https://github.com/ictnlp/awesome-transformer
A collection of transformer's guides, implementations and variants.
https://github.com/ictnlp/awesome-transformer
List: awesome-transformer
Last synced: 4 months ago
JSON representation
A collection of transformer's guides, implementations and variants.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/ictnlp/awesome-transformer
- Owner: ictnlp
- License: mit
- Created: 2018-12-05T14:22:09.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2019-12-22T07:00:07.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-05-22T09:01:39.400Z (about 1 year ago)
- Size: 32.2 KB
- Stars: 102
- Watchers: 7
- Forks: 14
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- ultimate-awesome - awesome-transformer - A collection of transformer's guides, implementations and variants. . (Other Lists / Julia Lists)
README

A collection of transformer's guides, implementations and so on(For those who want to do some research using transformer as a baseline or simply reproduce paper's performance).
Please feel free to pull requests or report issues.
* [Why this project](#why-this-project)
* [Papers](#papers)
* [NMT Basic](#nmt-basic)
* [Transformer original paper](#transformer-original-paper)
* [Implementations & How to reproduce paper's result](#implementations--how-to-reproduce-papers-result)
* [Minimal, paper-equavalent but not certainly performance-reproducable implementations(both PyTorch implementations)](#minimal-paper-equavalent-but-not-certainly-performance-reproducable-implementationsboth-pytorch-implementations)
* [Complex, performance-reproducable implementations](#complex-performance-reproducable-implementations)
* Paper's original implementation: tensor2tensor(using TensorFlow)]
* [Code](#code)
* [Code annotation](#code-annotation)
* [Steps to reproduce WMT14 English-German result:](#steps-to-reproduce-wmt14-english-german-result)
* [Resources](#resources)
* [Harvard NLP Group's implementation: OpenNMT-py(using PyTorch)](#harvard-nlp-groups-implementation-opennmt-pyusing-pytorch)
* [Code](#code-1)
* [Steps to reproduce WMT14 English-German result:](#steps-to-reproduce-wmt14-english-german-result-1)
* [Resources](#resources-1)
* [FAIR's implementation: fairseq-py(using PyTorch)](#fairs-implementation-fairseq-pyusing-pytorch)
* [Code](#code-2)
* [Steps to reproduce WMT14 English-German result:](#steps-to-reproduce-wmt14-english-german-result-2)
* [Resources](#resources-2)
* [Complex, not certainly performance-reproducable implementations](#complex-not-certainly-performance-reproducable-implementations)
* [Training tips](#training-tips)
* [Further](#further)
* [Contributors](#contributors)
## Why this project
Transformer is a powerful model applied in sequence to sequence learning. However, when we were using transformer as our baseline in NMT research we found no good & reliable guide to reproduce approximate result as reported in original paper(even official tensor2tensor implementation), which means our research would be unauthentic. We collected some implementations, obtained corresponding performance-reproducable approaches and other materials, which eventually formed this project.
## Papers
### NMT Basic
- seq2seq model: [Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.3215)
- seq2seq & attention: [Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.0473)
- refined attention: [Effective Approaches to Attention-based Neural Machine Translation](http://arxiv.org/abs/1508.04025)
- seq2seq using CGRU: [DL4MT](https://github.com/nyu-dl/dl4mt-tutorial)
- GNMT: [Google’s Neural Machine Translation System: Bridging the Gap between Human and Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.08144)
- bytenet: [Neural Machine Translation in Linear Time](https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.10099)
- convolutional NMT: [Convolutional Sequence to Sequence Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.03122)
- bpe: [Neural Machine Translation of Rare Words with Subword Units](https://arxiv.org/abs/1508.07909)
- word piece: [Japanese and Korean Voice Search](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6289079/)
- self attention paper: [A Structured Self-attentive Sentence Embedding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.03130)
### Transformer original paper
- [Attention is All You Need](https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762)
## Implementations & How to reproduce paper's result
Indeed there are lots of transformer implementations on the Internet, in order to simplify learning curve, here we only include **the most valuable** projects.
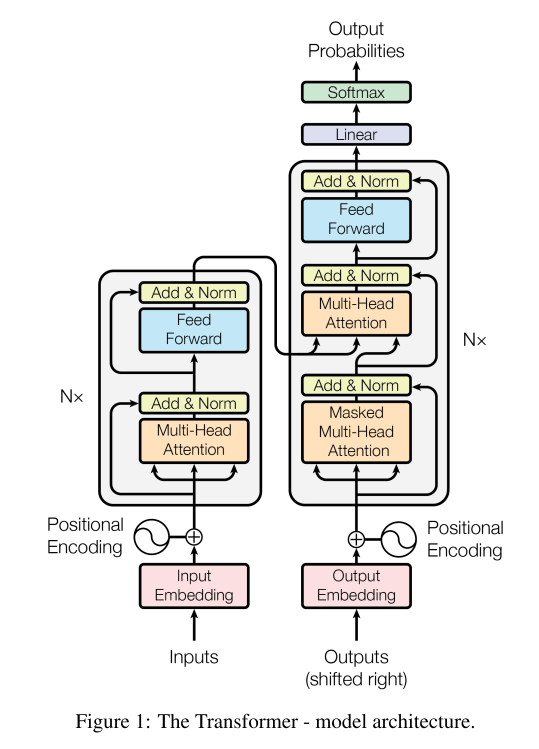
>**[Note]**: In transformer original paper, there are *WMT14 English-German*, *WMT14 English-French* two results
Here we regard a implementation as performance-reproducable **if there exists approaches to reproduce WMT14 English-German BLEU score**. Therefore, we'll also support corresponding approach to reproduce *WMT14 English-German* result.
### Minimal, paper-equavalent but not certainly performance-reproducable implementations(both *PyTorch* implementations)
1. attention-is-all-you-need-pytorch
- [code](https://github.com/jadore801120/attention-is-all-you-need-pytorch)
2. Harvard NLP Group's annotation
- [code](http://nlp.seas.harvard.edu/2018/04/03/attention.html)
### Complex, performance-reproducable implementations
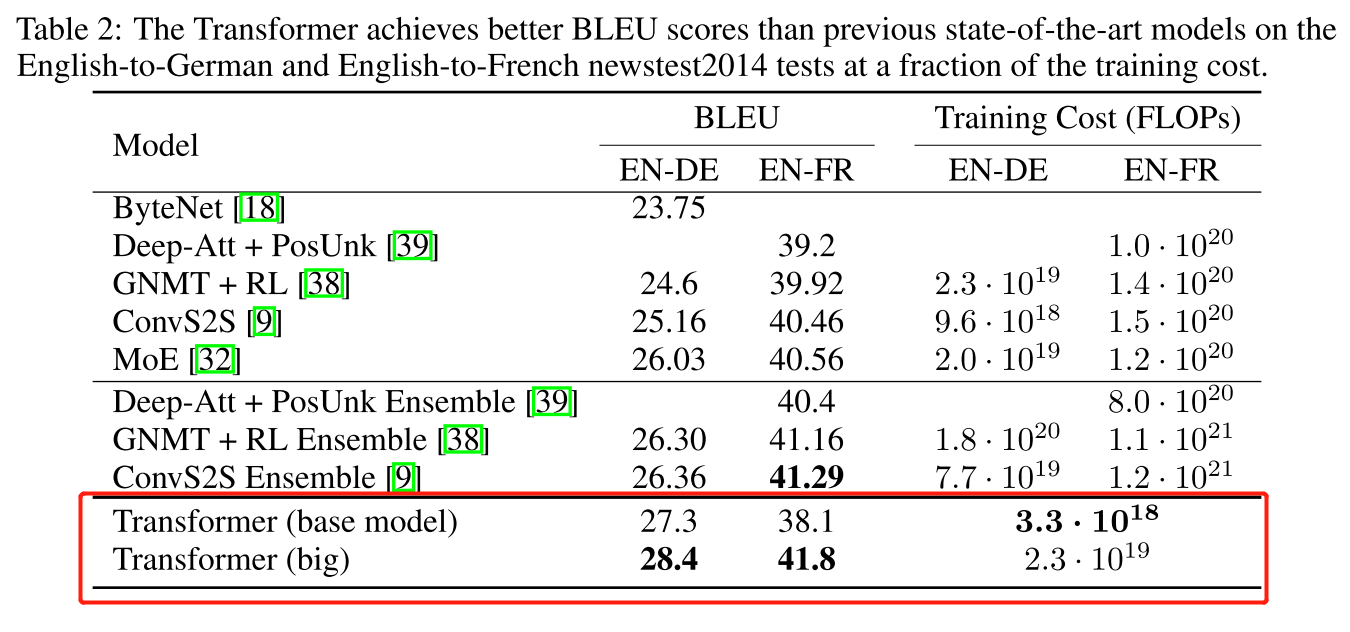
Because transformer's original implementation should run on **8 GPU** to replicate corresponding result, where each GPU loads one batch and after forward propagation 8 batch's loss is summed to execute backward operation, so we can **accumulate every 8 batch's loss** to execute backward operation if we **only have 1 GPU** to imitate this process. **You'd better assemble `gpu_count`, `tokens_on_each_gpu` and `gradient_accumulation_count` to satisfy `gpu_count * tokens_on_each_gpu * gradient_accumulation_count = 4096 * 8`**. See each implementation's guide for details.
Although original paper used `multi-bleu.perl` to evaluate bleu score, we recommend using [sacrebleu](https://github.com/awslabs/sockeye/tree/master/contrib/sacrebleu), which should be equivalent to `mteval-v13a.pl` but more convenient, to calculate bleu score and report the signature as `BLEU+case.mixed+lang.de-en+test.wmt17 = 32.97 66.1/40.2/26.6/18.1 (BP = 0.980 ratio = 0.980 hyp_len = 63134 ref_len = 64399)` for easy reproduction.
```
# calculate lowercase bleu on all tokenized text
cat model_prediction | sacrebleu -tok none -lc ground_truth
# calculate lowercase bleu on all tokenized text if you have 3 ground truth
cat model_prediction | sacrebleu -tok none -lc ground_truth_1 ground_truth_2 ground_truth_3
# calculate lowercase bleu on all untokenized romance-language text using v13a tokenization
cat model_prediction | sacrebleu -tok 13a -lc ground_truth
# calculate lowercase bleu on all untokenized romance-language text using v14 tokenization
cat model_prediction | sacrebleu -tok intl -lc ground_truth
```
The transformer paper's original model settings can be found in [tensor2tensor transformer.py](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensor2tensor/blob/master/tensor2tensor/models/transformer.py). For example, You can find `base model configs` in`transformer_base` function.
As you can see, [OpenNMT-tf](https://github.com/OpenNMT/OpenNMT-tf/tree/master/scripts/wmt) also has a replicable instruction but we prefer tensor2tensor as a baseline to reproduce paper's result if we have to use TensorFlow since it is official.
#### Paper's original implementation: tensor2tensor(using *TensorFlow*)
##### Code
- [tensor2tensor](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensor2tensor)
##### Code annotation
- [“变形金刚”为何强大:从模型到代码全面解析Google Tensor2Tensor系统](https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1153079)(only Chinese version, corresponding to tensor2tensor v1.6.3)
##### Steps to reproduce WMT14 English-German result:
**(updated on v1.10.0)**
```shell
# 1. Install tensor2tensor toolkit
pip install tensor2tensor
# 2. Basic config
# For BPE model use this problem
PROBLEM=translate_ende_wmt_bpe32k
MODEL=transformer
HPARAMS=transformer_base
# or use transformer_large to reproduce large model
# HPARAMS=transformer_large
DATA_DIR=$HOME/t2t_data
TMP_DIR=/tmp/t2t_datagen
TRAIN_DIR=$HOME/t2t_train/$PROBLEM/$MODEL-$HPARAMS
mkdir -p $DATA_DIR $TMP_DIR $TRAIN_DIR
# 3. Download and preprocess corpus
# Note that tensor2tensor has an inner tokenizer
t2t-datagen \
--data_dir=$DATA_DIR \
--tmp_dir=$TMP_DIR \
--problem=$PROBLEM
# 4. Train on 8 GPUs. You'll get nearly expected performance after ~250k steps and certainly expected performance after ~500k steps.
t2t-trainer \
--data_dir=$DATA_DIR \
--problem=$PROBLEM \
--model=$MODEL \
--hparams_set=$HPARAMS \
--output_dir=$TRAIN_DIR \
--train_steps=600000
# 5. Translate
DECODE_FILE=$TMP_DIR/newstest2014.tok.bpe.32000.en
BEAM_SIZE=4
ALPHA=0.6
t2t-decoder \
--data_dir=$DATA_DIR \
--problem=$PROBLEM \
--model=$MODEL \
--hparams_set=$HPARAMS \
--output_dir=$TRAIN_DIR \
--decode_hparams="beam_size=$BEAM_SIZE,alpha=$ALPHA" \
--decode_from_file=$DECODE_FILE \
--decode_to_file=$TMP_DIR/newstest2014.en.tok.32kbpe.transformer_base.beam5.alpha0.6.decode
# 6. Debpe
cat $TMP_DIR/newstest2014.en.tok.32kbpe.transformer_base.beam5.alpha0.6.decode | sed 's/@@ //g' > $TMP_DIR/newstest2014.en.tok.32kbpe.transformer_base.beam5.alpha0.6.decode.debpe
# Do compound splitting on the translation
perl -ple 's{(\S)-(\S)}{$1 ##AT##-##AT## $2}g' < $TMP_DIR/newstest2014.en.tok.32kbpe.transformer_base.beam5.alpha0.6.decode.debpe > $TMP_DIR/newstest2014.en.tok.32kbpe.transformer_base.beam5.alpha0.6.decode.debpe.atat
# Do same compound splitting on the ground truth and then score bleu
# ...
```
**Note that step 6 remains a postprocessing**. For some historical reasons, Google split compound words before getting the final BLEU results which will bring moderate increase. see [get_ende_bleu.sh](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensor2tensor/blob/master/tensor2tensor/utils/get_ende_bleu.sh) for more details.
If you have only 1 GPU, you can use `transformer_base_multistep8` hparams to imitate 8 GPU.
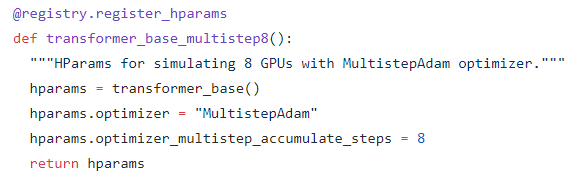
You can also modify `transformer_base_multistep8` function to accumulate gradient times you want. Here is an example using 4 GPU to run transformer big model. Note that `hparams.optimizer_multistep_accumulate_steps = 2` since we only need to accumulate gradient twice for 4 GPU.
```python
@registry.register_hparams
def transformer_base_multistep8():
"""HParams for simulating 8 GPUs with MultistepAdam optimizer."""
hparams = transformer_big()
hparams.optimizer = "MultistepAdam"
hparams.optimizer_multistep_accumulate_steps = 2
return hparams
```
##### Resources
- [t2t issue 539](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensor2tensor/issues/539)
- [t2t issue 444](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensor2tensor/issues/444)
- [t2t issue 317](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensor2tensor/issues/317)
- [Tensor2Tensor for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.07416)
#### Harvard NLP Group's implementation: OpenNMT-py(using *PyTorch*)
##### Code
- [OpenNMT-py](https://github.com/OpenNMT/OpenNMT-py)
##### Steps to reproduce WMT14 English-German result:
**(updated on v0.5.0)**
For command arguments meaning, see [OpenNMT-py doc](http://opennmt.net/OpenNMT-py/main.html) or [OpenNMT-py opts.py](https://github.com/OpenNMT/OpenNMT-py/blob/master/onmt/opts.py)
1. Download [corpus preprocessed by OpenNMT](https://s3.amazonaws.com/opennmt-trainingdata/wmt_ende_sp.tar.gz), [sentencepiece model preprocessed by OpenNMT](https://s3.amazonaws.com/opennmt-trainingdata/wmt_ende_sp_model.tar.gz). Note that the preprocess procedure includes tokenization, bpe/word-piece operation(here using [sentencepiece](https://github.com/google/sentencepiece) powered by Google which implements word-piece algorithm), see [OpenNMT-tf script](https://github.com/OpenNMT/OpenNMT-tf/blob/master/scripts/wmt/prepare_data.sh) for more details.
2. Preprocess. Because English and German are similar languages here we use `-share_vocab` to share vocabulary between source language and target language, which means you don't need to set this flag for distant language pairs such as Chinese-English. Meanwhile, we use a max sequence length of `100` to cover almostly all sentences on the basis of sentence length distribution of corpus.
For example:
```shell
python preprocess.py \
-train_src ../wmt-en-de/train.en.shuf \
-train_tgt ../wmt-en-de/train.de.shuf \
-valid_src ../wmt-en-de/valid.en \
-valid_tgt ../wmt-en-de/valid.de \
-save_data ../wmt-en-de/processed \
-src_seq_length 100 \
-tgt_seq_length 100 \
-max_shard_size 200000000 \
-share_vocab
```
3. Train. For example, if you only have 4 GPU:
```shell
python train.py -data /tmp/de2/data -save_model /tmp/extra \
-layers 6 -rnn_size 512 -word_vec_size 512 -transformer_ff 2048 -heads 8 \
-encoder_type transformer -decoder_type transformer -position_encoding \
-train_steps 200000 -max_generator_batches 2 -dropout 0.1 \
-batch_size 4096 -batch_type tokens -normalization tokens -accum_count 2 \
-optim adam -adam_beta2 0.998 -decay_method noam -warmup_steps 8000 -learning_rate 2 \
-max_grad_norm 0 -param_init 0 -param_init_glorot \
-label_smoothing 0.1 -valid_steps 10000 -save_checkpoint_steps 10000 \
-world_size 4 -gpu_ranks 0 1 2 3
```
Note that here `-accum_count` means every `N` batches accumulating loss to backward, so it's 2 for 4 GPUs and so on.
4. Translate. For example:
You can set `-batch_size`(default `30`) larger to boost the translation.
```shell
python translate.py -gpu 0 -replace_unk -alpha 0.6 -beta 0.0 -beam_size 5 -length_penalty wu -coverage_penalty wu \
-share_vocab vocab_file -max_length 200 -model model_file -src newstest2014.en.32kspe -output model.pred -verbose
```
Note that testset in corpus preprocessed by OpenNMT is newstest2017 while it is newstest2014 in original paper, which may be a mistake. To obtain newstest2014 testset as in paper, here we can use sentencepiece to encode `newstest2014.en` manually. You can find ``in step 1's downloaded archive.
```shell
spm_encode --model= --output_format=piece < newstest2014.en > newstest2014.en.32kspe
```
5. Detokenization. Since training data is processed by [sentencepiece](https://github.com/google/sentencepiece), step 4's translation should be sentencepiece-encoded style, so we need a decoding procedure to obtain a detokenized plain prediction.
For example:
```shell
spm_decode --model= --input_format=piece < input > output
```
6. Postprocess
There is also a [bpe-version](https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=0B_bZck-ksdkpM25jRUN2X2UxMm8) WMT'16 ENDE corpus preprocessed by Google. See [subword-nmt](https://github.com/rsennrich/subword-nmt) for bpe encoding and decoding.
##### Resources
- [OpenNMT-py FAQ](http://opennmt.net/OpenNMT-py/FAQ.html)
- ~~[OpenNMT-py issue](https://github.com/OpenNMT/OpenNMT-py/issues/637)(deprecated)~~
- [OpenNMT: Open-Source Toolkit for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.02810)
#### FAIR's implementation: fairseq-py(using *PyTorch*)
##### Code
- [fairseq-py](https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq/)
##### Steps to reproduce WMT14 English-German result:
**(updated on commit `7e60d45`)**
For arguments meaning, see [doc](https://fairseq.readthedocs.io/en/latest/command_line_tools.html). Note that we can use `--update-freq` when training to accumulate every `N` batches loss to backward, so it's `8` for 1 GPU, `2` for 4 GPUs and so on.
1. Download [the preprocessed WMT'16 EN-DE data provided by Google](https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=0B_bZck-ksdkpM25jRUN2X2UxMm8) and extract it.
```
TEXT=wmt16_en_de_bpe32k
mkdir $TEXT
tar -xzvf wmt16_en_de.tar.gz -C $TEXT
```
2. Preprocess the dataset with a joined dictionary
```
python preprocess.py --source-lang en --target-lang de \
--trainpref $TEXT/train.tok.clean.bpe.32000 \
--validpref $TEXT/newstest2013.tok.bpe.32000 \
--testpref $TEXT/newstest2014.tok.bpe.32000 \
--destdir data-bin/wmt16_en_de_bpe32k \
--joined-dictionary
```
3. Train. For a base model.
```
# train about 180k steps
python train.py data-bin/wmt16_en_de_bpe32k \
--arch transformer_wmt_en_de --share-all-embeddings \
--optimizer adam --adam-betas '(0.9, 0.98)' --clip-norm 0.0 \
--lr-scheduler inverse_sqrt --warmup-init-lr 1e-07 --warmup-updates 4000 \
--lr 0.0007 --min-lr 1e-09 \
--weight-decay 0.0 --criterion label_smoothed_cross_entropy \
--label-smoothing 0.1 --max-tokens 4096 --update-freq 2 \
--no-progress-bar --log-format json --log-interval 10 --save-interval-updates 1000 \
--keep-interval-updates 5
# average last 5 checkpoints
modelfile=checkpoints
python scripts/average_checkpoints.py --inputs $modelfile --num-update-checkpoints 5 \
--output $modelfile/average-model.pt
```
For a big model.
```
# train about 270k steps
python train.py data-bin/wmt16_en_de_bpe32k \
--arch transformer_vaswani_wmt_en_de_big --share-all-embeddings \
--optimizer adam --adam-betas '(0.9, 0.98)' --clip-norm 0.0 \
--lr-scheduler inverse_sqrt --warmup-init-lr 1e-07 --warmup-updates 4000 \
--lr 0.0005 --min-lr 1e-09 \
--weight-decay 0.0 --criterion label_smoothed_cross_entropy \
--label-smoothing 0.1 --max-tokens 4096 --update-freq 2\
--no-progress-bar --log-format json --log-interval 10 --save-interval-updates 1000 \
--keep-interval-updates 20
# average last 20 checkpoints
modelfile=checkpoints
python scripts/average_checkpoints.py --inputs $modelfile --num-update-checkpoints 20 \
--output $modelfile/average-model.pt
```
4. Inference
```
model=average-model.pt
subset=test
python generate.py data-bin/wmt16_en_de_bpe32k --path $modelfile/$model \
--gen-subset $subset --beam 4 --batch-size 128 --remove-bpe --lenpen 0.6 > pred.de
# because fairseq's output is unordered, we need to recover its order
grep ^H pred.de | cut -f1,3- | cut -c3- | sort -k1n | cut -f2- > pred.de
```
5. Postprocess
##### Resources
- [fairseq-py example](https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq/tree/master/examples/translation)
- [fairseq-py issue](https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq/issues/202). The corpus problem described in the issue has been fixed now, so we can directly follow the instruction above.
### Complex, not certainly performance-reproducable implementations
- [Marian](https://github.com/marian-nmt/marian-examples/tree/master/transformer)(purely c++ implementation without any deep learning framework)
## Training tips
- [Training Tips for the Transformer Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.00247)
## Further
- RNMT+: [The Best of Both Worlds: Combining Recent Advances in Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.09849)
- [Scaling Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.00187)
- Turing-complete Transformer: [Universal Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.03819)
- [Self-Attention with Relative Position Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.02155)
- [Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/openai-assets/research-covers/language-unsupervised/language_understanding_paper.pdf)
- [BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805)
## Contributors
This project is developed and maintained by Natural Language Processing Group, ICT/CAS.
- [Yong Shan](https://github.com/SkyAndCloud)
- [Jinchao Zhang](https://github.com/zhangjcqq)
- Shuhao Gu