Deploying and Monitoring Applications on AWS
### Lambda
> AWS Lambda is a compute service that runs your back-end code in response to events
- The code you run on AWS Lambda is called a Lambda function
- Low cost and does not require any up-front investment
- Select the event source to monitor such as an Amazon S3 bucket or Amazon DynamoDB table, event can trigger your function
- Charged for every 100ms your code executes and the number of times your code is triggered. This cost is also based on the memory consumption
- When you create or update Lambda functions that use environment variables, AWS Lambda encrypts them using the AWS Key Management Service (Storing Sensitive Information)
### Amazon API Gateway
> API Gateway is a fully managed service that makes it easy for developers to define, publish, deploy, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs at any scale
- Benefits
- API Logging
- Caching
- Throttling
- Bursting and Monitoring
### Amazon Kinesis
> ability to process and analyze becomes extremely important because that governs how you are going to serve your customers
- traditional analytics, you gather the data, load it periodically into a database, and analyze it hours, days, or weeks later
- stream-processing applications process data continuously in real time, even before it is stored
Three Categories
- Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
- enables you to build custom applications that process or analyze streaming data for specialized needs
- Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose
- easiest way to load streaming data into data stores and analytics tools
- pay only for the amount of data you transmit through the service
- Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics
- the easiest way to process and analyze real-time, streaming data
- use standard SQL to process your data streams, so you don’t have to learn any new programming language
### Amazon CloudFront
> allows you to distribute content with low latency and provides high data transfer speeds
- ensures that end-user requests are served by the closest edge location
- pay only for the data transfers and requests you actually use
- Lambda@Edge is a feature of Amazon CloudFront that lets you run code closer to users of your application, which improves performance and reduces latency
### CloudFront Key Concepts
- Edge Location
- data centers called edge locations
- located in major cities across the globe
- Regional edge Location
- located between your origin web server and the global edge locations that serve content directly to your viewers
- Regional edge caches have a larger cache width than any individual edge location, so objects remain in the cache longer at the nearest regional edge caches
#### Signed URL or Signed Cookies
> CloudFront signed URLs or signed cookies to limit access to files in your Amazon S3 bucket
- protect it from unauthorized access via CloudFront signed URLs (origin access identity (OAI))
- includes additional information, for example, an expiration date and time, that gives you more control over access to your content
#### Cache Invalidation
- Manual Clear Cache invalidation tab to Invalidating Files
### Amazon CloudWatch
> monitors your Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources and the applications you run on AWS in real time
- Metrics will be different based on services that we are going to use
- EC2
- [Instance Metric](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/viewing_metrics_with_cloudwatch.html) beyond of this metric will have to use custom metric e.g. Memory and Disk on EC2
### Amazon Route 53
- DNS translates human-readable names such as www.example.com into the numeric IP addresses such as 192.0.0.3
- phone book
#### DNS Component
- A (address record)
e.g. 74.125.224.147
- AAAA (IPv6 address record)
- CNAME (canonical name record)
e.g. www.example.com
- CAA (certification authority authorization)
- MX (mail exchange record)
- NAPTR (name authority pointer record)
- NS (name server record)
- PTR (pointer record)
- SOA (start of authority record)
- SPF (sender policy framework)
- SRV (service locator)
- TXT (text record)
Route 53 supports alias records (also known as zone apex support) which is the root domain of a web site (example.com, without the www)
- so you configure both http://www.example.com and http://example.com to point at the same CloudFront distribution
#### Routing Policies
- Weighted round robin
- Route traffic to those resources in proportions that you specify
- Latency-based routing
- Best latency, you can use latency-based routing
- Failover routing
- When this region fails, you can do failover routing and point to a static web site running from a different region
- Failover mode
- Active-Active
- all of your resources to be available the majority of the time. When a resource becomes unavailable, Route 53 can detect that it's unhealthy and stop including it when responding to queries.
- Active-Passive
- a primary resource or group of resources to be available the majority of the time and you want a secondary resource or group of resources to be on standby in case all the primary resources become unavailable
- Geo DNS routing
- Directing requests to specific endpoints based on the geographic location from which the request originates
##### Tips
- [How DNS Works](https://howdns.works/)
- [How HTTPS Works](https://howhttps.works/)
### Amazon ECS concept
Docker container service that handles the orchestration and provisioning of Docker containers
#### ECS Terms
- Cluster
- a logic group of EC2 instances
- Task Definition
- a blueprint that describes how a docker container should launch
- Task
- instance of Task Definition (running container with settings defined)
- Service
- long running Task of the same Task Definition, if a task in a service stops, the task is killed and a new task is launched
- Container Instance
- EC2 instance that is part of an ECS Cluster and has docker and the ecs-agent running on it
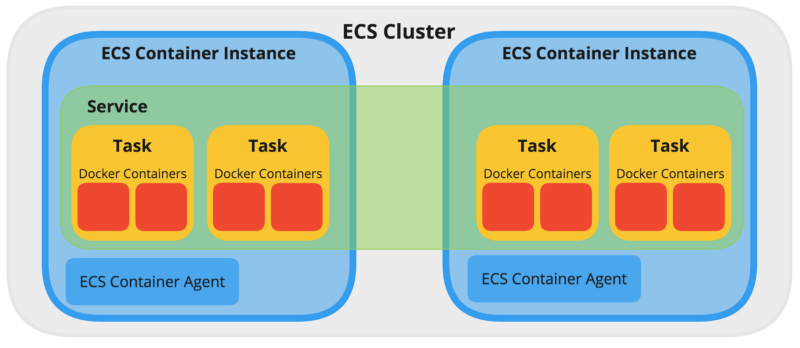
*Thanks image from [here](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/amazon-ecs-terms-and-architecture-807d8c4960fd/)*
### AWS Web Application Firewall (AWF)
> protect web sites and applications against attacks that could affect application availability, result in data breaches, cause downtime, compromise security, or consume excessive resources
- Integrated
- CloudFront
- Application Load Balancers (ALBs)
- Two types of rules in AWS
- Regular rules
- conditions to target specific requests
- Rate based rules
- same with regular but have rate limit in five-minute intervals
### AWS Simple Queue Service (SQS)
> Decouple the processing of larger jobs into small parts that can be run independent of each other
- A message queue is a form of asynchronous service-to-service communication
- Three players which is the producer, queue, and consumer
- Key Features of Amazon SQS
- redundant across multiple AZs in each region
- retained up to 14 days
- can contain up to 256KB of text data, including XML, JSON, and unformatted text
- Two types of SQS
- Standard
- It supports at-least-once message delivery
- FIFO
- A first in, first out (FIFO) queue guarantees first in, first out delivery and also exactly once processing
- 300 transactions per second
### AWS Simple Notification Service (SNS)
> web service used to send notifications from the cloud
- create a “topic” identifying a specific subject or event type
- the publisher and subscriber model
- SNS endpoints
- Email
- Short Message Service (SMS)
### AWS Step Functions And Amazon Simple Workflow (SWF)
> fully managed service that makes it easy to coordinate the components of distributed applications and microservices using visual workflow
- Define your application as a state machine, a series of steps that together capture the behavior of the app
- Tasks are units of work, and this work may be performed by AWS Lambda functions, Amazon EC2 instances, containers, or on-premises servers; anything that can communicate with the Step Functions API may be assigned a task
### AWS Elastic Beanstalk
> simplest and fastest way of deploying web applications, just upload your code
- provision all the resources such as Amazon EC2, Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS), Auto Scaling, and Elastic Load Balancing for you behind the scenes
### AWS Opsworks
- automate operational tasks like software configuration, server scaling, deployments, and database setup
- provides managed instances of Chef and Puppet
### AWS Cognito
- user identity and data synchronization service that makes it really easy for you to manage user data for your apps across multiple mobile or connected devices
- service also supports
- public login providers such as Google, Facebook, and Amazon, and through enterprise identity providers such as Microsoft Active Directory using SAML
### AWS Elastic MapReduce (EMR)
> managed Hadoop framework that distributes the computation of your data over multiple Amazon EC2 instances
### AWS CloudFormation
> provision infrastructure stacks directly from a collection of scripts, it is not simple
- template is a JSON- or YAML-formatted text file
- template you can specify the resource that CloudFormation is going to build. For example, you can specify a specific type of an EC2 instance as a resource in your CloudFormation template
### AWS CloudWatch
> monitor the health checks, look at the utilization, and view performance
- Apart from the default metrics available, you can also create your own custom metrics using your application and monitor them via Amazon CloudWatch
- one-minute data point, the retention is 15 days
- five-minute data point, the retention is 63 days
- one-hour data point, the retention is 15 months or 455 days
### AWS Config
> fully managed service that provides you with a detailed inventory of your AWS resources and their current configuration in an AWS account. It continuously records configuration changes to these resources
### AWS Trusted Advisor
> provides best practices (or checks) in five categories
- Cost Optimization
- Security
- Fault Tolerance
- Performance
- Service Limits
### AWS Organizations
> Some of these enterprises have added more accounts incrementally as individual teams and divisions make the move to the cloud
- offers policy-based management from multiple AWS accounts. You can create groups of accounts and then apply policies to those groups
### Amazon WorkSpaces
> is a fully managed desktop computing service in the cloud that allows its customers to provide cloud-based desktops to their end-users. Through this the end users can access the documents, applications, and resources using devices of their choice such as laptops, iPad, Kindle Fire, or Android tablets.
## Tips
- AWS commandline able to manage multiple credential by using `--profile [Name]`
## AWS Shared Responsibility Model

## Architecture Guideline
- [Microservices Design Guide](https://medium.com/platform-engineer/microservices-design-guide-eca0b799a7e8)
- [Scaling Up to Your First 10 Million Users](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ma3xWDXTxRg)
## Cost Management
- [EC2](https://www.ec2instances.info/) price comaprision
## Tools
- [AWS 2D Diagram](https://www.draw.io) visualize architecture
- [AWS 3D Diagram](https://cloudcraft.co) visualize architecture
- [CIDR RANGE VISUALIZER](http://cidr.xyz/)
- [Chaos Monkey](https://github.com/Netflix/chaosmonkey) randomly terminates virtual machine instances and containers that run inside of your production environment for testing production server [More](https://medium.com/netflix-techblog/the-netflix-simian-army-16e57fbab116)
- [AWS Infrastructure](https://www.infrastructure.aws/)
## Reference books
- [AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate All-in-One Exam Guide (Exam SAA-C01)](https://www.amazon.com/Certified-Solutions-Architect-Associate-SAA-C01-ebook/dp/B07GL9N75H)
- [AWS Whitepaper](https://aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/?whitepapers-main.sort-by=item.additionalFields.sortDate&whitepapers-main.sort-order=desc)
- [Udemy acloudguru](https://www.udemy.com/course/aws-certified-solutions-architect-associate/)
- [Builder Article](https://aws.amazon.com/builders-library/?cards-body.sort-by=item.additionalFields.customSort&cards-body.sort-order=asc)