https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide
MATLAB Guide
https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide
List: MATLAB-Guide
awesome awesome-list awesome-lists awesome-machine-learning awesome-matlab lists machine-learning mathematical-modelling matlab matlab-application matlab-bindings matlab-functions matlab-graphics matlab-gui matlab-image-processing-toolbox matlab-toolbox
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
MATLAB Guide
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide
- Owner: mikeroyal
- Created: 2020-09-25T19:03:15.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-04-03T19:04:46.000Z (about 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-05-23T09:21:47.813Z (about 1 year ago)
- Topics: awesome, awesome-list, awesome-lists, awesome-machine-learning, awesome-matlab, lists, machine-learning, mathematical-modelling, matlab, matlab-application, matlab-bindings, matlab-functions, matlab-graphics, matlab-gui, matlab-image-processing-toolbox, matlab-toolbox
- Language: MATLAB
- Homepage:
- Size: 178 KB
- Stars: 15
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 5
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- ultimate-awesome - MATLAB-Guide - MATLAB Guide. (Other Lists / Julia Lists)
README

MATLAB Guide
#### A guide covering MATLAB including the applications and tools that will make you a better and more efficient MATLAB developer.
**Note: You can easily convert this markdown file to a PDF in [VSCode](https://code.visualstudio.com/) using this handy extension [Markdown PDF](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=yzane.markdown-pdf).**

# Table of Contents
1. [MATLAB Learning Resources](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#MATLAB-Learning-Resources)
2. [MATLAB Tools](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#MATLAB-Tools)
3. [Machine Learning](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#Machine-Learning)
4. [Deep Learning Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#Deep-Learning-Development)
5. [Reinforcement Learning Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#Reinforcement-Learning-Development)
6. [Computer Vision Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#computer-vision-development)
7. [Natural Language Processing (NLP) Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#nlp-development)
8. [Bioinformatics](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#bioinformatics)
9. [Robotics](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#robotics)
10. [LiDAR](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#lidar-development)
11. [Photogrammetry](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#photogrammetry-development)
12. [CUDA Development](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#cuda-development)
13. [Linear Algebra](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#linear-algebra)
14. [Algorithms](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#algorithms)
# MATLAB Learning Resources
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)
[MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html) is a programming language that does numerical computing such as expressing matrix and array mathematics directly.

Creating a basic GUI in MATLAB
[MATLAB Documentation](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/)
[Getting Started with MATLAB ](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/getting-started-with-matlab.html)
### MATLAB & Simulink Training/Courses
- [MATLAB and Simulink Training from MATLAB Academy](https://matlabacademy.mathworks.com)
- [MathWorks Certification Program](https://www.mathworks.com/services/training/certification.html)
- [MATLAB Online Courses | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/matlab/)
- [MATLAB Online Courses | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=matlab)
- [MATLAB Online Courses | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/matlab)
- [MATLAB Essentials | edX](https://www.edx.org/course/matlab-essentials)
- [MATLAB Online Training Courses | LinkedIn Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/topics/matlab)
- [Introduction to MATLAB - MIT OpenCourseWare](https://ocw.mit.edu/resources/res-18-002-introduction-to-matlab-spring-2008/)
### MATLAB Tutorials & Books
- [Building a MATLAB GUI](https://www.mathworks.com/discovery/matlab-gui.html)
- [MATLAB Style Guidelines 2.0](https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/46056-matlab-style-guidelines-2-0)
- [Advanced Programming Techniques in MATLAB by Loren Shure (PDF)](https://www.mathworks.com/content/dam/mathworks/mathworks-dot-com/campaigns/portals/files/intel/may-12-2015-advanced-matlab.pdf)
- [Setting Up Git Source Control with MATLAB & Simulink](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/matlab_prog/set-up-git-source-control.html)
- [Pull, Push and Fetch Files with Git with MATLAB & Simulink](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/matlab_prog/push-and-fetch-with-git.html)
- [Create New Repository with MATLAB & Simulink](https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/matlab_prog/add-folder-to-source-control.html)
- [MATLAB GPU Computing Support for NVIDIA CUDA-Enabled GPUs](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/gpu-computing.html)
- [MATLAB for GPU Computing](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/gpu-computing/getting-started.html)
- [MATLAB Programming at Wikibooks](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/MATLAB_Programming)
- [MATLAB Quick Reference]() by Eric Peasley, Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford
- [PRMLT](http://prml.github.io/) is Matlab code for machine learning algorithms in the PRML book.
- [Awesome Matlab Robotics](https://github.com/mathworks-robotics/awesome-matlab-robotics) is a list of awesome demos, tutorials, utilities and overall resources for the robotics community that use MATLAB and Simulink.
- [Awesome MATLAB & Simulink Hackathons](https://github.com/mathworks/awesome-matlab-hackathons) is a resource center for hackathon participants!
# MATLAB Tools
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)
**[MATLAB and Simulink Services & Applications List](https://www.mathworks.com/products.html)**
[MATLAB in the Cloud](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/cloud.html) is a service that allows you to run in cloud environments from [MathWorks Cloud](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/cloud.html#browser) to [Public Clouds](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/cloud.html#public-cloud) including [AWS](https://aws.amazon.com/) and [Azure](https://azure.microsoft.com/).
[MATLAB Online™](https://matlab.mathworks.com) is a service that allows to users to uilitize MATLAB and Simulink through a web browser such as Google Chrome.
[Simulink](https://www.mathworks.com/products/simulink.html) is a block diagram environment for Model-Based Design. It supports simulation, automatic code generation, and continuous testing of embedded systems.
[Simulink Online™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/simulink-online.html) is a service that provides access to Simulink through your web browser.
[MATLAB Drive™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab-drive.html) is a service that gives you the ability to store, access, and work with your files from anywhere.
[MATLAB Parallel Server™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab-parallel-server.html) is a tool that lets you scale MATLAB® programs and Simulink® simulations to clusters and clouds. This alllows you to prototype your programs and simulations on the desktop and then run them on clusters and clouds without recoding. MATLAB Parallel Server supports batch jobs, interactive parallel computations, and distributed computations with large matrices.
[MATLAB Schemer](https://github.com/scottclowe/matlab-schemer) is a MATLAB package makes it easy to change the color scheme (theme) of the MATLAB display and GUI.
[LRSLibrary](https://github.com/andrewssobral/lrslibrary) is a Low-Rank and Sparse Tools for Background Modeling and Subtraction in Videos. The library was designed for moving object detection in videos, but it can be also used for other computer vision and machine learning problems.
[Gramm](https://github.com/piermorel/gramm) is a complete data visualization toolbox for Matlab. It provides an easy to use and high-level interface to produce publication-quality plots of complex data with varied statistical visualizations. Gramm is inspired by R's ggplot2 library.
[IFISS](https://www.maths.manchester.ac.uk/~djs/ifiss/) is a graphical package for the interactive numerical study of incompressible flow problems which can be run under MATLAB or Octave.
[Wavelab](https://statweb.stanford.edu/~wavelab/Wavelab_850/index_wavelab850.html) is a collection of MATLAB functions related to wavelet analysis.
[SEA-MAT](https://sea-mat.github.io/sea-mat/) is a collaborative effort to organize and distribute Matlab tools for the Oceanographic Community.
[hctsa](https://hctsa-users.gitbook.io/hctsa-manual) is a software package for running highly comparative time-series analysis using Matlab.
[Plotly](https://plot.ly/matlab/) is a Graphing Library for MATLAB.
[YALMIP](https://yalmip.github.io/) is a MATLAB toolbox for optimization modeling.
[OpenCL Toolbox](https://github.com/imaginairy-user/opencl-toolbox/) is a Toolbox that provides OpenCL support for MATLAB.
### MATLAB Toolboxes
- [Image Processing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/image.html) is a tool that provides a comprehensive set of reference-standard algorithms and workflow apps for image processing, analysis, visualization, and algorithm development. You can perform image segmentation, image enhancement, noise reduction, geometric transformations, image registration, and 3D image processing.
- [Computer Vision Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/computer-vision.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing and testing computer vision, 3D vision, and video processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, as well as feature detection, extraction, and matching.
- [Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/statistics.html) is a tool that provides functions and apps to describe, analyze, and model data. The toolbox let's you use descriptive statistics, visualizations, and clustering for exploratory data analysis; fit probability distributions to data; generate random numbers for Monte Carlo simulations, and perform hypothesis tests. Regression and classification algorithms let you draw inferences from data and build predictive models either interactively, using the Classification and Regression Learner apps, or programmatically, using AutoML.
- [Lidar Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/lidar.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing, analyzing, and testing lidar processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, semantic segmentation, shape fitting, lidar registration, and obstacle detection. Lidar Toolbox supports lidar-camera cross calibration for workflows that combine computer vision and lidar processing.
- [Mapping Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/mapping.html) is a tool that provides algorithms and functions for transforming geographic data and creating map displays. You can visualize your data in a geographic context, build map displays from more than 60 map projections, and transform data from a variety of sources into a consistent geographic coordinate system.
- [UAV Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/uav.html) is an application that provides tools and reference applications for designing, simulating, testing, and deploying unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and drone applications. It allows the user to design autonomous flight algorithms, UAV missions, and flight controllers. The Flight Log Analyzer app lets you interactively analyze 3D flight paths, telemetry information, and sensor readings from common flight log formats.
- [Parallel Computing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab-parallel-server.html) is a tool that lets you solve computationally and data-intensive problems using multicore processors, GPUs, and computer clusters. High-level constructs such as parallel for-loops, special array types, and parallelized numerical algorithms enable you to parallelize MATLAB® applications without CUDA or MPI programming. The toolbox lets you use parallel-enabled functions in MATLAB and other toolboxes. You can use the toolbox with Simulink® to run multiple simulations of a model in parallel.
- [Partial Differential Equation Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/pde.html) is a tool that provides functions for solving structural mechanics, heat transfer, and general partial differential equations (PDEs) using finite element analysis.
- [ROS Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/ros.html) is a tool that provides an interface connecting MATLAB® and Simulink® with the Robot Operating System (ROS & ROS 2), enabling you to create a network of ROS nodes. The toolbox includes MATLAB functions and Simulink blocks to import, analyze, and play back ROS data recorded in rosbag files. You can also connect to a live ROS network to access ROS messages.
- [Robotics Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/robotics.html) provides a toolbox that brings robotics specific functionality(designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots) to MATLAB, exploiting the native capabilities of MATLAB (linear algebra, portability, graphics). The toolbox also supports mobile robots with functions for robot motion models (bicycle), path planning algorithms (bug, distance transform, D*, PRM), kinodynamic planning (lattice, RRT), localization (EKF, particle filter), map building (EKF) and simultaneous localization and mapping (EKF), and a Simulink model a of non-holonomic vehicle.
- [Deep Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning.html) is a tool that provides a framework for designing and implementing deep neural networks with algorithms, pretrained models, and apps. You can use convolutional neural networks (ConvNets, CNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks to perform classification and regression on image, time-series, and text data. It can also build network architectures such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and Siamese networks using automatic differentiation, custom training loops, and shared weights.
- [Deep Learning HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning-hdl.html) is a tool that provides functions and tools to prototype and implement deep learning networks on FPGAs and SoCs. It provides pre-built bitstreams for running a variety of deep learning networks on supported Xilinx® and Intel® FPGA and SoC devices. Profiling and estimation tools let you customize a deep learning network by exploring design, performance, and resource utilization tradeoffs.
- [Reinforcement Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/reinforcement-learning.html) is a tool that provides an app, functions, and a Simulink® block for training policies using reinforcement learning algorithms, including DQN, PPO, SAC, and DDPG. You can use these policies to implement controllers and decision-making algorithms for complex applications such as resource allocation, robotics, and autonomous systems.
- [Model Predictive Control Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/model-predictive-control.html) is a tool that provides functions, an app, and Simulink® blocks for designing and simulating controllers using linear and nonlinear model predictive control (MPC). The toolbox lets you specify plant and disturbance models, horizons, constraints, and weights. By running closed-loop simulations, you can evaluate controller performance.
- [Vision HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/vision-hdl.html) is a tool that provides pixel-streaming algorithms for the design and implementation of vision systems on FPGAs and ASICs. It provides a design framework that supports a diverse set of interface types, frame sizes, and frame rates. The image processing, video, and computer vision algorithms in the toolbox use an architecture appropriate for HDL implementations.
- [SoC Blockset™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/soc.html) is a tool that provides Simulink® blocks and visualization tools for modeling, simulating, and analyzing hardware and software architectures for ASICs, FPGAs, and systems on a chip (SoC).
- [Wireless HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/wireless-hdl.html) is a tool that provides pre-verified, hardware-ready Simulink® blocks and subsystems for developing 5G, LTE, and custom OFDM-based wireless communication applications. It includes reference applications, IP blocks, and gateways between frame and sample-based processing.
- [ThingSpeak™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/thingspeak.html) is an IoT analytics service that allows you to aggregate, visualize, and analyze live data streams in the cloud. ThingSpeak provides instant visualizations of data posted by your devices to ThingSpeak. With the ability to execute MATLAB® code in ThingSpeak, you can perform online analysis and process data as it comes in. ThingSpeak is often used for prototyping and proof-of-concept IoT systems that require analytics.
[GNU Octave](https://www.gnu.org/software/octave/) is a high-level interpreted language, primarily intended for numerical computations. It provides capabilities for the numerical solution of linear and nonlinear problems, and for performing other numerical experiments. It also provides extensive graphics capabilities for data visualization and manipulation.
[Scilab](http://www.scilab.org/) is free and open source software for numerical computation providing a powerful computing environment for engineering and scientific applications.
[MathScript](https://www.ni.com/en-gb/support/downloads/software-products/download.labview-mathscript-module.html#345625) is an interpreter for MATLAB® code for the LabView programming language.
# Machine Learning
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Learning Resources for ML
[Machine Learning](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/machine-learning) is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) focused on building apps using algorithms that learn from data models and improve their accuracy over time without needing to be programmed.
[Machine Learning by Stanford University from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning)
[AWS Training and Certification for Machine Learning (ML) Courses](https://aws.amazon.com/training/learning-paths/machine-learning/)
[Machine Learning Scholarship Program for Microsoft Azure from Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/scholarships/machine-learning-scholarship-microsoft-azure)
[Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Scientist Associate](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/azure-data-scientist)
[Microsoft Certified: Azure AI Engineer Associate](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/azure-ai-engineer)
[Azure Machine Learning training and deployment](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/targets/azure-machine-learning)
[Learning Machine learning and artificial intelligence from Google Cloud Training](https://cloud.google.com/training/machinelearning-ai)
[Machine Learning Crash Course for Google Cloud](https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/)
[JupyterLab](https://jupyterlab.readthedocs.io/)
[Scheduling Jupyter notebooks on Amazon SageMaker ephemeral instances](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/machine-learning/scheduling-jupyter-notebooks-on-sagemaker-ephemeral-instances/)
[How to run Jupyter Notebooks in your Azure Machine Learning workspace](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/how-to-run-jupyter-notebooks)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/machine-learning/)
[Machine Learning Courses Online from Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=machine%20learning&)
[Learn Machine Learning with Online Courses and Classes from edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/machine-learning)
## ML Frameworks, Libraries, and Tools
[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org) is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
[Keras](https://keras.io) is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
[PyTorch](https://pytorch.org) is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab.
[Amazon SageMaker](https://aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/) is a fully managed service that provides every developer and data scientist with the ability to build, train, and deploy machine learning (ML) models quickly. SageMaker removes the heavy lifting from each step of the machine learning process to make it easier to develop high quality models.
[Azure Databricks](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/databricks/) is a fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering. Azure Databricks, sets up your Apache Spark environment in minutes, autoscale, and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace. Azure Databricks supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL, as well as data science frameworks and libraries including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
[Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cognitive-toolkit/) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
[Apple CoreML](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/coreml) is a framework that helps integrate machine learning models into your app. Core ML provides a unified representation for all models. Your app uses Core ML APIs and user data to make predictions, and to train or fine-tune models, all on the user's device. A model is the result of applying a machine learning algorithm to a set of training data. You use a model to make predictions based on new input data.
[Tensorflow_macOS](https://github.com/apple/tensorflow_macos) is a Mac-optimized version of TensorFlow and TensorFlow Addons for macOS 11.0+ accelerated using Apple's ML Compute framework.
[Apache OpenNLP](https://opennlp.apache.org/) is an open-source library for a machine learning based toolkit used in the processing of natural language text. It features an API for use cases like [Named Entity Recognition](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Named-entity_recognition), [Sentence Detection](), [POS(Part-Of-Speech) tagging](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Part-of-speech_tagging), [Tokenization](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tokenization_(data_security)) [Feature extraction](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feature_extraction), [Chunking](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chunking_(psychology)), [Parsing](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parsing), and [Coreference resolution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coreference).
[Apache Airflow](https://airflow.apache.org) is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
[Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX)](https://github.com/onnx) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
[Apache MXNet](https://mxnet.apache.org/) is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
[AutoGluon](https://autogluon.mxnet.io/index.html) is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
[Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/) is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
[PlaidML](https://github.com/plaidml/plaidml) is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
[Weka](https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/) is an open source machine learning software that can be accessed through a graphical user interface, standard terminal applications, or a Java API. It is widely used for teaching, research, and industrial applications, contains a plethora of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks, and additionally gives transparent access to well-known toolboxes such as scikit-learn, R, and Deeplearning4j.
[Caffe](https://github.com/BVLC/caffe) is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
[Theano](https://github.com/Theano/Theano) is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
[nGraph](https://github.com/NervanaSystems/ngraph) is an open source C++ library, compiler and runtime for Deep Learning. The nGraph Compiler aims to accelerate developing AI workloads using any deep learning framework and deploying to a variety of hardware targets.It provides the freedom, performance, and ease-of-use to AI developers.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[Jupyter Notebook](https://jupyter.org/) is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
[Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL](https://github.com/microsoft/sql-spark-connector) is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
[Apache PredictionIO](https://predictionio.apache.org/) is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
[Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK)](https://github.com/yahoo/CMAK) is a tool for managing [Apache Kafka](https://kafka.apache.org/) clusters.
[BigDL](https://bigdl-project.github.io/) is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
[Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J)](https://deeplearning4j.konduit.ai/) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
[Tensorman](https://github.com/pop-os/tensorman) is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by [System76]( https://system76.com).Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
[Numba](https://github.com/numba/numba) is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
[Chainer](https://chainer.org/) is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using [CuPy](https://github.com/cupy/cupy) for high performance training and inference.
[XGBoost](https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/) is an optimized distributed gradient boosting library designed to be highly efficient, flexible and portable. It implements machine learning algorithms under the Gradient Boosting framework. XGBoost provides a parallel tree boosting (also known as GBDT, GBM) that solve many data science problems in a fast and accurate way. It supports distributed training on multiple machines, including AWS, GCE, Azure, and Yarn clusters. Also, it can be integrated with Flink, Spark and other cloud dataflow systems.
[cuML](https://github.com/rapidsai/cuml) is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
# Deep Learning Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Deep Learning Learning Resources
[Deep Learning](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/deep-learning) is a subset of machine learning, which is essentially a neural network with three or more layers. These neural networks attempt to simulate the behavior of the human brain,though, far from matching its ability. This allows the neural networks to "learn" from large amounts of data. The Learning can be [supervised](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supervised_learning), [semi-supervised](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semi-supervised_learning) or [unsupervised](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unsupervised_learning).
[Deep Learning Online Courses | NVIDIA](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/training/online/)
[Top Deep Learning Courses Online | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=deep%20learning)
[Top Deep Learning Courses Online | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/deep-learning/)
[Learn Deep Learning with Online Courses and Lessons | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/deep-learning)
[Deep Learning Online Course Nanodegree | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/deep-learning-nanodegree--nd101)
[Machine Learning Course by Andrew Ng | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning?)
[Machine Learning Engineering for Production (MLOps) course by Andrew Ng | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/specializations/machine-learning-engineering-for-production-mlops)
[Data Science: Deep Learning and Neural Networks in Python | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/data-science-deep-learning-in-python/)
[Understanding Machine Learning with Python | Pluralsight ](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/python-understanding-machine-learning)
[How to Think About Machine Learning Algorithms | Pluralsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/machine-learning-algorithms)
[Deep Learning Courses | Stanford Online](https://online.stanford.edu/courses/cs230-deep-learning)
[Deep Learning - UW Professional & Continuing Education](https://www.pce.uw.edu/courses/deep-learning)
[Deep Learning Online Courses | Harvard University](https://online-learning.harvard.edu/course/deep-learning-0)
[Machine Learning for Everyone Courses | DataCamp](https://www.datacamp.com/courses/introduction-to-machine-learning-with-r)
[Artificial Intelligence Expert Course: Platinum Edition | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/artificial-intelligence-exposed-future-10-extreme-edition/)
[Top Artificial Intelligence Courses Online | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=artificial%20intelligence)
[Learn Artificial Intelligence with Online Courses and Lessons | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/artificial-intelligence)
[Professional Certificate in Computer Science for Artificial Intelligence | edX](https://www.edx.org/professional-certificate/harvardx-computer-science-for-artifical-intelligence)
[Artificial Intelligence Nanodegree program](https://www.udacity.com/course/ai-artificial-intelligence-nanodegree--nd898)
[Artificial Intelligence (AI) Online Courses | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/school-of-ai)
[Intro to Artificial Intelligence Course | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/intro-to-artificial-intelligence--cs271)
[Edge AI for IoT Developers Course | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/intel-edge-ai-for-iot-developers-nanodegree--nd131)
[Reasoning: Goal Trees and Rule-Based Expert Systems | MIT OpenCourseWare](https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-034-artificial-intelligence-fall-2010/lecture-videos/lecture-3-reasoning-goal-trees-and-rule-based-expert-systems/)
[Expert Systems and Applied Artificial Intelligence](https://www.umsl.edu/~joshik/msis480/chapt11.htm)
[Autonomous Systems - Microsoft AI](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/ai/autonomous-systems)
[Introduction to Microsoft Project Bonsai](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/autonomous-systems/intro-to-project-bonsai/)
[Machine teaching with the Microsoft Autonomous Systems platform](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/solution-ideas/articles/autonomous-systems)
[Autonomous Maritime Systems Training | AMC Search](https://www.amcsearch.com.au/ams-training)
[Top Autonomous Cars Courses Online | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/autonomous-cars/)
[Applied Control Systems 1: autonomous cars: Math + PID + MPC | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/applied-systems-control-for-engineers-modelling-pid-mpc/)
[Learn Autonomous Robotics with Online Courses and Lessons | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/autonomous-robotics)
[Artificial Intelligence Nanodegree program](https://www.udacity.com/course/ai-artificial-intelligence-nanodegree--nd898)
[Autonomous Systems Online Courses & Programs | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/school-of-autonomous-systems)
[Edge AI for IoT Developers Course | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/intel-edge-ai-for-iot-developers-nanodegree--nd131)
[Autonomous Systems MOOC and Free Online Courses | MOOC List](https://www.mooc-list.com/tags/autonomous-systems)
[Robotics and Autonomous Systems Graduate Program | Standford Online](https://online.stanford.edu/programs/robotics-and-autonomous-systems-graduate-program)
[Mobile Autonomous Systems Laboratory | MIT OpenCourseWare](https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-186-mobile-autonomous-systems-laboratory-january-iap-2005/lecture-notes/)
## Deep Learning Tools, Libraries, and Frameworks
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[NVIDIA DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling)](https://developer.nvidia.com/dlss) is a temporal image upscaling AI rendering technology that increases graphics performance using dedicated Tensor Core AI processors on GeForce RTX™ GPUs. DLSS uses the power of a deep learning neural network to boost frame rates and generate beautiful, sharp images for your games.
[AMD FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR)](https://www.amd.com/en/technologies/radeon-software-fidelityfx) is an open source, high-quality solution for producing high resolution frames from lower resolution inputs. It uses a collection of cutting-edge Deep Learning algorithms with a particular emphasis on creating high-quality edges, giving large performance improvements compared to rendering at native resolution directly. FSR enables “practical performance” for costly render operations, such as hardware ray tracing for the AMD RDNA™ and AMD RDNA™ 2 architectures.
[Intel Xe Super Sampling (XeSS)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y9hfpf-SqEg) is a temporal image upscaling AI rendering technology that increases graphics performance similar to NVIDIA's [DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling)](https://developer.nvidia.com/dlss). Intel's Arc GPU architecture (early 2022) will have GPUs that feature dedicated Xe-cores to run XeSS. The GPUs will have Xe Matrix eXtenstions matrix (XMX) engines for hardware-accelerated AI processing. XeSS will be able to run on devices without XMX, including integrated graphics, though, the performance of XeSS will be lower on non-Intel graphics cards because it will be powered by [DP4a instruction](https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/reference-guides/11th-gen-quick-reference-guide.pdf).
[Jupyter Notebook](https://jupyter.org/) is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
[Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL](https://github.com/microsoft/sql-spark-connector) is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
[Apache PredictionIO](https://predictionio.apache.org/) is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
[Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK)](https://github.com/yahoo/CMAK) is a tool for managing [Apache Kafka](https://kafka.apache.org/) clusters.
[BigDL](https://bigdl-project.github.io/) is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
[Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J)](https://deeplearning4j.konduit.ai/) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
[Deep Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning.html) is a tool that provides a framework for designing and implementing deep neural networks with algorithms, pretrained models, and apps. You can use convolutional neural networks (ConvNets, CNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks to perform classification and regression on image, time-series, and text data. You can build network architectures such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and Siamese networks using automatic differentiation, custom training loops, and shared weights. With the Deep Network Designer app, you can design, analyze, and train networks graphically. It can exchange models with TensorFlow™ and PyTorch through the ONNX format and import models from TensorFlow-Keras and Caffe. The toolbox supports transfer learning with DarkNet-53, ResNet-50, NASNet, SqueezeNet and many other pretrained models.
[Reinforcement Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/reinforcement-learning.html) is a tool that provides an app, functions, and a Simulink® block for training policies using reinforcement learning algorithms, including DQN, PPO, SAC, and DDPG. You can use these policies to implement controllers and decision-making algorithms for complex applications such as resource allocation, robotics, and autonomous systems.
[Deep Learning HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning-hdl.html) is a tool that provides functions and tools to prototype and implement deep learning networks on FPGAs and SoCs. It provides pre-built bitstreams for running a variety of deep learning networks on supported Xilinx® and Intel® FPGA and SoC devices. Profiling and estimation tools let you customize a deep learning network by exploring design, performance, and resource utilization tradeoffs.
[Parallel Computing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab-parallel-server.html) is a tool that lets you solve computationally and data-intensive problems using multicore processors, GPUs, and computer clusters. High-level constructs such as parallel for-loops, special array types, and parallelized numerical algorithms enable you to parallelize MATLAB® applications without CUDA or MPI programming. The toolbox lets you use parallel-enabled functions in MATLAB and other toolboxes. You can use the toolbox with Simulink® to run multiple simulations of a model in parallel. Programs and models can run in both interactive and batch modes.
[XGBoost](https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/) is an optimized distributed gradient boosting library designed to be highly efficient, flexible and portable. It implements machine learning algorithms under the Gradient Boosting framework. XGBoost provides a parallel tree boosting (also known as GBDT, GBM) that solve many data science problems in a fast and accurate way. It supports distributed training on multiple machines, including AWS, GCE, Azure, and Yarn clusters. Also, it can be integrated with Flink, Spark and other cloud dataflow systems.
[LIBSVM](https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/) is an integrated software for support vector classification, (C-SVC, nu-SVC), regression (epsilon-SVR, nu-SVR) and distribution estimation (one-class SVM). It supports multi-class classification.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a simple and efficient tool for data mining and data analysis. It is built on NumPy,SciPy, and mathplotlib.
[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org) is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
[Keras](https://keras.io) is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
[PyTorch](https://pytorch.org) is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab.
[Azure Databricks](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/databricks/) is a fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering. Azure Databricks, sets up your Apache Spark environment in minutes, autoscale, and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace. Azure Databricks supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL, as well as data science frameworks and libraries including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
[Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cognitive-toolkit/) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
[Tensorflow_macOS](https://github.com/apple/tensorflow_macos) is a Mac-optimized version of TensorFlow and TensorFlow Addons for macOS 11.0+ accelerated using Apple's ML Compute framework.
[Apache Airflow](https://airflow.apache.org) is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
[Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX)](https://github.com/onnx) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
[Apache MXNet](https://mxnet.apache.org/) is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
[AutoGluon](https://autogluon.mxnet.io/index.html) is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
[Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/) is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
[PlaidML](https://github.com/plaidml/plaidml) is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
[Weka](https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/) is an open source machine learning software that can be accessed through a graphical user interface, standard terminal applications, or a Java API. It is widely used for teaching, research, and industrial applications, contains a plethora of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks, and additionally gives transparent access to well-known toolboxes such as scikit-learn, R, and Deeplearning4j.
[Caffe](https://github.com/BVLC/caffe) is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
[Theano](https://github.com/Theano/Theano) is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
[Microsoft Project Bonsai](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/project-bonsai/) is a low-code AI platform that speeds AI-powered automation development and part of the Autonomous Systems suite from Microsoft. Bonsai is used to build AI components that can provide operator guidance or make independent decisions to optimize process variables, improve production efficiency, and reduce downtime.
[Microsoft AirSim](https://microsoft.github.io/AirSim/lidar.html) is a simulator for drones, cars and more, built on Unreal Engine (with an experimental Unity release). AirSim is open-source, cross platform, and supports [software-in-the-loop simulation](https://www.mathworks.com/help///ecoder/software-in-the-loop-sil-simulation.html) with popular flight controllers such as PX4 & ArduPilot and [hardware-in-loop](https://www.ni.com/en-us/innovations/white-papers/17/what-is-hardware-in-the-loop-.html) with PX4 for physically and visually realistic simulations. It is developed as an Unreal plugin that can simply be dropped into any Unreal environment. AirSim is being developed as a platform for AI research to experiment with deep learning, computer vision and reinforcement learning algorithms for autonomous vehicles.
[CARLA](https://github.com/carla-simulator/carla) is an open-source simulator for autonomous driving research. CARLA has been developed from the ground up to support development, training, and validation of autonomous driving systems. In addition to open-source code and protocols, CARLA provides open digital assets (urban layouts, buildings, vehicles) that were created for this purpose and can be used freely.
[ROS/ROS2 bridge for CARLA(package)](https://github.com/carla-simulator/ros-bridge) is a bridge that enables two-way communication between ROS and CARLA. The information from the CARLA server is translated to ROS topics. In the same way, the messages sent between nodes in ROS get translated to commands to be applied in CARLA.
[ROS Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/ros.html) is a tool that provides an interface connecting MATLAB® and Simulink® with the Robot Operating System (ROS and ROS 2), enabling you to create a network of ROS nodes. The toolbox includes MATLAB functions and Simulink blocks to import, analyze, and play back ROS data recorded in rosbag files. You can also connect to a live ROS network to access ROS messages.
[Robotics Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/robotics.html) provides a toolbox that brings robotics specific functionality(designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots) to MATLAB, exploiting the native capabilities of MATLAB (linear algebra, portability, graphics). The toolbox also supports mobile robots with functions for robot motion models (bicycle), path planning algorithms (bug, distance transform, D*, PRM), kinodynamic planning (lattice, RRT), localization (EKF, particle filter), map building (EKF) and simultaneous localization and mapping (EKF), and a Simulink model a of non-holonomic vehicle.
[Image Processing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/image.html) is a tool that provides a comprehensive set of reference-standard algorithms and workflow apps for image processing, analysis, visualization, and algorithm development. You can perform image segmentation, image enhancement, noise reduction, geometric transformations, image registration, and 3D image processing.
[Computer Vision Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/computer-vision.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing and testing computer vision, 3D vision, and video processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, as well as feature detection, extraction, and matching. You can automate calibration workflows for single, stereo, and fisheye cameras. For 3D vision, the toolbox supports visual and point cloud SLAM, stereo vision, structure from motion, and point cloud processing.
[Robotics Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/robotics.html) is a tool that provides a toolbox that brings robotics specific functionality(designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots) to MATLAB, exploiting the native capabilities of MATLAB (linear algebra, portability, graphics). The toolbox also supports mobile robots with functions for robot motion models (bicycle), path planning algorithms (bug, distance transform, D*, PRM), kinodynamic planning (lattice, RRT), localization (EKF, particle filter), map building (EKF) and simultaneous localization and mapping (EKF), and a Simulink model a of non-holonomic vehicle.
[Model Predictive Control Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/model-predictive-control.html) is a tool that provides functions, an app, and Simulink® blocks for designing and simulating controllers using linear and nonlinear model predictive control (MPC). The toolbox lets you specify plant and disturbance models, horizons, constraints, and weights. By running closed-loop simulations, you can evaluate controller performance.
[Predictive Maintenance Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/predictive-maintenance.html) is a tool that lets you manage sensor data, design condition indicators, and estimate the remaining useful life (RUL) of a machine. The toolbox provides functions and an interactive app for exploring, extracting, and ranking features using data-based and model-based techniques, including statistical, spectral, and time-series analysis.
[Vision HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/vision-hdl.html) is a tool that provides pixel-streaming algorithms for the design and implementation of vision systems on FPGAs and ASICs. It provides a design framework that supports a diverse set of interface types, frame sizes, and frame rates. The image processing, video, and computer vision algorithms in the toolbox use an architecture appropriate for HDL implementations.
[Automated Driving Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/automated-driving.html) is a MATLAB tool that provides algorithms and tools for designing, simulating, and testing ADAS and autonomous driving systems. You can design and test vision and lidar perception systems, as well as sensor fusion, path planning, and vehicle controllers. Visualization tools include a bird’s-eye-view plot and scope for sensor coverage, detections and tracks, and displays for video, lidar, and maps. The toolbox lets you import and work with HERE HD Live Map data and OpenDRIVE® road networks. It also provides reference application examples for common ADAS and automated driving features, including FCW, AEB, ACC, LKA, and parking valet.
[UAV Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/uav.html) is an application that provides tools and reference applications for designing, simulating, testing, and deploying unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and drone applications. You can design autonomous flight algorithms, UAV missions, and flight controllers. The Flight Log Analyzer app lets you interactively analyze 3D flight paths, telemetry information, and sensor readings from common flight log formats.
[Navigation Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/navigation.html) is a tool that provides algorithms and analysis tools for motion planning, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), and inertial navigation. The toolbox includes customizable search and sampling-based path planners, as well as metrics for validating and comparing paths. You can create 2D and 3D map representations, generate maps using SLAM algorithms, and interactively visualize and debug map generation with the SLAM map builder app.
[Lidar Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/lidar.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing, analyzing, and testing lidar processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, semantic segmentation, shape fitting, lidar registration, and obstacle detection. Lidar Toolbox supports lidar-camera cross calibration for workflows that combine computer vision and lidar processing.
[Mapping Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/mapping.html) is a tool that provides algorithms and functions for transforming geographic data and creating map displays. You can visualize your data in a geographic context, build map displays from more than 60 map projections, and transform data from a variety of sources into a consistent geographic coordinate system.
# Reinforcement Learning Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Reinforcement Learning Learning Resources
[Reinforcement Learning](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/deep-learning#toc-deep-learn-md_Q_Of3) is a subset of machine learning, which is a neural network with three or more layers. These neural networks attempt to simulate the behavior of the human brain,though, far from matching its ability. This allows the neural networks to "learn" from a process in which a model learns to become more accurate for performing an action in an environment based on feedback in order to maximize the reward. The Learning can be [supervised](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supervised_learning), [semi-supervised](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Semi-supervised_learning) or [unsupervised](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unsupervised_learning).
[Top Reinforcement Learning Courses | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=reinforcement%20learning)
[Top Reinforcement Learning Courses | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/reinforcement-learning/)
[Top Reinforcement Learning Courses | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/reinforcement-learning--ud600)
[Reinforcement Learning Courses | Stanford Online](https://online.stanford.edu/courses/xcs234-reinforcement-learning)
[Deep Learning Online Courses | NVIDIA](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/training/online/)
[Top Deep Learning Courses Online | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=deep%20learning)
[Top Deep Learning Courses Online | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/deep-learning/)
[Learn Deep Learning with Online Courses and Lessons | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/deep-learning)
[Deep Learning Online Course Nanodegree | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/deep-learning-nanodegree--nd101)
[Machine Learning Course by Andrew Ng | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning?)
[Machine Learning Engineering for Production (MLOps) course by Andrew Ng | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/specializations/machine-learning-engineering-for-production-mlops)
[Data Science: Deep Learning and Neural Networks in Python | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/data-science-deep-learning-in-python/)
[Understanding Machine Learning with Python | Pluralsight ](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/python-understanding-machine-learning)
[How to Think About Machine Learning Algorithms | Pluralsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/machine-learning-algorithms)
[Deep Learning Courses | Stanford Online](https://online.stanford.edu/courses/cs230-deep-learning)
[Deep Learning - UW Professional & Continuing Education](https://www.pce.uw.edu/courses/deep-learning)
[Deep Learning Online Courses | Harvard University](https://online-learning.harvard.edu/course/deep-learning-0)
[Machine Learning for Everyone Courses | DataCamp](https://www.datacamp.com/courses/introduction-to-machine-learning-with-r)
[Artificial Intelligence Expert Course: Platinum Edition | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/artificial-intelligence-exposed-future-10-extreme-edition/)
[Top Artificial Intelligence Courses Online | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=artificial%20intelligence)
[Learn Artificial Intelligence with Online Courses and Lessons | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/artificial-intelligence)
[Professional Certificate in Computer Science for Artificial Intelligence | edX](https://www.edx.org/professional-certificate/harvardx-computer-science-for-artifical-intelligence)
[Artificial Intelligence Nanodegree program](https://www.udacity.com/course/ai-artificial-intelligence-nanodegree--nd898)
[Artificial Intelligence (AI) Online Courses | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/school-of-ai)
[Intro to Artificial Intelligence Course | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/intro-to-artificial-intelligence--cs271)
[Edge AI for IoT Developers Course | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/intel-edge-ai-for-iot-developers-nanodegree--nd131)
[Reasoning: Goal Trees and Rule-Based Expert Systems | MIT OpenCourseWare](https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-034-artificial-intelligence-fall-2010/lecture-videos/lecture-3-reasoning-goal-trees-and-rule-based-expert-systems/)
[Expert Systems and Applied Artificial Intelligence](https://www.umsl.edu/~joshik/msis480/chapt11.htm)
[Autonomous Systems - Microsoft AI](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/ai/autonomous-systems)
[Introduction to Microsoft Project Bonsai](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/autonomous-systems/intro-to-project-bonsai/)
[Machine teaching with the Microsoft Autonomous Systems platform](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/solution-ideas/articles/autonomous-systems)
[Autonomous Maritime Systems Training | AMC Search](https://www.amcsearch.com.au/ams-training)
[Top Autonomous Cars Courses Online | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/autonomous-cars/)
[Applied Control Systems 1: autonomous cars: Math + PID + MPC | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/applied-systems-control-for-engineers-modelling-pid-mpc/)
[Learn Autonomous Robotics with Online Courses and Lessons | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/autonomous-robotics)
[Artificial Intelligence Nanodegree program](https://www.udacity.com/course/ai-artificial-intelligence-nanodegree--nd898)
[Autonomous Systems Online Courses & Programs | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/school-of-autonomous-systems)
[Edge AI for IoT Developers Course | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/intel-edge-ai-for-iot-developers-nanodegree--nd131)
[Autonomous Systems MOOC and Free Online Courses | MOOC List](https://www.mooc-list.com/tags/autonomous-systems)
[Robotics and Autonomous Systems Graduate Program | Standford Online](https://online.stanford.edu/programs/robotics-and-autonomous-systems-graduate-program)
[Mobile Autonomous Systems Laboratory | MIT OpenCourseWare](https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-186-mobile-autonomous-systems-laboratory-january-iap-2005/lecture-notes/)
## Reinforcement Learning Tools, Libraries, and Frameworks
[OpenAI](https://gym.openai.com/) is an open source Python library for developing and comparing reinforcement learning algorithms by providing a standard API to communicate between learning algorithms and environments, as well as a standard set of environments compliant with that API.
[ReinforcementLearning.jl](https://juliareinforcementlearning.org/) is a collection of tools for doing reinforcement learning research in Julia.
[Reinforcement Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/reinforcement-learning.html) is a tool that provides an app, functions, and a Simulink® block for training policies using reinforcement learning algorithms, including DQN, PPO, SAC, and DDPG. You can use these policies to implement controllers and decision-making algorithms for complex applications such as resource allocation, robotics, and autonomous systems.
[Amazon SageMaker](https://aws.amazon.com/robomaker/) is a fully managed service that provides every developer and data scientist with the ability to build, train, and deploy machine learning (ML) models quickly.
[AWS RoboMaker](https://aws.amazon.com/robomaker/) is a service that provides a fully-managed, scalable infrastructure for simulation that customers use for multi-robot simulation and CI/CD integration with regression testing in simulation.
[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org) is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
[Keras](https://keras.io) is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
[PyTorch](https://pytorch.org) is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a simple and efficient tool for data mining and data analysis. It is built on NumPy,SciPy, and mathplotlib.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[Jupyter Notebook](https://jupyter.org/) is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
[Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL](https://github.com/microsoft/sql-spark-connector) is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
[Apache PredictionIO](https://predictionio.apache.org/) is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
[Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK)](https://github.com/yahoo/CMAK) is a tool for managing [Apache Kafka](https://kafka.apache.org/) clusters.
[BigDL](https://bigdl-project.github.io/) is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
[Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J)](https://deeplearning4j.konduit.ai/) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
[Deep Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning.html) is a tool that provides a framework for designing and implementing deep neural networks with algorithms, pretrained models, and apps. You can use convolutional neural networks (ConvNets, CNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks to perform classification and regression on image, time-series, and text data. You can build network architectures such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and Siamese networks using automatic differentiation, custom training loops, and shared weights. With the Deep Network Designer app, you can design, analyze, and train networks graphically. It can exchange models with TensorFlow™ and PyTorch through the ONNX format and import models from TensorFlow-Keras and Caffe. The toolbox supports transfer learning with DarkNet-53, ResNet-50, NASNet, SqueezeNet and many other pretrained models.
[Deep Learning HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning-hdl.html) is a tool that provides functions and tools to prototype and implement deep learning networks on FPGAs and SoCs. It provides pre-built bitstreams for running a variety of deep learning networks on supported Xilinx® and Intel® FPGA and SoC devices. Profiling and estimation tools let you customize a deep learning network by exploring design, performance, and resource utilization tradeoffs.
[Parallel Computing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab-parallel-server.html) is a tool that lets you solve computationally and data-intensive problems using multicore processors, GPUs, and computer clusters. High-level constructs such as parallel for-loops, special array types, and parallelized numerical algorithms enable you to parallelize MATLAB® applications without CUDA or MPI programming. The toolbox lets you use parallel-enabled functions in MATLAB and other toolboxes. You can use the toolbox with Simulink® to run multiple simulations of a model in parallel. Programs and models can run in both interactive and batch modes.
[XGBoost](https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/) is an optimized distributed gradient boosting library designed to be highly efficient, flexible and portable. It implements machine learning algorithms under the Gradient Boosting framework. XGBoost provides a parallel tree boosting (also known as GBDT, GBM) that solve many data science problems in a fast and accurate way. It supports distributed training on multiple machines, including AWS, GCE, Azure, and Yarn clusters. Also, it can be integrated with Flink, Spark and other cloud dataflow systems.
[LIBSVM](https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/) is an integrated software for support vector classification, (C-SVC, nu-SVC), regression (epsilon-SVR, nu-SVR) and distribution estimation (one-class SVM). It supports multi-class classification.
[Azure Databricks](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/databricks/) is a fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering. Azure Databricks, sets up your Apache Spark environment in minutes, autoscale, and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace. Azure Databricks supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL, as well as data science frameworks and libraries including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
[Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cognitive-toolkit/) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
[Tensorflow_macOS](https://github.com/apple/tensorflow_macos) is a Mac-optimized version of TensorFlow and TensorFlow Addons for macOS 11.0+ accelerated using Apple's ML Compute framework.
[Apache Airflow](https://airflow.apache.org) is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
[Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX)](https://github.com/onnx) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
[Apache MXNet](https://mxnet.apache.org/) is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
[AutoGluon](https://autogluon.mxnet.io/index.html) is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
[Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/) is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
[PlaidML](https://github.com/plaidml/plaidml) is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
[Weka](https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/) is an open source machine learning software that can be accessed through a graphical user interface, standard terminal applications, or a Java API. It is widely used for teaching, research, and industrial applications, contains a plethora of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks, and additionally gives transparent access to well-known toolboxes such as scikit-learn, R, and Deeplearning4j.
[Caffe](https://github.com/BVLC/caffe) is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
[Theano](https://github.com/Theano/Theano) is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
[Microsoft Project Bonsai](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/project-bonsai/) is a low-code AI platform that speeds AI-powered automation development and part of the Autonomous Systems suite from Microsoft. Bonsai is used to build AI components that can provide operator guidance or make independent decisions to optimize process variables, improve production efficiency, and reduce downtime.
[Microsoft AirSim](https://microsoft.github.io/AirSim/lidar.html) is a simulator for drones, cars and more, built on Unreal Engine (with an experimental Unity release). AirSim is open-source, cross platform, and supports [software-in-the-loop simulation](https://www.mathworks.com/help///ecoder/software-in-the-loop-sil-simulation.html) with popular flight controllers such as PX4 & ArduPilot and [hardware-in-loop](https://www.ni.com/en-us/innovations/white-papers/17/what-is-hardware-in-the-loop-.html) with PX4 for physically and visually realistic simulations. It is developed as an Unreal plugin that can simply be dropped into any Unreal environment. AirSim is being developed as a platform for AI research to experiment with deep learning, computer vision and reinforcement learning algorithms for autonomous vehicles.
[CARLA](https://github.com/carla-simulator/carla) is an open-source simulator for autonomous driving research. CARLA has been developed from the ground up to support development, training, and validation of autonomous driving systems. In addition to open-source code and protocols, CARLA provides open digital assets (urban layouts, buildings, vehicles) that were created for this purpose and can be used freely.
[ROS/ROS2 bridge for CARLA(package)](https://github.com/carla-simulator/ros-bridge) is a bridge that enables two-way communication between ROS and CARLA. The information from the CARLA server is translated to ROS topics. In the same way, the messages sent between nodes in ROS get translated to commands to be applied in CARLA.
[ROS Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/ros.html) is a tool that provides an interface connecting MATLAB® and Simulink® with the Robot Operating System (ROS and ROS 2), enabling you to create a network of ROS nodes. The toolbox includes MATLAB functions and Simulink blocks to import, analyze, and play back ROS data recorded in rosbag files. You can also connect to a live ROS network to access ROS messages.
[Robotics Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/robotics.html) provides a toolbox that brings robotics specific functionality(designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots) to MATLAB, exploiting the native capabilities of MATLAB (linear algebra, portability, graphics). The toolbox also supports mobile robots with functions for robot motion models (bicycle), path planning algorithms (bug, distance transform, D*, PRM), kinodynamic planning (lattice, RRT), localization (EKF, particle filter), map building (EKF) and simultaneous localization and mapping (EKF), and a Simulink model a of non-holonomic vehicle. The Toolbox also including a detailed Simulink model for a quadrotor flying robot.
[Image Processing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/image.html) is a tool that provides a comprehensive set of reference-standard algorithms and workflow apps for image processing, analysis, visualization, and algorithm development. You can perform image segmentation, image enhancement, noise reduction, geometric transformations, image registration, and 3D image processing.
[Computer Vision Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/computer-vision.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing and testing computer vision, 3D vision, and video processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, as well as feature detection, extraction, and matching. You can automate calibration workflows for single, stereo, and fisheye cameras. For 3D vision, the toolbox supports visual and point cloud SLAM, stereo vision, structure from motion, and point cloud processing.
[Robotics Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/robotics.html) is a tool that provides a toolbox that brings robotics specific functionality(designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots) to MATLAB, exploiting the native capabilities of MATLAB (linear algebra, portability, graphics). The toolbox also supports mobile robots with functions for robot motion models (bicycle), path planning algorithms (bug, distance transform, D*, PRM), kinodynamic planning (lattice, RRT), localization (EKF, particle filter), map building (EKF) and simultaneous localization and mapping (EKF), and a Simulink model a of non-holonomic vehicle. The Toolbox also including a detailed Simulink model for a quadrotor flying robot.
[Model Predictive Control Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/model-predictive-control.html) is a tool that provides functions, an app, and Simulink® blocks for designing and simulating controllers using linear and nonlinear model predictive control (MPC). The toolbox lets you specify plant and disturbance models, horizons, constraints, and weights. By running closed-loop simulations, you can evaluate controller performance.
[Predictive Maintenance Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/predictive-maintenance.html) is a tool that lets you manage sensor data, design condition indicators, and estimate the remaining useful life (RUL) of a machine. The toolbox provides functions and an interactive app for exploring, extracting, and ranking features using data-based and model-based techniques, including statistical, spectral, and time-series analysis.
[Vision HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/vision-hdl.html) is a tool that provides pixel-streaming algorithms for the design and implementation of vision systems on FPGAs and ASICs. It provides a design framework that supports a diverse set of interface types, frame sizes, and frame rates. The image processing, video, and computer vision algorithms in the toolbox use an architecture appropriate for HDL implementations.
[Automated Driving Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/automated-driving.html) is a MATLAB tool that provides algorithms and tools for designing, simulating, and testing ADAS and autonomous driving systems. You can design and test vision and lidar perception systems, as well as sensor fusion, path planning, and vehicle controllers. Visualization tools include a bird’s-eye-view plot and scope for sensor coverage, detections and tracks, and displays for video, lidar, and maps. The toolbox lets you import and work with HERE HD Live Map data and OpenDRIVE® road networks. It also provides reference application examples for common ADAS and automated driving features, including FCW, AEB, ACC, LKA, and parking valet. The toolbox supports C/C++ code generation for rapid prototyping and HIL testing, with support for sensor fusion, tracking, path planning, and vehicle controller algorithms.
[Navigation Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/navigation.html) is a tool that provides algorithms and analysis tools for motion planning, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), and inertial navigation. The toolbox includes customizable search and sampling-based path planners, as well as metrics for validating and comparing paths. You can create 2D and 3D map representations, generate maps using SLAM algorithms, and interactively visualize and debug map generation with the SLAM map builder app.
[UAV Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/uav.html) is an application that provides tools and reference applications for designing, simulating, testing, and deploying unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and drone applications. You can design autonomous flight algorithms, UAV missions, and flight controllers. The Flight Log Analyzer app lets you interactively analyze 3D flight paths, telemetry information, and sensor readings from common flight log formats.
[Lidar Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/lidar.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing, analyzing, and testing lidar processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, semantic segmentation, shape fitting, lidar registration, and obstacle detection. Lidar Toolbox supports lidar-camera cross calibration for workflows that combine computer vision and lidar processing.
[Mapping Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/mapping.html) is a tool that provides algorithms and functions for transforming geographic data and creating map displays. You can visualize your data in a geographic context, build map displays from more than 60 map projections, and transform data from a variety of sources into a consistent geographic coordinate system.
# Computer Vision Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)
## Computer Vision Learning Resources
[Computer Vision](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/overview/what-is-computer-vision/) is a field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that focuses on enabling computers to identify and understand objects and people in images and videos.
[OpenCV Courses](https://opencv.org/courses/)
[Exploring Computer Vision in Microsoft Azure](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/explore-computer-vision-microsoft-azure/)
[Top Computer Vision Courses Online | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?languages=en&query=computer%20vision)
[Top Computer Vision Courses Online | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/computer-vision/)
[Learn Computer Vision with Online Courses and Lessons | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/computer-vision)
[Computer Vision and Image Processing Fundamentals | edX](https://www.edx.org/course/computer-vision-and-image-processing-fundamentals)
[Introduction to Computer Vision Courses | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/introduction-to-computer-vision--ud810)
[Computer Vision Nanodegree program | Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/computer-vision-nanodegree--nd891)
[Machine Vision Course |MIT Open Courseware ](https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-801-machine-vision-fall-2004/)
[Computer Vision Training Courses | NobleProg](https://www.nobleprog.com/computer-vision-training)
[Visual Computing Graduate Program | Stanford Online](https://online.stanford.edu/programs/visual-computing-graduate-program)
## Computer Vision Tools, Libraries, and Frameworks
[OpenCV](https://opencv.org) is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
[Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cognitive-toolkit/) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[Automated Driving Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/automated-driving.html) is a MATLAB tool that provides algorithms and tools for designing, simulating, and testing ADAS and autonomous driving systems. You can design and test vision and lidar perception systems, as well as sensor fusion, path planning, and vehicle controllers. Visualization tools include a bird’s-eye-view plot and scope for sensor coverage, detections and tracks, and displays for video, lidar, and maps. The toolbox lets you import and work with HERE HD Live Map data and OpenDRIVE® road networks. It also provides reference application examples for common ADAS and automated driving features, including FCW, AEB, ACC, LKA, and parking valet. The toolbox supports C/C++ code generation for rapid prototyping and HIL testing, with support for sensor fusion, tracking, path planning, and vehicle controller algorithms.
[LRSLibrary](https://github.com/andrewssobral/lrslibrary) is a Low-Rank and Sparse Tools for Background Modeling and Subtraction in Videos. The library was designed for moving object detection in videos, but it can be also used for other computer vision and machine learning problems.
[Image Processing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/image.html) is a tool that provides a comprehensive set of reference-standard algorithms and workflow apps for image processing, analysis, visualization, and algorithm development. You can perform image segmentation, image enhancement, noise reduction, geometric transformations, image registration, and 3D image processing.
[Computer Vision Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/computer-vision.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing and testing computer vision, 3D vision, and video processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, as well as feature detection, extraction, and matching. You can automate calibration workflows for single, stereo, and fisheye cameras. For 3D vision, the toolbox supports visual and point cloud SLAM, stereo vision, structure from motion, and point cloud processing.
[Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/statistics.html) is a tool that provides functions and apps to describe, analyze, and model data. You can use descriptive statistics, visualizations, and clustering for exploratory data analysis; fit probability distributions to data; generate random numbers for Monte Carlo simulations, and perform hypothesis tests. Regression and classification algorithms let you draw inferences from data and build predictive models either interactively, using the Classification and Regression Learner apps, or programmatically, using AutoML.
[Lidar Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/lidar.html) is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing, analyzing, and testing lidar processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, semantic segmentation, shape fitting, lidar registration, and obstacle detection. Lidar Toolbox supports lidar-camera cross calibration for workflows that combine computer vision and lidar processing.
[Mapping Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/mapping.html) is a tool that provides algorithms and functions for transforming geographic data and creating map displays. You can visualize your data in a geographic context, build map displays from more than 60 map projections, and transform data from a variety of sources into a consistent geographic coordinate system.
[UAV Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/uav.html) is an application that provides tools and reference applications for designing, simulating, testing, and deploying unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and drone applications. You can design autonomous flight algorithms, UAV missions, and flight controllers. The Flight Log Analyzer app lets you interactively analyze 3D flight paths, telemetry information, and sensor readings from common flight log formats.
[Parallel Computing Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab-parallel-server.html) is a tool that lets you solve computationally and data-intensive problems using multicore processors, GPUs, and computer clusters. High-level constructs such as parallel for-loops, special array types, and parallelized numerical algorithms enable you to parallelize MATLAB® applications without CUDA or MPI programming. The toolbox lets you use parallel-enabled functions in MATLAB and other toolboxes. You can use the toolbox with Simulink® to run multiple simulations of a model in parallel. Programs and models can run in both interactive and batch modes.
[Partial Differential Equation Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/pde.html) is a tool that provides functions for solving structural mechanics, heat transfer, and general partial differential equations (PDEs) using finite element analysis.
[ROS Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/ros.html) is a tool that provides an interface connecting MATLAB® and Simulink® with the Robot Operating System (ROS and ROS 2), enabling you to create a network of ROS nodes. The toolbox includes MATLAB functions and Simulink blocks to import, analyze, and play back ROS data recorded in rosbag files. You can also connect to a live ROS network to access ROS messages.
[Robotics Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/robotics.html) provides a toolbox that brings robotics specific functionality(designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots) to MATLAB, exploiting the native capabilities of MATLAB (linear algebra, portability, graphics). The toolbox also supports mobile robots with functions for robot motion models (bicycle), path planning algorithms (bug, distance transform, D*, PRM), kinodynamic planning (lattice, RRT), localization (EKF, particle filter), map building (EKF) and simultaneous localization and mapping (EKF), and a Simulink model a of non-holonomic vehicle. The Toolbox also including a detailed Simulink model for a quadrotor flying robot.
[Deep Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning.html) is a tool that provides a framework for designing and implementing deep neural networks with algorithms, pretrained models, and apps. You can use convolutional neural networks (ConvNets, CNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks to perform classification and regression on image, time-series, and text data. You can build network architectures such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and Siamese networks using automatic differentiation, custom training loops, and shared weights. With the Deep Network Designer app, you can design, analyze, and train networks graphically. It can exchange models with TensorFlow™ and PyTorch through the ONNX format and import models from TensorFlow-Keras and Caffe. The toolbox supports transfer learning with DarkNet-53, ResNet-50, NASNet, SqueezeNet and many other pretrained models.
[Reinforcement Learning Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/reinforcement-learning.html) is a tool that provides an app, functions, and a Simulink® block for training policies using reinforcement learning algorithms, including DQN, PPO, SAC, and DDPG. You can use these policies to implement controllers and decision-making algorithms for complex applications such as resource allocation, robotics, and autonomous systems.
[Deep Learning HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/deep-learning-hdl.html) is a tool that provides functions and tools to prototype and implement deep learning networks on FPGAs and SoCs. It provides pre-built bitstreams for running a variety of deep learning networks on supported Xilinx® and Intel® FPGA and SoC devices. Profiling and estimation tools let you customize a deep learning network by exploring design, performance, and resource utilization tradeoffs.
[Model Predictive Control Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/model-predictive-control.html) is a tool that provides functions, an app, and Simulink® blocks for designing and simulating controllers using linear and nonlinear model predictive control (MPC). The toolbox lets you specify plant and disturbance models, horizons, constraints, and weights. By running closed-loop simulations, you can evaluate controller performance.
[Vision HDL Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/vision-hdl.html) is a tool that provides pixel-streaming algorithms for the design and implementation of vision systems on FPGAs and ASICs. It provides a design framework that supports a diverse set of interface types, frame sizes, and frame rates. The image processing, video, and computer vision algorithms in the toolbox use an architecture appropriate for HDL implementations.
[Data Acquisition Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/data-acquisition.html) is a tool that provides apps and functions for configuring data acquisition hardware, reading data into MATLAB® and Simulink®, and writing data to DAQ analog and digital output channels. The toolbox supports a variety of DAQ hardware, including USB, PCI, PCI Express®, PXI®, and PXI Express® devices, from National Instruments® and other vendors.
[Microsoft AirSim](https://microsoft.github.io/AirSim/lidar.html) is a simulator for drones, cars and more, built on Unreal Engine (with an experimental Unity release). AirSim is open-source, cross platform, and supports [software-in-the-loop simulation](https://www.mathworks.com/help///ecoder/software-in-the-loop-sil-simulation.html) with popular flight controllers such as PX4 & ArduPilot and [hardware-in-loop](https://www.ni.com/en-us/innovations/white-papers/17/what-is-hardware-in-the-loop-.html) with PX4 for physically and visually realistic simulations. It is developed as an Unreal plugin that can simply be dropped into any Unreal environment. AirSim is being developed as a platform for AI research to experiment with deep learning, computer vision and reinforcement learning algorithms for autonomous vehicles.
# NLP Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)

## NLP Learning Resources
[Natural Language Processing (NLP)](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/natural-language-processing) is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) focused on giving computers the ability to understand text and spoken words in much the same way human beings can. NLP combines computational linguistics rule-based modeling of human language with statistical, machine learning, and deep learning models.
[Natural Language Processing With Python's NLTK Package](https://realpython.com/nltk-nlp-python/)
[Cognitive Services—APIs for AI Developers | Microsoft Azure](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/cognitive-services/)
[Artificial Intelligence Services - Amazon Web Services (AWS)](https://aws.amazon.com/machine-learning/ai-services/)
[Google Cloud Natural Language API](https://cloud.google.com/natural-language/docs/reference/rest)
[Top Natural Language Processing Courses Online | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/natural-language-processing/)
[Introduction to Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/natural-language-processing/)
[Top Natural Language Processing Courses | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?=&query=natural%20language%20processing)
[Natural Language Processing | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/language-processing)
[Natural Language Processing in TensorFlow | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/natural-language-processing-tensorflow)
[Learn Natural Language Processing with Online Courses and Lessons | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/natural-language-processing)
[Build a Natural Language Processing Solution with Microsoft Azure | Pluralsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/build-natural-language-processing-solution-microsoft-azure)
[Natural Language Processing (NLP) Training Courses | NobleProg](https://www.nobleprog.com/nlp-training)
[Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning Course | Standford Online](https://online.stanford.edu/courses/cs224n-natural-language-processing-deep-learning)
[Advanced Natural Language Processing - MIT OpenCourseWare](https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-864-advanced-natural-language-processing-fall-2005/)
[Certified Natural Language Processing Expert Certification | IABAC](https://iabac.org/artificial-intelligence-certification/certified-natural-language-processing-expert/)
[Natural Language Processing Course - Intel](https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/training/course-natural-language-processing.html)
## NLP Tools, Libraries, and Frameworks
[Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK)](https://www.nltk.org/) is a leading platform for building Python programs to work with human language data. It provides easy-to-use interfaces to over [50 corpora and lexical resources](https://nltk.org/nltk_data/) such as WordNet, along with a suite of text processing libraries for classification, tokenization, stemming, tagging, parsing, and semantic reasoning, wrappers for industrial-strength NLP libraries.
[spaCy](https://spacy.io) is a library for advanced Natural Language Processing in Python and Cython. It's built on the very latest research, and was designed from day one to be used in real products. spaCy comes with pretrained pipelines and currently supports tokenization and training for 60+ languages. It also features neural network models for tagging, parsing, named entity recognition, text classification and more, multi-task learning with pretrained transformers like BERT.
[CoreNLP](https://stanfordnlp.github.io/CoreNLP/) is a set of natural language analysis tools written in Java. CoreNLP enables users to derive linguistic annotations for text, including token and sentence boundaries, parts of speech, named entities, numeric and time values, dependency and constituency parses, coreference, sentiment, quote attributions, and relations.
[NLPnet](https://github.com/erickrf/nlpnet) is a Python library for Natural Language Processing tasks based on neural networks. It performs part-of-speech tagging, semantic role labeling and dependency parsing.
[Flair](https://github.com/flairNLP/flair) is a simple framework for state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing (NLP) models to your text, such as named entity recognition (NER), part-of-speech tagging (PoS), special support for biomedical data, sense disambiguation and classification, with support for a rapidly growing number of languages.
[Catalyst](https://github.com/curiosity-ai/catalyst) is a C# Natural Language Processing library built for speed. Inspired by [spaCy's design](https://spacy.io/), it brings pre-trained models, out-of-the box support for training word and document embeddings, and flexible entity recognition models.
[Apache OpenNLP](https://opennlp.apache.org/) is an open-source library for a machine learning based toolkit used in the processing of natural language text. It features an API for use cases like [Named Entity Recognition](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Named-entity_recognition), [Sentence Detection](), [POS(Part-Of-Speech) tagging](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Part-of-speech_tagging), [Tokenization](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tokenization_(data_security)) [Feature extraction](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feature_extraction), [Chunking](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chunking_(psychology)), [Parsing](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parsing), and [Coreference resolution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coreference).
[Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK)](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cognitive-toolkit/) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org) is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
[Tensorflow_macOS](https://github.com/apple/tensorflow_macos) is a Mac-optimized version of TensorFlow and TensorFlow Addons for macOS 11.0+ accelerated using Apple's ML Compute framework.
[Keras](https://keras.io) is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
[PyTorch](https://pytorch.org) is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab.
[Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J)](https://deeplearning4j.konduit.ai/) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
[Chainer](https://chainer.org/) is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using [CuPy](https://github.com/cupy/cupy) for high performance training and inference.
[Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/) is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
[PlaidML](https://github.com/plaidml/plaidml) is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
[Scikit-Learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html) is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
[Caffe](https://github.com/BVLC/caffe) is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
[Theano](https://github.com/Theano/Theano) is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
[Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/) is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
[Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL](https://github.com/microsoft/sql-spark-connector) is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
[Apache PredictionIO](https://predictionio.apache.org/) is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
[Apache Airflow](https://airflow.apache.org) is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
[Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX)](https://github.com/onnx) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
[BigDL](https://bigdl-project.github.io/) is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
[Numba](https://github.com/numba/numba) is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
# Bioinformatics
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Bioinformatics Learning Resources
[Bioinformatics](https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Bioinformatics) is a field of computational science that has to do with the analysis of sequences of biological molecules. This usually refers to genes, DNA, RNA, or protein, and is particularly useful in comparing genes and other sequences in proteins and other sequences within an organism or between organisms, looking at evolutionary relationships between organisms, and using the patterns that exist across DNA and protein sequences to figure out what their function is.
[European Bioinformatics Institute](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/)
[National Center for Biotechnology Information](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
[Online Courses in Bioinformatics |ISCB - International Society for Computational Biology](https://www.iscb.org/cms_addon/online_courses/index.php)
[Bioinformatics | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/specializations/bioinformatics)
[Top Bioinformatics Courses | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/Bioinformatics/)
[Biometrics Courses | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/biometrics/)
[Learn Bioinformatics with Online Courses and Lessons | edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/bioinformatics)
[Bioinformatics Graduate Certificate | Harvard Extension School](https://extension.harvard.edu/academics/programs/bioinformatics-graduate-certificate/)
[Bioinformatics and Biostatistics | UC San Diego Extension](https://extension.ucsd.edu/courses-and-programs/bioinformatics-and-biostatistics)
[Bioinformatics and Proteomics - Free Online Course Materials | MIT](https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-092-bioinformatics-and-proteomics-january-iap-2005/)
[Introduction to Biometrics course - Biometrics Institute](https://www.biometricsinstitute.org/event/introduction-to-biometrics-short-course/)
## Bioinformatics Tools, Libraries, and Frameworks
[Bioconductor](https://bioconductor.org/) is an open source project that provides tools for the analysis and comprehension of high-throughput genomic data. Bioconductor uses the [R statistical programming language](https://www.r-project.org/about.html), and is open source and open development. It has two releases each year, and an active user community. Bioconductor is also available as an [AMI (Amazon Machine Image)](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/AMIs.html) and [Docker images](https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/images/).
[Bioconda](https://bioconda.github.io) is a channel for the conda package manager specializing in bioinformatics software. It has a repository of packages containing over 7000 bioinformatics packages ready to use with conda install.
[UniProt](https://www.uniprot.org/) is a freely accessible database that provide users with a comprehensive, high-quality and freely accessible set of protein sequences annotated with functional information.
[Bowtie 2](https://bio.tools/bowtie2#!) is an ultrafast and memory-efficient tool for aligning sequencing reads to long reference sequences. It is particularly good at aligning reads of about 50 up to 100s or 1,000s of characters, and particularly good at aligning to relatively long (mammalian) genomes.
[Biopython](https://biopython.org/) is a set of freely available tools for biological computation written in Python by an international team of developers. It is a distributed collaborative effort to develop Python libraries and applications which address the needs of current and future work in bioinformatics.
[BioRuby](https://bioruby.open-bio.org/) is a toolkit that has components for sequence analysis, pathway analysis, protein modelling and phylogenetic analysis; it supports many widely used data formats and provides easy access to databases, external programs and public web services, including BLAST, KEGG, GenBank, MEDLINE and GO.
[BioJava](https://biojava.org/) is a toolkit that provides an API to maintain local installations of the PDB, load and manipulate structures, perform standard analysis such as sequence and structure alignments and visualize them in 3D.
[BioPHP](https://biophp.org/) is an open source project that provides a collection of open source PHP code, with classes for DNA and protein sequence analysis, alignment, database parsing, and other bioinformatics tools.
[Avogadro](https://avogadro.cc/) is an advanced molecule editor and visualizer designed for cross-platform use in computational chemistry, molecular modeling, bioinformatics, materials science, and related areas. It offers flexible high quality rendering and a powerful plugin architecture.
[Ascalaph Designer](https://www.biomolecular-modeling.com/Ascalaph/Ascalaph_Designer.html) is a program for molecular dynamic simulations. Under a single graphical environment are represented as their own implementation of molecular dynamics as well as the methods of classical and quantum mechanics of popular programs.
[Anduril](https://www.anduril.org/site/) is a workflow platform for analyzing large data sets. Anduril provides facilities for analyzing high-thoughput data in biomedical research, and the platform is fully extensible by third parties. Ready-made tools support data visualization, DNA/RNA/ChIP-sequencing, DNA/RNA microarrays, cytometry and image analysis.
[Galaxy](https://melbournebioinformatics.github.io/MelBioInf_docs/tutorials/galaxy_101/galaxy_101/) is an open source, web-based platform for accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational biomedical research. It allows users without programming experience to easily specify parameters and run individual tools as well as larger workflows. It also captures run information so that any user can repeat and understand a complete computational analysis.
[PathVisio](https://pathvisio.github.io/) is a free open-source pathway analysis and drawing software which allows drawing, editing, and analyzing biological pathways. It is developed in Java and can be extended with plugins.
[Orange](https://orangedatamining.com/) is a powerful data mining and machine learning toolkit that performs data analysis and visualization.
[Basic Local Alignment Search Tool](https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) is a tool that finds regions of similarity between biological sequences. The program compares nucleotide or protein sequences to sequence databases and calculates the statistical significance.
[OSIRIS](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/osiris/) is public-domain, free, and open source STR analysis software designed for clinical, forensic, and research use, and has been validated for use as an expert system for single-source samples.
[NCBI BioSystems](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/biosystems/) is a Database that provides integrated access to biological systems and their component genes, proteins, and small molecules, as well as literature describing those biosystems and other related data throughout Entrez.
# Robotics
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Robotics Learning Resources
[Robotics courses from Coursera](https://www.edx.org/learn/robotics)
[Learn Robotics with Online Courses and Classes from edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/robotics)
[Top Robotics Courses Online from Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/robotics/)
[Free Online AI & Robotics Courses](https://www.futurelearn.com/subjects/it-and-computer-science-courses/ai-and-robotics)
[REC Foundation Robotics Industry Certification](https://www.roboticseducation.org/industry-certifications/)
[Carnegie Mellon Robotics Academy](https://www.cmu.edu/roboticsacademy/Training/Certifications.html)
[RIA Robotic Integrator Certification Program](https://www.robotics.org/robotics/integrator-certification)
[AWS RoboMaker – Develop, Test, Deploy, and Manage Intelligent Robotics Apps](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/aws-robomaker-develop-test-deploy-and-manage-intelligent-robotics-apps/)
[Microsoft AI School](https://aischool.microsoft.com/en-us/home)
[Language Understanding (LUIS) for Azure Cognitive Services](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cognitive-services/luis/what-is-luis)
[ROS on Windows 10](https://ms-iot.github.io/ROSOnWindows/)
[Windows ML ROS Node](https://ms-iot.github.io/ROSOnWindows/ROSAtMS/WinML.html)
[Azure VM templates to bootstrap ROS and ROS 2 environments](https://ms-iot.github.io/ROSOnWindows/ROSAtMS/AzureVM.html)
[Google Robotics Research](https://research.google/teams/brain/robotics/)
## Robotics Tools and Frameworks
[Robot Framework](https://robotframework.org/) is a generic open source automation framework. It can be used for test automation and robotic process automation. It has easy syntax, utilizing human-readable keywords. Its capabilities can be extended by libraries implemented with Python or Java.
[The Robotics Library (RL)](https://github.com/roboticslibrary/rl) is a self-contained C++ library for robot kinematics, motion planning and control. It covers mathematics, kinematics and dynamics, hardware abstraction, motion planning, collision detection, and visualization.RL runs on many different systems, including Linux, macOS, and Windows. It uses CMake as a build system and can be compiled with Clang, GCC, and Visual Studio.
[Robot Structural Analysis Professional](https://www.autodesk.com/products/robot-structural-analysis/overview?term=1-YEAR) is structural load analysis software developed by Autodesk that verifies code compliance and uses BIM-integrated workflows to exchange data with Revit. It can help you to create more resilient, constructible designs that are accurate, coordinated, and connected to BIM.
[PowerMill](https://www.autodesk.com/products/powermill/overview) is a software developed by Autodesk that provides powerful, flexible, easy-to-use tools for offline programming of robots. Get tools to help you optimize robotic paths and simulate virtual mock-ups of manufacturing cells and systems.
[ROS](https://www.ros.org/) is robotics middleware. Although ROS is not an operating system, it provides services designed for a heterogeneous computer cluster such as hardware abstraction, low-level device control, implementation of commonly used functionality, message-passing between processes, and package management.
[ROS2](https://index.ros.org/doc/ros2/) is a set of [software libraries and tools](https://github.com/ros2) that help you build robot applications. From drivers to state-of-the-art algorithms, and with powerful developer tools, ROS has what you need for your next robotics project. And it’s all open source.
[MoveIt](https://moveit.ros.org/) is the most widely used software for manipulation and has been used on over 100 robots. It provides an easy-to-use robotics platform for developing advanced applications, evaluating new designs and building integrated products for industrial, commercial, R&D, and other domains.
[AutoGluon](https://autogluon.mxnet.io/index.html) is toolkit for [Deep learning](https://gitlab.com/maos20008/intro-to-machine-learning) that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
[Gazebo](http://gazebosim.org/) accurately and efficiently simulates indoor and outdoor robots. You get a robust physics engine, high-quality graphics, and programmatic and graphical interfaces.
[Robotics System Toolbox](https://www.mathworks.com/products/robotics.html) provides tools and algorithms for designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots. For manipulators and humanoid robots, the toolbox includes algorithms for collision checking, trajectory generation, forward and inverse kinematics, and dynamics using a rigid body tree representation.
For mobile robots, it includes algorithms for mapping, localization, path planning, path following, and motion control. The toolbox provides reference examples of common industrial robot applications. It also includes a library of
commercially available industrial robot models that you can import, visualize, and simulate.
[Intel Robot DevKit](https://github.com/intel/robot_devkit) is the tool to generate Robotics Software Development Kit (RDK) designed for autonomous devices, including the ROS2 core and capacibilities packages like perception, planning, control driver etc. It provides flexible build/runtime configurations to meet different autonomous requirement on top of diversity hardware choices, for example use different hareware engine CPU/GPU/VPU to accelerate AI related features.
[Neurorobotics Platform (NRP)](https://neurorobotics.net/) is an Internet-accessible simulation system that allows the simulation of robots controlled by spiking neural networks.
[ViSP](http://visp.inria.fr/) is an open-source visual servoing platform library, is able to compute control laws that can be applied to robotic systems.
[ROS Behavior Trees](https://github.com/miccol/ROS-Behavior-Tree) is an open-source library to create robot's behaviors in form of Behavior Trees running in ROS (Robot Operating System).
[g2core](https://github.com/synthetos/g2) is an open-source motion control software for CNC and Robotics, designed to run on Arduino Due class microcontrollers.
[ur5controller](https://github.com/roboticsleeds/ur5controller) is an open-source OpenRAVE controller for UR5 robot integrated with ROS.
[RBDL](https://github.com/rbdl/rbdl) is an open-source (zlib) C++ libray for both forward and inverse dynamics and kinematics. Also supports contacts and loops.
[Unity Robotics Hub](https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/Unity-Robotics-Hub) is a Central repository for open-source Unity packages, tutorials, and other resources demonstrating how to use Unity for robotics simulations. Includes new support for ROS integration.
[Arduino](https://www.arduino.cc/) is an open-source platform used for building electronics projects. Arduino consists of both a physical programmable circuit board (often referred to as a microcontroller) and a piece of software, or IDE (Integrated Development Environment) that runs on your computer, used to write and upload computer code to the physical board.
[ArduPilot](https://ardupilot.org/ardupilot/index.html) enables the creation and use of trusted, autonomous, unmanned vehicle systems for the peaceful benefit of all. ArduPilot provides a comprehensive suite of tools suitable for almost any vehicle and application.
[AirSim](https://github.com/Microsoft/AirSim) is a simulator for drones, cars and more, built on Unreal Engine (we now also have an experimental Unity release). It is open-source, cross platform, and supports hardware-in-loop with popular flight controllers such as PX4 for physically and visually realistic simulations.
[The JPL Open Source Rover](https://github.com/nasa-jpl/open-source-rover) is an open source, build it yourself, scaled down version of the 6 wheel rover design that JPL uses to explore the surface of Mars. The Open Source Rover is designed almost entirely out of consumer off the shelf (COTS) parts. This project is intended to be a teaching and learning experience for those who want to get involved in mechanical engineering, software, electronics, or robotics.
[Light Detection and Ranging(LiDAR)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lidar) is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser at an object, and uses the time and wavelength of the reflected beam of light to estimate the distance and in some applications ([Laser Imaging](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laser_scanning)), to create a 3D representation of the object and its surface characteristics. This technology is commonly used in aircraft and self-driving vehicles.
[AliceVision](https://github.com/alicevision/AliceVision) is a Photogrammetric Computer Vision Framework which provides a 3D Reconstruction and Camera Tracking algorithms. AliceVision aims to provide strong software basis with state-of-the-art computer vision algorithms that can be tested, analyzed and reused. The project is a result of collaboration between academia and industry to provide cutting-edge algorithms with the robustness and the quality required for production usage.
[CARLA](https://github.com/carla-simulator/carla) is an open-source simulator for autonomous driving research. CARLA has been developed from the ground up to support development, training, and validation of autonomous driving systems. In addition to open-source code and protocols, CARLA provides open digital assets (urban layouts, buildings, vehicles) that were created for this purpose and can be used freely. The simulation platform supports flexible specification of sensor suites and environmental conditions.
[ROS bridge](https://github.com/carla-simulator/ros-bridge) is a package to bridge ROS for CARLA Simulator.
[ROS-Industrial](https://rosindustrial.org/) is an open source project that extends the advanced capabilities of ROS software to manufacturing.
[AWS RoboMaker](https://aws.amazon.com/robomaker/) is the most complete cloud solution for robotic developers to simulate, test and securely deploy robotic applications at scale. RoboMaker provides a fully-managed, scalable infrastructure for simulation that customers use for multi-robot simulation and CI/CD integration with regression testing in simulation.
[Microsoft Robotics Developer Studio](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=29081) is a free .NET-based programming environment for building robotics applications.
[Visual Studio Code Extension for ROS](https://github.com/ms-iot/vscode-ros) is an extension provides support for Robot Operating System (ROS) development.
[Azure Kinect ROS Driver](https://github.com/microsoft/azure_kinect_ros_driver) is a node which publishes sensor data from the [Azure Kinect Developer Kit](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/kinect-dk/) to the [Robot Operating System (ROS)](http://www.ros.org/). Developers working with ROS can use this node to connect an Azure Kinect Developer Kit to an existing ROS installation.
[Azure IoT Hub for ROS](https://github.com/microsoft/ros_azure_iothub) is a ROS package works with the Microsoft Azure IoT Hub service to relay telemetry messages from the Robot to Azure IoT Hub or reflect properties from the Digital Twin to the robot using dynamic reconfigure.
[ROS 2 with ONNX Runtime](https://github.com/ms-iot/ros_msft_onnx) is a program that uses ROS 2 to run on different hardware platforms using their respective AI acceleration libraries for optimized execution of the ONNX model.
[Azure Cognitive Services LUIS ROS Node](https://github.com/ms-iot/ros_msft_luis) is a ROS node that bridges between ROS and the Azure Language Understanding Service. it can be configured to process audio directly from a microphone, or can subscribe to a ROS audio topic, then processes speech and generates "intent" ROS messages which can be processed by another ROS node to generate ROS commands.
# LiDAR Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)

## LiDAR Learning Resources
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/LiDAR-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Introduction to Lidar Course - NOAA](https://coast.noaa.gov/digitalcoast/training/intro-lidar.html)
[Lidar 101:An Introduction to Lidar Technology, Data, and Applications(PDF) - NOAA](https://coast.noaa.gov/data/digitalcoast/pdf/lidar-101.pdf)
[Understanding LiDAR Technologies - GIS Lounge](https://www.gislounge.com/understanding-lidar-technologies/)
[LiDAR University Free Lidar Training Courses on MODUS AI](https://www.modus-ai.com/lidar-university-2/)
[LiDAR | Learning Plan on ERSI](https://www.esri.com/training/catalog/5bccd52a6e9c0f01fb49e85d/lidar/#!)
[Light Detection and Ranging Sensors Course on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/lecture/state-estimation-localization-self-driving-cars/lesson-1-light-detection-and-ranging-sensors-3NXgp)
[Quick Introduction to Lidar and Basic Lidar Tools(PDF)](https://training.fws.gov/courses/references/tutorials/geospatial/CSP7304/documents/Lidar.pdf)
[LIDAR - GIS Wiki](http://wiki.gis.com/wiki/index.php/Lidar)
[OpenStreetMap Wiki](https://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Main_Page)
[OpenStreetMap Frameworks](https://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Frameworks)
## LiDAR Tools & Frameworks
[Light Detection and Ranging (lidar)](https://www.usgs.gov/news/earthword-lidar) is a technology used to create high-resolution models of ground elevation with a vertical accuracy of 10 centimeters (4 inches). Lidar equipment, which includes a laser scanner, a Global Positioning System (GPS), and an Inertial Navigation System (INS), is typically mounted on a small aircraft. The laser scanner transmits brief pulses of light to the ground surface. Those pulses are reflected or scattered back and their travel time is used to calculate the distance between the laser scanner and the ground. Lidar data is initially collected as a “point cloud” of individual points reflected from everything on the surface, including structures and vegetation. To produce a “bare earth” Digital Elevation Model (DEM), structures and vegetation are stripped away.
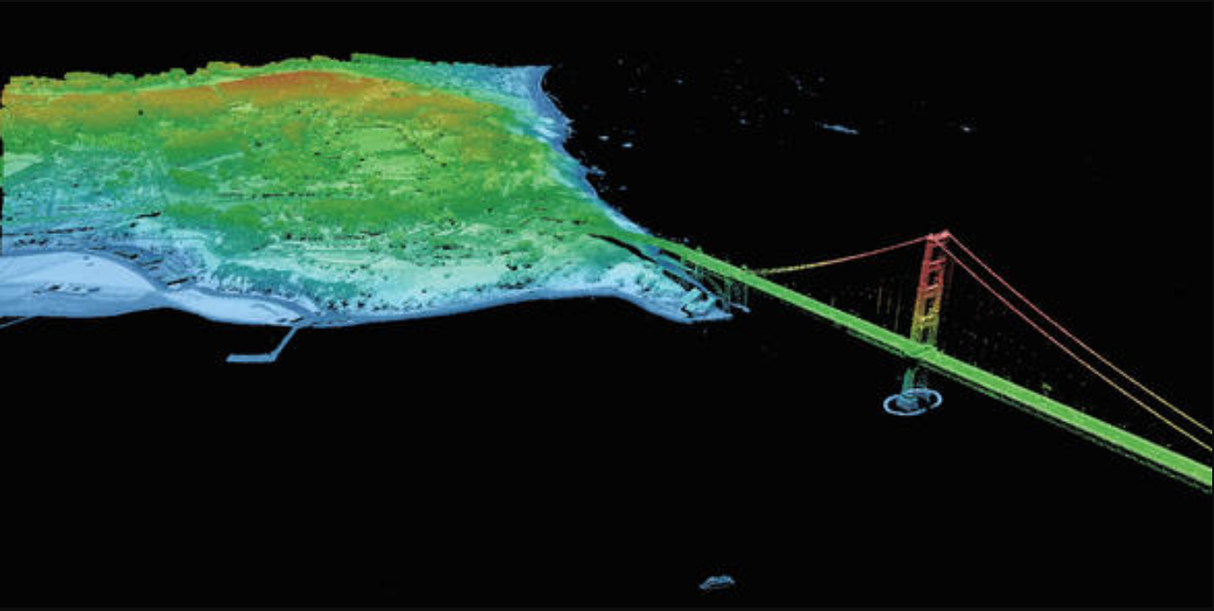
**3D Data Visualization of Golden Gate Bridge. Source: [USGS](https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/ngp/tnm-delivery)**
[Mola](https://docs.mola-slam.org/latest/) is a Modular Optimization framework for Localization and mApping (MOLA).

**3D LiDAR SLAM from KITTI dataset. Source: [MOLA](https://docs.mola-slam.org/latest/demo-kitti-lidar-slam.html)**
[Lidar Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/lidar.html) is a MATLAB tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing, analyzing, and testing lidar processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, semantic segmentation, shape fitting, lidar registration, and obstacle detection. Lidar Toolbox supports lidar-camera cross calibration for workflows that combine computer vision and lidar processing.
[Automated Driving Toolbox™](https://www.mathworks.com/products/automated-driving.html) is a MATLAB tool that provides algorithms and tools for designing, simulating, and testing ADAS and autonomous driving systems. You can design and test vision and lidar perception systems, as well as sensor fusion, path planning, and vehicle controllers. Visualization tools include a bird’s-eye-view plot and scope for sensor coverage, detections and tracks, and displays for video, lidar, and maps. The toolbox lets you import and work with HERE HD Live Map data and OpenDRIVE® road networks. It also provides reference application examples for common ADAS and automated driving features, including FCW, AEB, ACC, LKA, and parking valet. The toolbox supports C/C++ code generation for rapid prototyping and HIL testing, with support for sensor fusion, tracking, path planning, and vehicle controller algorithms.
[Microsoft AirSim](https://microsoft.github.io/AirSim/lidar.html) is a simulator for drones, cars and more, built on Unreal Engine (with an experimental Unity release). AirSim is open-source, cross platform, and supports [software-in-the-loop simulation](https://www.mathworks.com/help///ecoder/software-in-the-loop-sil-simulation.html) with popular flight controllers such as PX4 & ArduPilot and [hardware-in-loop](https://www.ni.com/en-us/innovations/white-papers/17/what-is-hardware-in-the-loop-.html) with PX4 for physically and visually realistic simulations. It is developed as an Unreal plugin that can simply be dropped into any Unreal environment. AirSim is being developed as a platform for AI research to experiment with deep learning, computer vision and reinforcement learning algorithms for autonomous vehicles.

**3D Autonomous Vehicle Simulation in AirSim. Source: [Microsoft](https://microsoft.github.io/AirSim)**
[LASer(LAS)](https://www.asprs.org/divisions-committees/lidar-division/laser-las-file-format-exchange-activities) is a public file format for the interchange of 3-dimensional point cloud data data between data users. Although developed primarily for exchange of lidar point cloud data, this format supports the exchange of any 3-dimensional x,y,z tuplet. This binary file format is an alternative to proprietary systems or a generic ASCII file interchange system used by many companies. The problem with proprietary systems is obvious in that data cannot be easily taken from one system to another. There are two major problems with the ASCII file interchange. The first problem is performance because the reading and interpretation of ASCII elevation data can be very slow and the file size can be extremely large even for small amounts of data. The second problem is that all information specific to the lidar data is lost. The LAS file format is a binary file format that maintains information specific to the lidar nature of the data while not being overly complex.
[3D point cloud](https://www.onyxscan-lidar.com/point-cloud/) is a set of data points defined in a given three-dimensional coordinates system.. Point clouds can be produced directly by 3D scanner which records a large number of points returned from the external surfaces of objects or earth surface. These data are exchanged between LiDAR users mainly through LAS format files (.las).
[ArcGIS Desktop](https://www.esri.com/en-us/arcgis/products/arcgis-desktop/overview) is powerful and cost-effective desktop geographic information system (GIS) software. It is the essential software package for GIS professionals. ArcGIS Desktop users can create, analyze, manage, and share geographic information so decision-makers can make intelligent, informed decisions.
[USGS 3DEP Lidar Point Cloud Now Available as Amazon Public Dataset](https://www.usgs.gov/news/usgs-3dep-lidar-point-cloud-now-available-amazon-public-dataset)
[National Geospatial Program](https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/national-geospatial-program)
[National Map Data Download and Visualization Services](https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/ngp/tnm-delivery)
[USGS Lidar Base Specification(LBS) online edition](https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/ngp/ss/lidar-base-specification-online)
# Photogrammetry Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)

## Photogrammetry Learning Resources
[Photogrammetry](https://www.autodesk.com/solutions/photogrammetry-software) is the art and science of extracting 3D information from photographs. The process involves taking overlapping photographs of an object, structure, or space, and converting them into 2D or 3D digital models. Photogrammetry is often used by surveyors, architects, engineers, and contractors to create topographic maps, meshes, point clouds, or drawings based on the real-world.
[Aerial photogrammetry](https://www.autodesk.com/solutions/photogrammetry-software) is process of utilizing aircrafts to produce aerial photography that can be turned into a 3D model or mapped digitally. Now, it is possible to do the same work with a drone.
[Terrestrial(Close-range) photogrammetry](https://www.autodesk.com/solutions/photogrammetry-software) is when images are captured using a handheld camera or with a camera mounted to a tripod. The output of this method is not to create topographic maps, but rather to make 3D models of a smaller object.
[Top Photogrammetry Courses Online | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/photogrammetry/)
[Photogrammetry With Drones: In Mapping Technology | Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/course/essentials-of-photogrammetry/)
[Introduction to Photogrammetry Course | Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/lecture/aerial-photography-with-uav/introduction-to-photogrammetry-KyP30)
[Photogrammetry Online Classes and Training | Linkedin Learning](https://www.linkedin.com/learning/search?keywords=Photogrammetry&upsellOrderOrigin=default_guest_learning&trk=learning-course_learning-search-bar_search-submit)
[Pix4D training and certification for mapping professionals](https://training.pix4d.com/)
[Drone mapping and photogrammetry workshops with Pix4D](https://training.pix4d.com/pages/workshops)
[Digital Photogrammetric Systems Course | Purdue Online Learning](https://engineering.purdue.edu/online/courses/digital-photogrammetric-systems)
[Photogrammetry Training | Deep3D Photogrammetry](https://deep3d.co.uk/photogrammetry-training/)
[ASPRS Certification Program](https://www.asprs.org/certification)
## Photogrammetry Tools, Libraries, and Frameworks
[Autodesk® ReCap™](https://www.autodesk.com/products/recap/free-trial) is a software tool that converts reality captured from laser scans or photos into a 3D model or 2D drawing that's ready to be used in your design built for UAV and drone processes.
[Autodesk® ReCap™ Photo](http://blogs.autodesk.com/recap/introducing-recap-photo/) is a cloud-connected solution tailored for drone/UAV photo capturing workflows. Using ReCap Photo, you can create textured meshes, point clouds with geolocation, and high-resolution orthographic views with elevation maps.
[Pix4D](https://www.pix4d.com/) is a unique suite of photogrammetry software for drone mapping. Capture images with our app, process on desktop or cloud and create maps and 3D models.
[PIX4Dmapper](https://www.pix4d.com/product/pix4dmapper-photogrammetry-software) is the leading photogrammetry software for professional drone mapping.
[RealityCapture](https://www.capturingreality.com/) is a state-of-the-art photogrammetry software solution that creates virtual reality scenes, textured 3D meshes, orthographic projections, geo-referenced maps and much more from images and/or laser scans completely automatically.
[Adobe Scantastic](https://labs.adobe.com/projects/scantastic/) is a tool that makes the creation of 3D assets accessible to everyone. It can be used with just a mobile device (combined with Adobe's server-based photogrammetry pipeline), users can easily scan objects in their physical environment and turn them into 3D models which can then be imported into tools like [Adobe Dimension](https://www.adobe.com/products/dimension.html) and [Adobe Aero](https://www.adobe.com/products/aero.html).
[Adobe Aero](https://www.adobe.com/products/aero.html) is a tool that helps you build, view, and share immersive AR experiences. Simply build a scene by bringing in 2D images from Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator, or 3D models from Adobe Dimension, Substance, third-party apps like Cinema 4D, or asset libraries like Adobe Stock and TurboSquid. Aero optimizes a wide array of assets, including OBJ, GLB, and glTF files, for AR, so you can visualize them in real time.
[Agisoft Metashape](https://www.agisoft.com/) is a stand-alone software product that performs photogrammetric processing of digital images and generates 3D spatial data to be used in GIS applications, cultural heritage documentation, and visual effects production as well as for indirect measurements of objects of various scales.
[MicroStation](https://www.bentley.com/en/products/brands/microstation) is a CAD software platform for 2D and 3D dimensional design and drafting, developed and sold by Bentley Systems. It generates 2D/3D vector graphics objects and elements and includes building information modeling (BIM) features.
[Leica Photogrammetry Suite (LPS)](https://support.hexagonsafetyinfrastructure.com/infocenter/index?page=product&facRef=LPS&facDisp=Leica%20Photogrammetry%20Suite%20(LPS)&landing=1) is a powerful photogrammetry system that delivers full analytical triangulation, the generation of digital terrain models, orthophoto production, mosaicking, and 3D feature extraction in a user-friendly environment that guarantees results even for photogrammetry novices.
[Terramodel](https://heavyindustry.trimble.com/products/terramodel) is a powerful software package for the surveyor, civil engineer or contractor who requires a CAD and design package with integrated support for raw survey data.
[MicMac](https://github.com/micmacIGN/micmac) is a free and open-source photogrammetry software tools for 3D reconstruction.
[3DF Zephyr] (https://www.3dflow.net/3df-zephyr-photogrammetry-software/) is a photogrammetry software solution by 3Dflow. It allows you automatically reconstruct 3D models from photos and deal with any 3D reconstruction and scanning challenge. No matter what camera sensor, drone or laser scanner device you are going to use.
[COLMAP](https://colmap.github.io/) is a general-purpose Structure-from-Motion (SfM) and Multi-View Stereo (MVS) pipeline with a graphical and command-line interface. It offers a wide range of features for reconstruction of ordered and unordered image collections.
[Multi-View Environment (MVE)](https://www.gcc.tu-darmstadt.de/home/proj/mve/) is an effort to ease the work with multi-view datasets and to support the development of algorithms based on multiple views. It features Structure from Motion, Multi-View Stereo and Surface Reconstruction. MVE is developed at the TU Darmstadt.
[AliceVision](https://github.com/alicevision/AliceVision) is a Photogrammetric Computer Vision Framework which provides 3D Reconstruction and Camera Tracking algorithms. AliceVision comes up with strong software basis and state-of-the-art computer vision algorithms that can be tested, analyzed and reused.
[Meshroom](https://github.com/alicevision/meshroom) is a free, open-source 3D Reconstruction Software based on the AliceVision framework.
[PhotoModeler](https://www.photomodeler.com/) is a software extracts Measurements and Models from photographs taken with an ordinary camera. A cost-effective way for accurate 2D or 3D measurement, photo-digitizing, surveying, 3D scanning, and reality capture.
[ODM](https://www.opendronemap.org/odm/) is an open source command line toolkit to generate maps, point clouds, 3D models and DEMs from drone, balloon or kite images.
[WebODM](https://www.opendronemap.org/webodm/) is a user-friendly, commercial grade software for drone image processing. Generate georeferenced maps, point clouds, elevation models and textured 3D models from aerial images. It supports multiple engines for processing, currently [ODM](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/ODM) and [MicMac](https://github.com/dronemapper-io/NodeMICMAC/).
[NodeODM](https://www.opendronemap.org/nodeodm/) is a [standard API specification](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/NodeODM/blob/master/docs/index.adoc) for processing aerial images with engines such as [ODM](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/ODM). The API is used by clients such as [WebODM](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/WebODM), [CloudODM](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/CloudODM) and [PyODM](https://github.com/OpenDroneMap/PyODM).
[ClusterODM]https://www.opendronemap.org/clusterodm/) is a reverse proxy, load balancer and task tracker with optional cloud autoscaling capabilities for NodeODM API compatible nodes. In a nutshell, it's a program to link together multiple NodeODM API compatible nodes under a single network address.
[FIELDimageR](https://www.opendronemap.org/fieldimager/) is an R package to analyze orthomosaic images from agricultural field trials.
[Regard3D](https://www.regard3d.org/) is a free and open source structure-from-motion program. It converts photos of an object, taken from different angles, into a 3D model of this object.
# CUDA Development
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)


**CUDA Toolkit. Source: [NVIDIA Developer CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-zone)**
## CUDA Learning Resources
[CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-zone) is a parallel computing platform and programming model developed by NVIDIA for general computing on graphical processing units (GPUs). With CUDA, developers are able to dramatically speed up computing applications by harnessing the power of GPUs. In GPU-accelerated applications, the sequential part of the workload runs on the CPU, which is optimized for single-threaded. The compute intensive portion of the application runs on thousands of GPU cores in parallel. When using CUDA, developers can program in popular languages such as C, C++, Fortran, Python and MATLAB.
[CUDA Toolkit Documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/index.html)
[CUDA Quick Start Guide](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-quick-start-guide/index.html)
[CUDA on WSL](https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/wsl-user-guide/index.html)
[CUDA GPU support for TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/gpu)
[NVIDIA Deep Learning cuDNN Documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/cudnn/api/index.html)
[NVIDIA GPU Cloud Documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/ngc/ngc-introduction/index.html)
[NVIDIA NGC](https://ngc.nvidia.com/) is a hub for GPU-optimized software for deep learning, machine learning, and high-performance computing (HPC) workloads.
[NVIDIA NGC Containers](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/gpu-cloud/containers/) is a registry that provides researchers, data scientists, and developers with simple access to a comprehensive catalog of GPU-accelerated software for AI, machine learning and HPC. These containers take full advantage of NVIDIA GPUs on-premises and in the cloud.
## CUDA Tools Libraries, and Frameworks
[CUDA Toolkit](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads) is a collection of tools & libraries that provide a development environment for creating high performance GPU-accelerated applications. The CUDA Toolkit allows you can develop, optimize, and deploy your applications on GPU-accelerated embedded systems, desktop workstations, enterprise data centers, cloud-based platforms and HPC supercomputers. The toolkit includes GPU-accelerated libraries, debugging and optimization tools, a C/C++ compiler, and a runtime library to build and deploy your application on major architectures including x86, Arm and POWER.
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for [deep neural networks](https://developer.nvidia.com/deep-learning). cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including [Caffe2](https://caffe2.ai/), [Chainer](https://chainer.org/), [Keras](https://keras.io/), [MATLAB](https://www.mathworks.com/solutions/deep-learning.html), [MxNet](https://mxnet.incubator.apache.org/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/).
[CUDA-X HPC](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/technologies/cuda-x/) is a collection of libraries, tools, compilers and APIs that help developers solve the world's most challenging problems. CUDA-X HPC includes highly tuned kernels essential for high-performance computing (HPC).
[NVIDIA Container Toolkit](https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-docker) is a collection of tools & libraries that allows users to build and run GPU accelerated Docker containers. The toolkit includes a container runtime [library](https://github.com/NVIDIA/libnvidia-container) and utilities to automatically configure containers to leverage NVIDIA GPUs.
[Minkowski Engine](https://nvidia.github.io/MinkowskiEngine) is an auto-differentiation library for sparse tensors. It supports all standard neural network layers such as convolution, pooling, unpooling, and broadcasting operations for sparse tensors.
[CUTLASS](https://github.com/NVIDIA/cutlass) is a collection of CUDA C++ template abstractions for implementing high-performance matrix-multiplication (GEMM) at all levels and scales within CUDA. It incorporates strategies for hierarchical decomposition and data movement similar to those used to implement cuBLAS.
[CUB](https://github.com/NVIDIA/cub) is a cooperative primitives for CUDA C++ kernel authors.
[Tensorman](https://github.com/pop-os/tensorman) is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by [System76]( https://system76.com).Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
[Numba](https://github.com/numba/numba) is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
[Chainer](https://chainer.org/) is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using [CuPy](https://github.com/cupy/cupy) for high performance training and inference.
[CuPy](https://cupy.dev/) is an implementation of NumPy-compatible multi-dimensional array on CUDA. CuPy consists of the core multi-dimensional array class, cupy.ndarray, and many functions on it. It supports a subset of numpy.ndarray interface.
[CatBoost](https://catboost.ai/) is a fast, scalable, high performance [Gradient Boosting](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gradient_boosting) on Decision Trees library, used for ranking, classification, regression and other machine learning tasks for Python, R, Java, C++. Supports computation on CPU and GPU.
[cuDF](https://rapids.ai/) is a GPU DataFrame library for loading, joining, aggregating, filtering, and otherwise manipulating data. cuDF provides a pandas-like API that will be familiar to data engineers & data scientists, so they can use it to easily accelerate their workflows without going into the details of CUDA programming.
[cuML](https://github.com/rapidsai/cuml) is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
[ArrayFire](https://arrayfire.com/) is a general-purpose library that simplifies the process of developing software that targets parallel and massively-parallel architectures including CPUs, GPUs, and other hardware acceleration devices.
[Thrust](https://github.com/NVIDIA/thrust) is a C++ parallel programming library which resembles the C++ Standard Library. Thrust's high-level interface greatly enhances programmer productivity while enabling performance portability between GPUs and multicore CPUs.
[AresDB](https://eng.uber.com/aresdb/) is a GPU-powered real-time analytics storage and query engine. It features low query latency, high data freshness and highly efficient in-memory and on disk storage management.
[Arraymancer](https://mratsim.github.io/Arraymancer/) is a tensor (N-dimensional array) project in Nim. The main focus is providing a fast and ergonomic CPU, Cuda and OpenCL ndarray library on which to build a scientific computing ecosystem.
[Kintinuous](https://github.com/mp3guy/Kintinuous) is a real-time dense visual SLAM system capable of producing high quality globally consistent point and mesh reconstructions over hundreds of metres in real-time with only a low-cost commodity RGB-D sensor.
[GraphVite](https://graphvite.io/) is a general graph embedding engine, dedicated to high-speed and large-scale embedding learning in various applications.
# Linear Algebra
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)

# Linear Algebra Learning Resources
[Linear algebra](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_algebra) is the math of vectors and matrices. The only prerequisite for this guide is a basic understanding of high school math concepts like numbers, variables, equations, and the fundamental arithmetic operations on real numbers: addition (denoted +), subtraction (denoted −), multiplication (denoted implicitly), and division (fractions). Also, you should also be familiar with functions that take real numbers as inputs and give real numbers as outputs, f : R → R.
[Linear Algebra - Online Courses | Harvard University](https://online-learning.harvard.edu/course/linear-algebra)
[Linear Algebra | MIT Open Learning Library](https://openlearninglibrary.mit.edu/courses/course-v1:OCW+18.06SC+2T2019/about)
[Linear Algebra - Khan Academy](https://www.khanacademy.org/math/linear-algebra)
[Top Linear Algebra Courses on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/courses?query=linear%20algebra)
[Mathematics for Machine Learning: Linear Algebra on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/learn/linear-algebra-machine-learning)
[Top Linear Algebra Courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/topic/linear-algebra/)
[Learn Linear Algebra with Online Courses and Classes on edX](https://www.edx.org/learn/linear-algebra)
[The Math of Data Science: Linear Algebra Course on edX](https://www.edx.org/course/math-of-data-science-linear-algebra)
[Linear Algebra in Twenty Five Lectures | UC Davis](https://www.math.ucdavis.edu/~linear/linear.pdf)
[Linear Algebra | UC San Diego Extension](https://extension.ucsd.edu/courses-and-programs/linear-algebra-1)
[Linear Algebra for Machine Learning | UC San Diego Extension](https://extension.ucsd.edu/courses-and-programs/linear-algebra-for-machine-learning)
[Introduction to Linear Algebra, Interactive Online Video | Wolfram](http://www.wolfram.com/wolfram-u/introduction-to-linear-algebra/)
[Linear Algebra Resources | Dartmouth](https://math.dartmouth.edu/~trs/linear-algebra-resources.php)
# Defintions
### i. Vector operations
We now define the math operations for vectors. The operations we can perform on vectors ~u = (u1, u2, u3) and ~v = (v1, v2, v3) are: addition, subtraction, scaling, norm (length), dot product, and cross product:
The dot product and the cross product of two vectors can also be described in terms of the angle θ between the two vectors.

**Vector Operations. Source: [slideserve](https://www.slideserve.com/krystal/streaming-simd-extension-sse)**

**Vector Operations. Source: [pinterest](https://www.pinterest.com/pin/41799102767414798/)**
### ii. Matrix operations
We denote by A the matrix as a whole and refer to its entries as aij .The mathematical operations defined for matrices are the following:
• determinant (denoted det(A) or |A|)
Note that the matrix product is not a commutative operation.
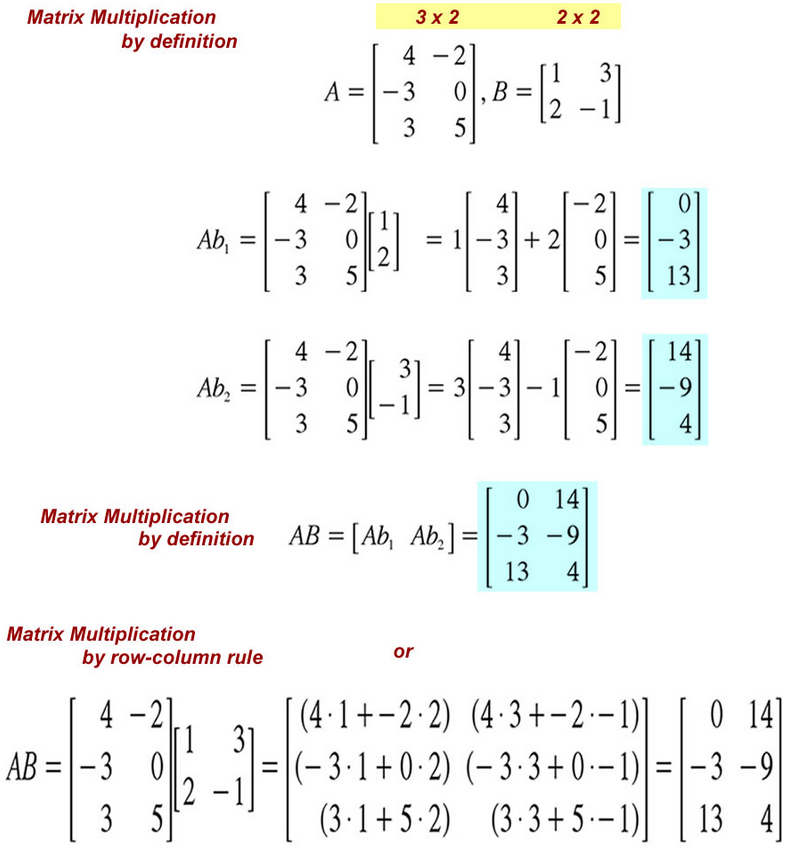
**Matrix Operations. Source: [SDSU Physics](https://sdsu-physics.org/math/pages/435_LA_ch2.html)**

**Check for modules that allow Matrix Operations. Source: [DPS Concepts](https://dspconcepts.com/forums/audio-weaver-designer/347-check-modules-allow-matrix-operations)**
### iii. Matrix-vector product
The matrix-vector product is an important special case of the matrix product.
There are two fundamentally different yet equivalent ways to interpret the matrix-vector product. In the column picture, (C), the multiplication of the
matrix A by the vector ~x produces a linear combination of the columns of the matrix: ~y = A~x = x1A[:,1] + x2A[:,2], where A[:,1] and A[:,2] are the first and second columns of the matrix A. In the row picture, (R), multiplication of the matrix A by the vector ~x produces a column vector with coefficients equal to the dot products of rows of the matrix with the vector ~x.

**Matrix-vector product. Source: [wikimedia](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Matrix_vector_product_qtl1.svg)**

**Matrix-vector Product. Source: [mathisfun](https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/scalar-vector-matrix.html)**
### iv. Linear transformations
The matrix-vector product is used to define the notion of a linear transformation, which is one of the key notions in the study of linear algebra. Multiplication by a matrix A ∈ R m×n can be thought of as computing a linear transformation TA that takes n-vectors as inputs and produces m-vectors as outputs:

**Linear Transformations. Source: [slideserve](https://www.slideserve.com/hall-cobb/chap-6-linear-transformations)**

**Elementary matrices for linear transformations in R^2. Source:[Quora](https://www.quora.com/What-is-a-linear-transformation)**
### v. Fundamental vector spaces

**Fundamental theorem of linear algebra for Vector Spaces. Source: [wikimedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fundamental_theorem_of_linear_algebra)**

**Fundamental theorem of linear algebra. Source: [wolfram](https://mathworld.wolfram.com/FundamentalTheoremofLinearAlgebra.html)**
# Computational Linear Algebra
### i. Solving systems of equations

**System of Linear Equations by Graphing. Source: [slideshare](https://www.slideshare.net/JITENDRATHAKOR/systems-of-linear-equations-43550732)**
### ii. Systems of equations as matrix equations

**Systems of equations as matrix equations. Source: [mathisfun](https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/systems-linear-equations-matrices.html?ref=binfind.com%2Fweb)**
# Computing the Inverse of a Matrix
In this section we’ll look at several different approaches for computing the inverse of a matrix. The matrix inverse is unique so no matter which
method we use to find the inverse, we’ll always obtain the same answer.

**Inverse of 2x2 Matrix. Source: [pinterest](https://www.pinterest.com/pin/375276581446966518/)**
### i. Using row operations
One approach for computing the inverse is to use the Gauss–Jordan elimination procedure.

**Elementray row operations. Source: [YouTube](http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DH2JSYx52nk)**
### ii. Using elementary matrices
Every row operation we perform on a matrix is equivalent to a leftmultiplication by an elementary matrix.

**Elementary Matrices. Source: [SDSU Physics](http://sdsu-physics.org/math/pages/435_LA_ch2.html)**
### iii. Transpose of a Matrix
Finding the inverse of a matrix is to use the Transpose method.
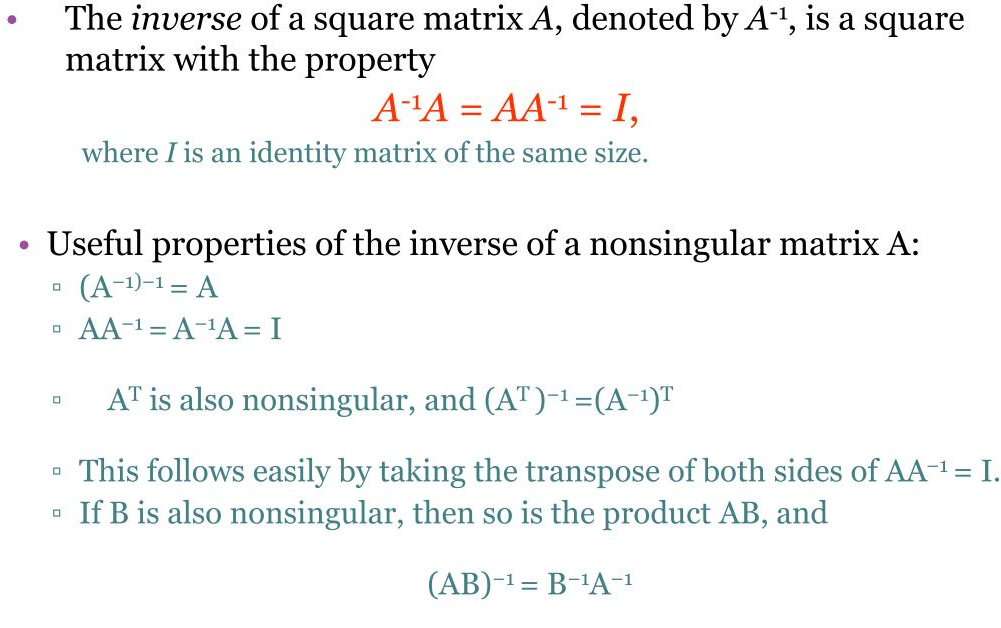
**Transpose of a Matrix. Source: [slideserve](https://www.slideserve.com/jaimin/matrix-inverse-and-transpose)**
# Other Linear Topics
In this section discuss a number of other important topics of linear algebra.
### i. Basis
Intuitively, a basis is any set of vectors that can be used as a coordinate system for a vector space. You are certainly familiar with the standard basis for the xy-plane that is made up of two orthogonal axes: the x-axis and the y-axis.
**Basis. Source: [wikimedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basis_(linear_algebra))**

**Change of Basis. Source: [wikimedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Change_of_basis)**
### ii. Matrix representations of linear transformations

**Matrix representations of linear transformations. Source: [slideserve](https://www.slideserve.com/sylvie/two-dimensional-geometric-transformations)**
### iii. Dimension and Basis for Vector Spaces
The dimension of a vector space is defined as the number of vectors in a basis for that vector space. Consider the following vector space S = span{(1, 0, 0),(0, 1, 0),(1, 1, 0)}. Seeing that the space is described by three vectors, we might think that S is 3-dimensional. This is not the case, however, since the three vectors are not linearly independent so they don’t form a basis for S. Two vectors are sufficient to describe any vector in S; we can write S = span{(1, 0, 0),(0, 1, 0)}, and we see these two vectors are linearly independent so they form a basis and dim(S) = 2. There is a general procedure for finding a basis for a vector space. Suppose you are given a description of a vector space in terms of m vectors V = span{~v1, ~v2, . . . , ~vm} and you are asked to find a basis for V and the dimension of V. To find a basis for V, you must find a set of linearly independent vectors that span V. We can use the Gauss–Jordan elimination procedure to accomplish this task. Write the vectors ~vi as the rows of a matrix M. The vector space V corresponds to the row space of the matrix M. Next, use row operations to find the reduced row echelon form (RREF) of the matrix M. Since row operations do not change the row space of the matrix, the row space of reduced row echelon form of the matrix M is the same as the row space of the original set of vectors. The nonzero rows in the RREF of the matrix form a basis for vector space V and the numbers of nonzero rows is the dimension of V.

**Basis and Dimension. Source: [sliderserve](https://www.slideserve.com/kalil/chapter-3-vector-space)**
### iv. Row space, columns space, and rank of a matrix
Recall the fundamental vector spaces for matrices that we defined in Section II-E: the column space C(A), the null space N (A), and the row space R(A). A standard linear algebra exam question is to give you a certain matrix A and ask you to find the dimension and a basis for each of its fundamental spaces. In the previous section we described a procedure based on Gauss–Jordan elimination which can be used “distill” a set of linearly independent vectors which form a basis for the row space R(A). We will now illustrate this procedure with an example, and also show how to use the RREF of the matrix A to find bases for C(A) and N (A).

**Row space and Column space. Source: [slideshare](https://www.slideshare.net/VishveshJasani/row-space-column-space-null-space-rank-nullity)**

**Row space and Column space. Source: [slideshare](http://www.slideshare.net/RonakMachhi/null-space-rank-and-nullity-theorem)**
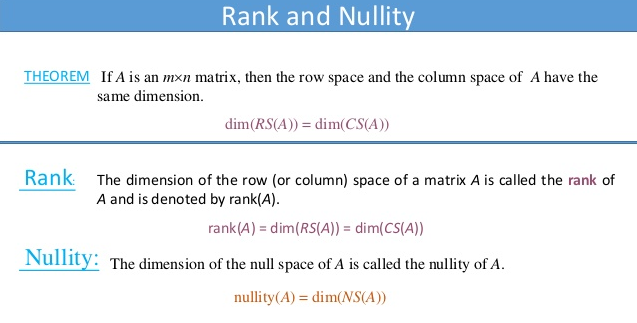
**Rank and Nullity. Source: [slideshare](https://www.slideshare.net/VishveshJasani/row-space-column-space-null-space-rank-nullity)**
### v. Invertible matrix theorem
There is an important distinction between matrices that are invertible and those that are not as formalized by the following theorem. Theorem. For an n×n matrix A, the following statements are equivalent:

**Invertible Matrix theorem. Source: [SDSU Physics](https://sdsu-physics.org/math/pages/435_LA_ch2.html)**
### vi. Determinants
The determinant of a matrix, denoted det(A) or |A|, is a special way to combine the entries of a matrix that serves to check if a matrix is invertible or not.

**Determinant of a Square Matrix. Source: [stackexchange](https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/1354148/proving-the-formula-for-finding-the-determinant-of-a-square-matrix)**

**Determinant of matrix. Source: [onlinemathlearning](https://www.onlinemathlearning.com/matrix-determinants.html)**
### vii. Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
The set of eigenvectors of a matrix is a special set of input vectors for which the action of the matrix is described as a simple scaling. When a matrix is multiplied by one of its eigenvectors the output is the same eigenvector multiplied by a constant A~eλ = λ~eλ. The constant λ is called an eigenvalue of A.

**Generalized EigenVectors. Source: [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xyhaYHGZN-w)**
### viii. Linear Regression
[Linear regression](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_regression) is an approach to model the relationship between two variables by fitting a linear equation to observed data. One variable is considered to be an explanatory variable, and the other is considered to be a dependent variable.

**Multiple Linear Regression. Source: [Medium](https://medium.com/@subarna.lamsal1/multiple-linear-regression-sklearn-and-statsmodels-798750747755)**
# Algorithms
[Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide#table-of-contents)
[Fuzzy logic](https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/fuzzy-logic.asp) is a heuristic approach that allows for more advanced decision-tree processing and better integration with rules-based programming.
**Architecture of a Fuzzy Logic System. Source: [ResearchGate](https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Architecture-of-a-fuzzy-logic-system_fig2_309452475)**
[Support Vector Machine (SVM)](https://web.stanford.edu/~hastie/MOOC-Slides/svm.pdf) is a supervised machine learning model that uses classification algorithms for two-group classification problems.
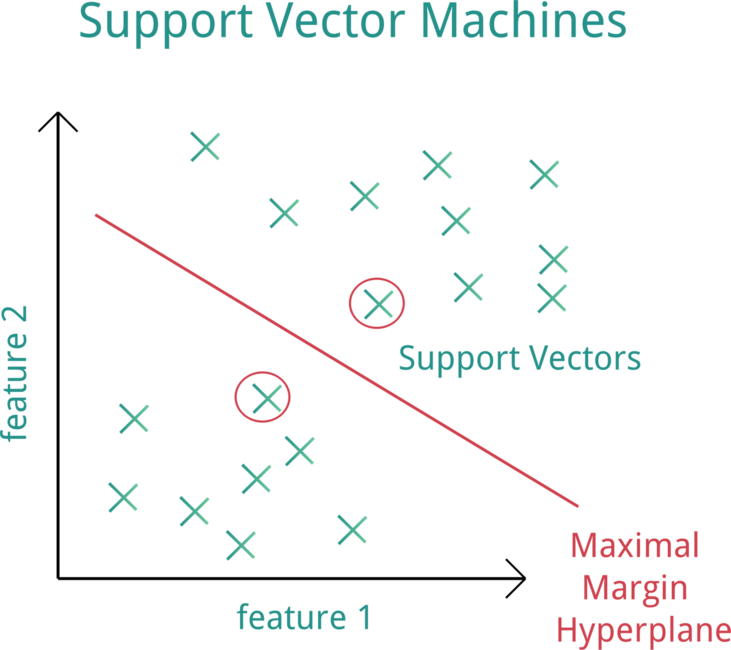
**Support Vector Machine (SVM). Source:[OpenClipArt](https://openclipart.org/detail/182977/svm-support-vector-machines)**
[Neural networks](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/neural-networks) are a subset of machine learning and are at the heart of deep learning algorithms. The name/structure is inspired by the human brain copying the process that biological neurons/nodes signal to one another.
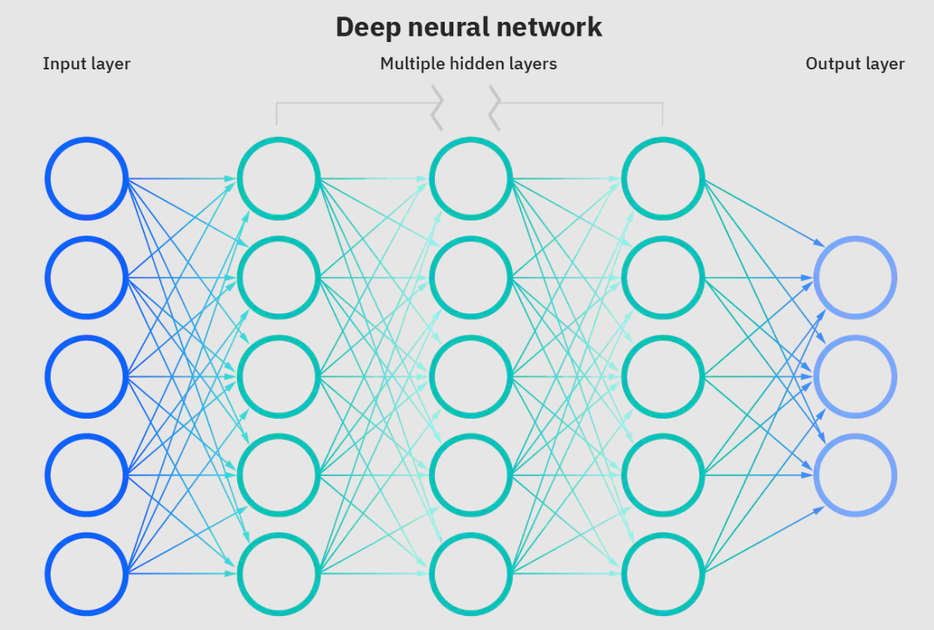
**Deep neural network. Source: [IBM](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/neural-networks)**
[Convolutional Neural Networks (R-CNN)](https://stanford.edu/~shervine/teaching/cs-230/cheatsheet-convolutional-neural-networks) is an object detection algorithm that first segments the image to find potential relevant bounding boxes and then run the detection algorithm to find most probable objects in those bounding boxes.
**Convolutional Neural Networks. Source:[CS231n](https://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/#conv)**
[Recurrent neural networks (RNNs)](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/recurrent-neural-networks) is a type of artificial neural network which uses sequential data or time series data.

**Recurrent Neural Networks. Source: [Slideteam](https://www.slideteam.net/recurrent-neural-networks-rnns-ppt-powerpoint-presentation-file-templates.html)**
[Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs)](https://deepai.org/machine-learning-glossary-and-terms/multilayer-perceptron) is multi-layer neural networks composed of multiple layers of [perceptrons](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perceptron) with a threshold activation.

**Multilayer Perceptrons. Source: [DeepAI](https://deepai.org/machine-learning-glossary-and-terms/multilayer-perceptron)**
[Random forest](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/random-forest) is a commonly-used machine learning algorithm, which combines the output of multiple decision trees to reach a single result. A decision tree in a forest cannot be pruned for sampling and therefore, prediction selection. Its ease of use and flexibility have fueled its adoption, as it handles both classification and regression problems.

**Random forest. Source: [wikimedia](https://community.tibco.com/wiki/random-forest-template-tibco-spotfirer-wiki-page)**
[Decision trees](https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~bhiksha/courses/10-601/decisiontrees/) are tree-structured models for classification and regression.

***Decision Trees. Source: [CMU](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~bhiksha/courses/10-601/decisiontrees/)*
[Naive Bayes](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Naive_Bayes_classifier) is a machine learning algorithm that is used solved calssification problems. It's based on applying [Bayes' theorem](https://www.mathsisfun.com/data/bayes-theorem.html) with strong independence assumptions between the features.

**Bayes' theorem. Source:[mathisfun](https://www.mathsisfun.com/data/bayes-theorem.html)**
## Contribute
- [x] If would you like to contribute to this guide simply make a [Pull Request](https://github.com/mikeroyal/MATLAB-Guide/pulls).
## License
Distributed under the [Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Public License](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).