https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide
Digital Signal Processing(DSP) Guide
https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide
List: DSP-Guide
awesome awesome-list awesome-readme digital-image-processing digital-signal-analyzer digital-signal-filtering digital-signal-processing digital-signal-processing-filters digital-signals dsp dsp-gateway dsp-library dsp-proxy dsp-receivers signal-processing
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
Digital Signal Processing(DSP) Guide
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide
- Owner: mikeroyal
- Created: 2021-08-22T19:54:53.000Z (almost 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2022-03-06T21:36:32.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-05-23T09:20:57.411Z (about 1 year ago)
- Topics: awesome, awesome-list, awesome-readme, digital-image-processing, digital-signal-analyzer, digital-signal-filtering, digital-signal-processing, digital-signal-processing-filters, digital-signals, dsp, dsp-gateway, dsp-library, dsp-proxy, dsp-receivers, signal-processing
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 289 KB
- Stars: 57
- Watchers: 6
- Forks: 10
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- ultimate-awesome - DSP-Guide - Digital Signal Processing(DSP) Guide. (Other Lists / Julia Lists)
README

Digital Signal Processing(DSP) Guide
#### A guide covering Digital Signal Processing(DSP) including the applications, libraries and tools that will make you a better and more efficient Digital Signal Processing(DSP) development.
**Note: You can easily convert this markdown file to a PDF in [VSCode](https://code.visualstudio.com/) using this handy extension [Markdown PDF](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=yzane.markdown-pdf).**

# Table of Contents
1. [Digital Signal Processing(DSP) Learning Resources](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#digital-signal-processingdsp-learning-resources)
2. [Digital Signal Processing(DSP) Tools and Frameworks](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#digital-signal-processingdsp-tools-libraries-and-frameworks)
3. [Computer Vision Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#computer-vision-development)
4. [Photogrammetry Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#photogrammetry-development)
5. [LiDAR Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#lidar-development)
6. [Algorithms](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#algorithms)
7. [Differential Equations](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#differential-equations)
8. [Electric charge, field, and potential](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#electric-charge-field-and-potential)
- Charge and electric force (Coulomb's law): Electric charge, field, and potential
- Electric field: Electric charge, field, and potential
- Electric potential energy, electric potential, and voltage: Electric charge, field, and potential
9. [Circuits](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#circuits)
- Ohm's law and circuits with resistors: Circuits
- Circuits with capacitors: Circuits
10. [Magnetic forces, magnetic fields, and Faraday's law](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#electromagnetic-waves-and-interference)
- Magnets and Magnetic Force: Magnetic forces, magnetic fields, and Faraday's law
- Magnetic field created by a current: Magnetic forces, magnetic fields, and Faraday's law
- Electric motors: Magnetic forces, magnetic fields, and Faraday's law
- Magnetic flux and Faraday's law
11. [Electromagnetic waves and interference](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#electromagnetic-waves-and-interference)
- Introduction to electromagnetic waves: Electromagnetic waves and interference
- Interference of electromagnetic waves
12. [Machine Learning](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#machine-learning)
13. [CUDA Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#cuda-development)
14. [OpenCL Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#opencl-development)
15. [MATLAB Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#matlab-development)
16. [C/C++ Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#cc-development)
# Digital Signal Processing(DSP) Learning Resources
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Digital Signal Processing (DSP)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_signal_processing) is the application of a digital computer to modify an analog or digital signal. It's wadely used in many applications including video/audio/data communications and networking, medical imaging and computer vision, speech synthesis and coding, digital audio and video, and control of complex systems and industrial processes.
[Learn Digital Signal Processing (DSP) | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/learn-digital-signal-processing/)
[Digital Signal Processing (DSP) From Ground Up™ in C | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/digital-signal-processing-dsp-from-ground-uptm-in-c/)
[Digital Signal Processing Courses | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/specializations/digital-signal-processing)
[DSP - Digital Signal Processing - Intel® FPGA](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/architecture-and-technology/programmable/digital-signal-processing/overview.html)
[Digital Signal Processing | Stanford Online](https://online.stanford.edu/courses/ee264-digital-signal-processing)
[Digital Signal Processing | UC San Diego Extension](https://extension.ucsd.edu/courses-and-programs/digital-signal-processing)
[Digital Signal Processing I Courses Online | Purdue](https://engineering.purdue.edu/online/courses/digital-signal-processing-i)
[Digital Signal Processing | MIT OpenCourseWare](https://ocw.mit.edu/resources/res-6-008-digital-signal-processing-spring-2011/)
[Creative Digital Signal Processing (DSP) for Music and Visuals](https://online.berklee.edu/courses/creative-digital-signal-processing-dsp-for-music-and-visuals)
[Digital Signal Processing Course | Prosoundtraining](https://www.prosoundtraining.com/digital-signal-processing/)
# Digital Signal Processing(DSP) Tools, Libraries and Frameworks
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)
[DSP System Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/dsp-system.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, apps, and scopes for designing, simulating, and analyzing signal processing systems in MATLAB® and Simulink®. You can model real-time DSP systems for communications, radar, audio, medical devices, IoT, and other applications. The DSP System Toolbox you can design and analyze FIR, IIR, multirate, multistage, and adaptive filters. You can stream signals from variables, data files, and network devices for system development and verification.
[Signal Processing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/signal.html) is a tool that provides functions and apps to analyze, preprocess, and extract features from uniformly and nonuniformly sampled signals. The toolbox includes tools for filter design and analysis, resampling, smoothing, detrending, and power spectrum estimation. The toolbox also provides functionality for extracting features like changepoints and envelopes, finding peaks and signal patterns, quantifying signal similarities, and performing measurements such as SNR and distortion.
[Phased Array System Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/phased-array.html) is a tool that provides algorithms and apps for designing and simulating sensor array and beamforming systems in wireless communication, radar, sonar, acoustic, and medical imaging applications. You can model and analyze the behavior of active and passive arrays, including subarrays and arbitrary geometries.
[Radar Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/radar.html) is a tool that includes algorithms and tools for designing, simulating, analyzing, and testing multifunction radar systems. Reference examples provide a starting point for implementing airborne, ground-based, shipborne, and automotive radar systems.
[Audio Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/audio.html) is a tool that provides tools for audio processing, speech analysis, and acoustic measurement. It includes algorithms for processing audio signals such as equalization and time stretching, estimating acoustic signal metrics such as loudness and sharpness, and extracting audio features such as MFCC and pitch. It also provides advanced machine learning models, including i-vectors, and pretrained deep learning networks, including VGGish and CREPE.
[Wavelet Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/wavelet.html) is a tool that provides functions and apps for analyzing and synthesizing signals and images. The toolbox includes algorithms for continuous wavelet analysis, wavelet coherence, synchrosqueezing, and data-adaptive time-frequency analysis.
[Antenna Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/antenna.html) is a tool that provides functions and apps for the design, analysis, and visualization of antenna elements and arrays. It can design standalone antennas and build arrays of antennas using predefined elements with parameterized geometry, arbitrary planar structures, or custom 3D structures described with STL files.
[RF Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/rftoolbox.html) is a tool that provides functions, objects, and apps for designing, modeling, analyzing, and visualizing networks of radio frequency (RF) components. It supports wireless communications, radar, and signal integrity applications.
[RF Blockset™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/rf-blockset.html) is a tool that provides a Simulink® model library and simulation engine for designing RF communications and radar systems. The RF Blockset lets you simulate RF transceivers and front-ends. You can model nonlinear RF amplifiers to estimate gain, noise, even-order, and odd-order intermodulation distortion, including memory effects. For RF mixers, you can predict image rejection, reciprocal mixing, local oscillator phase noise, and DC offset.
[Mixed-Signal Blockset™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/mixed-signal.html) is a tool that provides models of components and impairments, analysis tools, and test benches for designing and verifying mixed-signal integrated circuits (ICs).
[SerDes Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/serdes.html) is a tool that provides a MATLAB® and Simulink® model library and a set of analysis tools and apps for the design and verification of serializer/deserializer (SerDes) systems or high-speed memory PHYs such as DDR5.
[Communications Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/communications.html) is a tool that provides algorithms and apps for the analysis, design, end-to-end simulation, and verification of communications systems. Toolbox algorithms including channel coding, modulation, MIMO, and OFDM enable you to compose and simulate a physical layer model of your standard-based or custom-designed wireless communications system.
[WLAN Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/wlan.html) is a tool that provides standards-compliant functions for the design, simulation, analysis, and testing of wireless LAN communications systems. It includes configurable physical layer waveforms for the IEEE® 802.11 family of standards. It also provides transmitter, channel modeling, and receiver operations, including channel coding, modulation, spatial stream mapping, and MIMO receivers.
[LTE Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/lte.html) is a tool that provides standard-compliant functions and apps for the design, simulation, and verification of LTE, LTE-Advanced, and LTE-Advanced Pro communications systems. The system toolbox accelerates LTE algorithm and physical layer (PHY) development, supports golden reference verification and conformance testing, and enables test waveform generation.
[5G Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/5g.html) is a tool that provides standard-compliant functions and reference examples for the modeling, simulation, and verification of 5G New Radio (NR) communications systems. The toolbox supports link-level simulation, golden reference verification, conformance testing, and test waveform generation.
[Satellite Communications Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/satellite-communications.html) is a tool that provides standards-based tools for designing, simulating, and verifying satellite communications systems and links. The toolbox enables you to model and visualize satellite orbits and perform link analysis and access calculations.
[Data Acquisition Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/data-acquisition.html) is a tool that provides apps and functions for configuring data acquisition hardware, reading data into MATLAB® and Simulink®, and writing data to DAQ analog and digital output channels. The toolbox supports a variety of DAQ hardware, including USB, PCI, PCI Express®, PXI®, and PXI Express® devices, from National Instruments® and other vendors.
[Instrument Control Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/instrument.html) is a tool that lets you connect MATLAB® directly to instruments such as oscilloscopes, function generators, signal analyzers, power supplies, and analytical instruments. The toolbox connects to your instruments via instrument drivers such as IVI and VXIplug&play or via text-based SCPI commands over commonly used communication protocols such as GPIB, VISA, TCP/IP, and UDP.
[Embedded Coder®](https://www.mathworks.com/products/embedded-coder.html) is a tool that generates readable, compact, and fast C and C++ code for embedded processors used in mass production. It extends MATLAB Coder™ and Simulink Coder™ with advanced optimizations for precise control of the generated functions, files, and data. These optimizations improve code efficiency and facilitate integration with legacy code, data types, and calibration parameters.
### DSP Tools & Protocols for Audio/Video
[H.264(AVC)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/H.264/MPEG-4_AVC) is a video compression standard based on block-oriented and motion-compensated integer-DCT coding that defines multiple profiles (tools) and levels (max bitrates and resolutions) with support up to 8K.
[H.265(HEVC)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_Efficiency_Video_Coding) is a video compression standard that is the successor to H.264(AVC). It offers a 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or improved video quality at the same bit-rate.
[FFmpeg](https://ffmpeg.org) is a leading multimedia framework that can decode, encode, transcode, mux, demux, stream, filter and play pretty much anything that humans and machines have created. It supports the most obscure ancient formats up to the cutting edge ones on multiple platforms such as Windows, macOS, and Linux.
[HandBrake](https://handbrake.fr/) is a tool for transcoding video from almost any format with a selection of widely supported codecs. It is supported on Window, macOS, and Linux.
[HTTP Live Streaming (HLS)](https://developer.apple.com/streaming/) is a communications protocol developed by Apple that sends live and on‐demand audio and video to iPhone, iPad, Mac, Apple Watch, Apple TV, and PC.
[Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH)](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/DASH_Adaptive_Streaming_for_HTML_5_Video) is an adaptive streaming protocol that allows for a video stream to switch between bit rates on the basis of network performance, in order to keep a video playing.
[OpenMAX™](https://www.khronos.org/openmax/) is a cross-platform API that provides comprehensive streaming media codec and application portability by enabling accelerated multimedia components to be developed, integrated and programmed across multiple operating systems and silicon platforms.
[GStreamer](https://gstreamer.freedesktop.org/) is a library for constructing graphs of media-handling components. The applications it supports range from simple Ogg/Vorbis playback, audio/video streaming to complex audio (mixing) and video (non-linear editing) processing. Applications can take advantage of advances in codec and filter technology transparently.
[Media Source Extensions (MSE)](https://www.w3.org/TR/media-source/) is a [W3C specification](https://github.com/w3c/media-source) that allows JavaScript to send byte streams to media codecs within Web browsers that support HTML5 video and audio. Also, this allows the implementation of client-side prefetching and buffering code for streaming media entirely in JavaScript.
[WebRTC](https://webrtc.org/) is an open-source project that adds real-time communication capabilities to your application that works on top of an open standard. It supports video, voice, and generic data to be sent between peers, allowing developers to build powerful voice- and video-communication solutions.
[Apple ProRes](https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT200321) is a codec technology developed by Apple for high-quality & high-performance editing in Final Cut Pro that supports up to 8K.
[Logic Pro](https://www.apple.com/logic-pro/) is a digital audio workstation (DAW) and MIDI sequencer software application for macOS.
[JACK Audio Connection Kit AKA JACK](https://jackaudio.org/) is a professional sound server daemon that provides real-time, low-latency connections for both audio and MIDI data between applications that implement its API. JACK can be configured to send audio data over a network to a main machine, which then outputs the audio to a physical device. This can be useful to mix audio from a number of connected computers without requiring additional cables or hardware mixers, and keeping the audio path digital for as long as possible.
### Sensors
[CCD(charge coupled device)](https://global.canon/en/technology/s_labo/light/003/04.html) is a semiconductor image sensor used in digital cameras to convert light into electrical signals. CCD Sensors are made up of tiny elements known as pixels with expressions such as 6 MP(megapixel) or 12 MP(megapixel) refering to the number of pixels comprising the CCD Sensors of a camera. With each pixel there is a tiny photodiode that is sensitive to light(photon) and becomes electrically charged in accordance with the strength of light it captures.
[CMOS(Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) sensors](https://global.canon/en/technology/s_labo/light/003/05.html) are semiconductor image sensors that convert light into electrical signals. It includes features such as timing logic, exposure control, analog-to-digital conversion, shuttering, white balance, gain adjustment, and initial image processing algorithms. CMOS sensors contain rows of photodiodes coupled with individual amplifiers to amplify the electric signal from the photodiodes. This not only enables CMOS sensors to operate on less electrical power than CCDs, but also enables speedier and easier reading of electrical charges at a relatively low-cost.

**Sensors from Alps Alpine. Source: [Alps Alpine](https://tech.alpsalpine.com/e/category_sensor.html)**

**Different Types of Sensors. Source: [electronicshub](https://www.electronicshub.org/different-types-sensors/)**
# Computer Vision Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)
## Computer Vision Learning Resources
[Computer Vision](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/overview/what-is-computer-vision/) is a field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that focuses on enabling computers to identify and understand objects and people in images and videos.
[OpenCV Courses](https://opencv.org/courses/)
[Exploring Computer Vision in Microsoft Azure](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/explore-computer-vision-microsoft-azure/)
[Top Computer Vision Courses Online | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?languages=en&query=computer%20vision)
[Top Computer Vision Courses Online | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/computer-vision/)
[Learn Computer Vision with Online Courses and Lessons | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/computer-vision)
[Computer Vision and Image Processing Fundamentals | edX](https://www.edx.org/course/computer-vision-and-image-processing-fundamentals)
[Introduction to Computer Vision Courses | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/introduction-to-computer-vision--ud810)
[Computer Vision Nanodegree program | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/computer-vision-nanodegree--nd891)
[Machine Vision Course |MIT Open Courseware ](https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-801-machine-vision-fall-2004/)
[Computer Vision Training Courses | NobleProg](https://www.nobleprog.com/computer-vision-training)
[Visual Computing Graduate Program | Stanford Online](https://online.stanford.edu/programs/visual-computing-graduate-program)
## Computer Vision Tools, Libraries, and Frameworks
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Computer-Vision-Guide#table-of-contents)
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cognitive-toolkit/) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[Automated Driving Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/automated-driving.html) is a MATLAB tool that provides algorithms and tools for designing, simulating, and testing ADAS and autonomous driving systems. You can design and test vision and lidar perception systems, as well as sensor fusion, path planning, and vehicle controllers. Visualization tools include a bird’s-eye-view plot and scope for sensor coverage, detections and tracks, and displays for video, lidar, and maps. The toolbox lets you import and work with HERE HD Live Map data and OpenDRIVE® road networks. It also provides reference application examples for common ADAS and automated driving features, including FCW, AEB, ACC, LKA, and parking valet. The toolbox supports C/C++ code generation for rapid prototyping and HIL testing, with support for sensor fusion, tracking, path planning, and vehicle controller algorithms.
[LRSLibrary](https://github.com/andrewssobral/lrslibrary) is a Low-Rank and Sparse Tools for Background Modeling and Subtraction in Videos. The library was designed for moving object detection in videos, but it can be also used for other computer vision and machine learning problems.
[Image Processing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/image.html) is a tool that provides a comprehensive set of reference-standard algorithms and workflow apps for image processing, analysis, visualization, and algorithm development. You can perform image segmentation, image enhancement, noise reduction, geometric transformations, image registration, and 3D image processing.
[Computer Vision Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/computer-vision.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing and testing computer vision, 3D vision, and video processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, as well as feature detection, extraction, and matching. You can automate calibration workflows for single, stereo, and fisheye cameras. For 3D vision, the toolbox supports visual and point cloud SLAM, stereo vision, structure from motion, and point cloud processing.
[Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/statistics.html) is a tool that provides functions and apps to describe, analyze, and model data. You can use descriptive statistics, visualizations, and clustering for exploratory data analysis; fit probability distributions to data; generate random numbers for Monte Carlo simulations, and perform hypothesis tests. Regression and classification algorithms let you draw inferences from data and build predictive models either interactively, using the Classification and Regression Learner apps, or programmatically, using AutoML.
[Lidar Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/lidar.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing, analyzing, and testing lidar processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, semantic segmentation, shape fitting, lidar registration, and obstacle detection. Lidar Toolbox supports lidar-camera cross calibration for workflows that combine computer vision and lidar processing.
[Mapping Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/mapping.html) is a tool that provides algorithms and functions for transforming geographic data and creating map displays. You can visualize your data in a geographic context, build map displays from more than 60 map projections, and transform data from a variety of sources into a consistent geographic coordinate system.
[UAV Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/uav.html) is an application that provides tools and reference applications for designing, simulating, testing, and deploying unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and drone applications. You can design autonomous flight algorithms, UAV missions, and flight controllers. The Flight Log Analyzer app lets you interactively analyze 3D flight paths, telemetry information, and sensor readings from common flight log formats.
[Parallel Computing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab-parallel-server.html) is a tool that lets you solve computationally and data-intensive problems using multicore processors, GPUs, and computer clusters. High-level constructs such as parallel for-loops, special array types, and parallelized numerical algorithms enable you to parallelize MATLAB® applications without CUDA or MPI programming. The toolbox lets you use parallel-enabled functions in MATLAB and other toolboxes. You can use the toolbox with Simulink® to run multiple simulations of a model in parallel. Programs and models can run in both interactive and batch modes.
[Partial Differential Equation Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/pde.html) is a tool that provides functions for solving structural mechanics, heat transfer, and general partial differential equations (PDEs) using finite element analysis.
[ROS Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/ros.html) is a tool that provides an interface connecting MATLAB® and Simulink® with the Robot Operating System (ROS and ROS 2), enabling you to create a network of ROS nodes. The toolbox includes MATLAB functions and Simulink blocks to import, analyze, and play back ROS data recorded in rosbag files. You can also connect to a live ROS network to access ROS messages.
[Robotics Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/robotics.html) provides a toolbox that brings robotics specific functionality(designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots) to MATLAB, exploiting the native capabilities of MATLAB (linear algebra, portability, graphics). The toolbox also supports mobile robots with functions for robot motion models (bicycle), path planning algorithms (bug, distance transform, D*, PRM), kinodynamic planning (lattice, RRT), localization (EKF, particle filter), map building (EKF) and simultaneous localization and mapping (EKF), and a Simulink model a of non-holonomic vehicle. The Toolbox also including a detailed Simulink model for a quadrotor flying robot.
[Deep Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning.html) is a tool that provides a framework for designing and implementing deep neural networks with algorithms, pretrained models, and apps. You can use convolutional neural networks (ConvNets, CNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks to perform classification and regression on image, time-series, and text data. You can build network architectures such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and Siamese networks using automatic differentiation, custom training loops, and shared weights. With the Deep Network Designer app, you can design, analyze, and train networks graphically. It can exchange models with TensorFlow™ and PyTorch through the ONNX format and import models from TensorFlow-Keras and Caffe. The toolbox supports transfer learning with DarkNet-53, ResNet-50, NASNet, SqueezeNet and many other pretrained models.
[Reinforcement Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/reinforcement-learning.html) is a tool that provides an app, functions, and a Simulink® block for training policies using reinforcement learning algorithms, including DQN, PPO, SAC, and DDPG. You can use these policies to implement controllers and decision-making algorithms for complex applications such as resource allocation, robotics, and autonomous systems.
[Deep Learning HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning-hdl.html) is a tool that provides functions and tools to prototype and implement deep learning networks on FPGAs and SoCs. It provides pre-built bitstreams for running a variety of deep learning networks on supported Xilinx® and Intel® FPGA and SoC devices. Profiling and estimation tools let you customize a deep learning network by exploring design, performance, and resource utilization tradeoffs.
[Model Predictive Control Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/model-predictive-control.html) is a tool that provides functions, an app, and Simulink® blocks for designing and simulating controllers using linear and nonlinear model predictive control (MPC). The toolbox lets you specify plant and disturbance models, horizons, constraints, and weights. By running closed-loop simulations, you can evaluate controller performance.
[Vision HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/vision-hdl.html) is a tool that provides pixel-streaming algorithms for the design and implementation of vision systems on FPGAs and ASICs. It provides a design framework that supports a diverse set of interface types, frame sizes, and frame rates. The image processing, video, and computer vision algorithms in the toolbox use an architecture appropriate for HDL implementations.
[Microsoft AirSim](https://microsoft.github.io/AirSim/lidar.html) is a simulator for drones, cars and more, built on Unreal Engine (with an experimental Unity release). AirSim is open-source, cross platform, and supports [software-in-the-loop simulation](https://www.mathworks.com/help///ecoder/software-in-the-loop-sil-simulation.html) with popular flight controllers such as PX4 & ArduPilot and [hardware-in-loop](https://www.ni.com/en-us/innovations/white-papers/17/what-is-hardware-in-the-loop-.html) with PX4 for physically and visually realistic simulations. It is developed as an Unreal plugin that can simply be dropped into any Unreal environment. AirSim is being developed as a platform for AI research to experiment with deep learning, computer vision and reinforcement learning algorithms for autonomous vehicles.
# Photogrammetry Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Photogrammetry Learning Resources
[Photogrammetry](https://www.autodesk.com/solutions/photogrammetry-software) is the art and science of extracting 3D information from photographs. The process involves taking overlapping photographs of an object, structure, or space, and converting them into 2D or 3D digital models. Photogrammetry is often used by surveyors, architects, engineers, and contractors to create topographic maps, meshes, point clouds, or drawings based on the real-world.
[Aerial photogrammetry](https://www.autodesk.com/solutions/photogrammetry-software) is process of utilizing aircrafts to produce aerial photography that can be turned into a 3D model or mapped digitally. Now, it is possible to do the same work with a drone.
[Terrestrial(Close-range) photogrammetry](https://www.autodesk.com/solutions/photogrammetry-software) is when images are captured using a handheld camera or with a camera mounted to a tripod. The output of this method is not to create topographic maps, but rather to make 3D models of a smaller object.
[Top Photogrammetry Courses Online | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/photogrammetry/)
[Photogrammetry With Drones: In Mapping Technology | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/essentials-of-photogrammetry/)
[Introduction to Photogrammetry Course | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/lecture/aerial-photography-with-uav/introduction-to-photogrammetry-KyP30)
[Photogrammetry Online Classes and Training | Linkedin Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/search?keywords=Photogrammetry&upsellOrderOrigin=default_guest_learning&trk=learning-course_learning-search-bar_search-submit)
[Pix4D training and certification for mapping professionals](https://training.pix4d.com/)
[Drone mapping and photogrammetry workshops with Pix4D](https://training.pix4d.com/pages/workshops)
[Digital Photogrammetric Systems Course | Purdue Online Learning](https://engineering.purdue.edu/online/courses/digital-photogrammetric-systems)
[Photogrammetry Training | Deep3D Photogrammetry](https://deep3d.co.uk/photogrammetry-training/)
[ASPRS Certification Program](https://www.asprs.org/certification)
## Photogrammetry Tools, Libraries, and Frameworks
[Autodesk® ReCap™](https://www.autodesk.com/products/recap/free-trial) is a software tool that converts reality captured from laser scans or photos into a 3D model or 2D drawing that's ready to be used in your design built for UAV and drone processes.
[Autodesk® ReCap™ Photo](http://blogs.autodesk.com/recap/introducing-recap-photo/) is a cloud-connected solution tailored for drone/UAV photo capturing workflows. Using ReCap Photo, you can create textured meshes, point clouds with geolocation, and high-resolution orthographic views with elevation maps.
[Pix4D](https://www.pix4d.com/) is a unique suite of photogrammetry software for drone mapping. Capture images with our app, process on desktop or cloud and create maps and 3D models.
[PIX4Dmapper](https://www.pix4d.com/product/pix4dmapper-photogrammetry-software) is the leading photogrammetry software for professional drone mapping.
[RealityCapture](https://www.capturingreality.com/) is a state-of-the-art photogrammetry software solution that creates virtual reality scenes, textured 3D meshes, orthographic projections, geo-referenced maps and much more from images and/or laser scans completely automatically.
[Adobe Scantastic](https://labs.adobe.com/projects/scantastic/) is a tool that makes the creation of 3D assets accessible to everyone. It can be used with just a mobile device (combined with Adobe's server-based photogrammetry pipeline), users can easily scan objects in their physical environment and turn them into 3D models which can then be imported into tools like [Adobe Dimension](https://www.adobe.com/products/dimension.html) and [Adobe Aero](https://www.adobe.com/products/aero.html).
[Adobe Aero](https://www.adobe.com/products/aero.html) is a tool that helps you build, view, and share immersive AR experiences. Simply build a scene by bringing in 2D images from Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator, or 3D models from Adobe Dimension, Substance, third-party apps like Cinema 4D, or asset libraries like Adobe Stock and TurboSquid. Aero optimizes a wide array of assets, including OBJ, GLB, and glTF files, for AR, so you can visualize them in real time.
[Agisoft Metashape](https://www.agisoft.com/) is a stand-alone software product that performs photogrammetric processing of digital images and generates 3D spatial data to be used in GIS applications, cultural heritage documentation, and visual effects production as well as for indirect measurements of objects of various scales.
[MicroStation](https://www.bentley.com/en/products/brands/microstation) is a CAD software platform for 2D and 3D dimensional design and drafting, developed and sold by Bentley Systems. It generates 2D/3D vector graphics objects and elements and includes building information modeling (BIM) features.
[Leica Photogrammetry Suite (LPS)](https://support.hexagonsafetyinfrastructure.com/infocenter/index?page=product&facRef=LPS&facDisp=Leica%20Photogrammetry%20Suite%20(LPS)&landing=1) is a powerful photogrammetry system that delivers full analytical triangulation, the generation of digital terrain models, orthophoto production, mosaicking, and 3D feature extraction in a user-friendly environment that guarantees results even for photogrammetry novices.
[Terramodel](https://heavyindustry.trimble.com/products/terramodel) is a powerful software package for the surveyor, civil engineer or contractor who requires a CAD and design package with integrated support for raw survey data.
[MicMac](https://github.com/micmacIGN/micmac) is a free and open-source photogrammetry software tools for 3D reconstruction.
[3DF Zephyr] (https://www.3dflow.net/3df-zephyr-photogrammetry-software/) is a photogrammetry software solution by 3Dflow. It allows you automatically reconstruct 3D models from photos and deal with any 3D reconstruction and scanning challenge. No matter what camera sensor, drone or laser scanner device you are going to use.
[COLMAP](https://colmap.github.io/) is a general-purpose Structure-from-Motion (SfM) and Multi-View Stereo (MVS) pipeline with a graphical and command-line interface. It offers a wide range of features for reconstruction of ordered and unordered image collections.
[Multi-View Environment (MVE)](https://www.gcc.tu-darmstadt.de/home/proj/mve/) is an effort to ease the work with multi-view datasets and to support the development of algorithms based on multiple views. It features Structure from Motion, Multi-View Stereo and Surface Reconstruction. MVE is developed at the TU Darmstadt.
[AliceVision](https://github.com/alicevision/AliceVision) is a Photogrammetric Computer Vision Framework which provides 3D Reconstruction and Camera Tracking algorithms. AliceVision comes up with strong software basis and state-of-the-art computer vision algorithms that can be tested, analyzed and reused.
[Meshroom](https://github.com/alicevision/meshroom) is a free, open-source 3D Reconstruction Software based on the AliceVision framework.
[PhotoModeler](https://www.photomodeler.com/) is a software extracts Measurements and Models from photographs taken with an ordinary camera. A cost-effective way for accurate 2D or 3D measurement, photo-digitizing, surveying, 3D scanning, and reality capture.
[ODM](https://www.opendronemap.org/odm/) is an open source command line toolkit to generate maps, point clouds, 3D models and DEMs from drone, balloon or kite images.
[WebODM](https://www.opendronemap.org/webodm/) is a user-friendly, commercial grade software for drone image processing. Generate georeferenced maps, point clouds, elevation models and textured 3D models from aerial images. It supports multiple engines for processing, currently [ODM](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/ODM) and [MicMac](https://github.com/dronemapper-io/NodeMICMAC/).
[NodeODM](https://www.opendronemap.org/nodeodm/) is a [standard API specification](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/NodeODM/blob/master/docs/index.adoc) for processing aerial images with engines such as [ODM](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/ODM). The API is used by clients such as [WebODM](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/WebODM), [CloudODM](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/CloudODM) and [PyODM](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/PyODM).
[ClusterODM]https://www.opendronemap.org/clusterodm/) is a reverse proxy, load balancer and task tracker with optional cloud autoscaling capabilities for NodeODM API compatible nodes. In a nutshell, it's a program to link together multiple NodeODM API compatible nodes under a single network address.
[FIELDimageR](https://www.opendronemap.org/fieldimager/) is an R package to analyze orthomosaic images from agricultural field trials.
[Regard3D](https://www.regard3d.org/) is a free and open source structure-from-motion program. It converts photos of an object, taken from different angles, into a 3D model of this object.
# LiDAR Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)

## LiDAR Learning Resources
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/LiDAR-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Introduction to Lidar Course - NOAA](https://coast.noaa.gov/digitalcoast/training/intro-lidar.html)
[Lidar 101:An Introduction to Lidar Technology, Data, and Applications(PDF) - NOAA](https://coast.noaa.gov/data/digitalcoast/pdf/lidar-101.pdf)
[Understanding LiDAR Technologies - GIS Lounge](https://www.gislounge.com/understanding-lidar-technologies/)
[LiDAR University Free Lidar Training Courses on MODUS AI](https://www.modus-ai.com/lidar-university-2/)
[LiDAR | Learning Plan on ERSI](https://www.esri.com/training/catalog/5bccd52a6e9c0f01fb49e85d/lidar/#!)
[Light Detection and Ranging Sensors Course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/lecture/state-estimation-localization-self-driving-cars/lesson-1-light-detection-and-ranging-sensors-3NXgp)
[Quick Introduction to Lidar and Basic Lidar Tools(PDF)](https://training.fws.gov/courses/references/tutorials/geospatial/CSP7304/documents/Lidar.pdf)
[LIDAR - GIS Wiki](http://wiki.gis.com/wiki/index.php/Lidar)
[OpenStreetMap Wiki](https://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Main_Page)
[OpenStreetMap Frameworks](https://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Frameworks)
## LiDAR Tools & Frameworks
[Light Detection and Ranging (lidar)](https://www.usgs.gov/news/earthword-lidar) is a technology used to create high-resolution models of ground elevation with a vertical accuracy of 10 centimeters (4 inches). Lidar equipment, which includes a laser scanner, a Global Positioning System (GPS), and an Inertial Navigation System (INS), is typically mounted on a small aircraft. The laser scanner transmits brief pulses of light to the ground surface. Those pulses are reflected or scattered back and their travel time is used to calculate the distance between the laser scanner and the ground. Lidar data is initially collected as a “point cloud” of individual points reflected from everything on the surface, including structures and vegetation. To produce a “bare earth” Digital Elevation Model (DEM), structures and vegetation are stripped away.
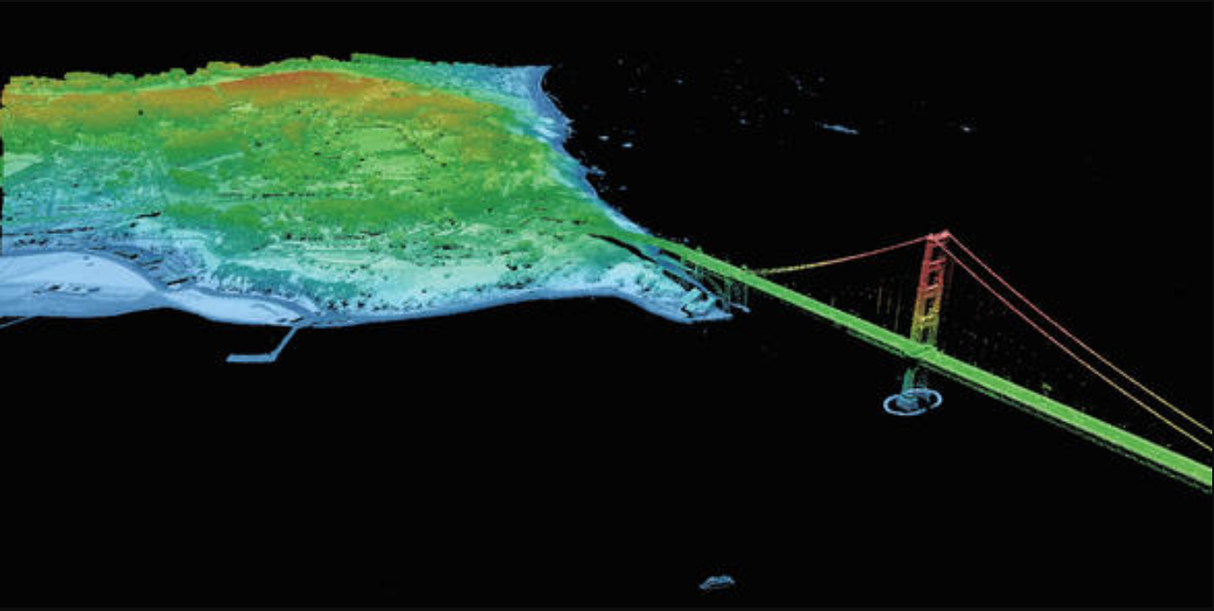
**3D Data Visualization of Golden Gate Bridge. Source: [USGS](https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/ngp/tnm-delivery)**
[Mola](https://docs.mola-slam.org/latest/) is a Modular Optimization framework for Localization and mApping (MOLA).

**3D LiDAR SLAM from KITTI dataset. Source: [MOLA](https://docs.mola-slam.org/latest/demo-kitti-lidar-slam.html)**
[Lidar Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/lidar.html) is a MATLAB tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing, analyzing, and testing lidar processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, semantic segmentation, shape fitting, lidar registration, and obstacle detection. Lidar Toolbox supports lidar-camera cross calibration for workflows that combine computer vision and lidar processing.
[Automated Driving Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/automated-driving.html) is a MATLAB tool that provides algorithms and tools for designing, simulating, and testing ADAS and autonomous driving systems. You can design and test vision and lidar perception systems, as well as sensor fusion, path planning, and vehicle controllers. Visualization tools include a bird’s-eye-view plot and scope for sensor coverage, detections and tracks, and displays for video, lidar, and maps. The toolbox lets you import and work with HERE HD Live Map data and OpenDRIVE® road networks. It also provides reference application examples for common ADAS and automated driving features, including FCW, AEB, ACC, LKA, and parking valet. The toolbox supports C/C++ code generation for rapid prototyping and HIL testing, with support for sensor fusion, tracking, path planning, and vehicle controller algorithms.
[Microsoft AirSim](https://microsoft.github.io/AirSim/lidar.html) is a simulator for drones, cars and more, built on Unreal Engine (with an experimental Unity release). AirSim is open-source, cross platform, and supports [software-in-the-loop simulation](https://www.mathworks.com/help///ecoder/software-in-the-loop-sil-simulation.html) with popular flight controllers such as PX4 & ArduPilot and [hardware-in-loop](https://www.ni.com/en-us/innovations/white-papers/17/what-is-hardware-in-the-loop-.html) with PX4 for physically and visually realistic simulations. It is developed as an Unreal plugin that can simply be dropped into any Unreal environment. AirSim is being developed as a platform for AI research to experiment with deep learning, computer vision and reinforcement learning algorithms for autonomous vehicles.

**3D Autonomous Vehicle Simulation in AirSim. Source: [Microsoft](https://microsoft.github.io/AirSim)**
[LASer(LAS)](https://www.asprs.org/divisions-committees/lidar-division/laser-las-file-format-exchange-activities) is a public file format for the interchange of 3-dimensional point cloud data data between data users. Although developed primarily for exchange of lidar point cloud data, this format supports the exchange of any 3-dimensional x,y,z tuplet. This binary file format is an alternative to proprietary systems or a generic ASCII file interchange system used by many companies. The problem with proprietary systems is obvious in that data cannot be easily taken from one system to another. There are two major problems with the ASCII file interchange. The first problem is performance because the reading and interpretation of ASCII elevation data can be very slow and the file size can be extremely large even for small amounts of data. The second problem is that all information specific to the lidar data is lost. The LAS file format is a binary file format that maintains information specific to the lidar nature of the data while not being overly complex.
[3D point cloud](https://www.onyxscan-lidar.com/point-cloud/) is a set of data points defined in a given three-dimensional coordinates system.. Point clouds can be produced directly by 3D scanner which records a large number of points returned from the external surfaces of objects or earth surface. These data are exchanged between LiDAR users mainly through LAS format files (.las).
[ArcGIS Desktop](https://www.esri.com/en-us/arcgis/products/arcgis-desktop/overview) is powerful and cost-effective desktop geographic information system (GIS) software. It is the essential software package for GIS professionals. ArcGIS Desktop users can create, analyze, manage, and share geographic information so decision-makers can make intelligent, informed decisions.
[USGS 3DEP Lidar Point Cloud Now Available as Amazon Public Dataset](https://www.usgs.gov/news/usgs-3dep-lidar-point-cloud-now-available-amazon-public-dataset)
[National Geospatial Program](https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/national-geospatial-program)
[National Map Data Download and Visualization Services](https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/ngp/tnm-delivery)
[USGS Lidar Base Specification(LBS) online edition](https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/ngp/ss/lidar-base-specification-online)
# Algorithms
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Fuzzy logic](https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/fuzzy-logic.asp) is a heuristic approach that allows for more advanced decision-tree processing and better integration with rules-based programming.
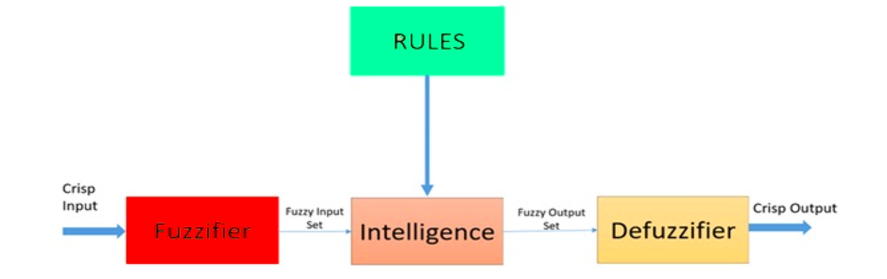
**Architecture of a Fuzzy Logic System. Source: [ResearchGate](https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Architecture-of-a-fuzzy-logic-system_fig2_309452475)**
[Support Vector Machine (SVM)](https://web.stanford.edu/~hastie/MOOC-Slides/svm.pdf) is a supervised machine learning model that uses classification algorithms for two-group classification problems.
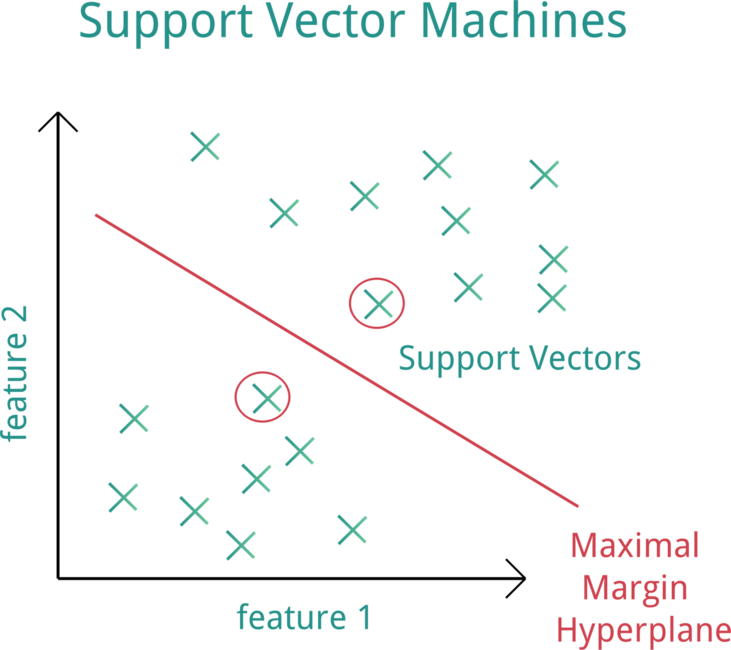
**Support Vector Machine (SVM). Source:[OpenClipArt](https://openclipart.org/detail/182977/svm-support-vector-machines)**
[Neural networks](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/neural-networks) are a subset of machine learning and are at the heart of deep learning algorithms. The name/structure is inspired by the human brain copying the process that biological neurons/nodes signal to one another.
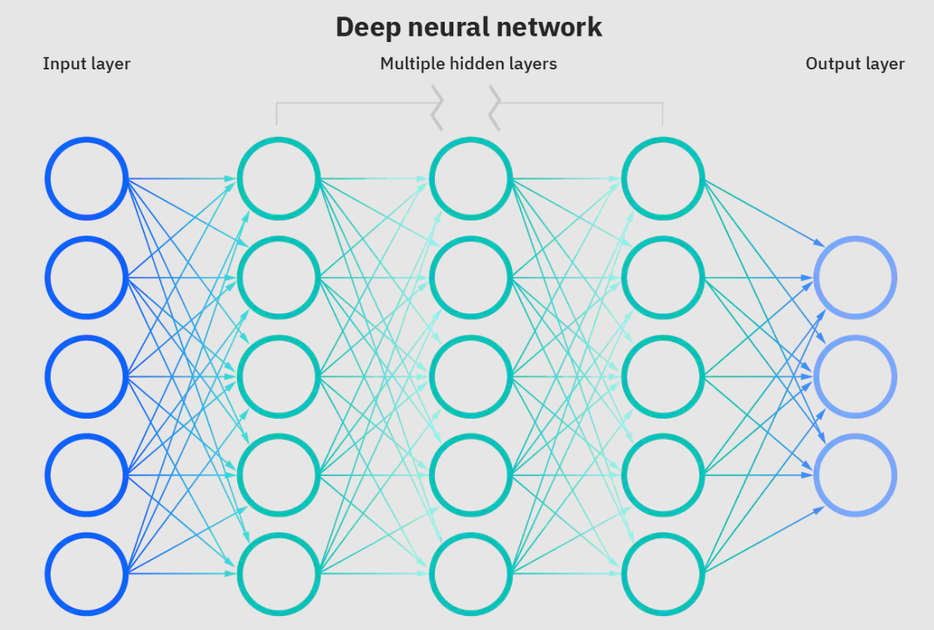
**Deep neural network. Source: [IBM](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/neural-networks)**
[Convolutional Neural Networks (R-CNN)](https://stanford.edu/~shervine/teaching/cs-230/cheatsheet-convolutional-neural-networks) is an object detection algorithm that first segments the image to find potential relevant bounding boxes and then run the detection algorithm to find most probable objects in those bounding boxes.
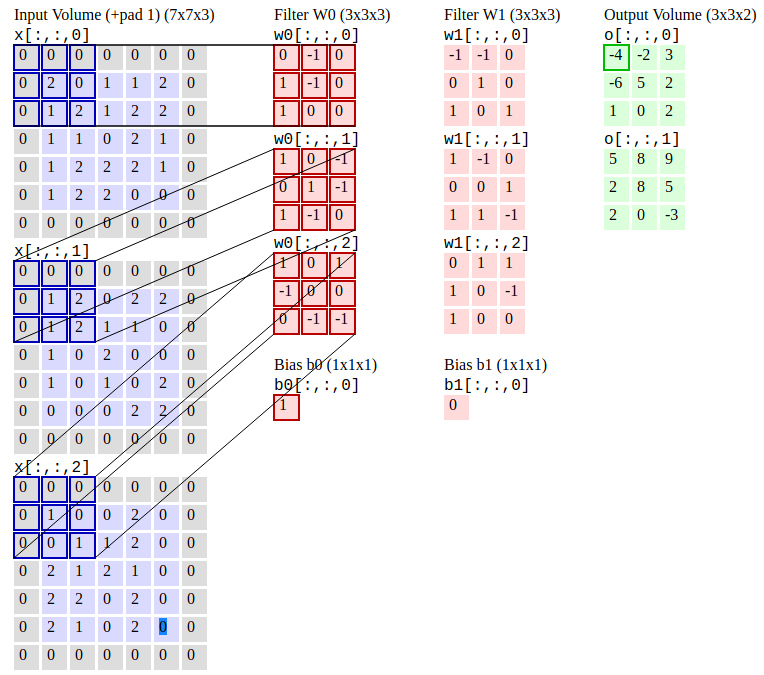
**Convolutional Neural Networks. Source:[CS231n](https://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/#conv)**
[Recurrent neural networks (RNNs)](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/recurrent-neural-networks) is a type of artificial neural network which uses sequential data or time series data.

**Recurrent Neural Networks. Source: [Slideteam](https://www.slideteam.net/recurrent-neural-networks-rnns-ppt-powerpoint-presentation-file-templates.html)**
[Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs)](https://deepai.org/machine-learning-glossary-and-terms/multilayer-perceptron) is multi-layer neural networks composed of multiple layers of [perceptrons](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perceptron) with a threshold activation.

**Multilayer Perceptrons. Source: [DeepAI](https://deepai.org/machine-learning-glossary-and-terms/multilayer-perceptron)**
[Random forest](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/random-forest) is a commonly-used machine learning algorithm, which combines the output of multiple decision trees to reach a single result. A decision tree in a forest cannot be pruned for sampling and therefore, prediction selection. Its ease of use and flexibility have fueled its adoption, as it handles both classification and regression problems.

**Random forest. Source: [wikimedia](https://community.tibco.com/wiki/random-forest-template-tibco-spotfirer-wiki-page)**
[Decision trees](https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~bhiksha/courses/10-601/decisiontrees/) are tree-structured models for classification and regression.

***Decision Trees. Source: [CMU](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~bhiksha/courses/10-601/decisiontrees/)*
[Naive Bayes](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Naive_Bayes_classifier) is a machine learning algorithm that is used solved calssification problems. It's based on applying [Bayes' theorem](https://www.mathsisfun.com/data/bayes-theorem.html) with strong independence assumptions between the features.

**Bayes' theorem. Source:[mathisfun](https://www.mathsisfun.com/data/bayes-theorem.html)**
# Differential Equations
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Differential Equations Learning Resources
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Differential-Equations-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Ordinary Differential Equation | Wolfram MathWorld](https://mathworld.wolfram.com/OrdinaryDifferentialEquation.html)
[Differential Equations - Wolfram|Alpha](https://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=differential+equations)
[Differential Equations | Mathematics | MIT OpenCourseWare](https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mathematics/18-03-differential-equations-spring-2010/)
[Differential Equations - Complete Review Course | YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lxGArmr4moI)
[Differential Equations Playlist | YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL96AE8D9C68FEB902)
[Introduction to Differential Equations | YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EWVSxND_iWA)
[Linear Systems of Differential Equations | YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TBoPC2I-WsI)
[Linear Algebra and Differential Equations | Harvard University](https://online-learning.harvard.edu/course/linear-algebra-and-differential-equations-1)
[Ordinary Differential Equations | Harvard University](https://online-learning.harvard.edu/course/ordinary-differential-equations)
[Partial Differential Equations in Engineering Course | Stanford Online](https://online.stanford.edu/courses/me300b-partial-differential-equations-engineering)
[Partial Differential Equations of Applied Mathematics Course | Stanford Online](https://online.stanford.edu/courses/math220-partial-differential-equations-applied-mathematics)
[Top Differential Equation Courses Online | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=differential%20equation&page=1)
[Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/ordinary-differential-equations)
[Differential Equations | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/differential-equations-sgt/)
[Top Differential Equations Courses Online | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/Differential-Equations/)
[Learn Differential Equations with Online Courses and lessons | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/differential-equations)
[Differential Equations Courses - Engineer4Free](https://www.engineer4free.com/differential-equations.html)
[Differential Equations Study Resources - Course Hero](https://www.coursehero.com/subjects/differential-equations/)
## First order differential equations
- Differential equations: First order differential equations
- Slope fields: First order differential equations
- Euler's Method: First order differential equations
- Separable equations: First order differential equations
- Exponential models: First order differential equations
- Logistic models: First order differential equations
- Exact equations and integrating factors: First order differential equations
- Homogeneous equations: First order differential equations

## Second order linear equations
- Linear homogeneous equations: Second order linear equations
- Complex and repeated roots of characteristic equation: Second order linear equations
- Method of undetermined coefficients: Second order linear equations

## Laplace transform
- Laplace transform: Laplace transform
- Properties of the Laplace transform: Laplace transform
- Laplace transform to solve a differential equation: Laplace transform
- The convolution integral

# Electric charge, field, and potential
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)
- Charge and electric force (Coulomb's law): Electric charge, field, and potential
- Electric field: Electric charge, field, and potential
- Electric potential energy, electric potential, and voltage: Electric charge, field, and potential

**Electric Potential Energy. Source: [sparkfun](https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/what-is-electricity/electric-potential-energy)**

# Circuits
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)
- Ohm's law and circuits with resistors: Circuits
- Circuits with capacitors: Circuits

**Electric Circuits. Source: [sdsu-physics](http://sdsu-physics.org/physics180/physics180B/Chapters/electric_currents.htm)**

**Symbols of Circuits .Source: [andrewpover.co.uk](https://andrewpover.co.uk/category/physics/)**
# Magnetic forces, magnetic fields, and Faraday's law
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)
- Magnets and Magnetic Force: Magnetic forces, magnetic fields, and Faraday's law
- Magnetic field created by a current: Magnetic forces, magnetic fields, and Faraday's law
- Electric motors: Magnetic forces, magnetic fields, and Faraday's law
- Magnetic flux and Faraday's law

**Magnetic Field. Source: [vecteezy](https://www.vecteezy.com/vector-art/593998-physics-science-about-the-movement-of-magnetic-fields-positive-and-negative)**

**Amphere's Law. Source: [sdsu-physics](https://sdsu-physics.org/physics180/physics196/Topics/magneticFields30.html)**

**Farady's law. Source: [sdsu-physics](http://sdsu-physics.org/physics180/physics196/Topics/faradaysLaw.html)**
# Electromagnetic waves and interference
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)
- Introduction to electromagnetic waves: Electromagnetic waves and interference
- Interference of electromagnetic waves

**Electromagnetic Wave. Source: [differencebetween](https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-wave-and-particle-nature-of-light/)**

**EMI Spectrum. Source: [electrical4u](https://www.electrical4u.com/electromagnetic-interference/)**
# Machine Learning
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)

**Machine Learning/Deep Learning Frameworks.**
## Learning Resources for ML
[Machine Learning](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/machine-learning) is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) focused on building apps using algorithms that learn from data models and improve their accuracy over time without needing to be programmed.
[Machine Learning by Stanford University from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning)
[AWS Training and Certification for Machine Learning (ML) Courses](https://aws.amazon.com/training/learning-paths/machine-learning/)
[Machine Learning Scholarship Program for Microsoft Azure from Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/scholarships/machine-learning-scholarship-microsoft-azure)
[Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Scientist Associate](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/azure-data-scientist)
[Microsoft Certified: Azure AI Engineer Associate](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/azure-ai-engineer)
[Azure Machine Learning training and deployment](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/targets/azure-machine-learning)
[Learning Machine learning and artificial intelligence from Google Cloud Training](https://cloud.google.com/training/machinelearning-ai)
[Machine Learning Crash Course for Google Cloud](https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/)
[JupyterLab](https://jupyterlab.readthedocs.io/)
[Scheduling Jupyter notebooks on Amazon SageMaker ephemeral instances](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/machine-learning/scheduling-jupyter-notebooks-on-sagemaker-ephemeral-instances/)
[How to run Jupyter Notebooks in your Azure Machine Learning workspace](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/how-to-run-jupyter-notebooks)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/machine-learning/)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=machine%20learning&)
[Learn Machine Learning with Online Courses and Classes from edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/machine-learning)
## ML Frameworks, Libraries, and Tools
[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org) is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
[Keras](https://keras.io) is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
[PyTorch](https://pytorch.org) is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab.
[Amazon SageMaker](https://aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/) is a fully managed service that provides every developer and data scientist with the ability to build, train, and deploy machine learning (ML) models quickly. SageMaker removes the heavy lifting from each step of the machine learning process to make it easier to develop high quality models.
[Azure Databricks](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/databricks/) is a fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering. Azure Databricks, sets up your Apache Spark environment in minutes, autoscale, and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace. Azure Databricks supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL, as well as data science frameworks and libraries including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
[Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cognitive-toolkit/) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
[Apple CoreML](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/coreml) is a framework that helps integrate machine learning models into your app. Core ML provides a unified representation for all models. Your app uses Core ML APIs and user data to make predictions, and to train or fine-tune models, all on the user's device. A model is the result of applying a machine learning algorithm to a set of training data. You use a model to make predictions based on new input data.
[Tensorflow_macOS](https://github.com/apple/tensorflow_macos) is a Mac-optimized version of TensorFlow and TensorFlow Addons for macOS 11.0+ accelerated using Apple's ML Compute framework.
[Apache OpenNLP](https://opennlp.apache.org/) is an open-source library for a machine learning based toolkit used in the processing of natural language text. It features an API for use cases like [Named Entity Recognition](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Named-entity_recognition), [Sentence Detection](), [POS(Part-Of-Speech) tagging](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Part-of-speech_tagging), [Tokenization](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tokenization_(data_security)) [Feature extraction](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feature_extraction), [Chunking](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chunking_(psychology)), [Parsing](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parsing), and [Coreference resolution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coreference).
[Apache Airflow](https://airflow.apache.org) is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
[Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX)](https://github.com/onnx) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
[Apache MXNet](https://mxnet.apache.org/) is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
[AutoGluon](https://autogluon.mxnet.io/index.html) is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
[Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/) is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
[PlaidML](https://github.com/plaidml/plaidml) is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
[Weka](https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/) is an open source machine learning software that can be accessed through a graphical user interface, standard terminal applications, or a Java API. It is widely used for teaching, research, and industrial applications, contains a plethora of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks, and additionally gives transparent access to well-known toolboxes such as scikit-learn, R, and Deeplearning4j.
[Caffe](https://github.com/BVLC/caffe) is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
[Theano](https://github.com/Theano/Theano) is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
[nGraph](https://github.com/NervanaSystems/ngraph) is an open source C++ library, compiler and runtime for Deep Learning. The nGraph Compiler aims to accelerate developing AI workloads using any deep learning framework and deploying to a variety of hardware targets.It provides the freedom, performance, and ease-of-use to AI developers.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[Jupyter Notebook](https://jupyter.org/) is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
[Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL](https://github.com/microsoft/sql-spark-connector) is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
[Apache PredictionIO](https://predictionio.apache.org/) is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
[Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK)](https://github.com/yahoo/CMAK) is a tool for managing [Apache Kafka](https://kafka.apache.org/) clusters.
[BigDL](https://bigdl-project.github.io/) is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
[Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J)](https://deeplearning4j.konduit.ai/) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
[Tensorman](https://github.com/pop-os/tensorman) is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by [System76]( https://system76.com).Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
[Numba](https://github.com/numba/numba) is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
[Chainer](https://chainer.org/) is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using [CuPy](https://github.com/cupy/cupy) for high performance training and inference.
[XGBoost](https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/) is an optimized distributed gradient boosting library designed to be highly efficient, flexible and portable. It implements machine learning algorithms under the Gradient Boosting framework. XGBoost provides a parallel tree boosting (also known as GBDT, GBM) that solve many data science problems in a fast and accurate way. It supports distributed training on multiple machines, including AWS, GCE, Azure, and Yarn clusters. Also, it can be integrated with Flink, Spark and other cloud dataflow systems.
[cuML](https://github.com/rapidsai/cuml) is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
# CUDA Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)


**CUDA Toolkit. Source: [NVIDIA Developer CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-zone)**
## CUDA Learning Resources
[CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-zone) is a parallel computing platform and programming model developed by NVIDIA for general computing on graphical processing units (GPUs). With CUDA, developers are able to dramatically speed up computing applications by harnessing the power of GPUs. In GPU-accelerated applications, the sequential part of the workload runs on the CPU, which is optimized for single-threaded. The compute intensive portion of the application runs on thousands of GPU cores in parallel. When using CUDA, developers can program in popular languages such as C, C++, Fortran, Python and MATLAB.
[CUDA Toolkit Documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/index.html)
[CUDA Quick Start Guide](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-quick-start-guide/index.html)
[CUDA on WSL](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/wsl-user-guide/index.html)
[CUDA GPU support for TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/gpu)
[NVIDIA Deep Learning cuDNN Documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/cudnn/api/index.html)
[NVIDIA GPU Cloud Documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/ngc/ngc-introduction/index.html)
[NVIDIA NGC](https://ngc.nvidia.com/) is a hub for GPU-optimized software for deep learning, machine learning, and high-performance computing (HPC) workloads.
[NVIDIA NGC Containers](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/gpu-cloud/containers/) is a registry that provides researchers, data scientists, and developers with simple access to a comprehensive catalog of GPU-accelerated software for AI, machine learning and HPC. These containers take full advantage of NVIDIA GPUs on-premises and in the cloud.
## CUDA Tools Libraries, and Frameworks
[CUDA Toolkit](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads) is a collection of tools & libraries that provide a development environment for creating high performance GPU-accelerated applications. The CUDA Toolkit allows you can develop, optimize, and deploy your applications on GPU-accelerated embedded systems, desktop workstations, enterprise data centers, cloud-based platforms and HPC supercomputers. The toolkit includes GPU-accelerated libraries, debugging and optimization tools, a C/C++ compiler, and a runtime library to build and deploy your application on major architectures including x86, Arm and POWER.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[CUDA-X HPC](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/technologies/cuda-x/) is a collection of libraries, tools, compilers and APIs that help developers solve the world's most challenging problems. CUDA-X HPC includes highly tuned kernels essential for high-performance computing (HPC).
[NVIDIA Container Toolkit](https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-docker) is a collection of tools & libraries that allows users to build and run GPU accelerated Docker containers. The toolkit includes a container runtime [library](https://github.com/NVIDIA/libnvidia-container) and utilities to automatically configure containers to leverage NVIDIA GPUs.
[Minkowski Engine](https://nvidia.github.io/MinkowskiEngine) is an auto-differentiation library for sparse tensors. It supports all standard neural network layers such as convolution, pooling, unpooling, and broadcasting operations for sparse tensors.
[CUTLASS](https://github.com/NVIDIA/cutlass) is a collection of CUDA C++ template abstractions for implementing high-performance matrix-multiplication (GEMM) at all levels and scales within CUDA. It incorporates strategies for hierarchical decomposition and data movement similar to those used to implement cuBLAS.
[CUB](https://github.com/NVIDIA/cub) is a cooperative primitives for CUDA C++ kernel authors.
[Tensorman](https://github.com/pop-os/tensorman) is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by [System76]( https://system76.com).Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
[Numba](https://github.com/numba/numba) is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
[Chainer](https://chainer.org/) is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using [CuPy](https://github.com/cupy/cupy) for high performance training and inference.
[CuPy](https://cupy.dev/) is an implementation of NumPy-compatible multi-dimensional array on CUDA. CuPy consists of the core multi-dimensional array class, cupy.ndarray, and many functions on it. It supports a subset of numpy.ndarray interface.
[CatBoost](https://catboost.ai/) is a fast, scalable, high performance [Gradient Boosting](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gradient_boosting) on Decision Trees library, used for ranking, classification, regression and other machine learning tasks for Python, R, Java, C++. Supports computation on CPU and GPU.
[cuDF](https://rapids.ai/) is a GPU DataFrame library for loading, joining, aggregating, filtering, and otherwise manipulating data. cuDF provides a pandas-like API that will be familiar to data engineers & data scientists, so they can use it to easily accelerate their workflows without going into the details of CUDA programming.
[cuML](https://github.com/rapidsai/cuml) is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
[ArrayFire](https://arrayfire.com/) is a general-purpose library that simplifies the process of developing software that targets parallel and massively-parallel architectures including CPUs, GPUs, and other hardware acceleration devices.
[Thrust](https://github.com/NVIDIA/thrust) is a C++ parallel programming library which resembles the C++ Standard Library. Thrust's high-level interface greatly enhances programmer productivity while enabling performance portability between GPUs and multicore CPUs.
[AresDB](https://eng.uber.com/aresdb/) is a GPU-powered real-time analytics storage and query engine. It features low query latency, high data freshness and highly efficient in-memory and on disk storage management.
[Arraymancer](https://mratsim.github.io/Arraymancer/) is a tensor (N-dimensional array) project in Nim. The main focus is providing a fast and ergonomic CPU, Cuda and OpenCL ndarray library on which to build a scientific computing ecosystem.
[Kintinuous](https://github.com/mp3guy/Kintinuous) is a real-time dense visual SLAM system capable of producing high quality globally consistent point and mesh reconstructions over hundreds of metres in real-time with only a low-cost commodity RGB-D sensor.
[GraphVite](https://graphvite.io/) is a general graph embedding engine, dedicated to high-speed and large-scale embedding learning in various applications.
# OpenCL Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)

# OpenCL Learning Resources
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/OpenCL-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Open Computing Language (OpenCL)](https://www.khronos.org/opencl/) is an open standard for [parallel programming](https://www.coursera.org/lecture/parprog1/introduction-to-parallel-computing-zNrIS) of heterogeneous platforms consisting of CPUs, GPUs, and other hardware accelerators found in supercomputers, cloud servers, personal computers, mobile devices and embedded platforms.
[OpenCL | GitHub](https://github.com/OpenCL/)
[Khronos Group | GitHub](https://github.com/KhronosGroup/)
[Khronos Technology Courses and Training](https://www.khronos.org/developers/training/)
[OpenCL Tutorials - StreamHPC](https://streamhpc.com/knowledge/for-developers/tutorials/)
[Introduction to Intel® OpenCL Tools](https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/articles/introduction-to-intel-opencl-tools.html)
[OpenCL | NVIDIA Developer](https://developer.nvidia.com/opencl)
[Introduction to OpenCL on FPGAs Course | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/opencl-fpga-introduction)
[Compiling OpenCL Kernel to FPGAs Course | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/lecture/opencl-fpga-introduction/compiling-opencl-kernel-to-fpgas-g7MnU)
# OpenCL Tools, Libraries and Frameworks
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/OpenCL-Guide#table-of-contents)
[RenderDoc](https://renderdoc.org) is a stand-alone graphics debugger that allows quick and easy single-frame capture and detailed introspection of any application using Vulkan, D3D11, OpenGL & OpenGL ES or D3D12 across Windows, Linux, Android, Stadia, or Nintendo Switch™.
[GPUVerify](https://streamhpc.com/knowledge/tools/gpuverify/) is a tool for formal analysis of GPU kernels written in OpenCL and CUDA. The tool can prove that kernels are free from certain types of defect, including data races.
[OpenCL ICD Loader](https://github.com/KhronosGroup/OpenCL-ICD-Loader) is an Installable Client Driver (ICD) mechanism to allow developers to build applications against an Installable Client Driver loader (ICD loader) rather than linking their applications against a specific OpenCL implementation.
[clBLAS](https://github.com/clMathLibraries/clBLAS) is a software library containing BLAS functions written in OpenCL.
[clFFT](https://github.com/clMathLibraries/clFFT) is a software library containing FFT functions written in OpenCL.
[clSPARSE](https://github.com/clMathLibraries/clSPARSE) is a software library containing Sparse functions written in OpenCL.
[clRNG](https://github.com/clMathLibraries/clRNG) is an OpenCL based software library containing random number generation functions.
[CLsmith](https://github.com/ChrisLidbury/CLSmith/) is a tool that makes use of two existing testing techniques, Random Differential Testing and Equivalence Modulo Inputs (EMI), applying them in a many-core environment, OpenCL. Its primary feature is the generation of random OpenCL kernels, exercising many features of the language. It also brings a novel idea of applying EMI, via dead-code injection.
[Oclgrind](https://github.com/jrprice/Oclgrind) is a virtual OpenCL device simulator, including an OpenCL runtime with ICD support. The goal is to provide a platform for creating tools to aid OpenCL development. In particular, this project currently implements utilities for debugging memory access errors, detecting data-races and barrier divergence, collecting instruction histograms, and for interactive OpenCL kernel debugging. The simulator is built on an interpreter for LLVM IR.
[NVIDIA® Nsight™ Visual Studio Edition](https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-visual-studio-edition) is an application development environment for heterogeneous platforms which brings GPU computing into Microsoft Visual Studio. NVIDIA Nsight™ VSE allows you to build and debug integrated GPU kernels and native CPU code as well as inspect the state of the GPU and memory.
[Radeon™ GPU Profiler](https://gpuopen.com/rgp/) is a performance tool that can be used by developers to optimize DirectX®12, Vulkan® and OpenCL™ applications for AMD RDNA™ and GCN hardware.
[Radeon™ GPU Analyzer](https://gpuopen.com/rga/) is a compiler and code analysis tool for Vulkan®, DirectX®, OpenGL® and OpenCL™.
[AMD Radeon ProRender](https://www.amd.com/en/technologies/radeon-prorender) is a powerful physically-based rendering engine that enables creative professionals to produce stunningly photorealistic images on virtually any GPU, any CPU, and any OS in over a dozen leading digital content creation and CAD applications.
[NVIDIA Omniverse](https://developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-omniverse-platform) is a powerful, multi-GPU, real-time simulation and collaboration platform for 3D production pipelines based on Pixar's Universal Scene Description and NVIDIA RTX.
[Intel® SDK For OpenCL™ Applications](https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/tools/opencl-sdk.html) is an offload compute-intensive workloads. Customize heterogeneous compute applications and accelerate performance with kernel-based programming.
[NVIDIA NGC](https://ngc.nvidia.com/) is a hub for GPU-optimized software for deep learning, machine learning, and high-performance computing (HPC) workloads.
[NVIDIA NGC Containers](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/gpu-cloud/containers/) is a registry that provides researchers, data scientists, and developers with simple access to a comprehensive catalog of GPU-accelerated software for AI, machine learning and HPC. These containers take full advantage of NVIDIA GPUs on-premises and in the cloud.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[NVIDIA Container Toolkit](https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-docker) is a collection of tools & libraries that allows users to build and run GPU accelerated Docker containers. The toolkit includes a container runtime [library](https://github.com/NVIDIA/libnvidia-container) and utilities to automatically configure containers to leverage NVIDIA GPUs.
# MATLAB Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)

## MATLAB Learning Resources
[MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html) is a programming language that does numerical computing such as expressing matrix and array mathematics directly.
[MATLAB Documentation](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/)
[Getting Started with MATLAB ](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/getting-started-with-matlab.html)
[MATLAB and Simulink Training from MATLAB Academy](https://matlabacademy.mathworks.com)
[MathWorks Certification Program](https://www.mathworks.com/services/training/certification.html)
[MATLAB Online Courses from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/matlab/)
[MATLAB Online Courses from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=matlab)
[MATLAB Online Courses from edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/matlab)
[Building a MATLAB GUI](https://www.mathworks.com/discovery/matlab-gui.html)
[MATLAB Style Guidelines 2.0](https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/46056-matlab-style-guidelines-2-0)
[Setting Up Git Source Control with MATLAB & Simulink](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/matlab_prog/set-up-git-source-control.html)
[Pull, Push and Fetch Files with Git with MATLAB & Simulink](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/matlab_prog/push-and-fetch-with-git.html)
[Create New Repository with MATLAB & Simulink](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/matlab_prog/add-folder-to-source-control.html)
[PRMLT](http://prml.github.io/) is Matlab code for machine learning algorithms in the PRML book.
## MATLAB Tools, Libraries, Frameworks
**[MATLAB and Simulink Services & Applications List](https://www.mathworks.com/products.html)**
[MATLAB in the Cloud](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/cloud.html) is a service that allows you to run in cloud environments from [MathWorks Cloud](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/cloud.html#browser) to [Public Clouds](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/cloud.html#public-cloud) including [AWS](https://aws.amazon.com/) and [Azure](https://azure.microsoft.com/).
[MATLAB Online™](https://matlab.mathworks.com) is a service that allows to users to uilitize MATLAB and Simulink through a web browser such as Google Chrome.
[Simulink](https://www.mathworks.com/products/simulink.html) is a block diagram environment for Model-Based Design. It supports simulation, automatic code generation, and continuous testing of embedded systems.
[Simulink Online™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/simulink-online.html) is a service that provides access to Simulink through your web browser.
[MATLAB Drive™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab-drive.html) is a service that gives you the ability to store, access, and work with your files from anywhere.
[MATLAB Parallel Server™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab-parallel-server.html) is a tool that lets you scale MATLAB® programs and Simulink® simulations to clusters and clouds. You can prototype your programs and simulations on the desktop and then run them on clusters and clouds without recoding. MATLAB Parallel Server supports batch jobs, interactive parallel computations, and distributed computations with large matrices.
[MATLAB Schemer](https://github.com/scottclowe/matlab-schemer) is a MATLAB package makes it easy to change the color scheme (theme) of the MATLAB display and GUI.
[LRSLibrary](https://github.com/andrewssobral/lrslibrary) is a Low-Rank and Sparse Tools for Background Modeling and Subtraction in Videos. The library was designed for moving object detection in videos, but it can be also used for other computer vision and machine learning problems.
[Image Processing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/image.html) is a tool that provides a comprehensive set of reference-standard algorithms and workflow apps for image processing, analysis, visualization, and algorithm development. You can perform image segmentation, image enhancement, noise reduction, geometric transformations, image registration, and 3D image processing.
[Computer Vision Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/computer-vision.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing and testing computer vision, 3D vision, and video processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, as well as feature detection, extraction, and matching. You can automate calibration workflows for single, stereo, and fisheye cameras. For 3D vision, the toolbox supports visual and point cloud SLAM, stereo vision, structure from motion, and point cloud processing.
[Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/statistics.html) is a tool that provides functions and apps to describe, analyze, and model data. You can use descriptive statistics, visualizations, and clustering for exploratory data analysis; fit probability distributions to data; generate random numbers for Monte Carlo simulations, and perform hypothesis tests. Regression and classification algorithms let you draw inferences from data and build predictive models either interactively, using the Classification and Regression Learner apps, or programmatically, using AutoML.
[Lidar Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/lidar.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing, analyzing, and testing lidar processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, semantic segmentation, shape fitting, lidar registration, and obstacle detection. Lidar Toolbox supports lidar-camera cross calibration for workflows that combine computer vision and lidar processing.
[Mapping Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/mapping.html) is a tool that provides algorithms and functions for transforming geographic data and creating map displays. You can visualize your data in a geographic context, build map displays from more than 60 map projections, and transform data from a variety of sources into a consistent geographic coordinate system.
[UAV Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/uav.html) is an application that provides tools and reference applications for designing, simulating, testing, and deploying unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and drone applications. You can design autonomous flight algorithms, UAV missions, and flight controllers. The Flight Log Analyzer app lets you interactively analyze 3D flight paths, telemetry information, and sensor readings from common flight log formats.
[Parallel Computing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab-parallel-server.html) is a tool that lets you solve computationally and data-intensive problems using multicore processors, GPUs, and computer clusters. High-level constructs such as parallel for-loops, special array types, and parallelized numerical algorithms enable you to parallelize MATLAB® applications without CUDA or MPI programming. The toolbox lets you use parallel-enabled functions in MATLAB and other toolboxes. You can use the toolbox with Simulink® to run multiple simulations of a model in parallel. Programs and models can run in both interactive and batch modes.
[Partial Differential Equation Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/pde.html) is a tool that provides functions for solving structural mechanics, heat transfer, and general partial differential equations (PDEs) using finite element analysis.
[ROS Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/ros.html) is a tool that provides an interface connecting MATLAB® and Simulink® with the Robot Operating System (ROS and ROS 2), enabling you to create a network of ROS nodes. The toolbox includes MATLAB functions and Simulink blocks to import, analyze, and play back ROS data recorded in rosbag files. You can also connect to a live ROS network to access ROS messages.
[Robotics Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/robotics.html) provides a toolbox that brings robotics specific functionality(designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots) to MATLAB, exploiting the native capabilities of MATLAB (linear algebra, portability, graphics). The toolbox also supports mobile robots with functions for robot motion models (bicycle), path planning algorithms (bug, distance transform, D*, PRM), kinodynamic planning (lattice, RRT), localization (EKF, particle filter), map building (EKF) and simultaneous localization and mapping (EKF), and a Simulink model a of non-holonomic vehicle. The Toolbox also including a detailed Simulink model for a quadrotor flying robot.
[Deep Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning.html) is a tool that provides a framework for designing and implementing deep neural networks with algorithms, pretrained models, and apps. You can use convolutional neural networks (ConvNets, CNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks to perform classification and regression on image, time-series, and text data. You can build network architectures such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and Siamese networks using automatic differentiation, custom training loops, and shared weights. With the Deep Network Designer app, you can design, analyze, and train networks graphically. It can exchange models with TensorFlow™ and PyTorch through the ONNX format and import models from TensorFlow-Keras and Caffe. The toolbox supports transfer learning with DarkNet-53, ResNet-50, NASNet, SqueezeNet and many other pretrained models.
[Reinforcement Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/reinforcement-learning.html) is a tool that provides an app, functions, and a Simulink® block for training policies using reinforcement learning algorithms, including DQN, PPO, SAC, and DDPG. You can use these policies to implement controllers and decision-making algorithms for complex applications such as resource allocation, robotics, and autonomous systems.
[Deep Learning HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning-hdl.html) is a tool that provides functions and tools to prototype and implement deep learning networks on FPGAs and SoCs. It provides pre-built bitstreams for running a variety of deep learning networks on supported Xilinx® and Intel® FPGA and SoC devices. Profiling and estimation tools let you customize a deep learning network by exploring design, performance, and resource utilization tradeoffs.
[Model Predictive Control Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/model-predictive-control.html) is a tool that provides functions, an app, and Simulink® blocks for designing and simulating controllers using linear and nonlinear model predictive control (MPC). The toolbox lets you specify plant and disturbance models, horizons, constraints, and weights. By running closed-loop simulations, you can evaluate controller performance.
[Vision HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/vision-hdl.html) is a tool that provides pixel-streaming algorithms for the design and implementation of vision systems on FPGAs and ASICs. It provides a design framework that supports a diverse set of interface types, frame sizes, and frame rates. The image processing, video, and computer vision algorithms in the toolbox use an architecture appropriate for HDL implementations.
[SoC Blockset™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/soc.html) is a tool that provides Simulink® blocks and visualization tools for modeling, simulating, and analyzing hardware and software architectures for ASICs, FPGAs, and systems on a chip (SoC). You can build your system architecture using memory models, bus models, and I/O models, and simulate the architecture together with the algorithms.
[Wireless HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/wireless-hdl.html) is a tool that provides pre-verified, hardware-ready Simulink® blocks and subsystems for developing 5G, LTE, and custom OFDM-based wireless communication applications. It includes reference applications, IP blocks, and gateways between frame and sample-based processing.
[ThingSpeak™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/thingspeak.html) is an IoT analytics service that allows you to aggregate, visualize, and analyze live data streams in the cloud. ThingSpeak provides instant visualizations of data posted by your devices to ThingSpeak. With the ability to execute MATLAB® code in ThingSpeak, you can perform online analysis and process data as it comes in. ThingSpeak is often used for prototyping and proof-of-concept IoT systems that require analytics.
[SEA-MAT](https://sea-mat.github.io/sea-mat/) is a collaborative effort to organize and distribute Matlab tools for the Oceanographic Community.
[Gramm](https://github.com/piermorel/gramm) is a complete data visualization toolbox for Matlab. It provides an easy to use and high-level interface to produce publication-quality plots of complex data with varied statistical visualizations. Gramm is inspired by R's ggplot2 library.
[hctsa](https://hctsa-users.gitbook.io/hctsa-manual) is a software package for running highly comparative time-series analysis using Matlab.
[Plotly](https://plot.ly/matlab/) is a Graphing Library for MATLAB.
[YALMIP](https://yalmip.github.io/) is a MATLAB toolbox for optimization modeling.
[GNU Octave](https://www.gnu.org/software/octave/) is a high-level interpreted language, primarily intended for numerical computations. It provides capabilities for the numerical solution of linear and nonlinear problems, and for performing other numerical experiments. It also provides extensive graphics capabilities for data visualization and manipulation.
# C/C++ Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)

## C/C++ Learning Resources
[C++](https://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/) is a cross-platform language that can be used to build high-performance applications developed by Bjarne Stroustrup, as an extension to the C language.
[C](https://www.iso.org/standard/74528.html) is a general-purpose, high-level language that was originally developed by Dennis M. Ritchie to develop the UNIX operating system at Bell Labs. It supports structured programming, lexical variable scope, and recursion, with a static type system. C also provides constructs that map efficiently to typical machine instructions, which makes it one was of the most widely used programming languages today.
[Embedded C](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Embedded_C) is a set of language extensions for the C programming language by the [C Standards Committee](https://isocpp.org/std/the-committee) to address issues that exist between C extensions for different [embedded systems](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Embedded_system). The extensions hep enhance microprocessor features such as fixed-point arithmetic, multiple distinct memory banks, and basic I/O operations. This makes Embedded C the most popular embedded software language in the world.
[C & C++ Developer Tools from JetBrains](https://www.jetbrains.com/cpp/)
[Open source C++ libraries on cppreference.com](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/links/libs)
[C++ Graphics libraries](https://cpp.libhunt.com/libs/graphics)
[C++ Libraries in MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/call-cpp-library-functions.html)
[C++ Tools and Libraries Articles](https://www.cplusplus.com/articles/tools/)
[Google C++ Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html)
[Introduction C++ Education course on Google Developers](https://developers.google.com/edu/c++/)
[C++ style guide for Fuchsia](https://fuchsia.dev/fuchsia-src/development/languages/c-cpp/cpp-style)
[C and C++ Coding Style Guide by OpenTitan](https://docs.opentitan.org/doc/rm/c_cpp_coding_style/)
[Chromium C++ Style Guide](https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromium/src/+/master/styleguide/c++/c++.md)
[C++ Core Guidelines](https://github.com/isocpp/CppCoreGuidelines/blob/master/CppCoreGuidelines.md)
[C++ Style Guide for ROS](http://wiki.ros.org/CppStyleGuide)
[Learn C++](https://www.learncpp.com/)
[Learn C : An Interactive C Tutorial](https://www.learn-c.org/)
[C++ Institute](https://cppinstitute.org/free-c-and-c-courses)
[C++ Online Training Courses on LinkedIn Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/topics/c-plus-plus)
[C++ Tutorials on W3Schools](https://www.w3schools.com/cpp/default.asp)
[Learn C Programming Online Courses on edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/c-programming)
[Learn C++ with Online Courses on edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/c-plus-plus)
[Learn C++ on Codecademy](https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-c-plus-plus)
[Coding for Everyone: C and C++ course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/specializations/coding-for-everyone)
[C++ For C Programmers on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/c-plus-plus-a)
[Top C Courses on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=c%20programming)
[C++ Online Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/c-plus-plus/)
[Top C Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/c-programming/)
[Basics of Embedded C Programming for Beginners on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/embedded-c-programming-for-embedded-systems/)
[C++ For Programmers Course on Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/c-for-programmers--ud210)
[C++ Fundamentals Course on Pluralsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/learn-program-cplusplus)
[Introduction to C++ on MIT Free Online Course Materials](https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-096-introduction-to-c-january-iap-2011/)
[Introduction to C++ for Programmers | Harvard ](https://online-learning.harvard.edu/course/introduction-c-programmers)
[Online C Courses | Harvard University](https://online-learning.harvard.edu/subject/c)
## C/C++ Tools and Frameworks
[Visual Studio](https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/) is an integrated development environment (IDE) from Microsoft; which is a feature-rich application that can be used for many aspects of software development. Visual Studio makes it easy to edit, debug, build, and publish your app. By using Microsoft software development platforms such as Windows API, Windows Forms, Windows Presentation Foundation, and Windows Store.
[Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/) is a code editor redefined and optimized for building and debugging modern web and cloud applications.
[Vcpkg](https://github.com/microsoft/vcpkg) is a C++ Library Manager for Windows, Linux, and MacOS.
[ReSharper C++](https://www.jetbrains.com/resharper-cpp/features/) is a Visual Studio Extension for C++ developers developed by JetBrains.
[AppCode](https://www.jetbrains.com/objc/) is constantly monitoring the quality of your code. It warns you of errors and smells and suggests quick-fixes to resolve them automatically. AppCode provides lots of code inspections for Objective-C, Swift, C/C++, and a number of code inspections for other supported languages. All code inspections are run on the fly.
[CLion](https://www.jetbrains.com/clion/features/) is a cross-platform IDE for C and C++ developers developed by JetBrains.
[Code::Blocks](https://www.codeblocks.org/) is a free C/C++ and Fortran IDE built to meet the most demanding needs of its users. It is designed to be very extensible and fully configurable. Built around a plugin framework, Code::Blocks can be extended with plugins.
[CppSharp](https://github.com/mono/CppSharp) is a tool and set of libraries which facilitates the usage of native C/C++ code with the .NET ecosystem. It consumes C/C++ header and library files and generates the necessary glue code to surface the native API as a managed API. Such an API can be used to consume an existing native library in your managed code or add managed scripting support to a native codebase.
[Conan](https://conan.io/) is an Open Source Package Manager for C++ development and dependency management into the 21st century and on par with the other development ecosystems.
[High Performance Computing (HPC) SDK](https://developer.nvidia.com/hpc) is a comprehensive toolbox for GPU accelerating HPC modeling and simulation applications. It includes the C, C++, and Fortran compilers, libraries, and analysis tools necessary for developing HPC applications on the NVIDIA platform.
[Thrust](https://github.com/NVIDIA/thrust) is a C++ parallel programming library which resembles the C++ Standard Library. Thrust's high-level interface greatly enhances programmer productivity while enabling performance portability between GPUs and multicore CPUs. Interoperability with established technologies such as CUDA, TBB, and OpenMP integrates with existing software.
[Boost](https://www.boost.org/) is an educational opportunity focused on cutting-edge C++. Boost has been a participant in the annual Google Summer of Code since 2007, in which students develop their skills by working on Boost Library development.
[Automake](https://www.gnu.org/software/automake/) is a tool for automatically generating Makefile.in files compliant with the GNU Coding Standards. Automake requires the use of GNU Autoconf.
[Cmake](https://cmake.org/) is an open-source, cross-platform family of tools designed to build, test and package software. CMake is used to control the software compilation process using simple platform and compiler independent configuration files, and generate native makefiles and workspaces that can be used in the compiler environment of your choice.
[GDB](http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/) is a debugger, that allows you to see what is going on `inside' another program while it executes or what another program was doing at the moment it crashed.
[GCC](https://gcc.gnu.org/) is a compiler Collection that includes front ends for C, C++, Objective-C, Fortran, Ada, Go, and D, as well as libraries for these languages.
[GSL](https://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/) is a numerical library for C and C++ programmers. It is free software under the GNU General Public License. The library provides a wide range of mathematical routines such as random number generators, special functions and least-squares fitting. There are over 1000 functions in total with an extensive test suite.
[OpenGL Extension Wrangler Library (GLEW)](https://www.opengl.org/sdk/libs/GLEW/) is a cross-platform open-source C/C++ extension loading library. GLEW provides efficient run-time mechanisms for determining which OpenGL extensions are supported on the target platform.
[Libtool](https://www.gnu.org/software/libtool/) is a generic library support script that hides the complexity of using shared libraries behind a consistent, portable interface. To use Libtool, add the new generic library building commands to your Makefile, Makefile.in, or Makefile.am.
[Maven](https://maven.apache.org/) is a software project management and comprehension tool. Based on the concept of a project object model (POM), Maven can manage a project's build, reporting and documentation from a central piece of information.
[TAU (Tuning And Analysis Utilities)](http://www.cs.uoregon.edu/research/tau/home.php) is capable of gathering performance information through instrumentation of functions, methods, basic blocks, and statements as well as event-based sampling. All C++ language features are supported including templates and namespaces.
[Clang](https://clang.llvm.org/) is a production quality C, Objective-C, C++ and Objective-C++ compiler when targeting X86-32, X86-64, and ARM (other targets may have caveats, but are usually easy to fix). Clang is used in production to build performance-critical software like Google Chrome or Firefox.
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org/) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time applications. Cross-Platform C++, Python and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Libcu++](https://nvidia.github.io/libcudacxx) is the NVIDIA C++ Standard Library for your entire system. It provides a heterogeneous implementation of the C++ Standard Library that can be used in and between CPU and GPU code.
[ANTLR (ANother Tool for Language Recognition)](https://www.antlr.org/) is a powerful parser generator for reading, processing, executing, or translating structured text or binary files. It's widely used to build languages, tools, and frameworks. From a grammar, ANTLR generates a parser that can build parse trees and also generates a listener interface that makes it easy to respond to the recognition of phrases of interest.
[Oat++](https://oatpp.io/) is a light and powerful C++ web framework for highly scalable and resource-efficient web application. It's zero-dependency and easy-portable.
[JavaCPP](https://github.com/bytedeco/javacpp) is a program that provides efficient access to native C++ inside Java, not unlike the way some C/C++ compilers interact with assembly language.
[Cython](https://cython.org/) is a language that makes writing C extensions for Python as easy as Python itself. Cython is based on Pyrex, but supports more cutting edge functionality and optimizations such as calling C functions and declaring C types on variables and class attributes.
[Spdlog](https://github.com/gabime/spdlog) is a very fast, header-only/compiled, C++ logging library.
[Infer](https://fbinfer.com/) is a static analysis tool for Java, C++, Objective-C, and C. Infer is written in [OCaml](https://ocaml.org/).
## Contribute
- [x] If would you like to contribute to this guide simply make a [Pull Request](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide/pulls).
## License
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/DSP-Guide#table-of-contents)
Distributed under the [Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Public License](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).